Global Nuclear Robotics Market Research Report - Segmentation by Type (Software, Robot Hardware, Services), By Application (Measurements, Inspections, Radiochemical Handling, Nuclear Decommissioning, Other), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa) – Industry Analysis (2024 to 2032).
Global Nuclear Robotics Market Size (2024 to 2032):
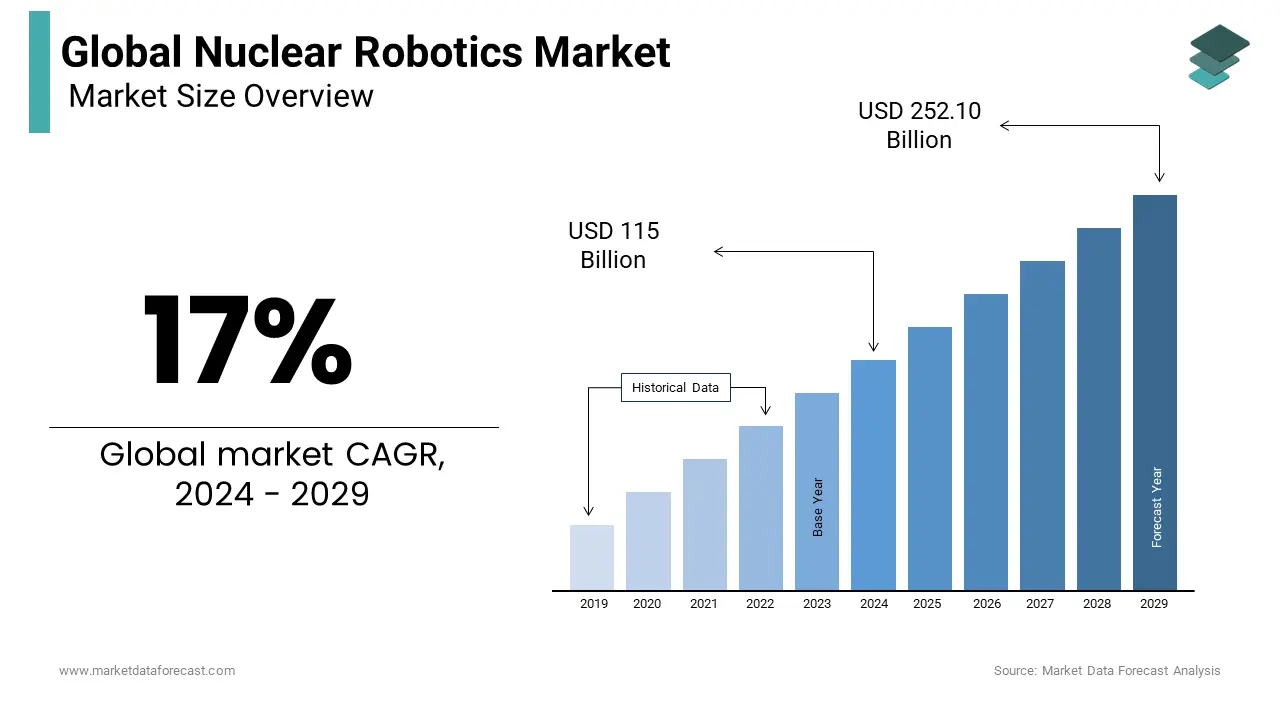
The Global Nuclear Robotics Market was worth USD 98.28 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach a valuation of USD 403.77 billion by 2032 from USD 115 billion in 2024, and it is predicted to register a CAGR of 17% during the forecast period 2024-2032.
MARKET SCENARIO
These robots are outfitted with various sensors and come in avariety of sizes. The vast majority of these robots are controlled remotely. These robots can aid people in the operation and maintenance of industrial nuclear facilities and nuclear reactor maintenance. They are beneficial in areas where human safety is a significant concern, such as decommissioning and dismantling nuclear sites and emergency intervention scenarios. Handling radioactive material, disposing of spent material, and detecting leaks in emergency scenarios are all dangerous nuclear tasks. The robots are specifically developed to help workers in these situations. Nuclear robots are presently being used in a few nations to control hazardous materials. Even though robots have been produced for many decades, they are still unable to adequately complement people in various duties, such as assisting them in nuclear power plants. This is no longer the case because robots with adequate mobility, sensors, size, and tooling have been developed to succeed in emergencies.
As a result, people in the nuclear business have begun to appreciate the benefits of automated technologies and invest in them. Single-purpose robots and reprogrammable robots are the two most common types. Single-purpose robots are limited in their capacity to do various tasks, whereas reprogrammable robots are versatile and have computer-based intelligence.
MARKET DRIVERS
Robotic technologies are most probably used in several firms, varying from automotive assembly lines to space exploration.
Not only can robots enable process automation, but they also bring safety benefits by allowing machines to execute activities that would otherwise be too risky or complex for humans to perform using traditional methods. Robots, for example, can conduct duties in situations with extreme temperatures, pressures, or radiation fields, as well as inspect equipment in difficult-to-access regions. As a result, robotic technologies have become a vital resource in a wide range of industries. Robots are now an essential part of nuclear operations.
