Global Pepper Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Product Type( Black Pepper, Whole Pepper, Ground/Crushed Pepper, White Pepper, Green Pepper, Red Pepper (Chilies)), Form, Application, And Region (North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East And Africa), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Global Pepper Market Size
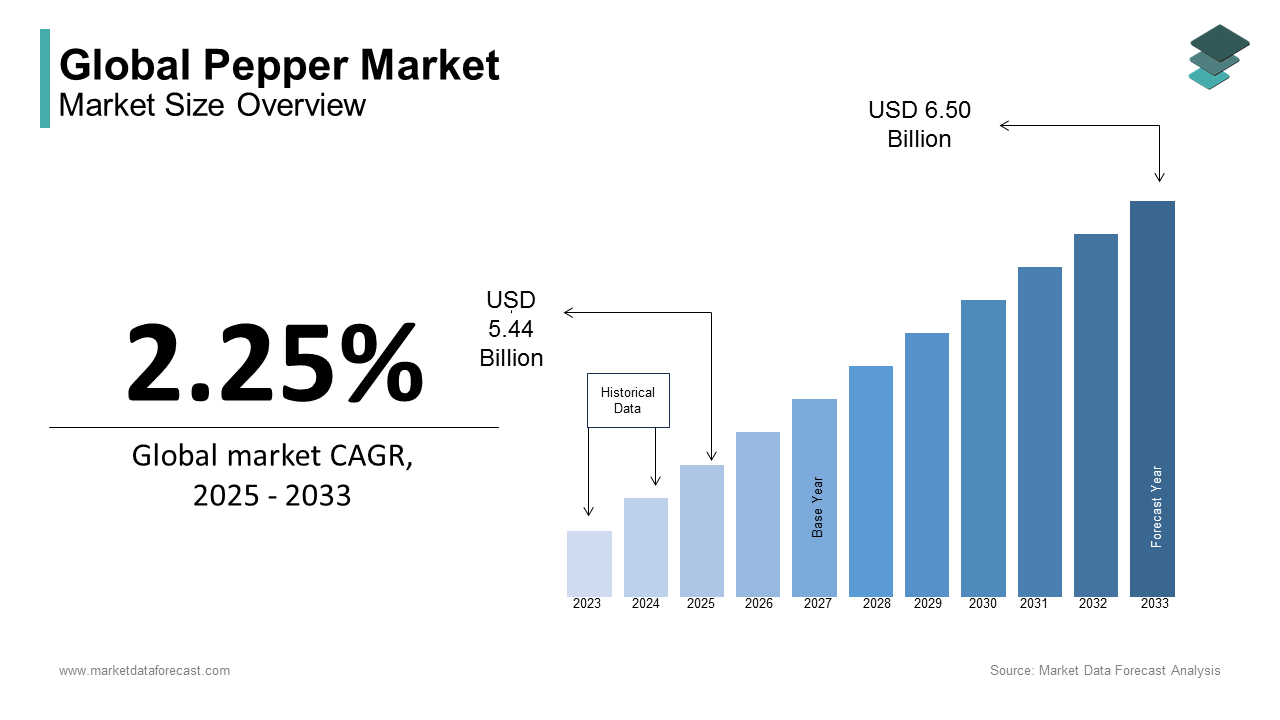
The global pepper market size was calculated to be USD 5.32 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 6.50 billion by 2033 from USD 5.44 billion In 2025, growing at a CAGR of 2.25% during the forecast period.
The global pepper market holds a crucial role in the spices industry. Black pepper (Piper nigrum) is one of the most widely traded spices. Moreover, Vietnam accounts for over 34% of the world’s total production while Brazil India and Indonesia are other key producers contributing significantly to the supply chain and ensuring global availability. Also, pepper has uses beyond cooking as it contains piperine which enhances the bioavailability of various nutrients and drugs by up to 200%. This quality makes it a valuable ingredient in the pharmaceutical sector. Furthermore, its plantations contribute to sustainable farming practices. Intercropping with coffee and cocoa improves soil health and enhances yield efficiency. Additionally, black pepper farming supports the livelihood of over 2 million farmers in major producing countries such as India and Vietnam providing economic stability to agricultural communities.
MARKET DRIVERS
Expansion of Global Agricultural Trade
The growing international trade of agricultural commodities is a key driver for the pepper market. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global primary crop production reached 9.6 billion tonnes in 2022 that increased by 56% since 2000. This growth facilitates the export and import of pepper to meet worldwide demand. Improved trade agreements and reduced barriers have streamlined cross-border exchanges which is enabling pepper-producing nations like Vietnam and Brazil to penetrate new markets. These developments ensure a stable supply chain by fostering consistent availability and helping producers leverage economies of scale which ultimately strengthens the market’s growth potential.
