North America Telecom Power Systems Market Research Report – Segmented By Component (Rectifiers, Converters, Controllers, Heat Management Systems, Generators, Others), Grid Type, Power Rating, Power Source, And Country (Us, Canada, And Rest Of North America) - Industry Analysis On Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast (2025 To 2033)
North America Telecom Power Systems Market Size
The North America telecom power systems market size was valued at USD 2.21 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 4.50 billion by 2033 from USD 2.39 billion in 2025. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.22%.
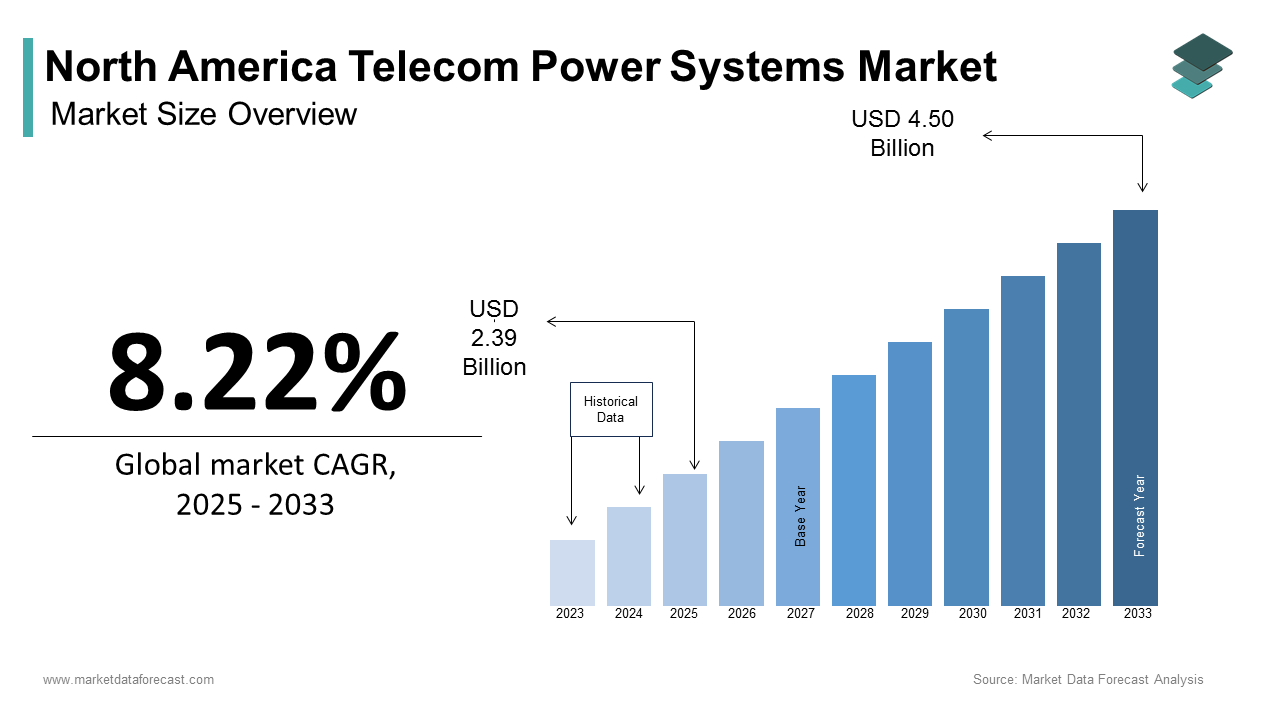
As per the U.S. Federal Communications Commission, over 97% of Americans now have access to high-speed broadband with a milestone achieved through extensive investments in telecom networks. This expansion has created a growing demand for reliable and efficient power systems to support telecom operations. The North America Telecom Power Systems market is further bolstered by the rollout of 5G networks, which require advanced power solutions to manage increased energy consumption. According to Deloitte, telecom operators spent approximately $25 billion on 5G infrastructure in 2022 alone, with power systems forming a critical component of this investment. Urban centers dominated the market landscape by leveraging grid-connected power systems due to their accessibility and cost-effectiveness. However, rural areas are emerging as a focal point for innovation with renewable energy integration. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory states that solar-powered telecom towers reduced operational costs by up to 40% in remote regions.
