Global Overactive Bladder Treatment Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Treatment, Disease and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033.
Global Overactive Bladder Treatment Market Size
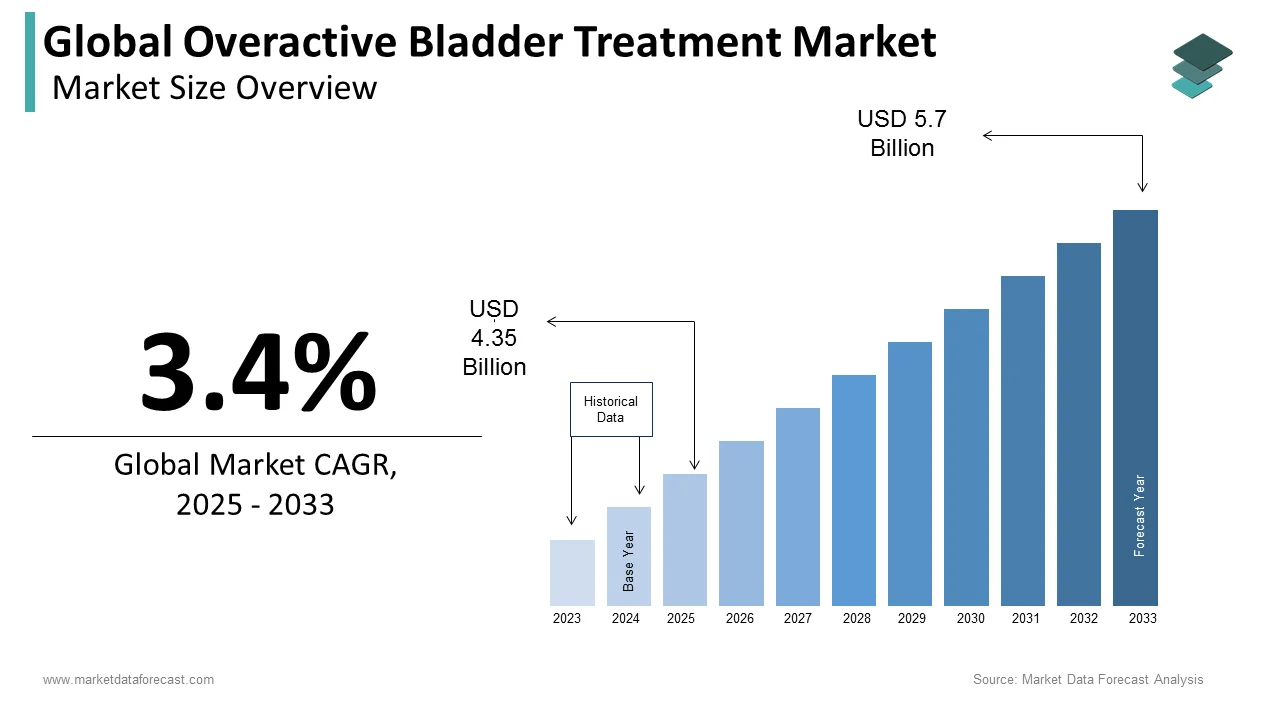
The size of the global overactive bladder treatment market was worth USD 4.21 billion in 2024. The global market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 5.7 billion by 2033 from USD 4.35 billion in 2025.
MARKET DRIVERS
YOY's growth in overactive bladder cases and age and increasing focus on drug development by crucial market participants drive the global overactive bladder treatment market.
