Global Robotics Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented by Type (Industrial Robotics and Services Robotics), Application (Disinfection, Shelf Scanning, Delivery, Security & Inspection, Advertising, Manufacturing, and Others), End-User (Disinfection, Shelf Scanning, Delivery, Security & Inspection, Advertising, Manufacturing, and Others) and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Robotics Market Size
The global robotics market was valued at USD 84.49 billion in 2024. The global market is estimated to reach USD 392.25 billion by 2033 from USD 100.21 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 18.60% from 2025 to 2033.
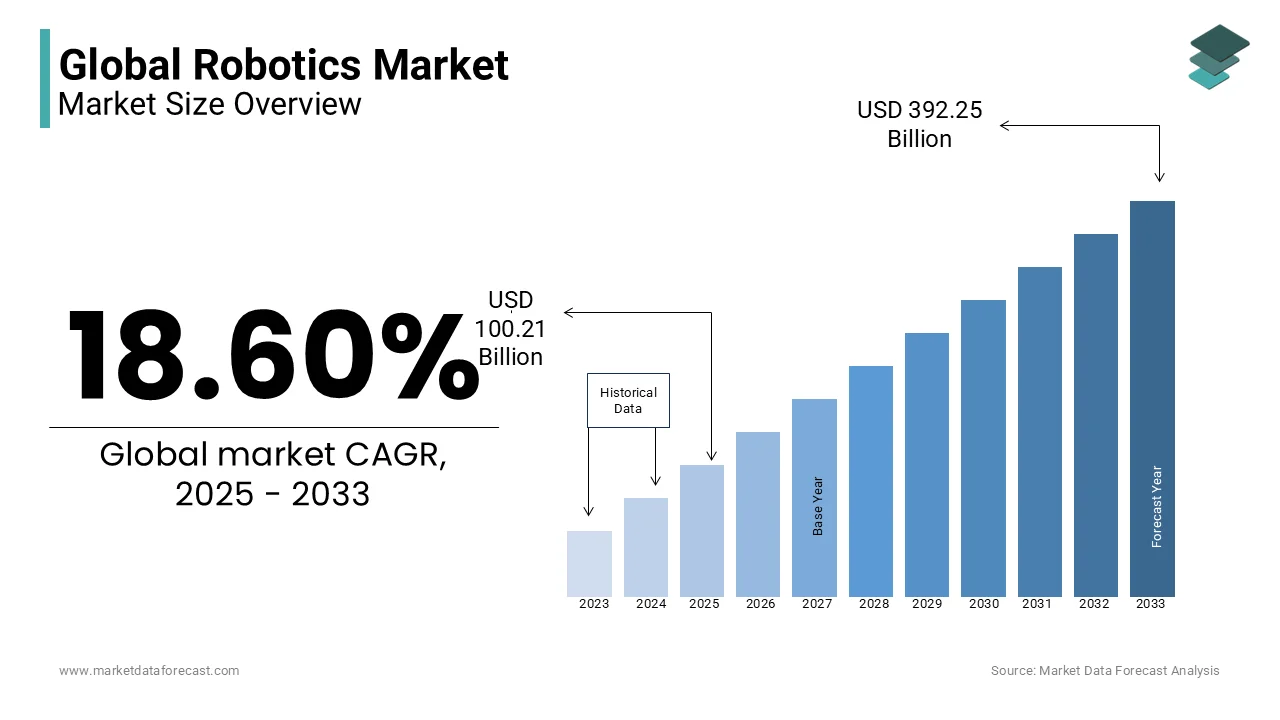
Robotics includes the design, development, and deployment of automated machines programmed to perform a wide range of tasks across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and defense. Robotics integrates technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, sensors, and advanced mechanics to enhance efficiency, precision, and operational capabilities. Modern robots are classified into various types, including industrial robots, service robots, humanoid robots, and collaborative robots (cobots), each designed for specific applications.
