Global Service Robotics Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Operating Environment (Aerial, Ground, Marine, Automated Underwater Vehicles, Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicles, and Unmanned Surface Vehicles Controls), Application (Professional, Personal), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Service Robotics Market Size
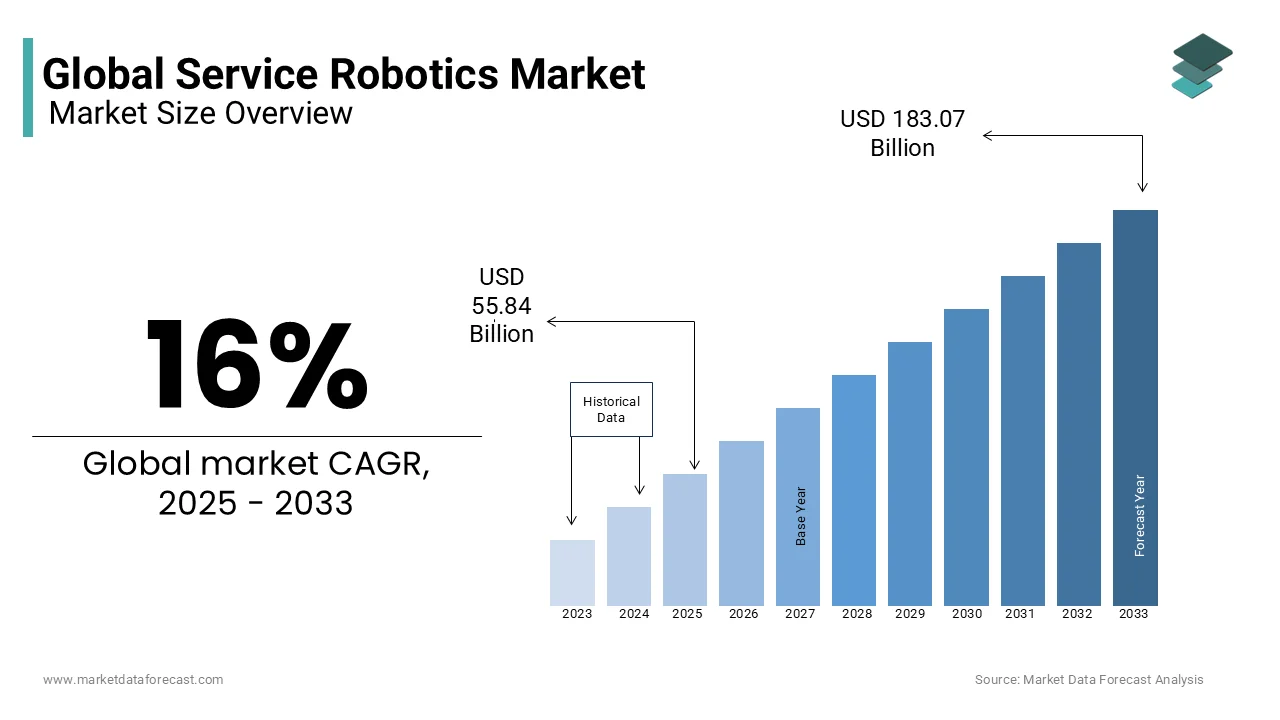
The global service robotics market was valued at USD 48.14 billion in 2024. The global market is estimated to reach USD 55.84 billion in 2025 and USD 183.07 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 16% during the forecast period.
The service robotics market includes the development and deployment of robots designed to assist humans in various non-industrial sectors, including healthcare, logistics, agriculture, and domestic services. These robots operate autonomously or semi-autonomously, leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sophisticated sensors to perform complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
In the healthcare sector, service robots have significantly transformed surgical procedures and patient care. Notably, the da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, has been utilized in over 10 million minimally invasive surgeries worldwide since its introduction, enhancing precision and reducing recovery times for patients. As of December 2021, more than 6,500 da Vinci systems were installed across 67 countries, with over 55,000 surgeons trained in their use.
In the logistics and supply chain industry, the adoption of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) has markedly improved operational efficiency. For instance, Amazon employs over 750,000 robots within its fulfillment centers, aiding in tasks such as storage, packing, sorting, and transportation of packages. The integration of these robotic systems has led to a 25% reduction in fulfillment costs during peak periods, as observed in Amazon's advanced facilities.
