Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Technology (Spatial Transcriptomics, Spatial Genomics), By Product (Instruments, Consumables, Software), By End-Use (Translational Research, Academic Customers, Diagnostic Customers, Pharmaceutical Manufacturers), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Global Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market Size
The size of the global spatial genomics transcriptomics market was worth USD 338 million in 2024. The global market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 11.7% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 915 million by 2033 from USD 377.55 million in 2025.

Spatial genomics transcriptomics enables the study of gene expression and genomic variations within the spatial context of tissues and cells. The market of spatial genomics transcriptomics includes a range of products such as sequencing platforms, bioinformatics tools, and consumables and serves sectors such as academic research, pharmaceuticals, diagnostics, and translational medicine, driving advancements in personalized healthcare and drug discovery. In 2024, 50% of clinical trials are incorporating genomic data to personalize treatment plans, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
MARKET DRIVERS
Advancements in Genomic Technologies
The continuous evolution of genomic sequencing technologies such as single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics is a key driver in this market. These technologies enable researchers to study gene expression patterns within tissue samples at a high resolution, driving demand for spatial biology tools. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), in 2024, more than 2,500 studies utilizing genomic technologies were published and is highlighting the expanding role of these tools in both research and clinical applications. These innovations are enhancing the accuracy of gene expression analysis which leads to breakthroughs in disease diagnosis and personalized medicine.
Increased Investment in Precision Medicine
The growing focus on precision medicine is driving the demand for spatial genomics and transcriptomics. By providing more granular insights into the spatial arrangement of gene activity within tissues, these technologies play a vital role in advancing precision medicine. The U.S. FDA has been promoting the development of precision medicine with regulatory pathways like the 21st Century Cures Act which allocated $6.3 billion in funding for such initiatives. This drive has spurred collaborations between biotech companies and academic institutions, accelerating market growth and facilitating novel therapeutic strategies for complex diseases like cancer and neurological disorders.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Technology
The high cost of spatial genomics and transcriptomics technologies is a significant barrier to market growth. Instruments such as spatial transcriptomic sequencers and associated consumables often require substantial investment which limits their accessibility to academic and clinical research labs, particularly in emerging markets. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), research funding constraints have led to only a small fraction (around 12%) of academic institutions being able to utilize advanced genomic tools fully. This financial barrier hampers broader adoption and particularly in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and lower-resource settings.
Data Complexity and Analysis Challenges
The integration and interpretation of large volumes of spatially resolved transcriptomic data present another major challenge. The complexity of combining spatial data with multi-omics information requires advanced bioinformatics tools and expertise which are not always readily available. The NIH’s National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) reported in 2024 that over 30% of genomic datasets face delays in analysis due to insufficient computational resources or lack of expertise. These challenges in data analysis may slow the adoption of spatial genomics technologies and is limiting their potential in clinical and commercial applications.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expanding Applications in Cancer Research
Spatial genomics and transcriptomics offer significant opportunities in cancer research by enabling detailed mapping of tumor microenvironments. These technologies can identify genetic markers and gene expression patterns that influence cancer progression and treatment resistance. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) in 2024 reported that over 50% of cancer research studies now incorporate advanced genomics to explore precision oncology that demonstrates a growing demand for spatial transcriptomics to further understand tumour biology. This provides a crucial opportunity for companies to develop specialized solutions for cancer diagnostics and therapeutic development.
Advancements in Neuroscience and Neurological Disorders
The ability to study gene expression in the context of tissue architecture opens new opportunities in neuroscience particularly in understanding neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) reported in 2024 that research funding for neurological disorders reached over $2 billion by supporting the application of spatial transcriptomics to uncover gene activity associated with brain function. This offers opportunities for companies to capitalize on the increasing demand for tools that can provide insights into complex neurological conditions and potential therapeutic targets.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Limited Standardization Across Platforms
One of the major challenges in the Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics market is the lack of standardization in data collection, processing, and analysis across different platforms. Variability in methodologies can lead to inconsistent results that hinders reproducibility and limiting the broader application of these technologies. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in 2024, over 40% of molecular biology studies faced challenges in standardization, which affects the reliability of data for clinical applications. This lack of consistency complicates comparisons across studies and slows down the adoption of these technologies in clinical practice.