Consumer Demand for Year-Round Availability
Shifting consumer preferences for uninterrupted access to fresh produce influence the pepper market significantly. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) highlights a 69% increase in bell pepper imports from Mexico during winter between 2008–10 and 2018–20 which showcases rising demand for off-season availability. This trend encourages producers to adopt advanced farming techniques and optimize logistics to maintain consistent supply throughout the year. Importers and distributors also invest in cold storage and efficient transport systems to cater to consumers’ expectations. This push for year-round access drives innovation and operational improvements and positions the pepper market for sustained growth and resilience.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Declining Domestic Output
The U.S. pepper industry faces significant constraints due to reduced domestic production. According to the USDA’s Economic Research Service, chili pepper production in states such as Arizona, California, New Mexico and Texas fell from over 480 million pounds in 2014 to approximately 175 million pounds in 2022 which is a decline of 60%. This reduction is linked to shrinking cultivation areas and lower yields and thereby increasing reliance on imports to meet demand. Dependence on foreign suppliers creates vulnerabilities in supply chains and exposes the market to price fluctuations and consequently undermining its dependence and contributing to instability in the sector.
Pest and Disease Management Issues
Pepper cultivation is hampered by persistent challenges in controlling pests and diseases. The USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture emphasizes that pests like the brown marmorated stink bug cause substantial yield losses and that escalates production costs. Additionally, soilborne diseases require constant innovation in resistant plant varieties and improved farming techniques. These hurdles not only increase operational expenses but also deter investment and hinder growth. Such challenges strain resources, limit scalability and pose a barrier for both new entrants and existing producers aiming to expand their market presence and ultmately restraining overall industry advancement.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growing Preference for Organic Products
The rising demand for organic foods presents a promising avenue for growth in the pepper market. Data from the USDA's Economic Research Service reveals that over 80% of U.S. households opted for organic foods in 2016 and millennials are mainly leading the shift. This preference has driven a significant increase in organic cropland since 2000. Organic fruits and vegetables contribute $22 billion in retail sales in 2022 which makes up 36% of total organic sales. Transitioning to organic pepper farming enables producers to tap into premium markets and achieve higher profitability by meeting this growing consumer demand.
Opportunities in Expanding Export Markets
Global interest in peppers creates excellent prospects for U.S. exporters. USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service highlights that U.S. agricultural exports reached $174.17 billion in 2023 which grew at a steady compound annual rate of 1.2% from 2014. U.S. producers secures a competitive edge in global markets by complying with stringent international standards and leveraging trade deals. This gives enhanced export opportunities which not only boost revenue but also contribute to economic diversification and ultimately making it an attractive focus for the pepper industry.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Labour Constraints and Mechanization Issues
The pepper industry faces ongoing challenges due to labour shortages and difficulties in adopting mechanization. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics, agricultural worker force participation has been declining steadily that saw a drop of 20% over the past two decades. Mechanizing pepper harvesting remains complex due to the fruit's delicate nature which can lead to significant losses if mishandled. Moreover, research initiatives aim to create more durable pepper varieties and enhance harvesting equipment. However, these innovations require substantial investment and time to implement placing pressure on growers who must balance production efficiency with limited workforce availability.
Challenges in Meeting Quality Parameters
Maintaining consistent quality in pepper production is an enduring issue. Studies by agricultural research institutions show that approximately 30% of crop yields in developing regions are lost annually due to pest infestations and diseases. Strict grading requirements including uniform size and blemish-free appearance necessitate meticulous farming techniques. Environmental changes such as rising temperatures and irregular rainfall exacerbate the difficulty of producing high-quality crops. Additionally, pest outbreaks, comprising those caused by aphids and thrips can impact visual and structural quality. Growers need to adopt resilient farming practices and invest in pest-resistant varieties to maintain marketable produce.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
2.25% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product Type, Form, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Olam International, McCormick & Company, Everest Spices, MDH Spices, Baria Pepper, Ajinomoto Co., Inc., Vietnam Spice Company, Kancor Ingredients Limited, British Pepper & Spice Company, and Worlée NaturProdukte GmbH |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Type Insights
The black pepper segment held the major role in the global market in 2024 by holding a share of 70.8% of the global pepper market in 2024. The widespread popularity of black pepper arises from its essential role as a seasoning in various culinary traditions. The United States has consistently increased its imports and usage over the past decade as the leading importer and consumer of spices. Black and white pepper rank among the top seven spices, collectively representing over 75% of the annual value of spice imports into the U.S., as per the Economic Research Service. This significant demand highlights the crucial position of black pepper in food preparation. Key producers such as Vietnam and India play a vital role in ensuring a steady global supply to satisfy the growing consumption.
