Global mRNA Market – By Type (Prophylactic Vaccines, Therapeutic Vaccines), By Application (Oncology, Respiratory Diseases, Infectious Diseases, Others), By End-User (Hospitals & Clinics, Research Organizations, Others), By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa) – Industrial Analysis on Size, Share, Trends, and Growth Factors (2024 to 2032)
Global mRNA Market Size (2024 to 2032)
The mRNA market size is estimated to be worth USD 54.84 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 182.61 billion by 2032 with a CAGR of 16.23% during the forecast period.
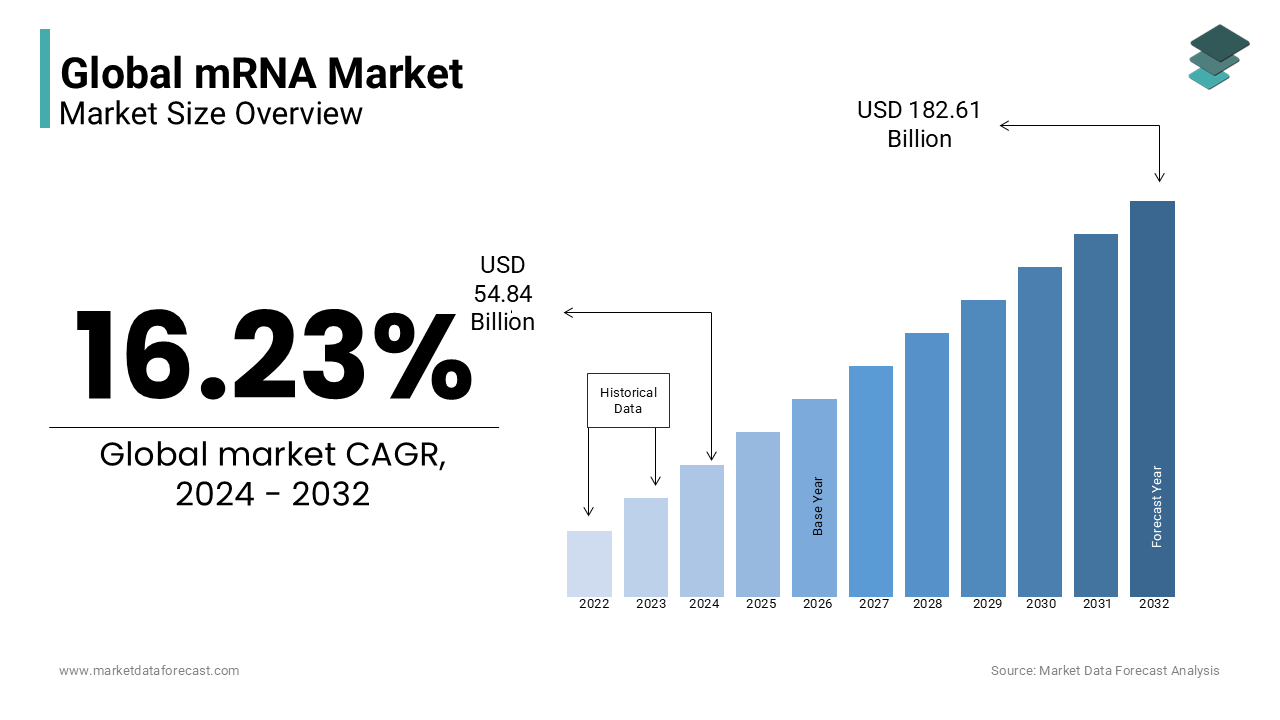
Overview:
The mRNA therapeutics and vaccines market has witnessed substantial growth over the past decade, fueled by significant advancements in biotechnology, particularly in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, mRNA technology was in its nascent stages; however, the successful deployment of vaccines such as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna thrust the technology into the global healthcare arena.
North America and Europe continue to lead the mRNA market, holding a dominant share of global sales, attributed to their well-established research infrastructure and strong pharmaceutical sectors. Conversely, the Asia-Pacific region is poised for rapid expansion, as China and India ramp up investments in mRNA research and manufacturing.
