Global Spatial Computing Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented by Component (Software, Hardware, and Services), Technology (Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, Mixed Reality, Artificial Intelligence, Digital Twins, Internet of Things, and Others), End User (Aerospace & Defense, Healthcare, Automotive, Gaming, Energy & Utilities, Consumer Electronics, Architecture, Engineering, & Construction, Government & Public Sector, Information Technology, and Others) & Region - Industry Forecast From 2024 to 2032
Global Spatial Computing Market Size (2024 to 2032)
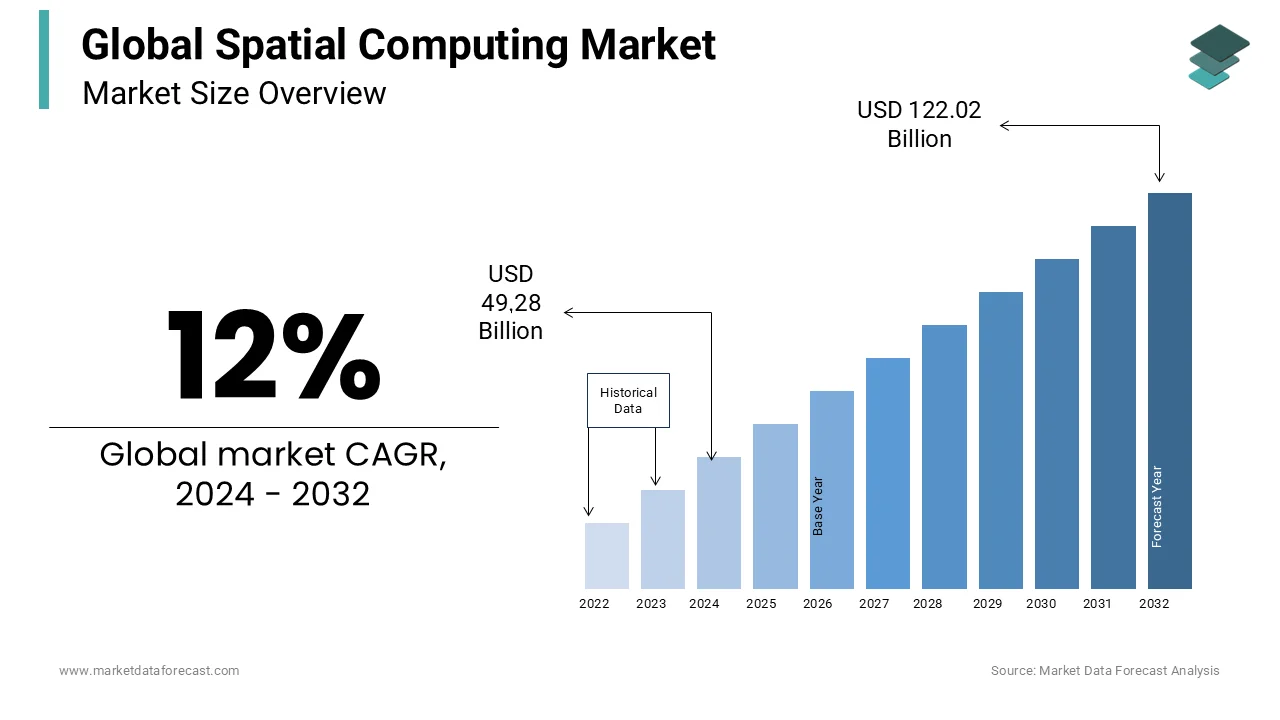
The global spatial computing market was valued at USD 44 billion in 2023. The global market is predicted to reach USD 49.28 billion in 2024 and USD 122.02 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 12% during the forecast period.
Market Overview
The spatial computing market has witnessed notable growth in recent years, driven by advancements in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies. These innovations are propelling growth in industries including gaming, healthcare, and manufacturing. The market remains highly competitive, with prominent players like Apple, Microsoft, and Google at the forefront. Microsoft's HoloLens and Apple's Vision Pro have set the standard for AR/MR hardware, further intensifying competition in this space.