MARKET DRIVERS
Expansion of 5G Networks
The proliferation of 5G technology is a primary driver propelling the North America telecom power systems market forward. The deployment of 5G networks demands substantial power to support ultra-fast data transmission and low latency. According to the Global System for Mobile Communications Association, 5G networks consume 2.5 times more energy than their 4G counterparts, necessitating advanced power systems capable of meeting these demands. In 2022, the U.S. added 113 million new 5G connections, as per the Federal Communications Commission. Telecom operators are investing heavily in rectifiers and inverters to ensure uninterrupted power supply for 5G base stations. As per a study by McKinsey, energy costs account for 20-40% of total network operating expenses is pushing providers to adopt energy-efficient technologies. Furthermore, urban centers are leading this transition, with cities like New York and Los Angeles witnessing a 30% increase in small cell deployments in 2022.
Integration of Renewable Energy Solutions
The shift toward renewable energy is another significant driver transforming the market. Solar and wind-powered systems are increasingly being integrated into telecom infrastructure to reduce reliance on traditional grids and lower carbon footprints. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, renewable energy adoption in the telecom sector grew by 15% annually between 2020 and 2022. This trend is particularly prominent in rural areas, where grid access is limited. For example, AT&T deployed 500 solar-powered cell sites across the U.S. to enhance sustainability and disaster preparedness. According to a BloombergNEF, lithium-ion battery prices dropped by 89% since 2010 by making renewable-powered systems more affordable. Additionally, government incentives, such as tax credits for clean energy projects, are encouraging telecom operators to adopt sustainable solutions.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs of Advanced Power Systems
One of the primary challenges hindering the growth of the North America telecom power systems market is the high upfront investment required for advanced technologies. Deploying state-of-the-art power systems, such as hybrid or renewable energy solutions, involves significant capital expenditure. A study by the National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners indicates that only 20% of rural telecom providers have adopted renewable energy solutions due to cost concerns. Additionally, integrating advanced systems with existing infrastructure can be complex and expensive, further exacerbating the issue. These financial constraints create a significant hurdle for widespread adoption of innovative power solutions, impeding market growth.
Grid Reliability and Outage Risks
Another critical restraint is the vulnerability of telecom power systems to grid instability and power outages. Despite advancements in grid infrastructure, the U.S. Department of Energy estimates that power outages cost the economy $150 billion annually, with telecom services being particularly affected. Natural disasters, such as hurricanes and wildfires, frequently disrupt grid connectivity, leaving telecom operations reliant on backup systems. For instance, during Hurricane Ida in 2021, over 1 million people in Louisiana lost access to telecom services due to prolonged power outages. While diesel generators provide temporary relief, they are not a sustainable solution due to environmental concerns and fuel dependency. Moreover, bad-grid scenarios, where voltage fluctuations damage equipment, pose additional risks. These challenges highlight the pressing need for resilient power systems but also underscore the limitations of current technologies in addressing grid-related vulnerabilities.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth in Rural Connectivity Initiatives
A significant opportunity for the North America telecom power systems market lies in expanding connectivity to rural and underserved areas. Government initiatives, such as the USDA’s ReConnect Program, have allocated $2.7 billion to bridge the digital divide by creating a fertile ground for off-grid and hybrid power solutions. According to the Federal Communications Commission, approximately 19 million Americans still lack access to high-speed internet, with rural communities accounting for a majority of this gap. Deploying renewable energy-powered systems, such as solar and wind, offers a cost-effective and sustainable solution for these regions. For example, Verizon partnered with SunPower to install solar panels at 200 rural cell sites, reducing operational costs by 35%. Additionally, advancements in battery storage technologies are enhancing the feasibility of off-grid systems. BloombergNEF reports that energy storage installations grew by 210% in 2022 by enabling telecom operators to maintain uninterrupted service even in remote locations. These developments position rural connectivity as a lucrative avenue for market expansion.