The agricultural sector also benefits from service robotics through the implementation of autonomous machines that perform tasks like precision spraying, harvesting, and soil analysis. These innovations address labor shortages and enhance productivity, contributing to increased food production.
MARKET DRIVERS
Technological Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Automation
The rapid progression of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies has significantly propelled the service robotics market. Innovations in machine learning, computer vision, and sensor technologies have enhanced robots' capabilities, enabling them to perform complex tasks with increased autonomy and precision. For instance, the integration of AI allows service robots to adapt to dynamic environments, improving their functionality in sectors such as healthcare, logistics, and domestic services. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has been actively involved in developing performance metrics and standards for AI-enabled robotic systems, facilitating their deployment across various industries. These technological strides have expanded the applicability of service robots, making them indispensable in modern society.
Demographic Shifts and Labor Shortages
Demographic changes, particularly aging populations in countries like Japan, have led to labor shortages in critical sectors such as healthcare and manufacturing. According to Japan's Statistics Bureau, as of October 1, 2022, individuals aged 65 and over constituted 29.0% of the total population, reflecting a significant aging demographic. This shift has intensified the demand for service robots to assist in eldercare and routine tasks, thereby alleviating the burden on the shrinking workforce. Similarly, China's working-age population has been declining, prompting increased adoption of automation and robotics to sustain economic productivity. The National Bureau of Statistics of China reported a continuous decrease in the working-age population over the past decade, underscoring the necessity for robotic solutions in addressing labor gaps.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
Implementing service robots requires significant upfront investments, particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) notes that the adoption of industrial robots by SMEs is often hindered by high initial investments and total cost of ownership. To mitigate these financial barriers, models like Robots-as-a-Service (RaaS) have emerged, allowing companies to utilize robotic automation without substantial capital expenditure. This approach offers benefits such as fixed costs and automatic upgrades, making automation more accessible to SMEs. However, the financial commitment associated with traditional robotic systems remains a significant restraint on the broader adoption of service robots across various industries.
Technical Challenges and Reliability Issues
Service robots are designed to operate in dynamic and unstructured environments, which presents substantial technical challenges. Ensuring consistent performance and reliability in such settings is critical, as failures can lead to operational disruptions and safety concerns. The International Federation of Robotics emphasizes the importance of focusing on reliable products that function without major issues over extended periods. Developing robots capable of interpreting complex sensory data and making appropriate decisions in real-time remains a significant hurdle. These technical challenges and potential reliability issues can undermine user confidence, thereby limiting the widespread adoption of service robotics solutions.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Robotics in Agriculture
The agricultural sector is increasingly adopting robotics and automation to enhance productivity and address labor shortages. In the United Kingdom, the government has allocated £12.5 million through the Farming Futures Automation and Robotics competition, part of the £270 million Farming Innovation Programme, to develop cutting-edge technologies in agriculture. This initiative aims to reduce dependency on manual labor and promote sustainable farming practices. Projects funded include systems for predicting and enhancing crop yields, digital mapping of vineyards using drones and sensors, and navigation systems for robotic vehicles in farming operations. These advancements are expected to revolutionize farming efficiency and sustainability.
Addressing Labor Shortages in Aging Populations
Developed nations are experiencing demographic shifts characterized by aging populations and declining birth rates, leading to labor shortages in various sectors. Japan, for instance, has seen its population decrease from a peak of 128.1 million in 2008 to approximately 126.2 million in 2020, with projections indicating a drop below 100 million by 2056 and to 87 million by 2070, as reported by the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research. This demographic trend results in a shrinking workforce, necessitating the integration of service robots to maintain economic stability and support the elderly. Robotic solutions are being developed to perform tasks ranging from eldercare to industrial automation, thereby alleviating the pressure on the limited labor force and ensuring continued productivity in the face of demographic challenges.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
The deployment of service robots, especially those equipped with advanced artificial intelligence and data collection capabilities, raises significant ethical and privacy issues. These robots often operate in close proximity to individuals, collecting and processing personal data to perform tasks effectively. This data collection can lead to potential misuse or unauthorized access, infringing on individual privacy rights. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) emphasizes the importance of implementing robust data protection measures and compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to safeguard personal information in robotic applications. Addressing these concerns is crucial to gaining public trust and ensuring the responsible integration of service robots into daily life.