North America and Europe have maintained leadership in market revenue contributions, though the Asia-Pacific region, including China and Japan, is quickly gaining momentum. This growth is largely attributed to increased investments in AR and VR technologies within these countries, positioning the region as a formidable competitor in the spatial computing landscape.
Key milestones in the spatial computing market include the release of consumer-grade AR glasses and high-profile acquisitions, such as Meta’s purchase of Oculus. Additionally, the rising adoption of enterprise solutions has further fueled market expansion.
These technological advancements, coupled with expanding applications across various sectors, have established spatial computing as a transformative force in the digital economy, redefining how businesses and consumers engage with digital content.
Market Trends
Increased Adoption of Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) in Enterprise Solutions
AR and MR technologies have gained significant traction across industries over the last decade, particularly in enterprise settings. Market leaders such as Microsoft and Apple are driving this trend, exemplified by Microsoft's HoloLens and Apple’s Vision Pro headsets. The AR market is expected to grow from $25.33 billion in 2023 to $80.8 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 17.2%. Industries like healthcare, automotive, and manufacturing are leveraging AR/MR to enhance training, streamline remote collaboration, and optimize product design. For instance, Porsche’s use of AR in remote maintenance has cut service times by up to 40%, while healthcare professionals employ AR to overlay critical data during procedures, significantly enhancing precision.
Growth of Spatial Computing in Retail and E-Commerce
Retailers are increasingly adopting spatial computing to enhance customer experiences and drive sales. Augmented reality (AR) applications, such as virtual try-ons and product visualizations, are becoming mainstream in retail. By 2024, an estimated 100 million consumers will shop using AR, spurred by companies like IKEA, which offers the "Place" app for real-time furniture visualization within customers' homes. This trend is not only improving customer engagement but also reducing product returns by up to 25%. The AR retail market, valued at $3.5 billion in 2022, is projected to reach $12 billion by 2027.
Expansion of Spatial Computing in Gaming and Entertainment
Gaming and entertainment remain key drivers of spatial computing adoption, particularly in virtual reality (VR). The global VR gaming market is expected to reach $53 billion by 2028, fueled by the success of products like Meta’s Oculus Quest 2, which has surpassed 20 million units in sales. Immersive entertainment experiences, such as VR concerts and movies, are also gaining traction. Platforms like VRChat and Rec Room are transforming how users interact in virtual spaces, creating fully immersive and interactive environments that are reshaping traditional media consumption.
Market Drivers
Increased Venture Capital in Spatial Computing Startups
Growing venture capital investment in spatial computing startups continues to drive market expansion. Investors are heavily backing AR, VR, and MR innovations, seen as key elements of the next digital revolution. For example, Magic Leap raised over $500 million in 2021 to advance its next-generation AR headset, Magic Leap 2, focusing on enterprise use. Global AR/VR startup funding reached $3.9 billion in 2022, marking a 31% year-over-year increase, according to CB Insights. This influx of capital is fostering innovation and competition within the spatial computing ecosystem across multiple sectors.
Government and Institutional Investments
Governments globally are increasingly acknowledging the transformative potential of spatial computing, with significant investments aimed at advancing its development. Countries such as the United States and China are allocating funds for research and development in AR and VR technologies for both civilian and military applications. For instance, the U.S. military has committed over $22 billion to Microsoft’s HoloLens AR system, known as the Integrated Visual Augmentation System (IVAS), for training and battlefield operations. Similarly, South Korea initiated a $186 million investment in 2021 to foster immersive content industries, including AR and VR. These initiatives are driving forward the adoption and innovation of spatial computing.
Demand for Enhanced Customer Experience
The growing demand for enhanced customer experiences is a key factor in the increasing adoption of spatial computing across industries. Retailers, for example, are utilizing AR technology to provide virtual try-ons, allowing consumers to preview products before purchasing. This level of personalization has proven effective, with 61% of online shoppers preferring sites that offer AR experiences, according to a Vertebrae study. In real estate, platforms like Zillow are leveraging VR to provide virtual property tours, enhancing customer engagement, reducing returns, and strengthening brand loyalty, contributing to market expansion.
