Global Satellite Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Nanosatellite, Micro Satellite, Mini Satellite, and Large Satellite), Application, End User, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Satellite Market Size
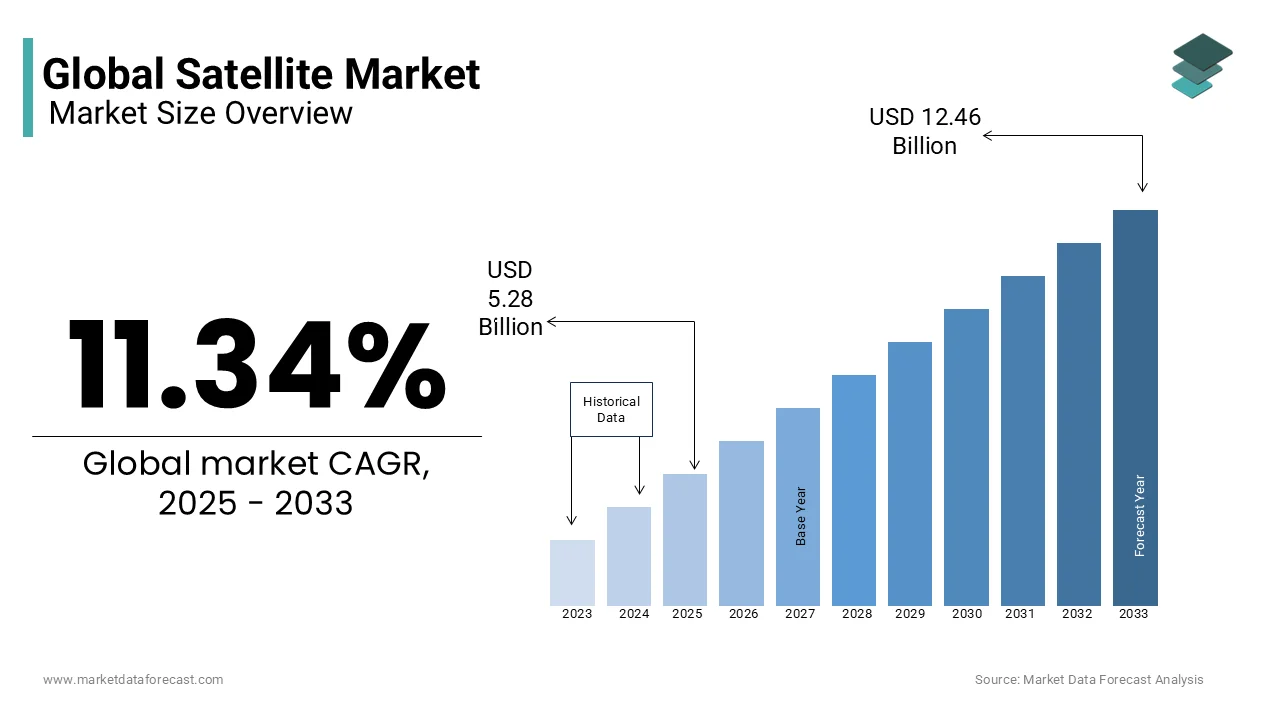
The global satellite market was worth USD 4.74 billion in 2024. The global market is projected to grow from USD 5.28 billion in 2025 to USD 12.46 billion by 2033, rising at a CAGR of 11.34% from 2025 to 2033.
The satellite market is a key part of modern technology. It involves creating, launching, and managing satellites for many uses like communication, observing Earth, navigation, science research, and defense. Satellites are man-made objects sent into space to orbit Earth and perform specific tasks. These tasks help improve global communication, monitor the environment, and support scientific discoveries. In 2023, the world depends more than ever on satellites. Their impact is felt in almost every industry and across different countries. The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs says that over 90 countries now own or use satellites. This shows that space technology is becoming easier to access and is no longer limited to a few advanced nations.
