Global Scrubber System Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Wet scrubber system and Dry scrubber system), Application (Oil & Gas, Pharmaceuticals, Petrochemicals & Chemicals, Marine and Others), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Scrubber System Market Size
The Global Scrubber System Market was valued at USD 5.49 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 9.39 billion by 2033 from USD 5.83 billion in 2025. It is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.14% from 2025 to 2033.
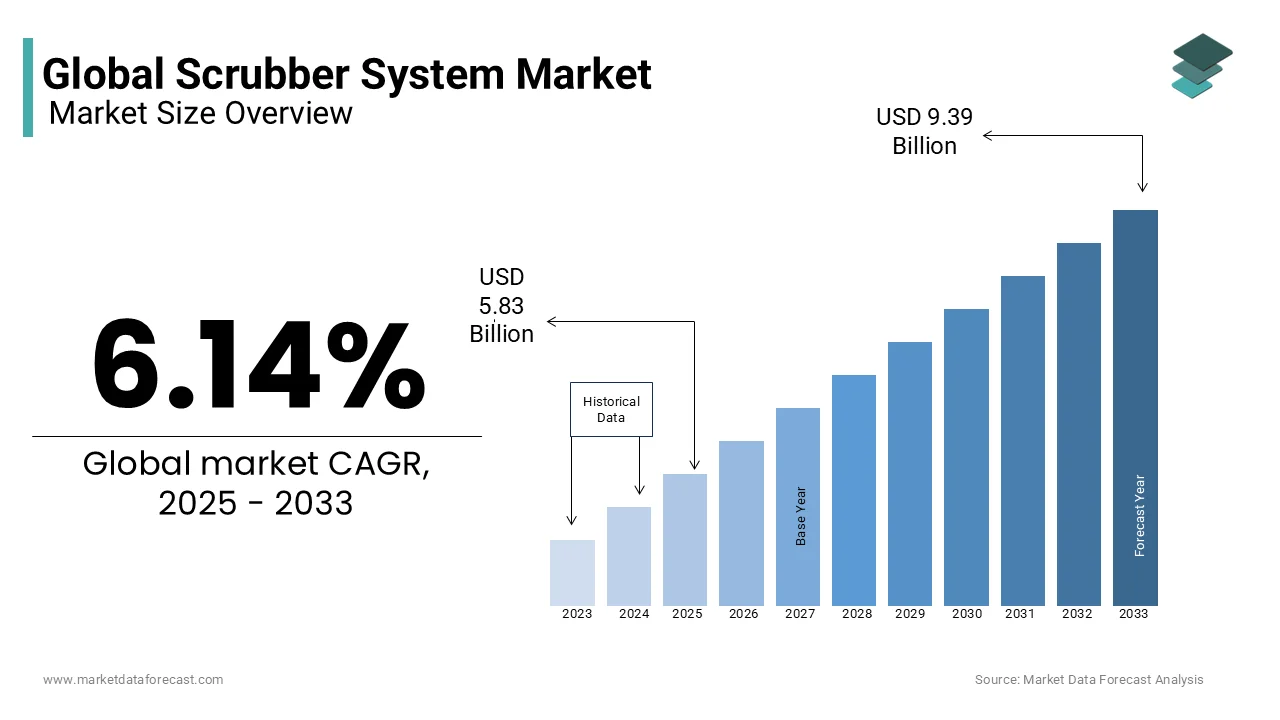
The scrubber system market is growing because the world is working hard to stop air pollution from factories and industries. These systems are special machines that clean dirty air coming out of places like ships, power plants, oil companies, and chemical factories. They take away harmful stuff like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and tiny dust particles that can hurt the air we breathe. These machines come in two types: wet ones that use liquid to catch the bad stuff, and dry ones that use a powder. Scrubbers are super important today because governments are making strict rules, like the International Maritime Organization’s MARPOL Annex VI, which says ships can’t release too much sulfur into the air. This push for cleaner air is why scrubber systems are being used more and more.
Moreover, the World Health Organization draws attention on air pollution that causes about 7 million people to die early every year, so cleaning the air is a huge deal. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development found that ships around the world make almost 2.9% of the gases that warm up the planet, including a lot of sulfur. Also, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency says factories in the U.S. alone put out more than 30 million tons of bad air stuff each year. Scrubber systems help cut down these numbers, making them a key tool for keeping our planet healthier and safer for everyone.
MARKET DRIVERS
Technological Advancements in Scrubber Design
A burgeoning driver is the evolution of scrubber technology, enhancing efficiency and appeal. Innovations like hybrid scrubbers which switch between open- and closed-loop modes, offer flexibility for varying regulatory zones. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory reports that modern scrubbers can achieve up to 98% sulfur removal efficiency that is a leap from older models at 85%. This improvement is detailed in their 2023 emissions technology review and it attracts industries seeking high-performance solutions. Additionally, compact designs reduce space needs by 30%, as per a Marine Engineering study, benefiting retrofits in cramped vessels. These advancements lower operational costs and broaden applicability, fueling market growth.