The competitive landscape remains intense, with key industry players, including Moderna, BioNTech, and Pfizer, focusing on the advancement of mRNA platform technologies. In addition, the influx of smaller biotechnology firms and research institutions is fostering innovation, particularly in personalized medicine and novel therapeutic applications.
Key market developments include the progression of next-generation mRNA vaccines and therapies, alongside strategic partnerships between biotechnology companies and major pharmaceutical firms aimed at scaling production capabilities and enhancing global distribution efforts.
Market Trends:
Expansion Beyond Vaccines
Originally recognized for its pivotal role in COVID-19 vaccine development, the mRNA market is swiftly broadening into diverse therapeutic applications. Major players such as Moderna and BioNTech are spearheading efforts to harness mRNA technology in areas like oncology, genetic disorders, and infectious diseases. Moderna’s pipeline, for instance, includes a promising cancer vaccine, developed in collaboration with Merck, which has shown encouraging results in clinical trials for melanoma. This evolution from vaccines to therapeutic applications is poised to reshape the industry, with significant investments in R&D directed towards chronic illnesses and rare disease treatments.
Growing Government Investments
Governments across the globe are increasingly recognizing the strategic importance of mRNA technology and are committing substantial investments to bolster its development. For example, in 2023, the U.S. government allocated $1 billion to expand Moderna’s mRNA research capabilities. Similarly, the European Union has invested €400 million towards the establishment of a regional mRNA vaccine platform. These strategic investments are designed to strengthen domestic manufacturing capabilities, reducing reliance on external sources during health crises. Partnerships between governments and biotech firms are expected to expedite research and commercialization efforts, enabling faster responses to future pandemics and other emerging health threats.
Advances in mRNA Manufacturing
Efficient and scalable manufacturing processes are emerging as critical components of mRNA’s future trajectory. Industry leaders are focusing on refining production techniques to drive down costs and build a more resilient supply chain. For instance, Pfizer announced a $1.2 billion investment in 2023 to expand its mRNA vaccine manufacturing capacity, aiming to meet the growing global demand. This trend highlights the shift toward decentralized, scalable production models. Moreover, innovations like self-amplifying mRNA (saRNA) have the potential to make vaccines and therapeutics more effective, reducing the required dosage for the same therapeutic outcomes. Such advancements are expected to be key drivers in the continued evolution of mRNA technologies in both medical and commercial sectors.
MARKET DRIVERS
Technological Innovation in mRNA Delivery Systems
Advancements in delivery mechanisms, particularly lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), are a significant driving force within the mRNA market. LNPs safeguard mRNA molecules and enhance their cellular entry, ensuring therapeutic efficiency. Pfizer and BioNTech's COVID-19 vaccine leveraged LNPs effectively, underscoring the broad application potential. Research aimed at refining these systems continues, with a focus on increasing the efficacy of mRNA therapies and minimizing side effects. Continued innovation in delivery mechanisms is anticipated to facilitate the expansion of mRNA therapies into oncology and rare diseases, offering more precise treatments.
Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine
The growing focus on personalized medicine is significantly boosting mRNA research. The versatility of mRNA makes it highly suitable for developing individualized treatments, particularly in areas such as cancer and genetic disorders. Leading companies like Moderna and BioNTech are at the forefront of this movement, with personalized cancer vaccines already in clinical trials. For instance, BioNTech's BNT122, an mRNA vaccine for melanoma, is showing promise in early-stage human trials. These personalized solutions are expected to become a key element of future healthcare strategies, offering tailored treatments for unique patient profiles.
Global Response to Infectious Diseases
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the mRNA market, highlighting its rapid-response capabilities in addressing infectious diseases. Governments and health agencies are increasingly investing in mRNA vaccines for diseases such as influenza, HIV, and malaria. For instance, Moderna is developing a combined flu and COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, which is projected to enter clinical trials by 2025. The adaptability of mRNA platforms to emerging pathogens positions them as essential tools in pandemic preparedness, ensuring swift vaccine development and global distribution.