Regulatory Hurdles for Clinical Applications
Spatial genomics technologies hold significant promise in clinical settings but regulatory hurdles for adoption remain a substantial challenge. As these technologies often involve new methods of diagnostic testing and treatment monitoring, they face rigorous approval processes from regulatory bodies like the U.S. FDA. The FDA’s 2024 report indicates that only 8% of advanced genomic technologies have received full regulatory approval for clinical use. These barriers, including the lack of clear regulatory frameworks for novel molecular techniques, slow down the transition of spatial genomics from research to clinical implementation and thereby hindering market growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
11.7% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, Product, End-use, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, and country-level analysis; Segment-Level Analysis, DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
10x Genomics, NanoString Technologies Inc., Bruker, Illumina, Novogene Co., Ltd., S2 Genomics, Visiopharm, Horizon Discovery Ltd., SciLife Lab, Akoya Biosciences, Inc, and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Technology Insights
The spatial transcriptomics segment accounted for 78.8% of the global spatial genomics transcriptions market share in 2024. This segment holds the largest share due to its widespread adoption in both research and clinical applications due to its ability to provide high-resolution insights into gene expression patterns within tissues. Sequencing-based methods dominate because of their ability to capture complex tissue structures and spatial variations in gene expression, offering precise and comprehensive data. These methods enable the identification of disease biomarkers by advancing both diagnostics and therapeutic strategies. This dominance is further supported by the increasing use of technologies like single-cell RNA sequencing and in situ sequencing which are gaining traction in understanding complex diseases such as cancer and neurological disorders. The importance of sequencing-based methods lies in their ability to provide a detailed with spatially resolved map of gene activity, which is crucial for applications in cancer research, neuroscience, and developmental biology. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), 60% of genomic studies in 2024 involved sequencing technologies, further validating their central role in spatial transcriptomics. These methods allow researchers to study gene expression at an unprecedented level of detail, enabling breakthroughs in understanding tissue microenvironments and cellular interactions.
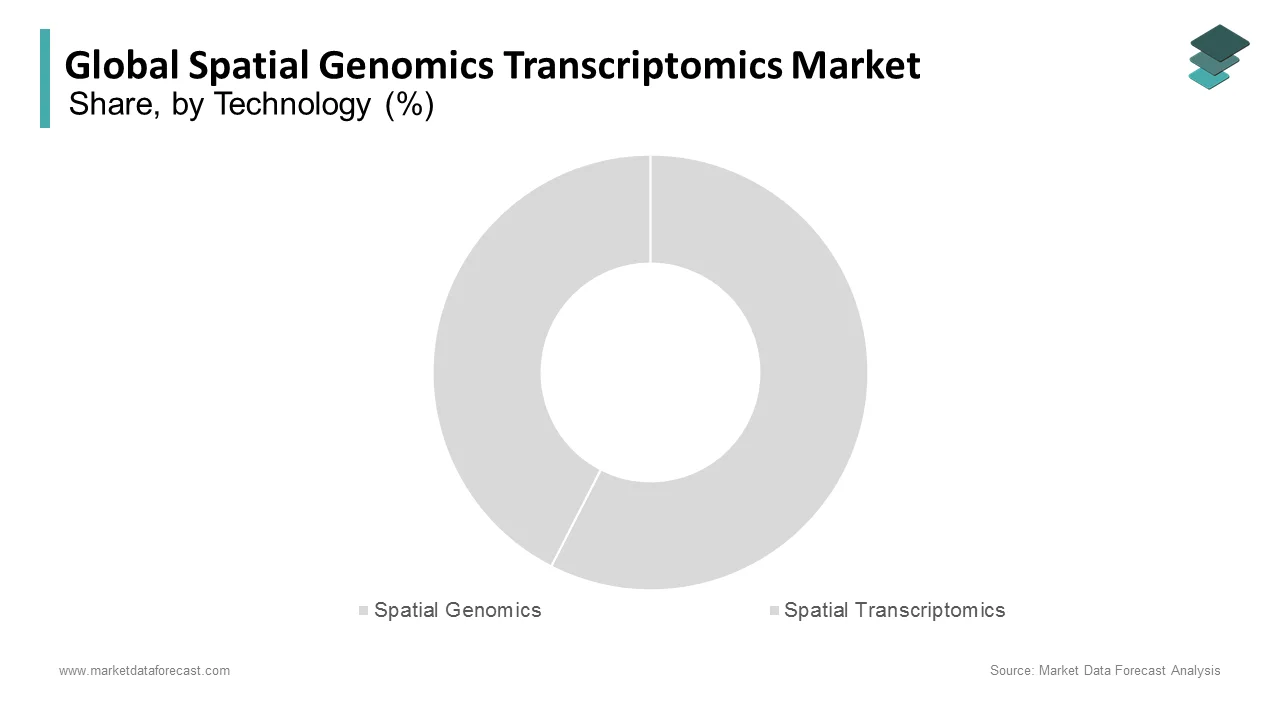
The spatial genomics segment is estimated to record a CAGR of 17.7% over the forecast period owing to the increasing demand for high-throughput sequencing methods capable of capturing genomic information from entire tissue samples in a parallel and scalable manner. This method enables the identification of genomic alterations across large populations of cells, which is crucial for understanding disease mechanisms, particularly in cancer and genetic disorders. Massively-Parallel Sequencing holds particular appeal due to its ability to generate comprehensive data at a much faster pace compared to traditional sequencing methods. It has become essential in studies aiming to map out the genomic landscapes of tumors and other complex diseases, enabling personalized treatment approaches. The increasing adoption of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) platforms further accelerates this growth. The importance of massively-parallel sequencing in spatial genomics lies in its ability to study the genome within its spatial context, offering more precise insights into genetic variations at the cellular level. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the adoption of parallel sequencing technologies has increased by over 30% annually since 2021, making it a driving force in the field of spatial genomics. This technique is poised to revolutionize the understanding of disease progression and contribute significantly to advancements in precision medicine.