Workforce Displacement and Socioeconomic Impact
The increasing adoption of service robots across various industries has the potential to displace human workers, particularly in roles involving repetitive or manual tasks. This shift can lead to significant socioeconomic challenges, including unemployment and the need for workforce reskilling. The International Labour Organization (ILO) reported that automation and robotics could affect a substantial portion of jobs, necessitating proactive measures such as upskilling and education programs to prepare the workforce for evolving job requirements. Balancing technological advancement with employment opportunities is essential to mitigate adverse socioeconomic impacts and promote inclusive growth in the era of automation.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
16% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Operating Environment, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Northrop Grumman Corporation (U.S.), KUKA AG (Germany), iRobot Corporation (U.S.), Kongsberg Maritime AS (Norway), DJI (China), Intuitive Surgical, Inc. (U.S.), Parrot SA (France), Gecko Systems Intl. Corp. (U.S.), Honda Motor Co. Ltd. (Japan), Adept Technology, Inc. (U.S.), Bluefin Robotics- now wholly owned subsidiary of General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (U.S.), ECA Group (France), Aethon Inc. (U.S.), DeLaval International AB (Sweden), and Lely Holding S.a.r.l. (Netherlands) and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Operating Environment Insights
The Ground segment commanded the service robotics market and captured 60.3% of the market share as of 2024 owing to the extensive adoption in industrial automation, logistics, and healthcare. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that manufacturing productivity grew by about 2.5% annually from 2010-2020 due to automation, boosting demand for ground robots like AGVs. Also, the National Institute of Standards and Technology notes increased use of ground robots in U.S. warehouses, with adoption rising significantly, enhancing cost efficiency. This segment’s versatility and scalability cement its market dominance.
The Marine segment, including Automated Underwater Vehicles (AUVs), Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicles (ROVs), and Unmanned Surface Vehicles, is the fastest-growing, with a CAGR of 17.2% from 2024-2029, per MarketsandMarkets. This growth is driven by defense and offshore exploration demands. The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration reports steady ocean exploration funding increases, supporting AUV and ROV use. The U.S. Department of Defense invested heavily in unmanned marine systems in 2023, showcasing maritime security needs. Its value lies in deep-sea research and threat mitigation, vital for sustainability and defense.
By Application Insights
The Professional Services segment dominated the service robotics market and held biggest portion of the global revenue share in 2024. Its rise is due to the widespread adoption in logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing where robots enhance operational efficiency. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics indicates that automation in manufacturing boosted productivity by 3.7% annually from 2010-2020 which is a key factor in its dominance. Moreover, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services notes a 15% increase in robotic surgeries from 2018-2022 emphasizes its critical role in precision and cost-effectiveness across industries.
The Personal Services segment is predicted to witness the highest CAGR of 14.8% from 2025-2033. This growth is because of the rising demand for domestic robots like vacuum cleaners and assistive devices, spurred by aging demographics and convenience. The U.S. Census Bureau reports a 38.6% rise in the 65+ population from 2010-2020, driving demand for assistive robotics. Furthermore, the National Institute of Standards and Technology states that 25% of U.S. households used robotic cleaners in 2023, up from 15% in 2018 which is spotlighting its importance in improving daily life and reducing manual effort.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific led the service robotics market and captured 41.7% of the share in 2024. Rapid industrialization and significant investments in automation technologies are the main reasons behind the growth of this region. China, in particular, has made substantial strides, with its robot density reaching 246 units per 10,000 employees in 2020, surpassing the global average of 126 units. This surge reflects China's commitment to integrating robotics into its manufacturing sector, enhancing efficiency and productivity. Government initiatives, such as the "Made in China 2025" plan, aim to boost domestic robotics production, further bolstering the region's leadership in the market. These efforts underscore the strategic importance placed on automation to sustain economic growth and competitiveness.
North America experienced swift rise in the service robotics market and is projected to advance at a CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period. This is largely attributed to advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning, which have expanded the capabilities of service robots across sectors such as healthcare and logistics. The United States, in particular, has seen a significant uptick in the adoption of service robots, driven by the need for automation to enhance operational efficiency and address labor shortages. The region's robust technological infrastructure and focus on innovation position it as a pivotal player in the global service robotics landscape.