Emergence of Smart Cities and IoT Applications
The rise of smart cities and Internet of Things (IoT) applications presents another promising opportunity for the market. Smart city initiatives, such as intelligent traffic management and connected public services, rely heavily on robust telecom infrastructure. According to the International Data Corporation, global spending on smart city technologies is projected to reach $203 billion by 2024, with North America leading the charge. Telecom power systems play a pivotal role in supporting IoT devices, which require consistent and reliable energy supply. For instance, Cisco estimates that there will be 50 billion connected devices globally by 2030, many of which will be deployed in urban environments. To meet these demands, telecom operators are investing in modular power solutions, such as compact inverters and heat management systems that is designed for high-density deployments. These innovations not only cater to current needs but also pave the way for future growth by making smart cities and IoT a transformative opportunity for the market.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Technological Fragmentation and Compatibility Issues
A significant challenge facing the North America telecom power systems market is the fragmentation of technologies and compatibility issues. The interoperability between legacy systems and new technologies becomes a critical concern as the industry transitions to 5G and adopts renewable energy solutions. According to the Telecommunications Industry Association, over 60% of telecom operators reported difficulties integrating advanced power systems with existing infrastructure. This technological fragmentation is exacerbated by the lack of standardized protocols. For example, solar-powered systems often require custom configurations to align with specific telecom equipment, increasing both time and costs. A study by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers highlights that compatibility issues lead to 15% higher operational expenses for telecom providers. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancements means that systems quickly become obsolete by forcing operators to invest in frequent upgrades.
Environmental Regulations and Compliance Burdens
Environmental regulations pose another critical challenge for the North America telecom power systems market. Stricter emission standards and sustainability mandates are compelling operators to phase out traditional diesel generators and adopt cleaner alternatives. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, diesel generators contribute to 2% of the nation’s greenhouse gas emissions, prompting regulatory bodies to impose penalties on non-compliant systems. Compliance with these regulations often requires significant investment in green technologies, which may not be financially viable for smaller operators. For instance, transitioning to solar-powered systems involves not only high upfront costs but also navigating complex permitting processes. A report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory states that regulatory hurdles delay project timelines by an average of 6-12 months. Furthermore, the lack of uniform policies across states adds to the complexity, making it challenging for operators to implement cohesive strategies. These regulatory burdens weigh heavily on the market, impeding progress and innovation.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
8.22% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Grid Type, Power Rating, Power Source, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
US, Canada, Mexico, and Rest of North America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Eaton Corporation Plc, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Cummins Inc., ZTE Corporation, General Electric Company, Delta Electronics Inc., ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Vertiv Group Corp., EnerSys. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights
The rectifiers segment dominated the North America telecom power systems market by capturing 35.3% of the total revenue share in 2024 due to its pivotal role in ensuring seamless power conversion for telecom infrastructure. Rectifiers are indispensable in converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), a process essential for powering sensitive telecom equipment such as base stations, routers, and switches. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights that rectifiers account for nearly 40% of all power conversion systems deployed across telecom networks, underscoring their widespread adoption and importance. One key factor driving the dominance of rectifiers is their adaptability to diverse grid conditions that is making them suitable for both urban and rural deployments. As per Navigant Research, advanced rectifier systems are compatible with on-grid, off-grid, and hybrid power setups, offering telecom operators flexibility in designing their networks. This versatility is particularly valuable in regions with inconsistent grid reliability, where rectifiers can seamlessly integrate with renewable energy sources like solar panels or battery storage systems. Additionally, the ongoing rollout of 5G networks has significantly increased demand for high-capacity rectifiers capable of handling elevated power requirements. Deloitte estimates that 70% of new 5G installations incorporate advanced rectifier systems, which are designed to support ultra-fast data transmission and low latency.