Expansion into Therapeutics for Rare Diseases
The mRNA market presents significant potential in treating rare genetic disorders, offering a promising alternative to conventional therapies. Traditional approaches often fail to address the underlying causes of these conditions, whereas mRNA technology enables a more targeted strategy by instructing cells to produce specific therapeutic proteins. Companies like Moderna and Arcturus Therapeutics are at the forefront of developing mRNA-based treatments for rare diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and glycogen storage disorders. By providing customizable treatment options, mRNA technology offers new hope for previously untreatable conditions, paving the way for improved patient outcomes and expanding market opportunities.
Emergence of mRNA Vaccines for Seasonal Illnesses
The development of mRNA vaccines for common seasonal illnesses, including influenza, represents a key growth area. Unlike traditional flu vaccines, which often face production delays and may struggle with viral mutation, mRNA vaccines can be swiftly updated to match circulating strains. Moderna is actively conducting clinical trials for an mRNA-based flu vaccine, anticipated to launch by 2025. The global influenza vaccine market, valued at $6.5 billion in 2021, presents a lucrative opportunity for mRNA technology to enhance both efficacy and responsiveness. This adaptability also opens the door to addressing other seasonal viruses, positioning mRNA as a versatile tool for combating future outbreaks.
Advances in Personalized Cancer Vaccines
The rise of personalized cancer vaccines, tailored to individual tumor profiles using mRNA, marks a transformative shift in oncology treatments. By sequencing a patient’s tumor and developing vaccines targeting specific mutations, mRNA therapies can effectively strengthen the body’s immune response. BioNTech, in collaboration with Roche, is developing personalized mRNA vaccines for colorectal cancer, which are expected to enter late-stage trials soon. With the global cancer vaccine market projected to grow to $17.2 billion by 2027, personalized mRNA approaches are gaining traction. As cancer remains a leading cause of mortality globally, these vaccines hold the potential to improve survival rates and revolutionize cancer care, opening new avenues for research and treatment.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production Costs
The production of mRNA vaccines and therapies remains costly due to the complex processes involved and the need for specialized infrastructure. Although technological advancements have been made, the expense of critical components like lipid nanoparticles and the requirement for ultra-cold storage continue to drive up production costs. For instance, Pfizer and BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine necessitates storage at -70°C, adding logistical hurdles. High production costs restrict access to mRNA vaccines in low- and middle-income countries, impeding global distribution. Industry reports suggest that mRNA vaccine production costs can exceed $20 per dose, compared to traditional vaccines that are often priced below $10, creating a significant challenge to widespread mRNA adoption.
Regulatory Challenges
The regulatory framework surrounding mRNA therapies is still developing, posing challenges for companies looking to introduce new products. Given that mRNA is a relatively new technology, regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA are continuing to adapt their guidelines, particularly regarding long-term safety and efficacy. For instance, Moderna experienced delays in Europe with its mRNA-based COVID-19 booster due to concerns over dosage levels. These regulatory obstacles can slow the approval process, prolonging time-to-market and increasing research and development (R&D) costs, which may impede innovation and limit the speed at which new mRNA products are launched.
Supply Chain Constraints
The supply chain for mRNA production is intricate and prone to disruption, especially in the sourcing of essential raw materials such as nucleotides, enzymes, and lipid nanoparticles. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed these vulnerabilities, with companies like Moderna and BioNTech struggling to meet global demand due to shortages of key materials. In 2023, disruptions across the global supply chain led to delays in mRNA vaccine distribution, particularly in regions such as Africa and Southeast Asia. The reliance on a limited number of suppliers for critical components further exacerbates these challenges, constraining the scalability of mRNA technologies and limiting their global reach.