When it comes to where satellites are located, most of them are in low-Earth orbit (LEO). The Union of Concerned Scientists reports that there are about 5,400 active satellites in space right now, with LEO being the most popular location. This is because LEO is ideal for tasks like observing Earth and testing new technologies. Recently, large groups of satellites called mega-constellations have been developed. These aim to provide internet access to people all over the world. The International Telecommunication Union explains that satellites are crucial for solving the digital divide. About 2.7 billion people still do not have internet access, and satellites can help fix this problem. Satellites also play a big role in protecting the environment. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) says that over 90% of the data used for weather forecasts comes from satellites. These facts show how important satellites are for solving today’s challenges, such as climate change and lack of connectivity. They are essential tools for improving life on Earth.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Need for Global Internet Access
The rising demand for internet access around the world is a key factor driving the satellite market. According to the International Telecommunication Union, about 2.7 billion people still do not have internet access as of 2023, especially in remote or underserved areas. Satellites, especially those in low-Earth orbit (LEO), are crucial in providing internet to these regions. Companies like SpaceX's Starlink and OneWeb are working to launch thousands of satellites to offer high-speed internet globally. Euroconsult predicts that over 100,000 ground terminals will be installed each year by 2025 to support these efforts. The growing number of IoT devices also boosts demand for satellite-based connectivity. This shows how important satellites are for modern communication and connectivity, making them essential for today’s infrastructure.
Smaller and Cheaper Satellites
Advances in making satellites smaller have greatly boosted the satellite market. Small satellites, like CubeSats and nanosatellites, cost less to build and launch, making space technology more accessible. NASA reports that small satellites now make up over 80% of all satellite launches, allowing startups and research groups to explore space. These small satellites are much cheaper, costing as little as $1 million each, compared to traditional satellites, which can cost hundreds of millions. The Space Foundation states that the small satellite market is expected to grow by 19% every year from 2023 to 2030. New technologies in propulsion and power systems have also made these satellites last longer, enabling long-term missions. This shift has opened up new opportunities for scientific research and commercial uses.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of Building and Launching Satellites
One big challenge in the satellite market is the high cost of building and launching satellites. The Aerospace Corporation says launching a single geostationary satellite can cost between $150 million and $400 million, depending on its size and complexity. Even small satellites, though cheaper, still cost between $1 million and $5 million each. Securing a launch vehicle is also expensive, with SpaceX charging about $62 million for a Falcon 9 launch. These costs create barriers for smaller companies and developing countries trying to enter the market. The World Economic Forum points out that only a few nations dominate satellite manufacturing and launches due to these financial hurdles. Such expenses limit innovation and make it harder for new players to join, slowing down the industry’s growth.
Space Debris and Crowded Orbits
Space debris is a major problem for the satellite market, threatening safety and sustainability. The European Space Agency estimates there are over 36,500 pieces of debris larger than 10 cm in orbit, along with millions of smaller fragments. Even tiny debris can damage satellites, as seen in the 2009 collision between Iridium and Cosmos satellites. The Secure World Foundation warns that the increasing number of satellite launches, especially mega-constellations, is making orbits more crowded. By 2030, projections suggest up to 100,000 active and inactive satellites could be in low-Earth orbit. This overcrowding raises the risk of chain reactions, called the Kessler Syndrome, which could make certain orbits unusable. Solving this issue requires global cooperation and advanced technologies, adding complexity and cost to satellite operations.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
New Uses for Earth Observation
A major opportunity in the satellite market is the growing use of Earth observation. The World Bank highlights that satellite images are now widely used for disaster management, urban planning, and monitoring farms. For example, the Food and Agriculture Organization says the use of satellite data in precision farming has grown by 25% annually since 2020. Earth observation satellites also help fight climate change, with NOAA stating that over 90% of climate data comes from satellites. Advances in imaging and AI-driven analytics make satellite data even more valuable. These innovations help governments and businesses make better decisions, creating new opportunities for satellite operators.