The heat management systems segment is likely to experience a fastest CAGR of 14.2% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by the increasing energy density of modern telecom equipment in 5G networks, which generate substantial heat during operation. According to the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers, cooling systems account for 30-40% of total energy consumption in telecom facilities with the critical need for efficient thermal management solutions. Advanced liquid cooling technologies, such as immersion cooling, are gaining traction due to their ability to reduce energy usage by 50% compared to traditional air-based systems, as per a study by Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory. These innovations not only lower operational costs but also enhance the lifespan of telecom equipment by maintaining optimal operating temperatures. For instance, Microsoft’s adoption of liquid cooling in its data centers resulted in a 40% reduction in carbon emissions, demonstrating the environmental and economic benefits of these systems.
By Grid Type Insights
The On-grid systems segment dominated the North America telecom power systems market in 2024 with an estimated share of 62.1% during the forecast period. This dominance is driven by the region’s robust electrical infrastructure, particularly in urban areas where grid connectivity is nearly universal. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, over 90% of the population has access to reliable grid electricity, enabling telecom operators to leverage on-grid systems for their cost-effectiveness and ease of deployment. A key factor behind the leadership of on-grid systems is their affordability. On-grid solutions reduce operational expenses by 30% compared to off-grid alternatives, as stated by the International Energy Agency. This cost advantage makes them especially appealing to small and medium-sized telecom operators with limited budgets. Additionally, on-grid systems are simpler to install and maintain, requiring minimal technical expertise. This simplicity ensures uninterrupted power supply, which is critical for maintaining seamless telecom services.
The Off-grid systems segment is esteemed to hit a CAGR of 12.7% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by the increasing need for connectivity in remote and underserved areas, where traditional grid infrastructure is either unreliable or nonexistent. According to the US Department of Agriculture, rural broadband initiatives have invested $2.7 billion to expand access, with off-grid systems playing a crucial role in bridging the digital divide. Solar-powered solutions are a major driver of this segment’s growth. BloombergNEF reports that lithium-ion battery prices have dropped by 89% since 2010 by making renewable energy-based systems more affordable and accessible. These systems are particularly valuable in rural areas, where they provide a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to diesel generators. For instance, AT&T has deployed 500 solar-powered cell sites across the U.S., enabling reliable connectivity while reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
By Power Rating Insights
The below 10 kW segment was accounted in holding 45.5% of the North America telecom power systems market share in 2024. According to the Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions, these systems are widely used in urban microcells and rural telecom towers, where energy demands are relatively low. Their compact design and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for deployments in space-constrained environments, such as densely populated cities or remote areas with limited infrastructure. A key factor contributing to the dominance of below 10 kW systems is their affordability. Systems in this category reduce installation costs by 25% compared to higher-rated systems, as per the U.S. Department of Commerce. This cost advantage is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized telecom operators looking to expand their networks without incurring significant capital expenditure. Additionally, the growing adoption of 5G small cells has further bolstered demand for low-power systems. Customization and integration capabilities are other factors driving the popularity of below 10 kW systems. These systems can be seamlessly integrated with existing infrastructure, enabling telecom providers to create cohesive and scalable power management ecosystems tailored to their specific needs. For example, Verizon recently launched its Smart Microcell Power Solution, a below 10 kW system designed for urban environments. This product combines compact rectifiers, battery backup, and intelligent energy management features, allowing operators to optimize power usage and reduce operational costs.
The Above 20 kW systems segment is likely to register a CAGR of 13.5% during the forecast period owing to increasing demand for high-capacity power solutions. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, these systems are essential for large-scale telecom facilities, such as data centers and macrocell towers, which require robust and reliable power infrastructure to support intensive operations. One major driver of this segment’s rapid growth is the rise of IoT and smart city applications, which are placing unprecedented demands on telecom networks. Cisco predicts that there will be 50 billion connected devices globally by 2030 with an increasing energy consumption. To meet these demands, telecom operators are investing in high-capacity systems capable of delivering consistent and scalable power. For instance, AT&T has deployed its PowerMax 20+ Solution, an above 20 kW system designed for macrocell towers. This product integrates advanced rectifiers, heat management systems, and renewable energy sources, ensuring optimal performance even under heavy load conditions.