Challenges:
Long-Term Safety Concerns
Despite the significant breakthroughs seen with mRNA technology, concerns regarding its long-term safety continue to persist. Although mRNA-based vaccines and therapies have shown safety in the short term, there remains limited long-term data, which raises questions about immune responses and potential autoimmune effects. Regulatory bodies are responding by demanding extensive post-marketing surveillance and long-term follow-up studies, which may delay the approval of future mRNA treatments. This challenge represents a major obstacle, as comprehensive long-term data will be crucial for fostering broader acceptance among healthcare providers and the public, thereby building trust in mRNA technologies.
Global Disparities in Access
Access to mRNA vaccines and therapies remains unequal across the globe, with stark differences between high-income and low-income regions. The sophisticated infrastructure required for mRNA production, such as ultra-cold storage and advanced distribution systems, is often lacking in developing nations. For example, during the COVID-19 vaccine rollout, Africa encountered significant delays due to logistical challenges in obtaining mRNA vaccines. While global initiatives like COVAX aim to address these disparities, the uneven distribution underscores the need for localized manufacturing and improved supply chain resilience. Bridging these gaps will be essential for ensuring that mRNA technology becomes a truly global healthcare solution.
Public Misinformation and Vaccine Hesitancy
Despite the scientific advancements in mRNA technology, misinformation and vaccine hesitancy continue to pose considerable barriers. During the COVID-19 pandemic, misinformation surrounding mRNA vaccines, such as false claims about altering DNA or affecting fertility, spread rapidly across social media. According to a 2022 World Health Organization (WHO) study, around 20% of the global population expressed hesitancy toward mRNA vaccines. This skepticism undermines public health efforts and hampers the broader adoption of mRNA-based treatments. Tackling this issue will require coordinated public education campaigns and transparent communication from both governments and private companies to build trust and dispel myths surrounding mRNA technologies.
Impact of COVID-19 on the mRNA Market:
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the growth of the mRNA market, propelling mRNA technology into a pivotal role within global healthcare. Prior to the pandemic, mRNA therapeutics were largely confined to early-stage research and development. However, the swift creation and deployment of mRNA vaccines, such as those produced by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, marked a crucial turning point for the sector. These vaccines demonstrated the remarkable speed, adaptability, and efficacy of mRNA platforms, leading to their rapid and widespread adoption. By the end of 2021, over 1.5 billion doses of mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines had been administered globally, underscoring the scalability of this technology.
The pandemic underscored the critical importance of rapid response capabilities in vaccine development, with mRNA technology serving as the primary enabler. As a result, the global mRNA market witnessed a sharp surge, reaching an estimated value of $39 billion by 2023. Companies operating in the sector experienced substantial investments, formed strategic partnerships, and benefited from government support, fostering advancements in mRNA research across therapeutic areas such as cancer, rare diseases, and infectious diseases.
In the post-pandemic landscape, the mRNA market is shifting its focus from COVID-19 vaccines to broader therapeutic applications. Although the demand for COVID-19 vaccines has declined, mRNA technology continues to evolve. Companies such as Moderna and Pfizer are directing their efforts toward next-generation vaccines targeting influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other respiratory infections. Additionally, the success of mRNA during the pandemic has paved the way for innovations in fields such as oncology and personalized medicine, with ongoing clinical trials for cancer vaccines and treatments for genetic disorders.