Growth of Navigation Systems
The expansion of satellite-based navigation systems is another big opportunity. GPS and other global navigation systems are vital for industries like transportation, logistics, and defense. The U.S. Department of Commerce estimates that GPS has contributed over $1.4 trillion to the global economy since 1980. New systems like Europe’s Galileo and China’s BeiDou have improved the accuracy and reliability of navigation services. The European GNSS Agency predicts there will be over 10 billion navigation devices by 2030. Autonomous vehicles and drones also rely heavily on precise satellite navigation, increasing demand for advanced systems. These developments show the huge potential for growth in navigation-related satellite applications, benefiting both businesses and governments.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Rules and Geopolitical Issues
Rules and geopolitical tensions are significant challenges for the satellite market. The International Telecommunication Union assigns orbital slots and radio frequencies, but disputes over these resources often delay projects. For instance, disagreements over spectrum allocation have held up several satellite initiatives. The Center for Strategic and International Studies notes that competition between countries, especially the U.S. and China, has led to fragmented rules and higher risks. National security concerns have also led to stricter export controls on satellite technologies, limiting international collaboration. These complexities create uncertainty for satellite operators and manufacturers, making it harder to innovate and invest. Navigating these challenges requires legal expertise and diplomacy, complicating entry for new players.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Challenges
Environmental concerns and sustainability issues are major challenges for the satellite market. Launching satellites contributes to carbon emissions, with each rocket launch releasing up to 300 tons of CO2, according to the European Space Agency. Additionally, old satellites left in orbit add to the space debris problem, threatening long-term sustainability. The Union of Concerned Scientists says only 10% of satellites are properly removed after their mission ends. Public concern about the environmental impact of space activities is growing, pushing companies to adopt greener practices. However, developing sustainable technologies like reusable rockets and eco-friendly fuels requires significant investment. Balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility remains a complex challenge, requiring innovative solutions and global cooperation.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
11.34% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, End User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Airbus SAS (Netherlands), Ball Corporation (US), Boeing (US), Eutelsat Communications SA (France), Intelsat (Luxembourg), Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd (Israel), Lockheed Martin Corporation (US), Northrop Grumman Corporation (US), Safran (France), SES SA (Luxembourg), Space Exploration Technologies Corp (US), Space Systems/Loral, LLC (US), Thales Group (France), Viasat, Inc. (US), Sierra Nevada Corporation (US), and L3 Harris Technologies (US). |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The Large satellites segment dominated the satellite market and held 45.7% of the market share in 2024. These satellites are primarily used for communication, weather forecasting, and surveillance due to their ability to carry advanced payloads and operate in geostationary orbits. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) states that large satellites provide over 90% of the data used for accurate weather predictions , making them critical for global safety. Their importance lies in their high capacity and long operational lifespan, often exceeding 15 years. Despite their high cost, ranging from $250 million to $400 million per unit, they remain indispensable for applications requiring extensive coverage and reliability.
The Nanosatellites segment is the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 20.4%. Their rapid growth is driven by their affordability, costing as little as $1 million per unit, and their ability to support diverse applications like Earth observation and IoT connectivity. NASA highlights that nanosatellites now account for over 80% of all satellite launches , enabling startups and research institutions to participate in space exploration. Innovations in propulsion systems have extended their operational life to up to 5 years. Their compact size and lower launch costs make them ideal for testing new technologies, driving their adoption across industries.
By Application Insights
The communication segment led the satellite market by capturing 40.2% of the total market share in 2024. Satellites play a vital role in providing internet, television, and phone services globally. SpaceX’s Starlink aims to deploy over 42,000 satellites to deliver high-speed internet worldwide, addressing the digital divide. The U.S. Department of Commerce estimates that GPS and communication satellites contribute over $1.4 trillion to the global economy . With increasing demand for connectivity, especially in remote areas, communication satellites remain essential for modern infrastructure and economic growth.