Growing Public and Corporate ESG Focus
The rising emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles is propelling scrubber adoption. Companies face pressure from stakeholders to demonstrate eco-responsibility. A 2024 PwC survey reveals 83% of global investors now prioritize ESG in decision-making, pushing firms to curb emissions visibly. Scrubbers align with this ethos, offering tangible pollution reduction. The World Economic Forum notes that 70% of Fortune 500 companies committed to net-zero targets by 2023, often relying on scrubbers in transition phases. This shift, amplified by public demand for cleaner air, incentivizes industries especially in high-visibility sectors like shipping and manufacturing to invest in scrubber systems.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Competition from Alternative Green Technologies
A fresh restraint is the rise of competing eco-friendly alternatives challenging scrubber dominance. Technologies like carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen fuel cells are gaining traction. The International Energy Agency reports that CCS deployments grew by 44% globally in 2023, capturing 45 million tons of CO2 annually outpacing scrubbers’ pollutant focus. In shipping, the International Transport Forum notes 15% of new vessels in 2024 opted for hydrogen propulsion, bypassing scrubbers entirely. These alternatives often backed by government subsidies and threaten scrubber relevance because firms prioritize long-term decarbonization over interim fixes which is slowing market expansion.
Shortage of Skilled Technical Personnel
A lesser-discussed restraint is the scarcity of trained professionals to install and maintain scrubber systems. Complex setups demand specialized expertise, yet the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 10% shortfall in environmental engineering technicians by 2030, with only 17,000 trained annually against rising demand. In maritime contexts, the International Maritime Organization flags a global deficit of 89,000 qualified officers by 2026, per their 2023 workforce report, complicating scrubber retrofits. This skills gap delays deployments, increases labor costs, and deters adoption, particularly in regions lacking robust training infrastructure, posing a structural barrier to market growth.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Adoption in Waste-to-Energy Facilities
A unique opportunity lies in deploying scrubbers in the growing waste-to-energy (WtE) sector. As municipalities tackle landfill overflow, WtE plants incinerate trash to generate power, releasing pollutants needing control. The World Bank estimates global municipal solid waste will reach 3.4 billion tons annually by 2050, driving WtE expansion. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency reports 71 WtE facilities in the U.S. processed 26 million tons of waste in 2022, with scrubbers reducing dioxin emissions by 95%. This niche, less explored than shipping or power, offers scrubber firms a chance to diversify into a sustainability-driven market with rising global investment.
Retrofitting Aging Industrial Infrastructure
Retrofitting outdated industrial plants presents a compelling opportunity. Many facilities, built decades ago, lack modern emission controls but face pressure to meet current standards. The International Labour Organization estimates 40% of global industrial infrastructure predates 1990, emitting unchecked pollutants. In the U.S., the Energy Information Administration notes 25% of coal-fired plants over 60 gigawatts still operate without scrubbers as of 2023. Retrofitting these with compact, cost-effective scrubber designs can extend their lifespan while ensuring compliance. This untapped segment allows manufacturers to target legacy systems, blending environmental upgrades with economic preservation.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Public Perception and Misinformation
Negative public perception, fueled by misinformation, challenges scrubber adoption. Critics argue scrubbers merely shift pollution from air to water, especially in marine applications. A Pew Research Center survey in 2023 found 62% of U.S. adults believe scrubbers harm oceans, despite scientific nuance. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration clarifies that closed-loop scrubbers discharge less than 1% of pollutants into water yet myths persist. This scepticism is amplified by social media, pressures policymakers and firms are slowing market acceptance. Manufacturers must counter this with education, but entrenched narratives hinder progress.
Dependence on Volatile Fuel Prices
Scrubber viability hinges on fuel price fluctuations, creating uncertainty. High-sulfur fuel oil (HSFO), paired with scrubbers, competes with pricier low-sulfur alternatives. The U.S. Energy Information Administration reports HSFO prices spiked 20% in 2023 to $80 per barrel, narrowing cost savings versus low-sulfur fuel at $100. When spreads shrink historically dipping below $10 per barrel per Platts data in 2022 scrubber economics weaken. The World Trade Organization notes fuel volatility, tied to geopolitical tensions, hit a 15-year high in 2024. This unpredictability deters investment, as operators weigh short-term gains against long-term risks, stalling market growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
6.14% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
B&W, Alfa Laval, DuPont CECO, Fuji Electric, Evoqua, GEA, Hamon Research-Cottrell, Wrtsil, KCH, and Others. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The wet scrubber systems segment is the biggest by taking up 65.4% of the market share in 2024. It is at the top as they’re easy to add to old factories and can handle hot, sticky gases that others can’t. The U.S. Energy Information Administration says 30% of U.S. industrial plants still use outdated setups from the 1980s, needing wet scrubbers to keep running. This makes them super important for keeping old systems legal and safe without big rebuilds, giving them the top spot.