Despite these advancements, the market faces ongoing challenges, including the need to maintain production efficiency and navigate regulatory hurdles for non-vaccine applications. Nevertheless, the pandemic has irrevocably transformed the mRNA landscape, establishing it as a critical technology in the future of medicine.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, End User and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Moderna Inc, BioNTech SE, CureVac N.V, Arcturus Therapeutics, Sanofi, GSK Plc., Argos Therapeutics Inc., Pfizer Inc., AstraZeneca, Ethris. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type of Drugs
- Prophylactic vaccines
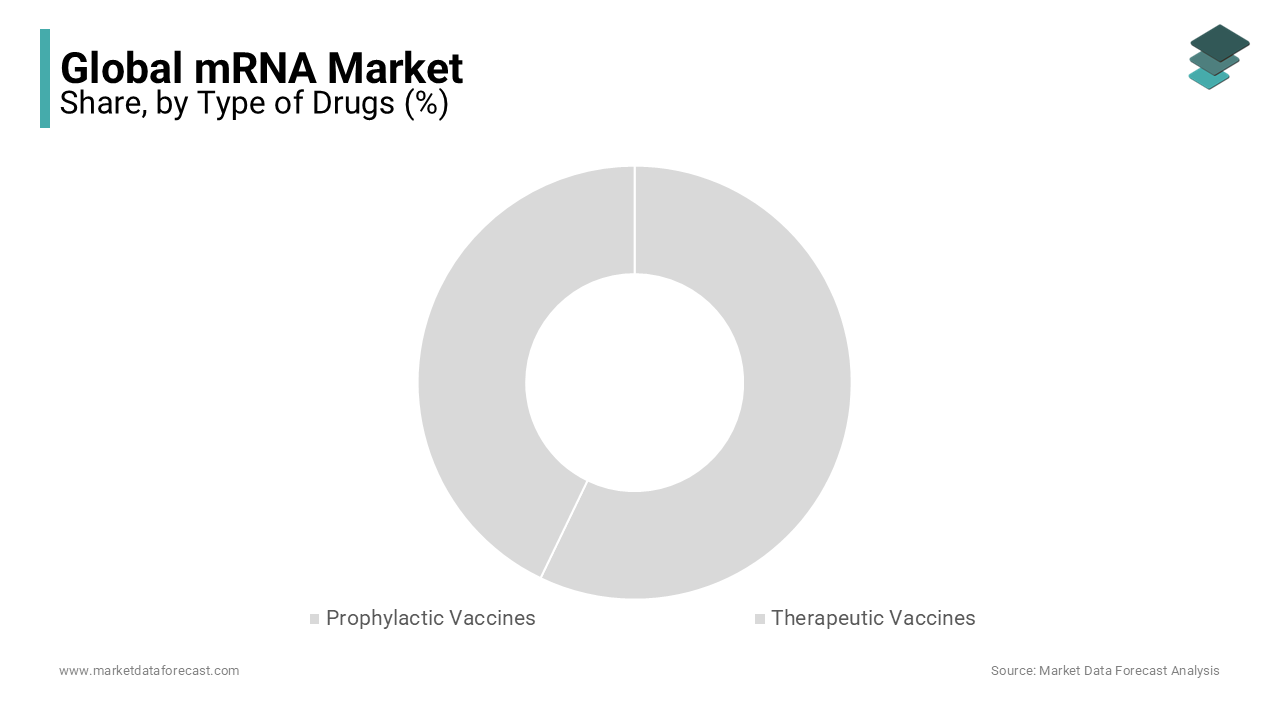
Prophylactic Vaccines is leading the mRNA Market
Prophylactic vaccines dominate the mRNA market, comprising approximately 70% of the overall market share. This segment is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.1% from 2023 to 2030. The COVID-19 pandemic played a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of mRNA technology, as Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccines showcased the platform’s ability for rapid, scalable production. Beyond COVID-19, there is increasing interest in mRNA-based vaccines for seasonal illnesses, including influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Moderna’s mRNA flu vaccine is anticipated to enter late-stage trials by 2025, offering a more efficient and quicker alternative to traditional vaccines. The capability to swiftly adjust mRNA vaccines to match emerging viral strains provides this segment with a competitive advantage, particularly in global pandemic preparedness. Furthermore, government initiatives, such as the U.S. investing over $1 billion in developing next-generation mRNA vaccines, are driving sustained growth. Increased public awareness of vaccination and improvements in logistics, particularly in cold chain storage, are additional factors bolstering the expansion of mRNA-based prophylactic vaccines. Vaccines like BioNTech’s personalized melanoma vaccine are revolutionizing cancer treatment by providing highly targeted therapies that enhance the immune system’s response. This emerging wave of innovation is set to redefine the landscape of mRNA vaccines.