The impact of robotics is evident in multiple sectors. According to the International Federation of Robotics (IFR), the global average robot density in manufacturing reached 141 robots per 10,000 employees in 2022, highlighting the increasing reliance on automation. In the automotive industry, South Korea leads with 1,000 robots per 10,000 workers, followed by Japan and Germany, reflecting the sector’s strong commitment to robotic integration.
In healthcare, surgical robotics is revolutionizing medical procedures. The da Vinci Surgical System, developed by Intuitive Surgical, has been used in over 10 million procedures globally, enhancing precision and reducing recovery times. Meanwhile, Boston Dynamics' robotic dog, Spot, has been deployed in disaster recovery and hazardous environments, showcasing robotics' role in safety and emergency response. Furthermore, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are transforming logistics. Amazon reported deploying over 750,000 robots in its warehouses as of 2023 to optimize inventory management and streamline operations. With ongoing advancements, robotics is set to play an even greater role in enhancing efficiency, safety, and innovation across diverse industries.
MARKET DRIVERS
Technological Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning into robotics has significantly enhanced capabilities such as perception, decision-making, and autonomy. This advancement enables robots to perform complex tasks with increased efficiency and precision. For instance, ABB Robotics reported a 20% increase in sales of AI-powered robots in 2024, primarily in the manufacturing sector, where robots optimize production lines. Boston Dynamics’ AI-powered robot, Spot, has been successfully adopted by logistics companies like DHL, leading to a 15% reduction in warehouse operational costs. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights that AI integration in robotics leads to improved performance in tasks like predictive maintenance, further driving the adoption of robotics across industries.
Government Initiatives and Funding
Government support plays a crucial role in accelerating the robotics market's growth. Many governments worldwide have recognized the strategic importance of robotics in enhancing national competitiveness and addressing labor shortages. For example, the South Korean government announced plans to invest approximately $2.3 billion to quadruple its robot market by 2030, aiming to alleviate labor shortages and advance automation. Similarly, the Chinese government has implemented policies and subsidies to promote the adoption of robotics in manufacturing, contributing to China becoming the world's largest market for industrial robots, as reported by the International Federation of Robotics.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs
The substantial capital required for acquiring and maintaining robotic systems poses a significant barrier, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The Business Research Company reports that a new industrial robot can cost between $50,000 to $80,000, with total system costs, including application-specific peripherals, ranging from $100,000 to $150,000. These high expenses can deter businesses from investing in robotics, particularly when the return on investment is uncertain or long-term. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and the need for specialized personnel to operate and service these machines further escalate costs, making it challenging for SMEs to justify the investment.
Workforce Displacement and Skill Gaps
The integration of robotics into various industries has raised concerns about workforce displacement and the emergence of skill gaps. As automated systems take over tasks traditionally performed by humans, there is a growing fear of job losses, particularly in manufacturing and assembly line positions. General Motors reported a reduction of 5,000 jobs in 2024 due to automation on its assembly lines. The U.S. Department of Labor emphasizes the need for workforce reskilling, and companies like Siemens have invested $10 million in retraining programs. However, there is a shortage of workers with the technical expertise to manage advanced robotic systems, hindering the adoption of robotics in sectors like logistics and manufacturing.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion in Healthcare Applications
The healthcare sector presents a substantial opportunity for robotics integration, particularly in areas such as surgery, rehabilitation, and patient care. Intuitive Surgical, the maker of the da Vinci Surgical System, reported a 15% increase in the number of robotic-assisted surgeries in 2024, reflecting the growing adoption of robotic systems in hospitals worldwide. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Stryker's robotic-assisted surgery platform in 2024, expanding its reach in the orthopedic sector. Additionally, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocated $30 million in funding for robotic rehabilitation technologies in 2024, further underscoring the healthcare sector’s shift toward robotic solutions to address the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and an aging population.