Market Restraints
High Cost of Spatial Computing Hardware
The adoption of spatial computing is hindered by the high costs associated with advanced AR/VR hardware, limiting its accessibility for both consumers and businesses. Devices such as Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 and Apple’s Vision Pro, priced around $3,500, pose significant barriers to widespread adoption, particularly for smaller enterprises and emerging markets. This cost challenge is further amplified by additional expenses, such as training, especially in price-sensitive regions like Asia-Pacific.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns
The collection and use of vast amounts of personal data in spatial computing have raised privacy concerns. Devices like Meta’s Oculus have faced scrutiny over data collection practices, while embedded technologies such as facial recognition and eye tracking introduce ethical issues regarding user consent. According to a Gartner report, 62% of users have expressed concerns about privacy in AR/VR applications, which may affect consumer trust and market growth if not properly addressed.
Lack of Standardization and Interoperability
A lack of standardization across spatial computing platforms poses a significant challenge for the market. Companies such as Apple, Microsoft, and Meta have developed proprietary ecosystems, leading to limited cross-platform compatibility. This fragmentation complicates the user experience, especially in enterprise environments where system integration is critical. The absence of standardized protocols may hinder innovation, as businesses are hesitant to adopt isolated platforms that do not easily integrate with others.
Market Opportunities
Expansion into Emerging Markets
The spatial computing market is poised for significant growth across emerging regions, including Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East. These areas are benefiting from rising investments in digital infrastructure and increased smartphone penetration, which is accelerating the adoption of AR and VR technologies. PwC projects that AR and VR could contribute $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with $370 billion expected from the Asia-Pacific region. Countries like China and India are at the forefront, with government initiatives promoting digitalization and smart city innovations. China’s 14th Five-Year Plan, for example, highlights AR/VR as key components of its technological advancements. Companies capitalizing on these opportunities are well-positioned to gain substantial traction as economic and technological development continues to unfold in these regions.
Integration with 5G Technology
The deployment of 5G networks presents a transformative opportunity for the spatial computing industry, enabling superior performance and enhanced user experiences for AR and VR applications. With faster transmission speeds, reduced latency, and increased bandwidth, 5G makes real-time, immersive interactions more viable, particularly in sectors like healthcare, where AR is facilitating remote surgeries, and gaming, where VR offers heightened interactivity. According to Qualcomm, 5G is expected to add $1.5 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with spatial computing emerging as a key beneficiary. South Korea’s advancements in 5G-based VR services, such as live-streamed concerts, further illustrate the immense potential for 5G to elevate digital experiences across multiple industries.
Adoption in Education and Training
Spatial computing is creating substantial opportunities in education and workforce training by offering immersive, interactive learning environments. AR and VR technologies enable students to explore complex subjects like medical anatomy and engineering in 3D, fostering a more engaging and accessible learning experience. The AR/VR education market is projected to reach $17.7 billion by 2026, with a CAGR of 16.2%. Initiatives such as Stanford University’s Virtual Human Interaction Lab use VR to teach students about environmental challenges, while companies like Walmart and Boeing integrate VR into employee training programs to reduce risk and operational costs. The growing use of these technologies provides a powerful tool for both educational institutions and businesses aiming to enhance skills and knowledge retention.
Market Challenges
Content Development and Availability
A significant challenge facing the spatial computing market is the limited availability of high-quality, immersive content. While AR and VR hardware has seen rapid advancements, the content landscape has not evolved at the same pace, especially in providing diverse experiences across industries. In gaming, only a handful of titles like Beat Saber and Half-Life: Alyx have gained widespread popularity, with many users citing a lack of engaging content as a barrier to adoption. Statista reported that 43% of potential VR users in 2022 were concerned about the lack of content. In enterprise settings, the creation of tailored AR/VR solutions demands significant time and investment, slowing down adoption rates. Addressing this gap will require coordinated efforts from developers, content creators, and industry stakeholders to expand the content ecosystem and meet the growing demand for immersive experiences.