The white pepper is experiencing the fastest growth in the global pepper market and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period. White pepper is a preferred choice in European and Asian cuisines especially in light-coloured sauces and dishes where black specks are undesirable. The rising consumer preference for diverse and authentic culinary experiences has contributed to the growing importance of white pepper in the global market. Additionally, its uses extend beyond cooking where white pepper is also used in traditional medicine and is recognized for its potential health benefits including anti-inflammatory properties. The awareness of these advantages grows along with the spice's unique flavour profile and thereby making its significance in the global market continues to increase.
By Form Insights
The whole pepper segment had 60.4% of the global market share in 2024 and emerged as the most dominating segment in the worldwide market. This dominance is attributed to its extensive use in culinary applications where whole peppercorns are preferred for their ability to retain flavor and aroma until ground. Additionally, this pepper is favoured in various traditional recipes and is often used in pickling and seasoning blends. The demand for whole pepper is sustained by its versatility and the growing consumer preference for freshly ground spices, which offer superior taste profiles.
The ground pepper segment is another promising segment and is esteemed to grow at a CAGR of 2.7% during the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by the convenience it offers to consumers and food service providers which allows for easy incorporation into recipes without the need for grinding. The increasing demand for ready-to-use spices in the fast-paced food industry and among home cooks contributes to the rising importance of ground pepper in the market.
By Application Insights
The food & beverages segment ruled the market in 2024 and held 40.1 % of the global market share due to its extensive use in seasoning and condiments. Globally, 95% of black pepper is used in food which is either in its natural form or as an ingredient in processed products. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), spices including pepper are critical in global cuisine having per capita spice consumption rising steadily over the past two decades. For example, the average consumption of spices comprising pepper in countries like the United States and India exceeds 2.5 kg per capita annually and thereby underlining its culinary significance.
The pharmaceuticals segment is the fastest growth in the global pepper market and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% over the forecast period. According to studies, piperine which is an active component of pepper can enhance the bioavailability of certain nutrients and drugs by up to 200% and that makes it valuable in therapeutic formulations. Additionally, the World Health Organization (WHO) reports that nearly 80% of the global population relies on plant-based medicines for primary health care, driving interest in natural products like pepper. Its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and digestive health benefits are key factors contributing to its increased adoption in pharmaceutical applications.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America held a dominant share of 25.6% of the global market in 2024. The regional pepper market and particularly in the United States has undergone significant changes in production and import trends in recent years. According to the USDA's National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS), U.S. farmers harvested over 31,000 acres of bell peppers and more than 10,000 acres of chile peppers in 2021 which resulted in a combined production value exceeding $536 million. Despite this substantial output, domestic production has been on a decline. Data from the USDA's Economic Research Service (ERS) shows that chili pepper production in key states like Arizona, California, New Mexico and Texas fell from over 480 million pounds in 2014 to around 175 million pounds by 2022 and reflecting a significant reduction of about 60%.
The Asia-Pacific region plays a crucial role in the global pepper market and is predicted to grow at he fastest CAGR of 4.2% during the forecast period. For instance, Indonesia has been a major producer of chilies and peppers with production figures reaching around 1,000,000 tonnes annually in the early 2000s. Indonesia continues to be an important player in the pepper market. In Cambodia, Kampot pepper has gained international fame thanks to its Geographical Indication (GI) registration. This designation has not only protected the unique qualities of Kampot pepper but has also increased its market value. For example, the price of red Kampot pepper rose from USD 10 per kilogram in 2010 to USD 25 per kilogram in 2020 with a remarkable increase of 150%. Similarly, the price of white Kampot pepper increased from USD 12 per kilogram to USD 28 per kilogram during the same period which reflectes a 133% growth. This GI status has led to sustainable development for Kampot pepper products, boosting revenue for local producers and their communities.
The Europe pepper market is estimated to grow at a notable CAGR over the forecast period. The European Union (EU) plays a crucial role in the global pepper market and is mainly an importer. In 2022, the EU imported around 62,900 tonnes of pepper from non-EU countries with Vietnam being the largest supplier by providing 56% of these imports. Within the EU, pepper falls under the broader category of fruits and vegetables. In 2020, approximately 0.7 million farms grew fresh vegetables including peppers across about 2 million hectares of land. Countries like Spain, Italy and Poland are among the top producers of fresh vegetables in the EU. Quality and authenticity are major concerns in the EU pepper market. A coordinated control plan by the European Commission found that 17% of pepper samples were at risk of adulteration which emphasizes the need for strict quality controls to ensure safety and compliance in food standards.