- Therapeutic Vaccines
Therapeutic Drugs: A Prominent Frontier for mRNA Technology
Therapeutics Drugs is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2023 to 2030, as mRNA technology enables the instruction of cells to produce cancer-fighting proteins. Companies like BioNTech and Moderna are making significant investments in clinical trials for mRNA-based cancer therapies, with BioNTech’s BNT122 vaccine for colorectal cancer emerging as a particularly promising candidate. These therapies’ personalized nature, tailored to individual tumor profiles, allows for highly targeted and effective treatments, outperforming traditional approaches. Strategic partnerships, such as BioNTech’s collaboration with Roche, are further accelerating the development of these therapies. Given the rising global incidence of cancer, projected to reach 28.4 million cases by 2040, this area is a critical focus for the mRNA market. Fast-track regulatory designations are also playing a key role in expediting the market entry of these therapies. The flexibility of mRNA technology in addressing specific genetic conditions is fueling its application in treating rare diseases, such as cystic fibrosis and glycogen storage diseases. This adaptability offers significant potential to transform how rare diseases are treated, presenting substantial opportunities for market growth.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
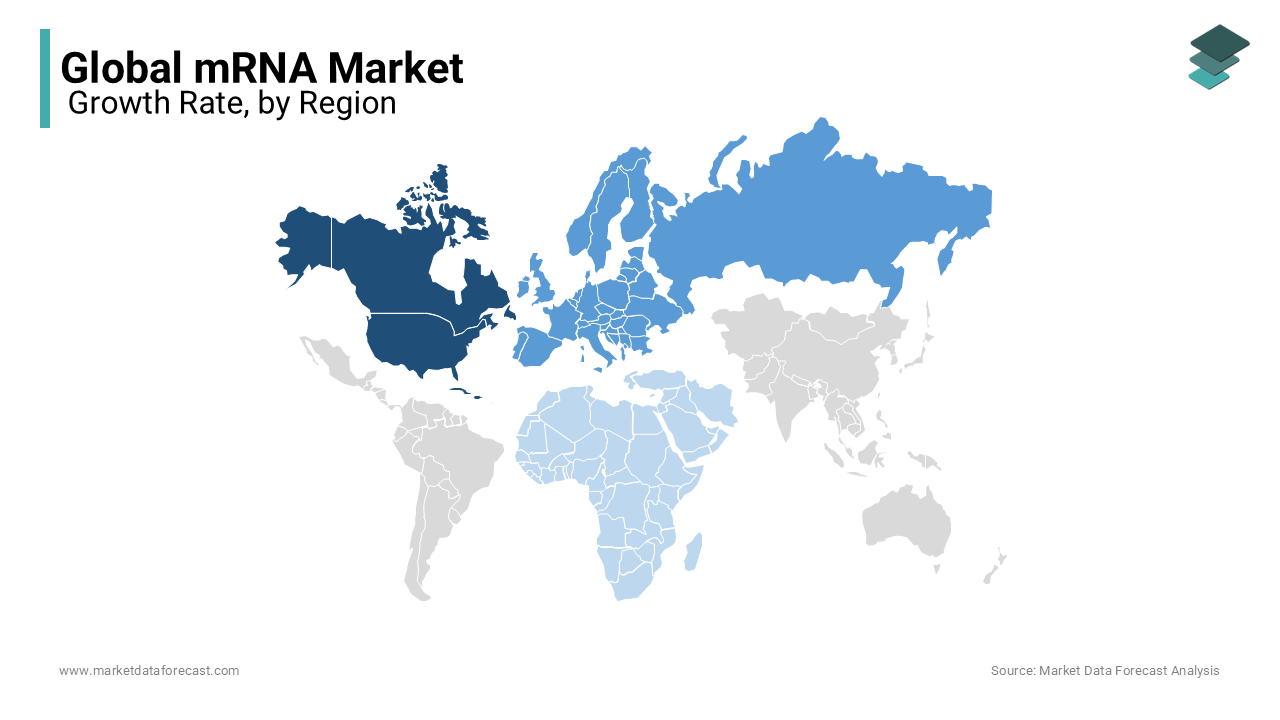
- North America: The Powerhouse of mRNA Innovation
North America leads the global mRNA market, supported by a robust infrastructure, established biotech companies, and substantial governmental backing. In 2023, the region captured approximately 45% of the global market share, with the United States at the forefront, home to key players such as Moderna and Pfizer. The North American mRNA market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.5% from 2023 to 2030, fueled by rising investments in research, expanding oncology applications, and increasing demand for personalized medicine. The U.S. government has committed over $2 billion to bolster mRNA research and infrastructure, focusing on advancing vaccines and therapeutics for infectious diseases and cancer. Canada is also progressing, with an emphasis on developing domestic mRNA vaccine production capabilities. The region remains a global leader in innovation, continually advancing the applications of mRNA technology beyond COVID-19. - Europe: The Rising Hub for mRNA Production
Europe holds an estimated 30% of the global mRNA market share, with a projected CAGR of 7.9% through 2030. The region's strong pharmaceutical industry and supportive regulatory frameworks position it as a key player in the mRNA landscape. Germany leads the European market, with BioNTech driving innovation in mRNA development. The European Union’s €400 million investment to expand mRNA vaccine manufacturing and research underscores the region’s commitment to achieving self-sufficiency in vaccine production. Nations like France and the U.K. are similarly advancing their mRNA capabilities through government initiatives focused on enhancing pandemic preparedness. Europe is emerging as a critical center for both mRNA research and production, particularly in personalized cancer vaccines and health security efforts. - Asia-Pacific: A Fast-Growing mRNA Market with Enormous Potential