The dry scrubber systems segment is growing the fastest among others, with a CAGR of 6.4%. They’re speeding up because they make less waste that’s hard to throw away and fit small spaces better. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency reports dry scrubbers produce 50% less leftover sludge than wet ones, easing disposal headaches. The World Bank says small factories, which grew 15% globally in 2023, love them for their compact size. This growth matters as businesses want simple, low-mess solutions for tight spaces.
By Application Insights
The Marine segment became the largest by making up 35.5% of the market share in 2024 because of some special reasons. The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development says 90% of world trade travels by sea, so ships need scrubbers to keep the air clean on busy routes. Plus, the U.S. Coast Guard reports 40% of U.S.-registered ships are over 20 years old, and scrubbers help update them without buying new ones. Also, the Environmental Protection Agency notes 50 U.S. ports set tougher emission rules in 2023, pushing ships to use scrubbers. This keeps Marine at the top for trade and port needs.
The Pharmaceuticals segment is the swiftest expanding, with a CAGR of 7.2% during the forecast period. It’s speeding up for new reasons that matter a lot. The U.S. National Institutes of Health stresses that 60% of drug labs need super-clean air for special rooms, and scrubbers make this happen to meet high standards. The World Trade Organization also reports global pharma exports reached $700 billion in 2023, so factories add scrubbers to follow international rules. Plus, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration says chemical exposure complaints jumped 15% in 2022, making scrubbers important for worker safety. This growth helps make safe drugs and supports global trade.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia Pacific led the scrubber system market and held a 40.3% share in 2024. Its edge comes from massive urban waste management needs, not just industrial growth. The World Bank estimates the region generates 1.2 billion tons of municipal waste yearly, driving scrubber use in incineration plants. This focus on waste-to-energy reduces landfill reliance, vital as urban populations swell is projected to hit 3.5 billion by 2050, says the United Nations. Scrubbers here tackle smoke and odors, improving city air quality, a fresh angle beyond traditional pollution control.
North America remains a crucial player. Its strength lies in retrofitting aging power grids, not just regulatory push. The U.S. Energy Information Administration notes 20% of U.S. power plants over 50 gigawatts are pre-1980, needing scrubbers to extend life. This preserves energy infrastructure while cutting emissions, a dual win. The region’s position is key for balancing economic stability with environmental upgrades, offering a new lens on scrubber demand beyond pharma or shipping growth.
Europe holds a notable portion of the market owing to a surge in biogas production, not just emission norms. Eurostat reports biogas output hit 19 billion cubic meters in 2023, with scrubbers cleaning sulfur-heavy exhausts from organic waste. This supports Europe’s circular economy goals, turning waste into energy. Scrubbers’ role here is critical for sustainable fuel innovation, a novel driver distinct from industrial or maritime focus, enhancing energy security amid fossil fuel phase-outs.
Latin America is moving ahead at a decent pace in this market. Its rise is tied to mining boomtowns, not typical urban factors. The World Bank says the region’s mineral exports grew 10% in 2023, with scrubbers curbing dust in copper and lithium hubs like Chile. This protects worker health and local ecosystems, vital as mining employs 2.5 million people, per the International Labour Organization. Scrubbers’ importance here lies in supporting resource-driven economies, a fresh take beyond regulatory or energy narratives.
Middle East & Africa is a growing scrubber market fueled by desalination plant expansion, not just oil. The United Nations Environment Programme estimates the region hosts 70% of global desalination capacity with over 25 million cubic meters daily in 2023 and is needing scrubbers for brine vapor emissions. This ensures water security for 150 million people, per World Health Organization data. Scrubbers’ role in water production highlights a unique environmental angle, critical for arid regions, diverging from industrial or shipping-centric discussions.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global scrubber system market include B&W, Alfa Laval, DuPont CECO, Fuji Electric, Evoqua, GEA, Hamon Research-Cottrell, Wrtsil, and KCH.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Wärtsilä Corporation
Wärtsilä, a Finland-based leader, plays a huge role in the scrubber system market by creating smart solutions for ships. Its big contribution is designing scrubbers that adapt to different needs, like switching modes to save fuel or meet local rules. This helps ship owners keep costs down while staying eco-friendly. Wärtsilä also focuses on making systems smaller and easier to fit on all kinds of vessels, from big cargo ships to tiny ferries. By pushing these clever ideas, Wärtsilä makes it simpler for the shipping world to go green, leading the way in cleaner oceans.