The Latin America pepper market is anticipated to witness a healthy CAGR during the forecast period. Latin America plays a vital role in the global pepper market with countries like Brazil and Mexico leading in both production and export. The region is expected to account for over 25% of global agricultural and fisheries exports by 2028 which highlightes its strong position in the international market. Moreover, in Jamaica, the hot pepper industry is set to boost earnings through a three-year project focused on improving compliance with food safety and plant health standards. This initiative aims to enhance production and expand exports to markets such as the EU, UK, USA, and Canada. Meanwhile, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines is working to grow its hot pepper industry by identifying suitable pepper varieties and addressing market gaps to ensure consistent production. These efforts reflect the region's commitment to enhancing its presence in the global pepper market.
The pepper market in Middle East and Africa is likely to see a CAGR of 7.7%. The MEA region presents a diverse landscape in the pepper market involving both production and import activities. The region actively participates in the global pepper trade with various countries serving as both exporters and importers. According to Trade Map data, several nations in the MEA region are engaged in the export and import of pepper products by showcasing their involvement in the international market. However, the MEA region faces challenges such as water scarcity, pest management issues and the need for improved agricultural practices to enhance pepper production. Despite these hurdles, there are opportunities for growth through the adoption of sustainable farming techniques, better irrigation systems and access to international markets. These improvements could significantly boost the pepper industry's development in the region.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Major Players of the global pepper market include Olam International, McCormick & Company, Everest Spices, MDH Spices, Baria Pepper, Ajinomoto Co., Inc., Vietnam Spice Company, Kancor Ingredients Limited, British Pepper & Spice Company, and Worlée NaturProdukte GmbH
The pepper market is intensely competitive involving established producers, exporters and emerging players striving to meet rising global demand. Competition hinges on factors such as product quality, pricing strategies, origin authenticity, certifications and streamlined supply chains.
Vietnam leads as the top producer and exporter by leveraging advanced farming practices, large-scale output and cost efficiency. Brazil, Indonesia and India also play pivotal roles. India is renowned for premium varieties like Malabar and Tellicherry which appeal to niche segments while Brazil emphasizes consistent production and high yields to maintain its position.
Evolving trade policies and volatile pricing add complexity because exporters face challenges from synthetic alternatives that compete on cost. Growing interest in organic and sustainably sourced products has further heightened competition which drives companies to adopt eco-friendly practices to appeal to conscious consumers.
Key players such as Olam International, Everest Spices and MDH Spices focus on differentiation through innovation, branding and expanding global distribution. Smaller regional producers capitalize on local branding and geographical indicators by adding diversity to the competitive landscape. This dynamic market continues to evolve as businesses strive to balance quality, sustainability and customer preferences to secure their market share and cater to diverse consumer demands.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In July 2024, Ed Currie, founder of the PuckerButt Pepper Company, introduced 'Pepper X,' setting a new record as the world's hottest pepper at 2.69 million Scoville Heat Units.
- In October 2024, Keurig Dr Pepper acquired a 60% stake in energy drink maker Ghost for $990 million, aiming to expand its beverage portfolio.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global pepper market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on product type, form, application, and region.
By Product Type
- Black Pepper
- Whole Pepper
- Ground/Crushed Pepper
- White Pepper
- Green Pepper
- Red Pepper (Chilies)
By Form
- Whole
- Ground
- Essential Oil
- Pepper Extracts (Oleoresins)
By Application
- Food & Beverages
- Seasonings and Condiments
- Processed Foods
- Beverages (Tea, Alcoholic Mixes)
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cosmetics
- Skin Care (Exfoliants, Anti-aging Products)
- Hair Care Products
- Personal Care
- Animal Feed
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- The Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- The Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which factors contribute to Pepper Market’s growth?
Pepper Market's growth is driven by factors such as increasing consumer demand for organic and locally sourced products, strategic partnerships with suppliers, expansion into new locations, and a strong digital presence through e-commerce.
2. Who are Pepper Market’s main competitors?
Our main competitors include other specialty grocery stores, organic markets, and large supermarket chains that offer similar high-quality products. However, our focus on unique, curated selections and exceptional customer service sets us apart.
3. How does Pepper Market measure success and growth?
We track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as revenue growth, customer retention, online engagement, store foot traffic, and sales trends to measure our success.
4. What challenges does Pepper Market face in increasing market share?
Some challenges include competition from larger retailers, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuations in consumer preferences. However, we continuously adapt our strategies to stay ahead.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]