Ethical and Social Implications
The widespread adoption of spatial computing technologies introduces several ethical and social considerations. AR and VR have the potential to significantly alter human interactions with the world, raising concerns about their long-term psychological and societal effects. Prolonged use of immersive VR environments has been linked to issues such as dissociation from reality, anxiety, and desensitization. A 2021 study by the University of Oxford found that participants reported feelings of disorientation and isolation after extended VR use. Furthermore, AR applications that overlay digital content onto the physical world raise concerns about privacy breaches, surveillance, and the manipulation of information. Addressing these concerns will require the development of robust ethical guidelines, responsible technology design, and open public discourse on the societal impacts of spatial computing.
User Adoption and Acceptance
Despite the advancements in spatial computing technologies, user adoption remains a key challenge. Many consumers and businesses are reluctant to fully integrate AR and VR due to usability concerns, such as motion sickness in VR environments or discomfort from wearing bulky headsets for long durations. According to a 2022 survey by Perkins Coie, 35% of respondents identified discomfort with current hardware as a barrier to adoption. Additionally, there is a steep learning curve for users unfamiliar with immersive interfaces, further hindering widespread acceptance. To overcome these barriers, manufacturers must focus on improving device comfort, making them lighter and more intuitive, ensuring that both consumers and enterprises perceive clear value in adopting AR and VR technologies for everyday use.
Impact of COVID-19 on the Spatial Computing Market
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly influenced the spatial computing market, accelerating its adoption in several sectors while stalling progress in others. The demand for remote communication, training, and entertainment surged, driving the increased utilization of AR and VR technologies across industries such as healthcare, education, and retail. AR applications were leveraged to facilitate remote maintenance in sectors like automotive and manufacturing, while VR became more prevalent in medical training and therapy. As noted by Statista, the global AR/VR market expanded by 54% in 2020, as companies rapidly adapted to lockdown measures and social distancing protocols.
However, supply chain disruptions presented notable challenges, particularly in hardware production for AR/VR devices. Factory shutdowns and capacity reductions delayed product launches and slowed innovation within the spatial computing industry. Additionally, economic instability prompted businesses, particularly in tourism and entertainment, to reduce investments in immersive technologies, which were disproportionately impacted by the global downturn.
In the post-pandemic landscape, the spatial computing market is experiencing renewed growth, with a focus on hybrid work environments, digital transformation, and enhanced remote collaboration. Companies have increasingly recognized the value of AR and VR for remote operations, driving sustained demand in industries like healthcare, education, and enterprise. A report by PwC forecasts that by 2030, 23.5 million jobs globally will utilize AR and VR, underscoring the pandemic’s lasting impact on the sector. As organizations continue to adopt immersive technologies for training, design, and collaboration, spatial computing is emerging as an essential tool for the evolving future of work and customer engagement in the post-pandemic era.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
CAGR |
12% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Technology, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Qualcomm (US), Meta (US), Google (US), Microsoft (US), PTC (US). Epson (Japan), Apple (US), Samsung (South Korea), Sony (Japan), and Magic Leap (US). |
Segment Analysis
By Component
Largest Segment: Hardware
The hardware component commands the largest share of the spatial computing market, representing 55% of the total market in 2023. This growth is fueled by the widespread adoption of AR/VR headsets, smart glasses, and sensors across various sectors. Leading companies such as Microsoft (HoloLens), Apple (Vision Pro), and Meta (Oculus Quest) continue to dominate this space with advanced technologies. The hardware segment is projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16% through 2030, driven by increasing demand for enterprise-grade AR/VR devices, particularly in healthcare, manufacturing, and automotive industries. Innovations in sensor technology and edge computing are further enhancing these experiences.
Fastest Growing Segment: Services
The services segment is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth in the spatial computing market, with an expected CAGR of 19% from 2023 to 2030. As adoption of AR and VR technologies accelerates, the demand for implementation, maintenance, and training services continues to rise. Custom-tailored solutions are increasingly sought by businesses, particularly in healthcare and retail, to meet their specific needs. Growth in consulting, integration, and managed services is expected to soar as enterprises seek expert guidance in AR/VR deployments. Companies like Accenture have expanded their offerings in spatial computing services, providing AR/VR implementations to enhance business operations and customer experiences. Enterprise applications are growing rapidly, creating a robust demand for related services across various industries.