The rising prevalence of overactive bladder is a significant factor driving the overactive bladder treatment market growth. According to the National Overactive Bladder Evaluation (NOBLE) report, 16.5% of study participants meet the requirements for OAB. 6.1% of those met the criteria for OAB with urgency incontinence, and 10.4% met the criteria for OAB without urgency incontinence. 45% with OAB and urgency incontinence have mixed effects (urgency incontinence plus stress incontinence). About 22 million people in Europe are affected by OAB. OAB affects 6.48 million adults in Germany, with 2.18 million experiencing incontinence. Despite this, numerous patients remain undiagnosed for a variety of causes. If this figure rises, so will the need for overactive bladder therapy. The many minimally invasive therapies available are all equivalent in managing drug-resistant overactive bladder syndrome. A different treatment may be tried if the outcomes of the first are unsatisfactory. The treatment plan is determined by several variables, including patient preferences, surgical experience, age, comorbidity, and budgetary considerations. The aging population also contributes to the rise of the global overactive bladder treatment market. Urinary incontinence, or the involuntary leakage of urine, is a common disorder in persons over 60. According to WHO, integrated treatment for older people (2017), urinary incontinence is twice as common in older women as in older men. In addition, the population number and percentage of people aged 60 and over is growing. In 2019, there were 1 billion people aged 60 and over. This figure is expected to rise to 1.4 billion by 2030 and 2.1 billion by 2050. This rise occurs exponentially and is expected to intensify in the coming decades, especially in developed countries. As a result, the senior population grows, so makes a demand for overactive bladder therapy.
The growing number of drug discovery services is also increasing the need for overactive bladder care.
Many organizations are collaborating to create novel intravesical therapies. Furthermore, several new and advanced medications are in clinical trials, and gaining clearance for these drugs raises demand. Moreover, pharmaceutical firms are also using aggressive marketing tactics, which have increased awareness and increased product demand. Currently, there are about 77 clinical trials for overactive bladder. For example, the herbal medication drug AOBO-001 has been launched for adult OAB incontinence and frequency, and a phase II clinical trial is currently underway to study its effectiveness in adults.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Side effects of the medicines are expected to restrain the global overactive bladder treatment market.
Nonetheless, unfavorable drug side effects are stifling the overactive bladder treatment market. The medications being used have adverse effects on the patients' bodies. These medications have common side effects, such as dry skin, constipation, dry mouth, dry or itchy skin, blurred vision, indigestion, urinary tract infection, urinary dysfunction, and drowsiness. In addition, although many neurostimulators help in OAB treatment effectively, they have serious laboratory complications like seroma, infection, implant site pain, epidural bleeding, allergic reaction, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage, paralysis, and skin breakdown. At the same time, certain medications may trigger memory loss, hallucinations, insomnia, and other side effects. As a result, key players struggle in the overactive bladder treatment market.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Analysed |
By Treatment, Disease, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Analysed |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Pfizer, Allergan Plc, Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, Astellas Pharma Inc, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries, Mylan N.V, Sanofi, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd, and Endo International. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Treatment Insights
The anticholinergics segment is forecasted to dominate the global overactive bladder treatment market due to its mass utility. Being the first-line drug therapy for overactive bladder syndrome, they are widely used to treat overactive bladder as a first choice of drugs. They help in blocking special receptors, muscarinic receptors, to reduce bladder contractility in the detrusor muscle and, therefore, the urgency to urinate and the associated episodes of bedwetting, and also help in treating other bladder conditions, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), symptoms of Parkinson's disease, and gastrointestinal disorders.
On the other hand, the botox segment is predicted to be another lucrative segment and is expected to register a healthy growth rate during the forecast period. Botox is rapidly increasing over time, being an option for treating urges incontinence with patients on whom other treatments showed no effect, like behavioral and exercise therapies and medications. A well-established treatment for an overactive bladder is the injection of Botox into the bladder associated with neurological diseases.
Neurostimulation is also expected to hold a significant market share over the forecast period under this segment. Several stimulators are used to treat the problem of OAB. In sacral nerve stimulation, a small device is implanted at the base of the spine in the back since sacral nerves carry signals between the bladder, spinal cord, and brain. Tibial nerve stimulation uses electrical signals to help control bladder contractions, which not only reduces the frequency of urination but also in reducing urine leakage.
By Disease Insights
Based on disease, the neurogenic segment is estimated to account for most of the market share during the forecast period, owing to the increasing prevalence of quality treatment services. Mostly, the disease is more likely found in women post-pregnancy due to bladder muscle weakness. In 2017, More than 200 million people worldwide were affected by urinary incontinence, according to National Association for Incontinence. Due to that, big companies in the market are investing in these segments.