By Power Source Insights
The diesel-battery power sources segment was the largest by capturing 50.2% of the North America telecom power systems market share in 2024. This segment’s leadership is driven by its reliability and widespread adoption in rural and remote areas, where grid access is limited or inconsistent. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, these systems are commonly used in telecom towers located in underserved regions, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during outages. A key factor behind the dominance of diesel-battery systems is their ability to provide backup power during emergencies. Diesel generators, combined with battery storage, offer a reliable solution for maintaining connectivity when grid power is unavailable. Additionally, these systems are cost-effective for short-term deployments, with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory estimating a 20% lower upfront cost compared to solar-powered alternatives.
The multiple power sources segment is likely to exhibit a CAGR of 15.3% from 2025 to 2033 owing to the increasing demand for resilient and sustainable power solutions. According to BloombergNEF, hybrid systems combining solar, wind, and battery storage reduce operational costs by 35% while enhancing reliability. These systems are particularly valuable in regions prone to natural disasters or grid instability, as they provide a diversified power supply that minimizes downtime. Government incentives are a major driver of this segment’s rapid growth. The USDA’s ReConnect Program has allocated $2.7 billion to rural broadband projects using hybrid systems, encouraging telecom operators to adopt renewable energy solutions. Additionally, the push for carbon neutrality is accelerating adoption. The International Renewable Energy Agency states that hybrid systems accounted for 25% of new installations in 2022.
By Technology Insights
The DC power systems segment was the largest by occupying dominant share of the North America telecom power systems market in 2024 due to its compatibility with modern telecom equipment, which operates on direct current (DC) for efficiency and reliability. According to the Telecommunications Industry Association, DC systems account for 70% of all power systems used in telecom base stations. One key factor driving this dominance is the increasing deployment of 5G networks. Deloitte estimates that 70% of new 5G installations use DC power systems due to their ability to handle high energy demands while minimizing losses. Additionally, advancements in battery technology have enhanced performance. DC systems reduce operational costs by 25% compared to AC alternatives, as per the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Their modular design also allows seamless integration with renewable energy sources by aligning with sustainability goals.
The AC power systems are projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2025 to 2033 due to their versatility and adaptability to diverse applications. According to Navigant Research, AC systems are increasingly used in urban microcells and small-scale deployments, where flexibility is paramount. Cisco predicts 50 billion connected devices globally by 2030 that is requiring scalable AC solutions. Additionally, innovations in energy management software enable remote monitoring, enhancing operational efficiency. For example, Schneider Electric launched its EcoStruxure AC Power System in mid-2024, offering predictive maintenance and real-time analytics. Government incentives are also boosting adoption.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The United States was the largest contributor in the North America telecom power systems market with a share of 85.3% in 2024 owing to the robust telecommunications infrastructure and its aggressive push toward 5G network expansion. According to the Federal Communications Commission, the U.S. added 113 million new 5G connections in 2022 by creating a surge in demand for advanced power systems to support these networks. A key factor driving the U.S. market is the widespread availability of grid electricity, which enables telecom operators to rely on cost-effective on-grid solutions. The U.S. Energy Information Administration states that over 90% of Americans have access to reliable grid power by making it easier to deploy telecom power systems across urban and suburban areas. Additionally, government initiatives like the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which allocates $65 billion to broadband expansion, are further propelling growth. Renewable energy integration is another critical driver. AT&T deployed 500 solar-powered cell sites in rural areas that is reducing operational costs by 35%.