By Product Insights
The instruments segment led the market by holding 45.9% of the global market share in 2024. The domination of the instruments segment in the global market is majorly driven by the increasing demand for high-throughput sequencing technologies capable of analyzing complex gene expression profiles in spatially-resolved tissue samples. Sequencing platforms are critical for spatial transcriptomics as they allow researchers to generate large-scale and high-resolution gene expression data from tissues which is crucial for advancing research in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and precision medicine. This growth is driven by the continuous advancements in sequencing technology, including next-generation sequencing (NGS) and single-cell RNA sequencing, which are enabling more detailed and comprehensive insights into cellular heterogeneity and gene activity. These platforms are becoming indispensable tools in molecular biology, especially in oncology and immunology, where spatial information is critical for understanding disease mechanisms. The importance of sequencing platforms lies in their ability to provide precise, reproducible data on gene expression within tissue contexts, allowing for new insights into cellular interactions and microenvironmental factors. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the utilization of sequencing platforms for cancer research has increased by over 40% since 2020, reflecting their growing role in personalized medicine and drug development. Sequencing technologies enable breakthroughs in understanding complex diseases by mapping gene activity within specific tissue regions, facilitating more effective therapeutic strategies.
The software is predicted to showcase a CAGR of 16.4% over the forecast period due to the increasing need for advanced computational tools that can handle the massive datasets generated by spatial genomics and transcriptomics technologies. The demand for bioinformatics tools to analyze, interpret, and visualize this data is growing exponentially with sequencing platforms generate vast amounts of data. These tools are essential for integrating genomic, transcriptomic, and spatial data to uncover insights into cellular behaviors and tissue organization. This growth is fueled by the increasing complexity of data and the need for more sophisticated algorithms and software solutions to analyze high-dimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics tools are playing a crucial role in enhancing the resolution and accuracy of spatial genomics studies, particularly in areas such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine. The importance of bioinformatics tools is evident in their ability to manage and analyze the large volumes of spatially-resolved transcriptomic data that are generated in cutting-edge research. According to the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the use of bioinformatics tools in genomic research increased by 35% in 2023, highlighting their central role in facilitating data-driven discoveries. As the spatial genomics and transcriptomics fields continue to expand, the reliance on bioinformatics tools to interpret complex data will only intensify by making them critical to advancing personalized healthcare and precision medicine.
By End-Use Insights
The pharmaceutical manufacturers segment held the largest share of the 50.8% of the global market in 2024. The increasing demand for spatial transcriptomics and genomics technologies in drug discovery and development is propelling the growth of the pharmaceutical manufacturers segment in the global market. Pharmaceutical manufacturers are using these tools to better understand the mechanisms of diseases, develop targeted therapies, and improve patient outcomes through personalized medicine. These technologies are particularly valuable in oncology, neurology, and immunology, where spatial information about gene expression is crucial for understanding disease progression and identifying therapeutic targets. The growth of this segment is driven by the continuous adoption of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and spatial transcriptomics technologies in drug development pipelines. Pharmaceutical companies are increasingly relying on these tools to gain insights into tumor microenvironments, cellular heterogeneity, and gene expression patterns to support the discovery of novel therapeutic compounds. The importance of this segment lies in its ability to accelerate the drug development process and improve the precision of treatments. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) approximately 30% of clinical trials now incorporate genomic or spatial omics data to enhance their precision and efficacy, demonstrating the increasing reliance of pharmaceutical manufacturers on these technologies. Spatial genomics and transcriptomics enable the identification of biomarkers and therapeutic targets, playing a crucial role in the development of personalized medicine.