Advancements in Agricultural Robotics
Agriculture is increasingly adopting robotic technologies to enhance productivity and address labor shortages. John Deere reported a 12% increase in sales of its autonomous tractors and harvesters in 2024, driven by demand from farms seeking labor-saving solutions. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) highlights the development of autonomous systems for tasks such as harvesting, planting, and monitoring crop health. For instance, robotic harvesters equipped with machine vision, like those from FFRobotics, reduced labor costs by 30% on farms in California in 2024. The USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) allocated $25 million to robotics projects in agriculture, demonstrating the sector's commitment to technological advancement.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
The deployment of robots, especially in public and personal spaces, raises significant regulatory and safety concerns. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) emphasizes that the increasing presence of service robots in public areas heightens the likelihood of accidents, potential injuries, and property damage. In 2024, Tesla's autonomous delivery robot was involved in an accident that resulted in a $500,000 settlement, drawing attention to the need for clearer safety regulations. The process of establishing and updating these regulations often lags behind technological advancements, with $2 million in funding from NIST allocated in 2024 to develop safety standards for human-robot interactions. This regulatory bottleneck can stifle innovation and delay the deployment of beneficial robotic applications.
Ethical and Privacy Issues
The integration of robots equipped with advanced sensors and data collection capabilities into various aspects of daily life raises ethical and privacy concerns. The U.S. Department of Commerce highlights the potential for these devices to collect sensitive personal information, leading to issues related to data security and individual privacy rights. In 2024, iRobot recalled 50,000 units of its Roomba vacuum due to concerns over unauthorized data collection, underscoring the importance of safeguarding consumer privacy. Moreover, Boston Dynamics partnered with Google in 2024 to ensure robust data protection for its robotic systems, investing $10 million to implement privacy-focused technologies. Addressing these concerns is crucial to maintaining public trust and ensuring the responsible deployment of robotic technologies.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
16.4% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, End-User, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
FANUC, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., Denso Corporation, Universal Robots, Comau LLC, KUKA AG, ABB, IRobot, Carbon Robotics, Venca Robotics, Boston Dynamics, Nvidia, Scythe Robotics, and others |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insighta
The industrial robotics segment is anticipated to be a considerable supporter of the expansion of the robotics market in 2024, because of its application in several industrial use cases like material handling, painting, cutting, welding, and grinding. Producers throughout different sectors are predicted to employ intelligent robotics manufacturing technologies in the future to improve factory productivity, competitiveness, and functional excellence. Moreover, smart manufacturing and robots are being utilized progressively in the commercial sector as per the developing pattern of Industry 5.0. With the advent of Industry 5.0, makers are expanding their facilities to meet the heightened demand for industrial robotics. For example, ABB Ltd. disclosed a novel, huge robot factory in Shanghai, China, in December 2022. To open the 67,000 square meter plant, the company infused nearly 150 million dollars. These underlines that the players are constantly trying to broaden their production to serve the rising need for commercial robots which strengthens the segment’s predominant position. The service segment is also growing owing to a large number of applications such as medical uses and logistics.
By Application Insights
The manufacturing segment dominated the robotics market and is believed to continue to move forward on the same pattern in the coming years. In this ever-changing industry, robots are revolutionizing production activities and are driving other sectors into a coming era with uniqueness and effectiveness. Moreover, the segment benefited from the demand for energy saving, which has never been better, with increasing fuel prices propelling players to have competitive advantages. For instance, in Mexico in 2023, the manufacturing sector witnessed 5868 robot installations. The nation´s key adopter is the automobile segment, which held about 69 percent of the robot deployments in the same year, selling up to 4068 units. It is the third-best performance since 2017 reaching the best 4805 units.
On the other hand, the Shelf scanning segment is expected to gain traction due to consistent labor shortages and other related issues. According to industry experts, worker scarcity will continue worldwide, with the global labor shortage reaching an estimated 85 million by 2030.
By End-user Insights
The automotive segment captured the maximum portion of the robotics market share in 2024. As per the International Federation of Robotics, the automotive sector has the highest volume of robots employed in manufacturing plants across the world: Functional inventory achieved a new record of around one million units. This depicts one-third of the overall quantity of robots deployed throughout all sectors. The automotive industry is a major contributor to the expansion of the global robotics market. For instance, in Canada, the sale of automobile robots jumped by 99 percent in 2023 with 2549 units, an all-time high.