Canada is lucratively to show up with the prominent CAGR of 7.8% during the forecast period. Despite its smaller population, Canada’s expansive geography and focus on rural connectivity drive demand for innovative power solutions. According to Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada, the government has committed $2.75 billion to bridge the digital divide, with off-grid systems playing a pivotal role in remote regions. A major driver is the country’s commitment to sustainability. According to the Canadian Renewable Energy Association, renewable energy adoption grew by 10% annually between 2020 and 2022, with solar-powered telecom towers emerging as a cost-effective solution. For instance, Bell Canada partnered with Solantro to deploy hybrid power systems in northern territories, achieving a 40% reduction in fuel consumption.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Delta Electronics
Delta Electronics is a Taiwan-based multinational company and a dominant player in the telecom power systems market. Delta specializes in energy-efficient power management solutions, including uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems and renewable energy integration for telecom infrastructure. In North America, Delta has partnered with major telecom operators to deploy solar-powered hybrid systems, reducing reliance on traditional energy sources by up to 40% . Its focus on R&D, with over 8% of annual revenue reinvested into innovation that ensures it remains at the forefront of developing sustainable technologies. Globally, Delta’s contributions to green energy adoption have positioned it as a leader in decarbonizing telecom operations.
Huawei Technologies
Despite geopolitical challenges, Huawei Technologies remains a major player in the global telecom power systems market. Huawei’s expertise lies in providing end-to-end power solutions for 5G networks, which are critical for high-speed connectivity. In North America, Huawei has collaborated with utility providers to integrate smart grid technologies into telecom infrastructure, improving energy efficiency by up to 35% . The company’s innovative modular power systems enable flexible deployment in remote areas, making it a preferred choice for rural broadband expansion projects. On a global scale, Huawei’s commitment to sustainability, evidenced by its pledge to achieve carbon neutrality by 2040 , reinforces its leadership role in advancing eco-friendly telecom solutions.
Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric, headquartered in France, is another prominent player in the North American telecom power systems market. Schneider focuses on delivering intelligent power management solutions that combine IoT-enabled monitoring, automation, and renewable energy integration. Its EcoStruxure platform has been widely adopted in North America, enabling telecom operators to optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs by up to 25% . Globally, Schneider’s emphasis on digital transformation and sustainability has made it a trusted partner for large-scale infrastructure projects. The company’s recent initiative, the Zero Carbon Project , aims to help businesses transition to carbon-neutral operations by 2030, further solidifying its influence in the global market.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Investment in Research and Development (R&D)
Key players like Delta Electronics , Huawei Technologies , and Schneider Electric have heavily invested in R&D to develop advanced, energy-efficient solutions tailored to the telecom industry’s needs. For instance, Delta Electronics allocates over 8% of its annual revenue to R&D , enabling it to pioneer solar-powered hybrid systems that reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Similarly, Huawei has developed modular power systems optimized for 5G networks, which are critical for high-speed connectivity. These innovations not only enhance operational efficiency but also align with global trends toward sustainability and digital transformation.
Focus on Renewable Energy Integration
Sustainability is a core focus for major players as governments and consumers increasingly demand eco-friendly solutions. Schneider Electric has leveraged its EcoStruxure platform to integrate renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into telecom power systems, reducing carbon footprints and operational costs by up to 25% . Huawei has also introduced smart grid technologies that enable seamless integration of renewables into telecom infrastructure. This emphasis on clean energy helps companies comply with stringent environmental regulations while positioning themselves as leaders in green technology.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations with telecom operators, utility providers, and government agencies have been instrumental in expanding market reach. For example, Huawei has partnered with North American utility providers to deploy smart grid solutions, improving energy efficiency by up to 35% . Similarly, Delta Electronics has collaborated with telecom giants to implement solar-powered systems in rural areas, supporting broadband expansion initiatives like Canada’s Universal Broadband Fund . These partnerships enhance brand credibility and ensure the adoption of cutting-edge solutions across diverse geographies.
Expansion into Emerging Markets and Rural Areas
Key players are targeting underserved regions to expand their footprint and address the growing demand for connectivity. Huawei and Schneider Electric have actively participated in projects aimed at bridging the digital divide, such as deploying hybrid power systems in remote areas. By aligning with government programs like the U.S. Federal Communications Commission $20 billion 5G investment plan and Canada’s CAD 2.75 billion Universal Broadband Fund , these companies are strengthening their presence in both urban and rural markets.