By Technology
Augmented Reality (AR)
The augmented reality (AR) segment holds the largest share within spatial computing technologies, comprising 45% of the market in 2023. Its expansion is driven by its widespread use in industries such as retail, healthcare, and manufacturing, where it enhances real-time visualizations, training, and product customization. Forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 14% through 2030, AR is becoming mainstream, with technologies such as Google Lens and Snapchat’s AR lenses gaining traction. In healthcare, AR is employed for surgery planning and medical training, while retail giants like IKEA and Amazon leverage AR for virtual product demonstrations. AR's capability to integrate digital information into real-world environments underscores its broad applicability across sectors.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the fastest-growing technology segment in the spatial computing market, expected to expand at a CAGR of 22% from 2023 to 2030. AI is driving advancements by enabling more intelligent and interactive spatial computing applications. AI-powered tools such as real-time object recognition, predictive analytics, and personalized experiences are transforming industries. In retail, AI integrated into AR glasses facilitates personalized shopping experiences, while in healthcare, AI-driven AR aids in diagnosis and treatment planning. With the ability to process vast datasets in real-time, AI is reshaping the spatial computing landscape. Leading companies, including NVIDIA and Google, are making significant investments in AI-based spatial computing solutions.
By End User
Healthcare
The healthcare sector is the largest end-user of spatial computing, accounting for 30% of the market in 2023. The adoption of AR and VR technologies in healthcare is driven by the need for enhanced medical training, remote surgeries, and patient care. VR therapies for conditions like PTSD and anxiety, along with AR-based surgical navigation systems, are becoming increasingly widespread. Institutions like Cleveland Clinic are utilizing AR for improved visualization in complex surgeries. The healthcare segment is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 18% through 2030, as the demand for remote consultations and virtual therapies continues to rise, accelerated by the pandemic’s push toward digital transformation.
Retail & E-commerce
Retail and e-commerce represent the fastest-growing end-user segment in the spatial computing market, with a projected CAGR of 20% from 2023 to 2030. AR is transforming the retail experience, as virtual try-ons and product visualizations become commonplace. By 2024, it is anticipated that 100 million consumers will use AR in their shopping activities. Retail giants such as IKEA, Amazon, and Sephora have incorporated AR into their platforms to enhance customer engagement. The surge in online shopping during the pandemic prompted retailers to embrace spatial computing, creating immersive shopping experiences that increase sales and reduce product returns.
Regional Analysis
North America: "Driving Innovation through Enterprise Adoption" & "Pioneering Growth Through Enterprise Adoption"
North America currently commands the largest share of the spatial computing market, accounting for around 35% of global revenue in 2023. The region is forecasted to maintain its dominance, expanding at a CAGR of 15% through 2030.
Rapid advancements in sectors such as healthcare, manufacturing, and entertainment are propelling North America’s leadership in spatial computing. The U.S. and Canada are central to this growth due to their robust technology ecosystems, widespread deployment of 5G networks, and a proliferation of AR/VR startups. Major tech players, including Apple, Microsoft, Meta, and Google, further solidify the region’s stronghold in the market. Microsoft's HoloLens is a leader in healthcare and defense, while Meta’s Oculus Quest reigns supreme in consumer VR.
- United States: As a frontrunner in enterprise AR/VR adoption, the U.S. leads innovation, with over $22 billion invested in Microsoft’s HoloLens for military applications. AR is also transforming healthcare, with applications in medical training and procedures.
- Canada: Canada has emerged as a key player in the VR space, particularly in gaming and entertainment. With studios like Felix & Paul leading the charge, the country has become a hub for immersive VR experiences, fostering growth across the region.
Europe: "Smart Cities and Sustainability Leading the Charge"
Europe accounts for approximately 28% of the spatial computing market and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 14% through 2030.
Europe’s commitment to sustainability and smart city integration sets it apart, with AR and VR playing pivotal roles in sectors like manufacturing and automotive. Countries like Germany and the U.K. are leading the way in applying these technologies to industrial solutions. The region’s focus on energy efficiency and sustainable development is further emphasized through the use of AR in smart infrastructure and environmental monitoring.