The electric segment is another key robot user and is the largest end-user in China, with more than 100000 units installed in 2022. The segment also dominated the Japanese industry in 2022 with 18359 units. A similar trend is in the Republic of Korea, i.e., 9629 units from 6913 units in 2021. Hence, the segment is largely driven by the Asia Pacific countries.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific was the top performing regional segment in the global robotics market in 2024 and accounted for 41.7% of the global market share. This dominance is driven by the region's rapid industrialization, particularly in countries like China, Japan, and South Korea, which are leaders in robotics adoption. China alone accounts for over 30% of the global robotic installations, with significant investments in automation across sectors such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. Japan’s robotic technology continues to advance, with companies like Fanuc and Yaskawa leading the way in industrial robotics. The increasing demand for automation in industries like automotive manufacturing and electronics further contributes to the region's substantial market share.
North America captured a substantial share of the global robotics market in 2024 and is anticipated to account rapid growth during the forecast period owing to the advancements in artificial intelligence and increased automation across industries. The U.S. Department of Labor estimates that the adoption of industrial robots in the U.S. manufacturing sector has increased by 35% in the last five years. The region's growth is driven by the rising demand for automation in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics sectors, with companies like Boston Dynamics and iRobot expanding their operations. Government initiatives, such as the Manufacturing USA Program, which has received $2.5 billion in funding since its inception, further bolster this expansion, positioning North America as a significant contributor to the global robotics market.
Europe maintains a significant position in the global robotics market. This is driven by strong industrial automation, particularly in countries like Germany, where the automotive industry accounts for nearly 45% of the region's industrial robot installations, and Italy, with its focus on precision manufacturing. The region's emphasis on Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing has led to increased adoption of advanced robotics in sectors like automotive, electronics, and food processing. The European Union’s Horizon 2020 program, with a €80 billion budget, continues to support digitalization and innovation, positioning Europe as a key player in the global robotics landscape.
Latin America is gradually embracing robotics with a focus on enhancing productivity in industries like automotive, electronics and food & beverage. Mexico, a major player, has seen a 5.4% increase in industrial robot installations in the automotive sector over the past two years. Brazil has committed to investing approximately $1.5 billion in robotics and automation over the next five years to improve manufacturing efficiency. The region's efforts to integrate robotics are expected to yield positive outcomes, with Mexico's automotive exports growing by 7% annually in recent years and is contributing to economic growth and technological advancement.
The robotics market in Middle East and Africa is witnessing a growing interest in robotics, particularly in sectors such as oil & gas, healthcare, and logistics. This growth is driven by supportive government initiatives and the adoption of automation technologies to enhance operational efficiency. For instance, the introduction of the Dubai Robotics and Automation Program aims to position the city as a leader in robotics innovation.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies that play a notable role in the global robotics market include FANUC, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries Ltd., Denso Corporation, Universal Robots, Comau LLC, KUKA AG, ABB, IRobot, Carbon Robotics, Venca Robotics, Boston Dynamics, Nvidia and Scythe Robotics.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The robotics market is highly competitive, driven by continuous technological advancements and increasing adoption across various industries. Established players such as ABB Ltd., Yaskawa Electric Corporation, Fanuc Corporation, and KUKA AG dominate the industrial robotics sector, leveraging their extensive research and development capabilities to introduce innovative automation solutions. These companies compete based on factors such as precision, efficiency, and adaptability to industry-specific needs.
Emerging companies are also gaining traction, particularly in the field of collaborative robots (cobots) and service robotics. Startups and mid-sized firms are focusing on AI-driven robotics, autonomous systems, and human-robot collaboration to carve a niche in the market. Companies specializing in healthcare robotics, such as surgical and rehabilitation robots, are witnessing growing demand due to advancements in AI and sensor technology.
The market also sees increasing partnerships between robotics firms and technology companies to enhance machine learning capabilities and automation efficiency. Additionally, government regulations and standardization efforts play a crucial role in shaping competition, as companies must adhere to safety and operational guidelines.