Digital Transformation and IoT-Enabled Solutions
The integration of IoT, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud-based platforms has become a cornerstone of competitive strategy. Schneider Electric’s EcoStruxure platform offers real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities, enabling telecom operators to optimize energy usage and minimize downtime. Similarly, Huawei’s AI-driven power management systems enhance network reliability and performance. These digital solutions not only improve customer satisfaction but also create new revenue streams through value-added services.
Acquisitions and Mergers
Acquisitions have been another key strategy to consolidate market leadership. For instance, Schneider Electric acquired UK-based AVEVA Group to bolster its software capabilities for industrial automation and energy management. Such moves allow companies to diversify their product portfolios and gain access to new technologies, further solidifying their competitive edge.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS And COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players of the North America Telecom Power Systems Market include Eaton Corporation Plc, Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd., Cummins Inc., ZTE Corporation, General Electric Company, Delta Electronics Inc., ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Vertiv Group Corp., EnerSys.
The North American telecom power systems market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the rapid expansion of 5G networks, increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, and the integration of renewable energy sources. Key players such as Delta Electronics , Huawei Technologies , and Schneider Electric dominate the market, leveraging their expertise in advanced power management technologies to maintain their leadership positions. These companies focus on innovation, with significant investments in R&D to develop cutting-edge solutions like modular power systems, hybrid energy solutions, and IoT-enabled platforms.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by collaborations with telecom operators and government agencies to support initiatives like broadband expansion and rural connectivity. For instance, Huawei has partnered with utility providers to deploy smart grid technologies, while Delta Electronics has collaborated on solar-powered systems for underserved areas. Sustainability is another critical factor, with companies emphasizing renewable energy integration to comply with environmental regulations and meet consumer demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Additionally, the market sees competition through geographic expansion and acquisitions. Schneider Electric’s acquisition of AVEVA Group highlights efforts to enhance software capabilities, while smaller players focus on niche markets. The push toward digital transformation, including AI-driven predictive maintenance and cloud-based monitoring, adds another layer of differentiation. Overall, the North American telecom power systems market is a dynamic arena where innovation, sustainability, and strategic partnerships are key to gaining a competitive edge. Companies that adapt to evolving trends and regulatory frameworks are likely to thrive in this rapidly growing sector.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, Vertiv Co. launched its Smart Grid Integration Solution, enabling seamless integration with renewable energy sources.
- In June 2024, Eaton Corporation partnered with SunPower to develop hybrid power systems for rural deployments.
- In July 2024, Delta Electronics acquired an AI-driven energy management startup to enhance its product offerings.
- In August 2024, Schneider Electric introduced its EcoStruxure AC Power System, offering predictive maintenance features.
- In September 2024, AT&T deployed 500 solar-powered cell sites in collaboration with Solantro, reducing operational costs by 35%.
DETAILED SEGMENTATION OF NORTH AMERICA TELECOM POWER SYSTEMS MARKET INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT
This research report on the North America telecom power systems market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on Component, Grid Type, Power Rating, Power Source & region.
By Component
- Rectifiers
- Converters
- Controllers
- Heat Management Systems
- Generators
- Others
By Grid Type
- On-Grid
- Off-Grid
- Bad Grid
By Power Rating
- Below 10 kW
- 10–20 kW
- Above 36 kW
By Power Source
- Diesel-Battery
- Diesel-Solar
- Diesel-Wind
- Multiple Sources
By Region
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which companies are the key players in the North America telecom power systems market?
Major players include Eaton Corporation, Huawei Technologies, Cummins Inc., ZTE Corporation, General Electric, Delta Electronics, ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric, Vertiv Group, and EnerSys.
2. Who regulates the telecom power systems market in North America?
Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Department of Energy (DOE) oversee power system standards and energy efficiency regulations.
3. How do telecom power systems ensure uninterrupted communication services?
They use backup batteries, diesel generators, and renewable energy sources to provide continuous power during outages or grid failures.
4. What are the latest trends in telecom power systems?
Trends include the adoption of hybrid power solutions, AI-based energy management, and smart grid integration for improved efficiency and sustainability.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]