Europe maintains a strong presence in the service robotics market, with countries like Germany leading in automation and robotics integration. Germany's robot density stood at 371 units per 10,000 employees in 2020, reflecting a steady annual growth rate. The region's emphasis on precision engineering and quality manufacturing drives the adoption of service robots, particularly in industries such as automotive and electronics. However, Europe faces increasing competition from Asia-Pacific countries, necessitating continued investment in research and development to maintain its competitive edge in the global market.
Latin America is gradually embracing service robotics, with a focus on sectors like agriculture and healthcare. The adoption rate, however, remains modest due to economic constraints and limited technological infrastructure. Countries such as Brazil and Mexico are exploring the integration of robotics to enhance productivity and address labor challenges. As technological accessibility improves and costs decrease, the region is poised to witness a gradual increase in the adoption of service robots which is contributing to economic development and operational efficiency in key industries.
The Middle East and Africa region is in the nascent stages of adopting service robotics. The market's expansion is propelled by the increasing demand for automation and the integration of advanced technologies to enhance operational efficiency across various sectors. As awareness of the benefits of service robotics grows and technological infrastructure develops, the region is expected to see a gradual increase in adoption rates, contributing to economic diversification and modernization efforts.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global service robotics market include Northrop Grumman Corporation (U.S.), KUKA AG (Germany), iRobot Corporation (U.S.), Kongsberg Maritime AS (Norway), DJI (China), Intuitive Surgical, Inc. (U.S.), Parrot SA (France), Gecko Systems Intl. Corp. (U.S.), Honda Motor Co. Ltd. (Japan), Adept Technology, Inc. (U.S.), Bluefin Robotics- now wholly owned subsidiary of General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (U.S.), ECA Group (France), Aethon Inc. (U.S.), DeLaval International AB (Sweden), andLely Holding S.a.r.l. (Netherlands).
Top 3 Players in the Market
Nvidia Corporation
Nvidia, a global leader in AI and GPU technologies, has established a strong presence in the service robotics market through its Jetson AI Robotics platform. This platform enables the development of autonomous machines used across industries such as logistics, healthcare, and industrial automation. By leveraging AI-powered computing, Nvidia is driving innovations in robotic vision, real-time data processing, and automation. While Nvidia does not directly manufacture offshore support vessels, its AI and machine learning technologies play a crucial role in optimizing their automation capabilities. These advancements help improve navigation, predictive maintenance, and operational efficiency in Europe's offshore energy sector, supporting remote and autonomous vessel operations.
ABB Robotics
ABB Robotics, headquartered in Switzerland, is a major force in industrial automation and service robotics. The company has pioneered collaborative robots (cobots) designed to enhance human-robot interaction across various industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. ABB’s ongoing investments in AI-driven robotics solutions have solidified its position as a key player in the service robotics market. In the European offshore support vessels sector, ABB provides critical automation and control systems that enhance vessel performance, safety, and energy efficiency. Its advanced propulsion solutions, including electric and hybrid systems, contribute to reducing emissions and improving sustainability in offshore operations.
Kongsberg Maritime
Kongsberg Maritime, a subsidiary of Norway-based Kongsberg Gruppen, specializes in maritime robotics and automation technologies. The company is a leader in developing autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), which are extensively used for offshore support operations, including underwater inspections, maintenance, and mapping. Kongsberg’s robotic solutions enhance the efficiency and safety of offshore support vessels operating in the European oil, gas, and renewable energy sectors. By integrating advanced sensor technologies, real-time data analytics, and autonomous navigation systems, Kongsberg Maritime plays a critical role in driving the future of unmanned and remotely operated offshore vessels.
Top Strategies Used by The Key Market Participants
AI-Driven Innovation and Technological Advancements
Leading companies in the service robotics market, such as Nvidia, ABB Robotics, and Kongsberg Maritime, are heavily investing in AI and machine learning to enhance the capabilities of their robots. Nvidia leverages its Jetson AI platform to provide real-time data processing, advanced robotic vision, and autonomous navigation capabilities, making service robots more efficient and intelligent. ABB Robotics is integrating AI-driven collaborative robots (cobots) into industrial and healthcare environments, improving safety and productivity. Meanwhile, Kongsberg Maritime incorporates AI-driven data analysis into its underwater drones and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), enabling better automation in offshore and subsea operations. These innovations ensure that companies remain at the forefront of robotics development, catering to the growing demand for smart and autonomous systems.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaboration with other market leaders, research institutions, and technology firms enables companies to accelerate innovation and improve their product offerings. Nvidia partners with numerous robotics manufacturers to integrate its AI processors, allowing for more powerful and intelligent robotic systems. ABB Robotics has established partnerships with major corporations such as Amazon and BMW, incorporating its robotics technology into supply chains and production lines. Kongsberg Maritime works closely with Norwegian government agencies and offshore energy companies to develop autonomous maritime solutions. These partnerships enable companies to access new technologies, expand their reach, and deliver more advanced robotics solutions.