Asia-Pacific is rapidly becoming a pivotal player in the global mRNA market. The region currently holds about 15% of the global market, with countries such as China, Japan, and India taking the lead. China has made significant strides in the development of mRNA vaccines, with companies like Walvax and Suzhou Abogen making advancements. In 2023, China approved its first domestically developed mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, reducing reliance on imports and boosting local production. India is following suit, emerging as a production hub with global partnerships aimed at localizing mRNA vaccine production. Japan is channeling investments into research and development, particularly in mRNA technology for cancer therapies and infectious disease vaccines. The combination of high population growth and increased healthcare investment positions Asia-Pacific as a rising force in the mRNA market. - Latin America: mRNA Advancements on the Horizon
Latin America mRNA market growth is esteemed to continue with the steady growth pace during the forecast period. Government initiatives to expand local vaccine production are driving this growth, with Brazil and Argentina at the forefront of mRNA research and manufacturing. In 2023, Brazil established its first mRNA vaccine research facility to reduce reliance on imports. Mexico is also making progress, with plans to develop domestic production capabilities, ensuring quicker access to future mRNA vaccines. The region’s growth is supported by local investments and international collaborations focused on strengthening healthcare infrastructure and boosting pandemic preparedness. - Middle East and Africa: Building a Foundation for Growth
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) represent a smaller but growing segment of the mRNA market, currently accounting for about 5% of global share, with a projected CAGR of 8.7% through 2030. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are leading the Middle East’s mRNA adoption, with significant investments in research and local production facilities. In 2023, the UAE partnered with G42 Healthcare to establish an mRNA vaccine manufacturing facility, signaling increased regional interest in mRNA technology. In Africa, countries such as South Africa and Egypt are focusing on building domestic manufacturing capacity, supported by global initiatives like COVAX. Despite infrastructure challenges, the region's growing international partnerships and investments highlight a promising future for mRNA technology expansion in the MEA market.
Key Market Players:
- Pfizer, Inc.
- CureVac N.V.
- Sanofi S.A.
- BioNTech SE
- Moderna, Inc.
- Arcturus Therapeutics Holdings Inc.