The Earth observation and remote sensing segment is the swiftest emerging one, with a CAGR of 12.5%owing to the rising demand for disaster management, urban planning, and climate monitoring. NOAA reports that over 90% of climate data comes from Earth observation satellites. For instance, precision agriculture using satellite imagery has grown by 25% annually since 2020 , according to the Food and Agriculture Organization. Innovations in hyperspectral imaging and AI-driven analytics enhance the value of satellite data, enabling governments and businesses to make informed decisions. This segment’s versatility ensures its continued expansion.
By End User Insights
The commercial segment captured the largest share of the satellite market and accounted for 60.7 of the total market in 2024. Commercial satellites are widely used for communication, navigation, and Earth observation, supporting industries like media, transportation, and agriculture. Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are investing heavily in satellite constellations to provide global internet access. The commercial sector’s focus on innovation and cost-efficiency drives its dominance in the satellite market.
The Military and defense segment is the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 8.7% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by rising geopolitical tensions and the need for advanced surveillance, navigation, and secure communication systems. The U.S. Department of Defense allocates over $15 billion annually to space-based defense programs. Satellites are critical for missile detection, border security, and intelligence gathering. For example, the Secure World Foundation notes that military satellites played a key role in tracking over 36,500 pieces of space debris to ensure operational safety.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America spearheaded in the satellite market by holding 40.3% of the global share in 2024. This region is ahead because of big companies like SpaceX, Lockheed Martin, and Boeing, as well as strong government spending on space and defense. The U.S. Department of Defense spends over $15 billion every year on satellite programs to stay ahead in technology. NASA’s satellites also play a key role, providing 90% of the data used for weather and climate studies, as stated by NOAA. Projects like SpaceX’s Starlink plan to launch 42,000 satellites to provide internet worldwide. North America’s success comes from its advanced infrastructure, focus on innovation, and high demand for better connectivity, making it the center of satellite development.
Europe plays a major role in the satellite market, with 25.2% of the global share in 2024. The region benefits from teamwork through organizations like the European Space Agency (ESA), which runs projects like Galileo for navigation and Copernicus for Earth observation. The ESA spends over €6 billion each year on space programs, encouraging new ideas in satellite technology. Europe is also working on eco-friendly satellite systems to reduce environmental impact.
The Asia Pacific region is quickly becoming a major player in the satellite market, thanks to countries like China, India, and Japan. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, this region operates over 1,300 active satellites, making up 25% of the world’s total. China’s BeiDou system and India’s low-cost satellite launches have made the region a leader in affordable space technology. For example, India’s space agency, ISRO, launched 20 satellites in one mission, showing how efficient they are. With more investments in IoT and broadband, the region is helping both cities and rural areas. Asia Pacific’s growth is driven by government support, rising demand for communication, and progress in space exploration, making it a key part of the global satellite industry.
The Middle East and Africa are becoming important players in the satellite market, especially for communication and Earth observation. Projects like the UAE’s Hope Probe and Saudi Arabia’s satellite programs show their commitment to space exploration. According to the International Telecommunication Union, over 600 million people in Africa still don’t have internet access, so satellites are being used to connect remote areas. Companies like Yahsat and Nilesat are helping bring connectivity to these regions. The African Space Agency is working on regional projects worth over $7 billion to improve collaboration. By focusing on solving the digital divide and tackling climate challenges, this region is becoming more significant in the global satellite landscape.