Neurogenic bladder is a severe condition that must be treated with close monitoring to make patients see significant improvements in their quality of life. Overactive and underactive are the two general types of neurogenic bladder. An overactive bladder may leak urine if the muscles are overactive, leading to more contraction and compression of the bladder. In contrast, an underactive bladder may make the person difficult for urine passage since the muscles do not contract to urinate. Unfortunately, nervous system-related neurogenic bladder problems are on the rise globally, leading to the growth of OAB treatment devices under this segment.
The idiopathic overactive bladder segment is anticipated to dominate in this segment. Chronic Kidney Diseases (CKD) are owing to an increase in prevalence. In addition, an older generation increase is this segment's primary asset. Idiopathic overactive bladder is due to the absence of any metabolic, underlying neurological, or other cause for the overactive bladder, which may mimic overactive bladders like bladder stones, urinary tract infection, bladder cancer, bladder inflammation, or bladder outlet obstruction. This is generally treated with a safe injection of BTX-A, performed with minimal restrictions, capable of improving quality of life at the first injection itself.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS

Geographically, the North American region is estimated to dominate the global overactive bladder treatment market during the forecast period. Between 2025 to 2033, the North American market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 3.14%. The availability of a well-established healthcare structure in this region is a critical factor in North American overactive bladder treatment growth. In addition, the U.S. market is expected to lead within this region.
The European regional market was worth USD 0.93 billion in 2021 and is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 3.2% during the forecast period.
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing globally overactive bladder treatment market due to the growing awareness and the increasing market penetration of pharmaceutical companies.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Pfizer, Allergan Plc, Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, Astellas Pharma Inc, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries are some notable companies profiled in the global overactive bladder treatment market Mylan N.V., Sanofi, Aurobindo Pharma Ltd, Endo International are the major players operating in the overactive bladder treatment market and profiled in this report.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
-
In November 2022, BlueWind Medical, Ltd. announced three leadership appointments for transforming neuromodulation therapy to treat an overactive bladder by developing a miniature tibial neuromodulation solution implanted in the ankle region as a minimally invasive outpatient procedure under local anesthesia.
-
In October 2022, Urovant Sciences announced a Phase 1 study of the pharmacokinetic profile of GEMTESA (vibegron), which can be crushed for administration with applesauce, suggesting potential use in elderly patients in long-term care due to the increasing prevalence of overactive bladder.
- In October 2022, Zydus Lifesciences received the final green light from the US FDA for the 25 mg and 50 mg tablets in Mirabegron treatment, manufactured in Ahmedabad SEZ, to treat overactive bladder (OAB) with symptoms of urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency.
- In May 2022, Urovant Sciences announced new analyses from GEMTESA's EMPOWER Phase 3 extension study for overactive bladder treatment to provide effective therapies for urological disorders.
- On April 22, 2019, Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., one of the key players in the overactive bladder treatment market, launched a generic version of VESIcare ®1 Tablets 5 mg, and 10 mg, in the U.S.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global overactive bladder treatment market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Treatment
- Mirabegron
- Anticholinergics
- Solifenacin
- Fesoterodine
- Tolterodine
- Oxybutynin
- Darifenacin
- Trospium
- Other Anticholinergics
- Botox
- Intravesical Instillation
- Neurostimulation
By Disease
- Neurogenic
- Spinal Cord Injury
- Parkinson's disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Other Disorders
- Idiopathic
By Region
- North America
- The United States
- Canada
- Rest of North America
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- Italy
- Spain
- France
- Rest of E.U.
- Asia-Pacific
- India
- China
- Japan
- Australia
- New Zealand
- South Korea
- Rest of APAC
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Chile
- Rest of Latin America
- Middle East
- Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
At What CAGR, the global overactive bladder treatment market is expected to grow from 2025 to 2033?
The global overactive bladder treatment market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 3.4% from 2025 to 2033.
Which region has the highest market share in the overactive bladder treatment market ?
The North American region led the overactive bladder treatment market in 2023 and is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR. On the other hand, the APAC region is estimated to showcase the fastest CAGR from 2024 to 2032.
How big is the global overactive bladder treatment market ?
As per our research report, the global overactive bladder treatment market size is projected to be USD 5.7 billion by 2033.
Which are the significant players operating in the overactive bladder treatment market?
Pfizer, Allergan Plc, Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, Astellas Pharma Inc., and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries are some of the significant players operating in the overactive bladder treatment market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]