- GSK (GlaxoSmithKline)
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Translate Bio, Inc. (acquired by Sanofi)
Competitive Landscape
The mRNA market is characterized by intense competition, driven by rapid advancements in technology and the increasing demand for innovative vaccines and therapies. Moderna, BioNTech, and Pfizer currently hold dominant positions in the market, largely due to their success in developing COVID-19 vaccines. These companies have secured significant market shares and are expanding their pipelines into new areas such as cancer treatments, rare diseases, and other infectious diseases. CureVac, an early entrant in the field, is focusing on next-generation mRNA vaccines to address challenges encountered during the pandemic.
Major pharmaceutical companies like Sanofi, following its acquisition of Translate Bio, and GSK are making aggressive moves into the mRNA space, concentrating on the development of vaccines for seasonal flu and other infectious diseases. These firms are leveraging the flexibility and rapid development capabilities of mRNA to compete with the established leaders. Additionally, AstraZeneca and Vertex Pharmaceuticals are making strategic advancements in therapeutic applications, particularly in oncology and rare diseases.
Competition in the market is fueled by the need for innovation, speed to market, and the development of scalable manufacturing processes. Partnerships, such as BioNTech’s collaboration with Roche to develop cancer vaccines, are common, enabling companies to combine their resources and expertise. As more companies enter the space, the competitive landscape will continue to intensify, driving further innovation in mRNA applications across multiple therapeutic areas.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In 2023, Moderna invested over $1 billion to expand its research and development into cancer and rare disease therapeutics, a move aimed at strengthening its market leadership and diversifying beyond COVID-19 vaccines.
- In 2023, BioNTech partnered with Roche to develop personalized mRNA-based cancer vaccines. This collaboration is designed to capitalize on BioNTech’s mRNA expertise, enhancing its presence in the oncology market.
- In 2023, Pfizer allocated $1.2 billion to expand its mRNA vaccine production capacity, positioning itself to meet future demand for seasonal and pandemic-related vaccines, while reinforcing its manufacturing capabilities.
- In 2021, Sanofi acquired Translate Bio for $3.2 billion, bolstering its position in the mRNA space and enabling it to advance the development of flu and other infectious disease vaccines.
- In 2023, CureVac focused on second-generation mRNA vaccines with improved efficacy and easier storage requirements, aiming to enhance its competitive position against industry leaders like Moderna and BioNTech.
- In 2021, GSK partnered with CureVac, investing €150 million to co-develop mRNA vaccines targeting infectious diseases. This collaboration is expected to accelerate GSK’s vaccine development and broaden its mRNA portfolio.
- In 2023, AstraZeneca advanced its research into mRNA-based therapies for lung and colorectal cancers, a move that is anticipated to strengthen its position in the oncology sector.
- In 2023, Vertex Pharmaceuticals entered into a collaboration with Moderna to develop mRNA therapies for cystic fibrosis, expanding Vertex’s presence in the rare disease treatment market.
- In 2023, Arcturus Therapeutics forged global partnerships with several governments to develop mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases, aiming to secure funding and enhance its international footprint.
- In 2023, BioNTech acquired InstaDeep, an artificial intelligence company, to enhance its drug discovery capabilities. This acquisition is expected to bolster BioNTech’s development of personalized mRNA cancer vaccines.
DETAILED SEGMENTATION OF THE GLOBAL mRNA MARKET INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT
This research report on the global mRNA market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on the following categories.
By Type of Drugs
- Prophylactic Vaccines
- Therapeutic Vaccines
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the mRNA market
The mRNA market has seen significant growth due to the success of COVID-19 vaccines. It is projected to expand further with the development of new vaccines and therapeutic applications. Estimates suggest that the market could reach several billion dollars in the next few years.
What future applications are being explored for mRNA technology
Beyond vaccines, future applications include personalized cancer treatments, autoimmune disease therapies, rare genetic disorder treatments, and regenerative medicine.
What are the advantages of mRNA Market
mRNA technology allows for rapid development and production of vaccines and therapies. It is also highly versatile, as it can be tailored to target specific proteins or cells. Additionally, it doesn’t require live pathogens, making it safer to produce.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