The diagnostic customers segment is growing steadily and is predicted to showcase a CAGR of 14.2% during the forecast period. The increasing use of spatial genomics and transcriptomics in clinical diagnostics is majorly promoting the growth rate of the market. This segment is growing rapidly as the need for more accurate and precise diagnostic tools increases. Spatial genomics and transcriptomics are being integrated into diagnostic practices, particularly for complex diseases like cancer, neurological disorders, and genetic conditions, where traditional diagnostic methods are not sufficient. These technologies provide in-depth insights into tissue-specific gene expression, helping to detect diseases at earlier stages and enabling more targeted treatment options. The rise in personalized medicine and the shift towards early disease detection are driving the demand for these technologies in diagnostic applications. The growing focus on non-invasive diagnostics and liquid biopsies, where spatial transcriptomics can be applied to study circulating tumor cells or tissue samples, is also contributing to the rapid expansion of this segment. The importance of diagnostic customers in the spatial genomics and transcriptomics market lies in their potential to revolutionize diagnostic practices. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 15% of new molecular diagnostic tests approved in 2024 incorporated genomic or transcriptomic profiling, emphasizing the role of these technologies in improving diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. As precision diagnostics become more critical in healthcare, the demand for spatial transcriptomics in clinical settings is expected to grow significantly.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America dominated the market by occupying 43.1% of the global market share in 2024.
The United States in particular leads in research funding and technological advancements. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocated approximately $45 billion for biomedical research in 2024, a substantial portion of which supports genomic studies. This robust investment fosters innovation and positions North America at the forefront of the market.
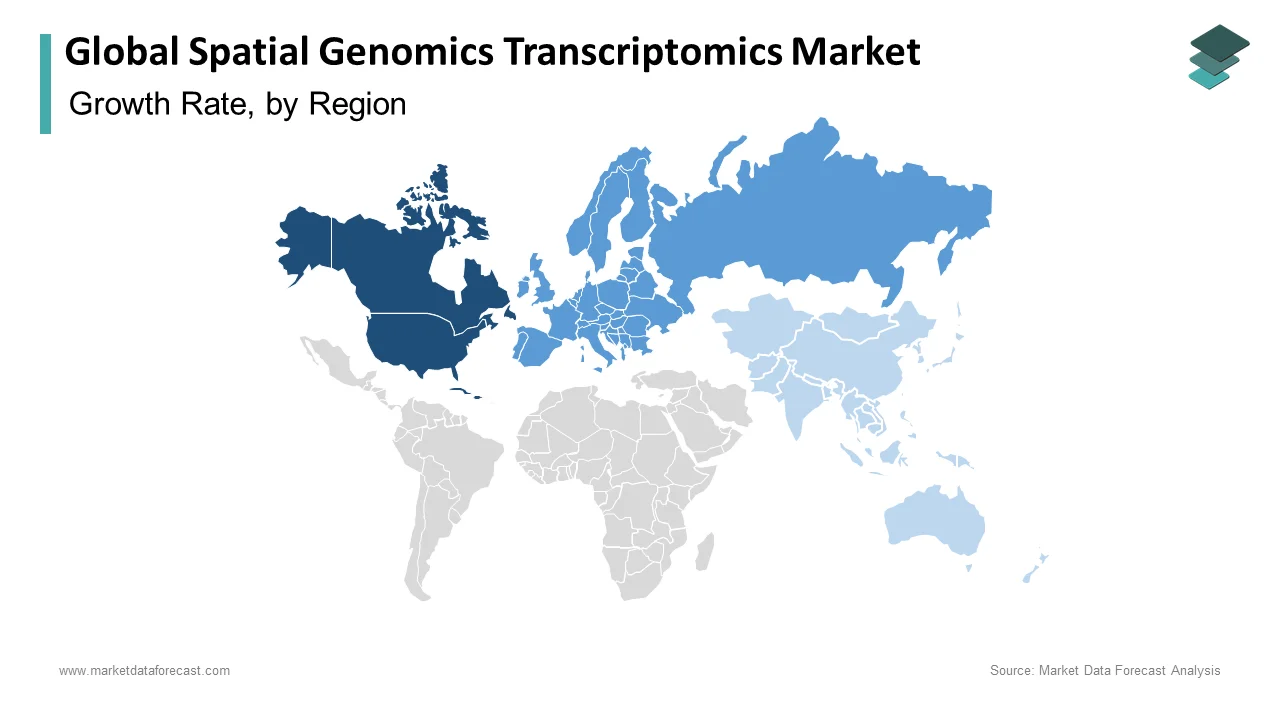
Europe is another prominent regional market for spatial genomics transcriptomics and is expected to experience a steady CAGR of 11.2% over the forecast period. It maintains a strong presence in the market, with countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France leading in research and development. The European Commission's Horizon Europe program, with a budget of €95.5 billion for 2021-2027, includes significant funding for genomic research initiatives. This financial commitment underscores Europe's dedication to advancing spatial genomics and transcriptomics.