- Germany: As an industrial powerhouse, Germany is utilizing AR for automation and design within factories, particularly in automotive virtual design simulations and workforce training.
- United Kingdom: The U.K., a leader in media and entertainment, is pushing AR and VR boundaries in virtual concerts, events, and gaming. Government investment in spatial computing is also driving progress in defense and public services.
- France: Tech investment in France is boosting VR applications across tourism and education, from immersive experiences in cultural heritage sites to virtual classrooms, further cementing its role in the region’s digital future.
Asia-Pacific: "A Fast-Emerging Hub of Spatial Computing"
Asia-Pacific captures 25% of the global spatial computing market, with projections indicating it will grow at the highest CAGR of 18% from 2023 to 2030.
Technological advancements and strategic investments are propelling rapid growth across China, Japan, and South Korea. The rise of 5G technology serves as a key driver, enabling more integrated AR/VR experiences across diverse industries. Government initiatives further bolster spatial computing in sectors like education, retail, and manufacturing.
- China: With the spatial computing market expected to surpass $20 billion by 2025, China’s government has embraced VR for educational purposes and urban planning, while companies like Nreal and Xiaomi continue to push AR glasses forward.
- Japan: Known for innovation in robotics and AI, Japan is embedding spatial computing into smart factories and healthcare systems, with Sony's PlayStation VR reshaping the gaming landscape.
- South Korea: A leader in 5G deployment, South Korea is at the forefront of AR/VR adoption in entertainment and retail, from virtual concerts to interactive shopping, driven by its strong digital infrastructure.
Middle East & Africa: "A Digital Economy Poised for Growth"
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) comprise around 10% of the spatial computing market and are projected to expand at a CAGR of 17% through 2030.
Growth in MEA is fueled by rising investments in digital infrastructure and smart city initiatives, especially in the UAE and Saudi Arabia. Spatial computing technologies are increasingly utilized in construction, tourism, and defense sectors. Mega-projects like Saudi Arabia’s NEOM are leveraging AR/VR to support urban planning and development.
- United Arab Emirates: The UAE is employing AR and VR technologies in tourism and urban development, with Dubai’s government integrating AR into public services and utilizing VR for law enforcement and emergency training.
- Saudi Arabia: Under Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia is focusing on spatial computing technologies to enhance infrastructure development and entertainment, incorporating AR into the NEOM smart city project.
- South Africa: Leading AR/VR adoption in Africa, South Africa is advancing in education and healthcare, with virtual classrooms and AR-based medical training gaining momentum.
Latin America: "Empowering Industries through Digital Transformation"
Latin America holds 7% of the global spatial computing market, with an anticipated CAGR of 16% between 2023 and 2030. The region is progressively embracing spatial computing technologies as sectors such as education, healthcare, and retail undergo digital transformation. Brazil and Mexico are leading in AR/VR integration, fueled by government investments aimed at enhancing digital literacy and infrastructure.
• Brazil: As the largest economy in Latin America, Brazil is advancing AR in retail, with brands like L’Oréal utilizing AR for virtual makeup trials. VR is also being introduced into higher education and training initiatives.
• Mexico: Mexico is leveraging AR and VR technologies in tourism and education. Virtual tours of historical landmarks are becoming popular, while educational institutions adopt VR for remote learning and skill development programs.
Key players in the global spatial computing market include
- Google LLC
- Meta (Facebook Technologies, LLC)
- Nreal
- Sony Corporation
- Microsoft Corporation
- Magic Leap, Inc.
- Apple Inc.
- HTC Corporation
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.
- Unity Technologies
Competitive Landscape
The spatial computing landscape is marked by intense competition, with both major tech players and specialized firms striving for market dominance. Industry leaders such as Apple, Microsoft, Google, and Meta continue to make substantial investments in hardware and software innovations. Apple’s Vision Pro and Microsoft’s HoloLens are advancing enterprise adoption, while Meta’s Oculus Quest focuses on consumer VR experiences. Google remains a pivotal force in augmented reality, with its ARCore platform catering to mobile applications.
Companies like Magic Leap and Nreal, though smaller, are gaining traction by targeting both enterprise and consumer markets. Their emphasis on hardware innovation and ability to secure funding keep them competitive against larger industry players.