They acts as a variety of nuclear reactors include cleaning, waste swabbing, inspection, pallet loading, taking routine measurements, handling nuclear chemicals, and nuclear decommissioning, and others boosts the global nuclear robotics market growth. To prevent risking human life, robots are widely chosen for working in dangerous environments. This is the primary factor influencing the expansion of the nuclear robotics sector. Robots employed in the nuclear industry must work in confined spaces, adhere to facility regulations, and carry heavyweights. The Fukushima nuclear power station event in Japan prompted worries about plant safety after such catastrophes. Thus, technical advancement will continue to be a significant concern in the safe operation of nuclear power plants. Nuclear robot innovation will be aided by the fact that additional nuclear power stations will be built in the future, with security as the most significant concern.
The primary drivers of robotics applications in the nuclear sector are to reduce human exposure to hazardous environments while increasing efficiency and safety while lowering costs in performing inspection, maintenance, decontamination, waste handling, and post-accidental activities which are considered as the major tasks. Currently, the nuclear business employs teleoperated robots to do dangerous work in hazardous environments and mobile monitoring, surveillance and cleaning. These advancements have enabled access to formerly forbidden places. They have enhanced efficiency, lowering the workforce time that human operators are exposed to radiation and the necessity for operator access in polluted environments.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Some concerns must be addressed before technology may be widely adopted. Primarily, material availability may operate as a constraint on technological growth. In addition, to withstand radiation exposure, the material must be of good quality and not change with the reach of gamma rays. Another critical challenge for the nuclear robotics business is inconsistent wireless connections in emergency scenarios.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
CAGR |
17% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, and Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Framatome, Qualter Hall, RAIN Hub, Kurion (Veolia), Northrop Grumman, Forth Engineering, Cyberia, BAE Systems, KUKA AG, Boston Dynamics, and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
Global Nuclear Robotics Market Analysis By Type
- Robot Hardware
- Software
- Services
The market is segmented into Robot Hardware, Software, and Services.
The hardware component will dominate the nuclear robotics market. This can be related to the necessity for novel hardware designs. Sensors and control units on commercial service robots continue to be costly. This rising trend is not only associated with the revolution in robotics, automation, and nuclear technology, but it is also a result of growing concern for human and environmental safety. Even in the presence of high-tech control systems and mechanization, such events necessitate even better state-of-the-art robotics technology and its dependable operating strength. Robots can help with ordinary tasks and deal with delicate and intricate situations requiring mobility, teleoperations, and radiation hardening.
Global Nuclear Robotics Market Analysis By Application
- Measurements
- Inspections
- Radiochemical Handling
- Nuclear Decommissioning
- Other
These robots are outfitted with various sensors and come in multiple sizes based on their use. The vast majority of these robots are controlled remotely. These robots can aid people in the operation and maintenance of industrial nuclear facilities and nuclear reactor maintenance. They are beneficial in areas where human safety is a significant concern, such as decommissioning and dismantling nuclear sites and emergency intervention scenarios.
Pneumatic-driven robots have rapid speed, limited position control, and minimal force potential and are hence employed in limited nuclear applications. Electrically driven robots are more precise and offer more advanced control choices. These robots are smaller and faster than hydraulic robots. Hydraulic robots have a strong force and a long reach. These robots are more robust and have a higher tolerance to shock loads and more excellent recovery alternatives.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
The Asia Pacific region is foreseen to lead the worldwide nuclear robotics business. Countries such as China, India, Brazil, Mexico, the Middle East, and Africa have deployed nuclear robotics technology, considerably strengthening the domestic market. Japan is leading the nuclear robotics market in the Asia Pacific region. State regulation and the introduction of robotics technologies in Europe have boosted the industry. As a result, the European market for nuclear robotics is projected to grow in the coming years. On the other hand, North America is expected to grow over the assessment period.
MARKET KEY PLAYERS
Companies playing a prominent role in the global nuclear robotics market include Framatome, Qualter Hall, RAIN Hub, Kurion (Veolia), Northrop Grumman, Forth Engineering, Cyberia, BAE Systems, KUKA AG, Boston Dynamics, and Others.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- Researchers from the U.K. and Japan have collaborated to create new, safer techniques for deconstructing existing nuclear power stations such as the Fukushima Daiichi reactors. A long-reach robotic system utilized in this scientific cooperation named 'LongOps' would reduce hazards to public health while also speeding up the dismantling of outdated facilities. Besides Fukushima, such robots will be installed at Sellafield in Cumbria, northwest England, where nuclear material is processed and stockpiled.
- The IAEA has chosen the five top crowdsourcing competition submissions, seeking novel concepts or project outlines for furthering nuclear facility dismantling or environmental clean-up of highly radioactive polluted locations. Three of them concentrated on deactivation and two on ecological clean-up, with tools ranging from characterization tools to field tests and 3D radiation research instruments to automation and artificial intelligence.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]