Global Lead Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Isotope (Lead-204, Lead-207, Lead-208, Lead-206, Others), Application, and Region (Latin America, North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis from 2025 to 2033
Global Lead Market Size
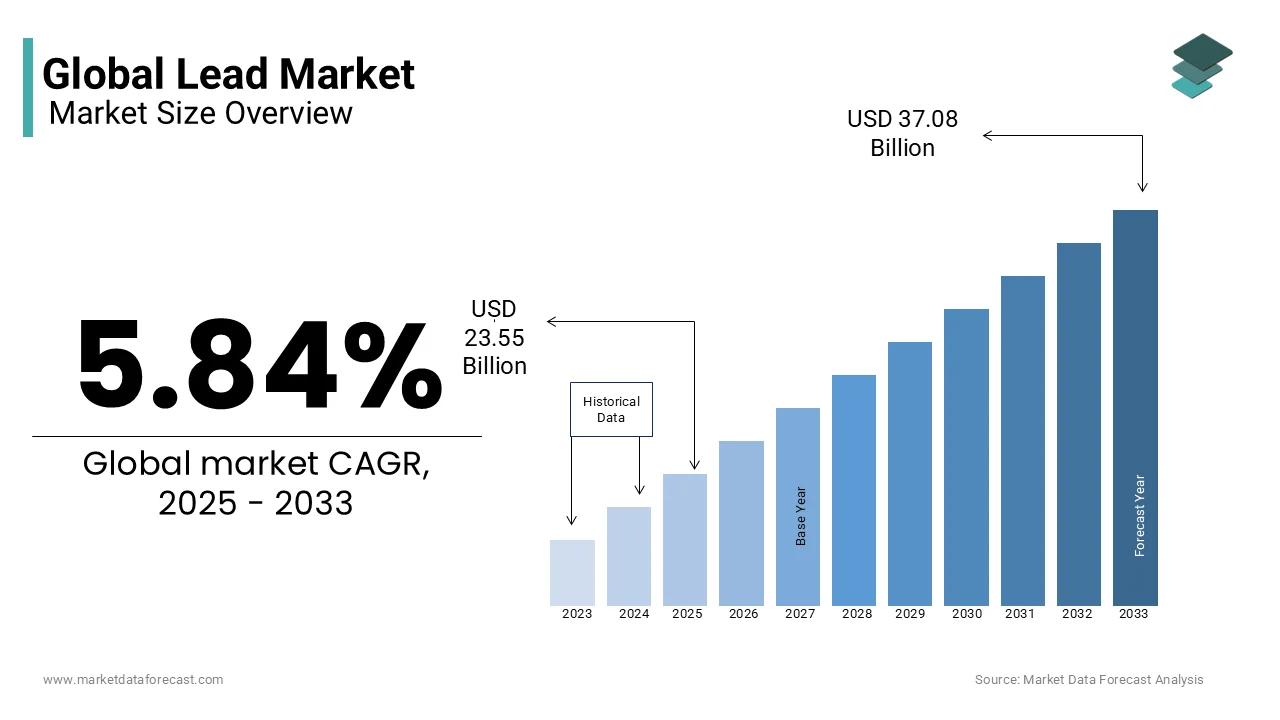
The global Lead market size was valued at USD 22.25 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 37.08 billion by 2033 from USD 23.55 billion in 2025. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.84%.
Lead is denoted by the symbol Pb and is a dense and malleable metal known for its corrosion resistance and high density. Historically, it has been utilized in various applications, including paints, pipes, and gasoline additives. However, due to its toxicity, stringent regulations have curtailed its use in many areas, confining its contemporary applications primarily to sectors where suitable alternatives are limited.
The global lead market has experienced prominent growth over the last few years owing to the increasing demand for lead-acid batteries that account for approximately 86% of total lead consumption as of 2022, according to United Nations Environment Programme. These batteries are essential in automotive applications, uninterruptible power supplies, and energy storage systems. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy storage solutions has further amplified the need for lead-acid batteries.
In terms of production, China stands as the leading producer of lead, with an output of 1.9 million metric tons in 2023, as reported by the U.S. Geological Survey. Australia follows, holding substantial lead reserves estimated at 35 million metric tons. The Asia-Pacific region covers major consumers like China, Japan, and India and is dominating global lead consumption. This is linked to the region's burgeoning automotive and construction industries which are significant consumers of lead-based products.
MARKET DRIVERS
Advancements in Lead Recycling Technologies
The lead market has witnessed major progress in recycling technologies which is improving the efficiency and environmental sustainability of lead recovery processes. Modern methods such as hydrometallurgical processes have been developed to extract lead from used products with reduced energy consumption and lower emissions compared to traditional pyrometallurgical techniques. These advancements not only eliminate environmental concerns but also ensure a steady supply by reintroducing recycled material into the market. According to the International Lead and Zinc Study Group, approximately 65.5% of refined lead production in 2022 was sourced from recycled materials and as a result emphasizing the pivotal role of recycling in meeting global lead demand.