The Asia-Pacific region is rapidly emerging in the global spatial genomics transcriptomics market and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 15.6% during the forecast period. The Asia-Pacific region is experiencing rapid growth is driven by countries such as China, Japan, and India. China's investment in biotechnology has surged, with the National Natural Science Foundation of China allocating over ¥30 billion to life sciences research in 2024. This substantial funding is propelling advancements in genomic technologies and expanding the market's footprint in the region.
Latin America is projected to grow at a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. The Brazilian Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovations allocated approximately R$1.5 billion to biotechnology research in 2024 by indicating a commitment to advancing genomic sciences. This investment is fostering growth in the spatial genomics and transcriptomics sectors.
The market in the Middle East and Africa is likely to showcase steady pace over the forecast period. The Middle East and Africa are in the early stages of market development, with countries like South Africa and the United Arab Emirates investing in genomic research. South Africa's National Research Foundation allocated R1.2 billion to life sciences research in 2024 by supporting the growth of genomic technologies. While the market share is currently smaller these investments are laying the groundwork for future expansion.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
10x Genomics, NanoString Technologies Inc., Bruker, Illumina, Novogene Co., Ltd., S2 Genomics, Visiopharm, Horizon Discovery Ltd., SciLife Lab, Akoya Biosciences, Inc, and Others.
COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS
The competition in the Spatial Genomics Transcriptomics Market is growing as innovations in molecular biology and genomics technologies fuel the need for spatially resolved gene expression analysis. Companies are focused on developing advanced platforms that integrate genomics with spatial mapping, offering insights into tissue structures and cellular functions in situ. Key players, including 10x Genomics, Nanostring Technologies, and Illumina, lead the market with state-of-the-art solutions combining spatial transcriptomics, single-cell RNA sequencing, and imaging techniques.
These industry leaders benefit from strong product portfolios and partnerships with academic and research institutions. Meanwhile, new entrants are challenging the status quo by introducing specialized technologies that enhance data resolution or improve throughput and scalability. As a result, established companies are increasingly investing in innovation, mergers, and acquisitions to maintain their edge.
The field is expanding beyond academic research into clinical applications, driving the demand for more tailored solutions. This shift is intensifying competition as businesses aim to capture opportunities within the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and healthcare industries. The push for more accurate, scalable, and cost-effective solutions is set to drive the evolution of this market, making it one of the most dynamic sectors in biotechnology today.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In October 2024, Vizgen, specializing in single-cell spatial genomics, merged with Ultivue, known for multiplex proteomic profiling technologies. This merger aimed to create a comprehensive entity offering both single-cell spatial genomics and multiplex proteomic profiling solutions, thereby broadening their technological portfolio and market reach.
- In December 2024, in Harvard University, researchers at Harvard's Children's Hospital Boston utilized spatial transcriptomics to enhance in vitro bone marrow models. This advancement aims to improve the understanding of hematopoiesis and related disorders.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global spatial genomics transcriptomics market has been segmented based on the technology, product, end-use, and region.
By Technology
- Spatial Genomics
- Spatial Transcriptomics
By Product
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Software
By End-Use
- Translational research
- Academic Customers
- Diagnostic Customers
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some emerging trends in the spatial genomics transcriptomics market?
Emerging trends include the development of multiplexed spatial profiling technologies capable of simultaneously measuring the expression of hundreds to thousands of genes within spatially defined regions, as well as advances in computational methods for analyzing and interpreting spatially resolved gene expression data.
What are the primary challenges hindering spatial genomics transcriptomics market growth?
Challenges include the high cost associated with spatial genomics transcriptomics technologies, the need for specialized expertise in data analysis and interpretation, and regulatory hurdles related to the approval and commercialization of spatial genomics-based diagnostics and therapeutics.
What factors are driving the growth of the spatial genomics transcriptomics market?
Key drivers include the growing adoption of precision medicine approaches, rising demand for single-cell analysis technologies, increasing investment in biomedical research, and advancements in computational biology and bioinformatics.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