Focus on Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
With increasing global emphasis on sustainability, robotics companies are prioritizing the development of energy-efficient and eco-friendly technologies. ABB Robotics has introduced low-energy robotic systems to reduce power consumption in manufacturing, thereby lowering operational costs and carbon footprints. Kongsberg Maritime is leading the push for sustainable maritime solutions by developing hybrid and fully electric autonomous vessels, which significantly cut emissions in offshore operations. By focusing on sustainability, these companies not only contribute to environmental protection but also position themselves as leaders in the transition toward greener industrial and maritime automation.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The service robotics market is experiencing intense competition, driven by rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), automation, and machine learning. The market is dominated by key players such as Nvidia, ABB Robotics, Kongsberg Maritime, Boston Dynamics, iRobot, and Intuitive Surgical, all competing to enhance robotic capabilities across various industries, including healthcare, logistics, manufacturing, and maritime services.
Competition is primarily fueled by technological innovation, as companies strive to develop more autonomous, efficient, and intelligent robots. AI-driven robotics, collaborative robots (cobots), and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are key areas where firms are investing heavily. Additionally, the integration of 5G, IoT, and cloud computing is reshaping the competitive landscape by enabling real-time data processing and seamless robot communication.
Another key aspect of competition is strategic acquisitions and partnerships, as companies seek to expand their market presence and integrate new technologies. Firms like ABB and Kongsberg Maritime acquire smaller automation and robotics companies to strengthen their expertise, while Nvidia collaborates with robotics manufacturers to integrate its AI-powered chips into their systems.
As demand for robotics increases across healthcare, logistics, retail, and offshore operations, competition is expected to intensify. Companies that prioritize innovation, sustainability, and global expansion will likely emerge as leaders in this rapidly evolving market.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2025, Swedish private equity firm EQT expressed interest in acquiring Device Technologies, a medical technology service provider specializing in healthcare robotics and ophthalmology. The auction, expected to exceed $1 billion, is set to commence by the end of March 2025.
- In January 2025, automation firm Symbotic agreed to acquire Walmart's robotics business for $200 million in cash. This acquisition aims to enhance Walmart's automated supply chain capabilities and includes a partnership to develop pickup and delivery centers utilizing Symbotic's AI-enabled robotics platform.
- In October 2024, Ashtead Technology Holdings acquired Seatronics and J2 Subsea from Acteon Group for £63 million. This move expanded Ashtead's subsea robotics and surveying operations, strengthening its presence in the UK and Asia markets.
- In February 2025, Waseda University in Japan developed AIREC, a humanoid robot designed to assist in elderly care by performing tasks such as changing diapers and cooking. The robot is expected to address Japan’s caregiver shortage and is planned for market release by 2030.
- In February 2025, Amazon announced plans to invest up to $25 billion in robotics and AI to improve retail operations. This initiative includes robotics-led warehouses to reduce costs and optimize delivery times.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global service robotics market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Operating Environment
- Ground
- Aerial
- Marine
- Automated Underwater Vehicles
- Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicles
- Unmanned Surface Vehicles Controls
By Application
- Personal Services
- Professional Services
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the adoption of service robotics impacting labor markets worldwide?
While service robotics automation can lead to displacement of certain jobs, it also creates new opportunities for skilled workers in areas such as robotics engineering, programming, and maintenance.
What are the major challenges hindering the growth of the service robotics market?
Challenges include high initial investment costs, concerns regarding data security and privacy, regulatory hurdles, and the need for interoperability standards in multi-robot environments.
How are advancements in artificial intelligence impacting the capabilities of service robots?
Advancements in AI are enabling service robots to perform more complex tasks, adapt to dynamic environments, and interact with humans more intuitively, enhancing their utility across various applications.
How do ethical considerations factor into the development and deployment of service robotics?
Ethical considerations such as ensuring safety, transparency, and accountability in the design and use of service robots are paramount to building trust among users and stakeholders, thereby facilitating wider acceptance and adoption.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]