Latin America is starting to make its mark in the satellite market, thanks to its ideal location for launching satellites. Countries like Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico are leading the way. Brazil’s Alcântara Launch Center offers cost-effective launches because of its position near the equator. The Inter-American Development Bank says satellite technology in Latin America helps over 100 million people in rural areas by supporting farming, disaster management, and internet access. Satellites also monitor deforestation in the Amazon rainforest, which is critical for environmental protection. With over 30% of the population lacking internet, satellite-based solutions are being developed to close this gap. Partnerships with global agencies and a focus on sustainability are driving Latin America’s growth in the satellite industry.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
SpaceX (United States)
SpaceX is a dominant player in the global satellite market, primarily due to its revolutionary Starlink project. The company aims to deploy over 42,000 satellites in low-Earth orbit (LEO) to provide high-speed internet globally. As of 2023, SpaceX has already launched more than 5,000 Starlink satellites , serving millions of users in remote and underserved areas. According to Euroconsult, SpaceX’s reusable Falcon 9 rockets have reduced launch costs by up to 30% , making satellite deployment more affordable. SpaceX’s innovations in reusable rocket technology and satellite miniaturization have set new standards in the industry. Beyond connectivity, SpaceX’s satellite systems contribute significantly to disaster response, military communications, and bridging the global digital divide, strengthen its leadership in the market.
Boeing (United States)
Boeing is a key player in the satellite market, specializing in large geostationary satellites for communication, weather forecasting, and defense. The company holds a significant share of the commercial satellite manufacturing market, with over 200 satellites built and launched since 2000 , as reported by the Satellite Industry Association. Boeing’s advanced satellite systems, such as the 702 series, are known for their long operational life of up to 15 years and high payload capacity. The U.S. Department of Defense relies heavily on Boeing’s satellites for secure communications and missile detection, while its partnerships with operators like SES have expanded broadband services across Asia and Africa. Boeing’s contributions to reliable, cutting-edge satellite technology ensure robust global communication networks and support critical applications like climate monitoring and national security.
ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation)
ISRO has emerged as a major player in the satellite market, particularly in cost-effective satellite launches and Earth observation. Known for its affordable yet highly efficient missions, ISRO successfully launched 20 satellites in a single mission in 2016, showcasing its capability to meet global demand. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, India operates over 100 active satellites , contributing significantly to navigation, communication, and climate monitoring. ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is one of the most reliable launch systems globally, attracting international customers. The organization’s emphasis on sustainability is evident in its development of small satellites and eco-friendly propulsion systems. By addressing both domestic and global needs, ISRO plays a vital role in democratizing access to space technology, supporting applications like disaster management, agricultural planning, and environmental monitoring.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Pioneering Technological Breakthroughs
Innovation remains a cornerstone for industry leaders like SpaceX and Boeing , enabling them to maintain a competitive edge. SpaceX has transformed the satellite launch landscape with its reusable Falcon 9 rockets, which cut costs by up to 30% , as highlighted by Euroconsult. This advancement has made satellite deployment more economical and environmentally sustainable. Boeing, on the other hand, excels in designing advanced satellite systems such as the 702 series, known for their extended operational lifespan of up to 15 years and high payload capacity. By integrating cutting-edge technologies like AI-driven analytics and miniaturized satellites, these companies cater to diverse applications, from global communication to climate monitoring.
Building Collaborative Networks
Strategic alliances and partnerships play a pivotal role in expanding market reach. For instance, Boeing collaborates with global operators like SES to extend broadband services to underserved regions in Asia and Africa. Such partnerships enable companies to access new markets and enhance their service offerings. Similarly, ISRO works closely with international space agencies and private entities to share expertise and resources, facilitating affordable launches and fostering inclusivity in space exploration. These collaborations not only drive revenue growth but also strengthen the capabilities of all stakeholders involved.
Achieving Cost Efficiency Through Scalability
Reducing costs while maintaining quality is a key priority for industry leaders. SpaceX’s Starlink project exemplifies this approach by leveraging mass production techniques to manufacture thousands of small satellites at a fraction of traditional costs. Meanwhile, ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) is celebrated for its affordability, making it a preferred choice for customers in developing nations. By focusing on scalability and optimizing production processes, these companies offer competitive pricing, democratizing access to satellite technology for a wider audience.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The satellite market is very competitive with many big and small players working to grow their share. Big companies like SpaceX and Boeing lead the market because they have advanced technology and strong financial support. SpaceX focuses on low-cost reusable rockets and its Starlink project which aims to provide internet to remote areas. Boeing makes large satellites for communication and defense which are used by governments and businesses worldwide. These companies spend a lot on research to stay ahead.