In the software realm, competition is growing as Unity Technologies and Qualcomm provide essential infrastructure for immersive content development. Unity’s real-time 3D platform and Qualcomm’s Snapdragon processors are foundational to AR/VR performance.
The integration of emerging technologies, including 5G, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), is accelerating the pace of innovation. This drive for technological convergence is enhancing device connectivity and user experiences, with companies racing to secure market share in this rapidly evolving sector.
Recent Developments in the Spatial Computing Market
- In January 2023, Apple Inc. entered the spatial computing sector with the launch of the Vision Pro headset, aimed at integrating AR/VR solutions across both consumer and enterprise markets.
- In March 2024, Microsoft Corporation expanded the capabilities of its HoloLens 2 with Azure Mixed Reality services, strengthening its position in enterprise AR through enhanced cloud integration for training and remote collaboration.
- In December 2023, Meta (formerly Facebook Technologies) committed over $10 billion to its Reality Labs division to advance VR and AR technologies, emphasizing its focus on building the metaverse and maintaining leadership in immersive tech.
- In October 2023, Google LLC upgraded its ARCore platform, introducing enhanced mobile AR experiences, further expanding its reach in mobile applications through strategic partnerships with Google Search and Google Maps.
- In February 2023, Sony Corporation introduced PlayStation VR2, offering significant improvements in visual fidelity and interactivity for gaming, reinforcing Sony’s dominance in consumer VR entertainment.
- In June 2023, Magic Leap, Inc. pivoted to enterprise AR with the release of Magic Leap 2, targeting sectors such as healthcare and manufacturing to solidify its presence in the enterprise space.
- In September 2023, Nreal launched Nreal Air, lightweight AR glasses aimed at expanding its footprint in entertainment and productivity, further positioning itself competitively in the market.
- In July 2023, HTC Corporation extended its VIVE XR Suite, focusing on business applications like remote work and training, bolstering its role in enterprise VR solutions.
- In November 2023, Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. released the Snapdragon XR2 platform, a next-generation processor designed to enhance AR/VR device performance, strengthening its leadership in spatial computing hardware.
- In April 2023, Unity Technologies partnered with Autodesk to integrate real-time 3D tools for industrial design, further expanding its influence in industrial applications of spatial computing.
DETAILED SEGMENTATION OF THE GLOBAL SPATIAL COMPUTING MARKET INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT
This research report on the global spatial computing market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on the component, technology, end user, and region.
By Component
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
By Technology
- Augmented Reality
- Virtual Reality
- Mixed Reality
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Twins
- Internet of Things
- Others
By End User
- Aerospace & Defense
- Healthcare
- Automotive
- Gaming
- Energy & Utilities
- Consumer Electronics
- Architecture
- Engineering, & Construction
- Government & Public Sector
- Information Technology
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Which industries are the primary drivers of growth in the Spatial Computing market globally?
The primary industries driving growth in the Spatial Computing market include healthcare, retail, manufacturing, automotive, and entertainment. The healthcare sector, in particular, has seen significant adoption of spatial computing for surgical simulations, medical training, and patient care, while retail and manufacturing leverage these technologies for enhanced customer experiences and operational efficiencies.
What are the key challenges faced by the Spatial Computing market globally?
The key challenges include high development and deployment costs, privacy and security concerns, and the need for standardized platforms. Additionally, there is a shortage of skilled professionals who can design and implement spatial computing solutions, which hinders widespread adoption.
How does the regulatory environment affect the Spatial Computing market globally?
The regulatory environment significantly impacts the Spatial Computing market, particularly in terms of data privacy, security, and the ethical use of immersive technologies. Different regions have varying regulations, with Europe leading in strict data protection laws like GDPR, which influences how companies can collect and use spatial data. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for market players.
What future trends are expected to shape the global Spatial Computing market?
Future trends shaping the Spatial Computing market include the integration of AI and machine learning for more intelligent and interactive spatial experiences, the rise of metaverse-related applications, and the development of more compact, user-friendly AR/VR devices. Additionally, increasing collaboration between tech giants and startups is expected to drive innovation and accessibility in the market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]