Infrastructure Development and Urbanization
Rapid urbanization and infrastructure development, particularly in emerging economies, have escalated the demand for lead-based products. Lead is extensively utilized in construction materials, including roofing, cladding, and radiation shielding. The United Nations reports that by 2050, approximately 68% of the global population is projected to reside in urban areas, up from 55% in 2018. This urban expansion necessitates substantial infrastructure projects and consequently increasing the consumption of lead in various construction applications. Additionally, the development of new power generation facilities and communication networks often incorporates lead-acid batteries for energy storage and backup power, further bolstering lead demand.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Environmental and Health Concerns
Lead exposure remains a major public health challenge due to its severe neurotoxic effects, especially in children and pregnant women. The UK Health Security Agency has linked low-level environmental lead exposure to intellectual and developmental impairments in children, with adverse effects observed at blood lead concentrations as low as 0.24 μmol/L (5 μg/dL). Chronic exposure can also result in cardiovascular diseases and kidney dysfunction in adults. To mitigate these risks, regulatory bodies have imposed strict guidelines such as the UK's revised public health intervention concentration for lead which was lowered to 0.24 μmol/L in July 2021. Increased regulatory oversight has led to operational constraints and heightened compliance costs for industries engaged in lead production, refining, and usage. As a result, companies face mounting pressure to adopt alternative materials or invest in safer processing technologies to maintain market viability. These environmental and health concerns have significantly influenced policy decisions, affecting global lead market dynamics and prompting industries to reconsider their reliance on lead-based products. The continued tightening of exposure limits by agencies such as the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reinforced the need for more stringent industrial practices and consumer safety initiatives.
Regulatory Restrictions and Market Dynamics
Governments worldwide have introduced stringent regulatory measures to limit lead usage due to its toxicological impact. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has mandated the removal of approximately 9.2 million lead service lines over the next decade and that is aiming to minimize lead contamination in drinking water supplies. Similarly, the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has proposed severe restrictions on lead usage in outdoor ammunition and fishing tackle which could eliminate thousands of tons of lead from the environment annually. These regulations significantly impact industries relying on lead-based products, consequently increasing compliance costs and limiting the feasibility of lead-based applications. Companies operating in lead mining, refining, and manufacturing must now navigate a complex regulatory landscape, requiring investments in lead substitutes such as tin, bismuth, and polymer-based alternatives. Additionally, the tightening of international trade regulations, including the Basel Convention's restrictions on the transboundary movement of hazardous lead waste, has further complicated the market. The growing push for cleaner, lead-free technologies especially in the battery sector poses a long-term challenge for lead-dependent industries, accelerating the search for alternative energy storage solutions. These regulatory shifts are expected to reshape global lead consumption patterns, favoring sustainable and less hazardous materials in various industrial applications.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Renewable Energy Storage Systems
The increasing deployment of renewable energy sources has created a growing need for efficient energy storage solutions to balance fluctuations in power generation. Lead-acid batteries are known for their cost-effectiveness and durability continue to play a crucial role in energy storage applications and particularly in off-grid and backup power systems. According to the study, lead-acid batteries accounted for approximately 88% of apparent U.S. lead consumption. As global investments in renewable energy infrastructure expand, particularly in solar and wind power, the demand for lead-acid batteries is expected to increase. The International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts that by 2030, energy storage capacity must increase nearly six-fold to meet renewable energy goals. This presents a substantial opportunity for the market as lead-acid batteries remain a viable solution for grid stability, microgrid storage, and rural electrification projects. Additionally, emerging hybrid energy storage systems that integrate lead-acid batteries with lithium-ion technology further reinforce their relevance in the clean energy transition. With government incentives and infrastructure investments in renewable energy increasing worldwide, the role of lead in sustainable energy solutions remains significant.
Advancements in Lead Recycling Technologies
The lead market has seen notable advancements in recycling technologies, improving both efficiency and sustainability. It is one of the most highly recycled metals with a recycling rate exceeding 95% in many developed economies. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, secondary lead production accounted between 55% and 65% of total lead consumption. Innovations in hydrometallurgical and electrochemical recycling methods have enhanced the recovery of lead from used batteries, industrial waste, and lead-based products and is reducing reliance on primary lead mining. These developments align with global environmental policies aimed at minimizing hazardous waste and promoting circular economies. For example, the European Union has set stringent regulations requiring 100% of spent lead-acid batteries to be collected and recycled under its Battery Directive. The increasing adoption of sustainable recycling technologies helps industries meet environmental compliance while ensuring a continuous and cost-effective supply of refined lead. As global industries push for higher sustainability standards, investment in advanced lead recycling presents a promising opportunity for long-term market growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fluctuating Global Lead Prices
The lead market experiences serious challenges due to the volatility of global lead prices, affecting production, trade, and investment. According to the U.S. Geological Survey's Mineral Commodity Summaries 2024, the average North American lead price was 115 cents per pound during the first ten months of 2023 that reflected a slight decrease from 116.5 cents per pound in 2022. Price fluctuations are caused by factors such as changes in global demand, disruptions in mining output, and shifting regulatory policies. Such volatility impacts profitability for lead producers and recyclers making long-term financial planning difficult. Additionally, unpredictable price swings can reduce investor confidence, limiting capital inflows into lead mining and refining projects. The instability in lead prices also affects end-user industries such as battery manufacturers, construction, and radiation shielding sectors because fluctuating raw material costs influence product pricing and market competitiveness. So, there is need for risk management strategies, including futures contracts and hedging mechanisms, to protect market stakeholders from sharp price movements. Ensuring price stability through diversified supply chains and policy frameworks could mitigate the economic risks associated with lead price fluctuations.