At the same time smaller companies and startups are also entering the market. They focus on small satellites which are cheaper to build and launch. For example companies in India and Europe make affordable satellites for Earth observation and IoT services. This has made the market more diverse and opened new opportunities.
Countries like China and India are also growing fast in this field. China’s BeiDou system competes with GPS while India’s ISRO offers low-cost launches. This global competition pushes companies to innovate and reduce costs.
The market is also seeing more partnerships. Companies team up with governments or other firms to share resources and expand their reach. Despite the competition all players face challenges like space debris and high costs. To succeed companies must focus on sustainability and finding new uses for satellites. This mix of big players and new entrants makes the satellite market dynamic and full of opportunities.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global satellite market include Airbus SAS (Netherlands), Ball Corporation (US), Boeing (US), Eutelsat Communications SA (France), Intelsat (Luxembourg), Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd (Israel), Lockheed Martin Corporation (US), Northrop Grumman Corporation (US), Safran (France), SES SA (Luxembourg), Space Exploration Technologies Corp (US), Space Systems/Loral, LLC (US), Thales Group (France), Viasat, Inc. (US), Sierra Nevada Corporation (US), and L3 Harris Technologies (US).
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2025, Thales Alenia Space received an order from Japan's SKY Perfect JSAT to construct the JSAT-32 geostationary communications satellite. Scheduled for launch in 2027, the satellite is designed for an operational lifespan exceeding 15 years.
- In March 2025, Larsen & Toubro (L&T) invested in India's private rocket and satellite industry, collaborating with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to assemble India's first privately built PSLV and develop equipment for ISRO’s deep space exploration projects.
- In February 2025, Vodafone successfully conducted the world’s first satellite video call using a regular smartphone, partnering with AST SpaceMobile. The technology aims to provide mobile broadband services via satellites, with a European rollout planned for 2025.
- In June 2024, SES launched the Astra 1P satellite aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. Built by Thales Alenia Space, Astra 1P replaces four satellites at 19.2°E, delivering direct-to-home TV services to European markets, including Germany, France, and Spain.
- In February 2025, India announced new policies engaging private sector companies in rocket and satellite manufacturing, aiming to establish the country as a global exporter of small satellites and space technology, targeting a $4-$5 billion business opportunity.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global satellite market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Nanosatellite
- Micro Satellite
- Mini Satellite
- Large Satellite
By Application
- Earth Observation and Remote Sensing
- Scientific Research
- Communication
- Direct Broadcast
- Mapping and Navigation
- Weather Forecasting
- Surveillance and Security
By End User
- Military and Defense
- Commercial
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the satellite market’s growth?
Increased demand for global broadband, advancements in miniaturized satellites, and government investments in space technology are key drivers. The rise of private space companies and reusable rockets has reduced costs. Expansion of 5G networks and smart city initiatives also fuel demand.
How does satellite technology impact global internet access?
Satellite internet, led by companies like Starlink and OneWeb, provides high-speed connectivity to remote and underserved regions. It bypasses the need for traditional infrastructure, making broadband accessible worldwide. This technology supports economic growth, education, and disaster response.
What are the latest innovations in satellite technology?
Advances include reusable rockets, AI-powered satellite analytics, and laser-based communication. Mega-constellations like Starlink are changing broadband accessibility. Quantum encryption for secure space communications is also gaining interest.
How is the defense sector using satellite technology?
Military satellites provide secure communication, intelligence gathering, and missile tracking. They support navigation for troops and enhance battlefield awareness. Governments invest in satellite-based surveillance to strengthen national security.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]