With the rapid evolution of robotics, competition is expected to intensify, fostering innovation and leading to the development of more sophisticated and versatile robotic solutions across industries such as manufacturing, logistics, agriculture, and healthcare.
Top 3 Players in the Market
FANUC Corporation
FANUC Corporation, headquartered in Japan, is a leading manufacturer of industrial robots and factory automation systems. The company holds a substantial share of the global market, with a market capitalization of approximately $27 billion as of 2024, according to Statista. FANUC's extensive product line includes a variety of industrial robots utilized across sectors such as automotive, electronics, and manufacturing. Their commitment to precision and reliability has established them as a preferred choice for companies seeking to enhance production efficiency through automation.
ABB Ltd.
ABB Ltd., a Swiss-Swedish multinational corporation, is a prominent player in the industrial robotics sector. In 2022, ABB dominated the market with a 21% global share, as reported by Statista. The company's robotics division offers a wide range of solutions, including collaborative robots (cobots) designed to work alongside humans safely. ABB's innovations have been instrumental in advancing automation in industries such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, contributing significantly to increased productivity and operational efficiency.
KUKA AG
KUKA AG, based in Germany, is renowned for its industrial robots and automation solutions. Holding a 9% share of the global industrial robotics market in 2022, as indicated by Statista, KUKA specializes in providing robots for applications like welding, assembly, and material handling. Their advanced automation technologies are widely adopted in the automotive industry and other manufacturing sectors, underscoring their role in driving the evolution of automated production processes.
Top Strategies Used by the Key Market Participants
Strategic Investments and Acquisitions
Companies are actively investing in and acquiring startups to enhance their technological capabilities. For instance, SoftBank is in discussions to lead a funding round for Skild AI, a robotics startup, potentially valuing it at nearly $4 billion. Skild AI aims to develop a scalable foundation model for robotics, enabling safe and dexterous human-robot interactions. This investment aligns with SoftBank's strategy to advance AI and robotics integration.
Focus on Purpose-Built Solutions
Successful robotics companies prioritize developing robots that address specific industry challenges. By concentrating on purpose-built solutions, these companies ensure their products meet market demands and provide practical applications, leading to increased adoption and customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Digital Marketing and Brand Positioning
Robotics firms are leveraging digital marketing strategies to educate potential customers about new threats, robotic capabilities, and best practices. This approach positions brands as tech-savvy and research-driven, fueling search engine optimization (SEO) with advanced robotics or AI topics, and engaging target audiences effectively.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, HowToRobot and Gain & Co merged to form a global automation market platform and vendor-independent advisory company. The merger aims to support businesses in their automation journey by providing guidance and access to automation and robotics suppliers worldwide.
- In October 2024, Automated Industrial Robotics Inc. (AIR) acquired Robotics & Drives (RDS), an Ireland-based industrial automation company. This acquisition strengthens AIR's presence in Europe and enhances its ability to integrate robotics solutions into automated systems.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global robotics market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Industrial Robotics
- Services Robotics
By Application
- Disinfection
- Shelf Scanning
- Delivery
- Security & Inspection
- Advertising
- Manufacturing
- Others
By End-User
- Automotive
- Logistics & Transportation
- Agriculture
- Chemical
- Healthcare
- Entertainment
- Electric
- Domestic Service
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major factors driving the growth of the robotics market?
Key drivers include advancements in AI and machine learning, increased automation across industries, labor shortages, and the push for operational efficiency and productivity.
What are the primary applications of robotics in industry?
Robotics are primarily used in manufacturing (automotive, electronics, metals), healthcare (surgery, rehabilitation), logistics (warehousing, delivery), and agriculture (harvesting, monitoring).
What challenges are faced by the robotics market?
Challenges include high initial investment costs, technological complexities, cybersecurity risks, and the need for skilled personnel to develop and maintain robotic systems.
What is the impact of robotics on employment?
While robotics can lead to the displacement of certain jobs, they also create new opportunities in robot maintenance, programming, and oversight. The net impact on employment varies by industry and region.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]