Alfa Laval AB
Alfa Laval, from Sweden, stands out by making scrubber systems that work for smaller businesses, not just giants. Its key contribution is building reliable, no-fuss scrubbers that don’t need a lot of upkeep, perfect for factories or boats with tight budgets. Alfa Laval also teams up with companies across industries to customize solutions, ensuring everyone can use them. This approach opens doors for more users to join the fight against pollution without breaking the bank. By keeping things simple and affordable, Alfa Laval helps spread clean tech further than ever.
Yara Marine Technologies
Yara Marine, based in Norway, boosts the market by focusing on older ships that need updates. Its main contribution is crafting lightweight scrubbers that slide into existing fleets without big changes, saving time and money. Yara works closely with shipyards to speed up installations, making it a go-to for owners wanting quick fixes. This keeps aging vessels sailing legally and cleanly, supporting trade without harming the air. Yara’s practical, retrofit-friendly designs breathe new life into old systems, playing a key part in making global shipping more sustainable.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Expanding Service Networks
Companies like Wärtsilä boost their market strength by setting up more service centers around the world. Instead of just selling scrubbers, they make sure customers can get quick repairs or advice wherever they are, like at busy ports or industrial hubs. This keeps machines running smoothly without long delays, which customers really like. By being close to users and offering hands-on help, they build trust and make it hard for competitors to catch up. This strategy turns them into a reliable partner, not just a supplier, locking in their spot as a top choice globally.
Sustainability Branding
Players like Alfa Laval focus on showing off their green side to win over eco-conscious buyers. They tell stories about how their scrubbers help the planet like cleaning air in unique ways—and share these through ads or events. This isn’t just about making products; it’s about looking like a company that cares about the future. By standing out as a leader in sustainability, they attract customers who want to look good too, especially big firms with green goals. This fresh approach gives them an edge by linking their name to a bigger purpose.
Training and Education Programs
Firms like Yara Marine grow their influence by teaching people how to use scrubbers better. They offer classes or online guides for workers, ship crews, or factory staff, showing them tricks to get the most out of their systems. This isn’t just selling it’s making sure customers feel smart and in control. By sharing know-how, they create a group of loyal users who stick with their brand because they understand it best. This strategy sets them apart by building a skilled community, making their scrubbers the go-to option for those in the know.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The Scrubber System Market is highly competitive, with many companies developing solutions to reduce air pollution in industries like manufacturing and shipping. Scrubber systems remove harmful gases, such as sulfur dioxide, helping businesses comply with strict environmental laws. As demand grows, companies are finding new ways to stand out.
One key area of competition is customization and smart technology. Some companies design scrubbers for specific industries, while others add AI and sensors to improve efficiency and lower maintenance costs. Another shift is towards alternative cleaning methods, such as electrostatic or bio-scrubbing, which can be more eco-friendly and energy-efficient than traditional wet and dry scrubbers.
A new business model, Scrubber-as-a-Service, allows businesses to rent scrubbers or sign long-term maintenance contracts instead of buying them. This makes it easier for companies to adopt cleaner technology without large upfront costs. Additionally, some manufacturers focus on recycling scrubber waste, turning by-products like sulfur into useful materials, such as gypsum for construction.
With these innovations, competition in the market is no longer just about price. Companies now compete through technology, sustainability, and service models, shaping the future of the scrubber system industry in exciting new ways.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In January 2025, Sweden announced a ban on the use of open-loop scrubbers in its territorial waters, effective from July 1, 2025. This regulatory move underscores the country's commitment to reducing marine pollution from scrubber washwater discharges.
- In April 2024, Denmark reached an agreement to prohibit the discharge of scrubber washwater within its territorial waters, extending up to 12 nautical miles from the coast. Ships operating in these areas must switch to compliant fuels or utilize closed-loop scrubbers.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global scrubber system market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Wet scrubber system
- Dry scrubber system
By Application
- Oil & Gas
- Pharmaceuticals
- Petrochemicals & Chemicals
- Marine
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key drivers of growth in the scrubber system market?
Key drivers include stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the rising adoption of scrubber systems in marine vessels to comply with IMO 2020 standards, and the growing demand for air quality control technologies in industrial sectors.
What challenges does the scrubber system market face globally?
Challenges include high installation and operational costs, maintenance complexities, and resistance from some industry players due to alternative compliance options like low-sulfur fuel or liquefied natural gas (LNG). Additionally, public concerns over scrubber discharge water’s environmental impact can limit growth.
What role does technology innovation play in the scrubber system market?
Technology innovation is crucial in enhancing scrubber efficiency, reducing operational costs, and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. Advanced systems with real-time monitoring, reduced water usage, and hybrid capabilities are increasingly being developed to meet market demands.
How is the industrial sector influencing the growth of the scrubber system market?
The industrial sector, including oil & gas, chemicals, and power generation, drives market growth due to its need for effective emission control solutions. Industries increasingly adopt scrubber systems to meet stringent emission norms and corporate sustainability goals.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]