Declining Domestic Production Capacity
The reduction in primary lead refining capacity has created supply chain vulnerabilities, increasing reliance on imports and secondary production. The U.S. Geological Survey states that nearly all lead concentrate production has been exported since the closure of the last primary lead refinery in the United States in 2013. In 2023, domestic mine production of recoverable lead declined slightly while secondary lead production remained unchanged from 2022 levels. This decline in domestic capacity has heightened concerns regarding supply security, particularly in industries that depend on lead-acid batteries and industrial lead products. Dependence on foreign sources exposes the lead market to geopolitical risks, trade restrictions, and supply chain disruptions, potentially driving up costs for domestic manufacturers. Addressing this challenge requires government support for lead recycling infrastructure and policy incentives to enhance sustainable lead production. Without proactive investment, the United States risks becoming increasingly reliant on external sources for a critical industrial metal which may affect national energy storage strategies and the broader industrial supply chain. Strengthening domestic capabilities in lead processing can ensure stability in supply while reducing exposure to global market uncertainties.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
5.84% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Isotope, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Glencore (Switzerland/UK), Doe Run (USA), Hindustan Zinc (India), Teck Resources Limited (Canada), BHP Billiton (Australia/UK), Canada Metal North America Ltd (Canada), East Penn Manufacturing Company (USA), Johnson Controls (USA), M. A. Metal Corporation (Turkey), Nyrstar (Belgium), and others |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Isotope Insights
The lead-208 segment dominated the market by constituting 52.4% of global market share in 2024. The lead-208 is the most abundant naturally occurring lead isotope. It is the final stable product of the thorium-232 decay series that is making it more prevalent in nature. Also, due to its high atomic mass and strong radiation absorption properties, this isotope is widely used in radiation shielding for nuclear reactors, medical imaging, and particle accelerators. Additionally, it plays a critical role in lead-acid batteries which remain the primary source of energy storage for automotive and industrial applications. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, lead-acid batteries account for 86% of lead consumption in the U.S., reinforcing the dominance of lead-208 in the global lead market.
The lead-206 segment is estimated to showcase a promising CAGR of 8.7% during the forecast period due to its significant role in uranium-lead dating. This method is widely used in geochronology to determine the age of the Earth’s oldest rocks and mineral deposits. The accuracy of uranium-lead dating has made lead-206 essential in archaeological studies, planetary sciences, and resource exploration. The increasing global focus on mineral exploration and historical climate research has driven demand for lead-206. Expanding applications in radiogenic dating and scientific research further support the segment’s rapid growth.
By Application Insights
The batteries segment was the dominant application in the lead market and held the major share of the global market share in 2024. This supremacy is credited to the widespread use of lead-acid batteries which are essential in automobiles, industrial power backup systems, and renewable energy storage. The United Nations Environment Programme states that over 85% of lead-acid batteries are recycled that makes them one of the most sustainable battery types. Additionally, a standard automotive lead-acid battery contains up to 10 kilograms of lead which is strengthening the extensive demand. With the increasing adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles, lead-acid batteries continue to play a crucial role in power storage solutions across multiple industries.
The electronics segment is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 8.1% over the forecast period owing to the rising demand for consumer and industrial electronic devices. Lead is widely used in soldering materials, cable sheathing, and radiation shielding for sensitive electronic components. The rapid expansion of the global electronics market is driving this growth. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, lead-based solder remains essential in manufacturing circuit boards, telecommunications equipment, and microelectronics. The shift toward miniaturized, high-performance electronics continues to boost lead consumption in this sector.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The Asia-Pacific region led the lead market by holding for a significant share of the global market in 2024. This position is primarily caused by China's substantial demand which alone represents about 44% of worldwide lead usage. The region's extensive consumption is largely attributed to its robust automotive and electronics industries, which heavily rely on lead-acid batteries and lead-based components. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, China's lead mine production was approximately 1.9 million metric tons in 2023, underscoring its significant role in both production and consumption within the lead market.
The Middle East and Africa region is estimated to progress at a CAGR of 5.2% over the forecast period owing to the increasing infrastructure development and urbanization, leading to heightened demand for lead-acid batteries in sectors such as telecommunications and renewable energy storage. The International Energy Agency reports that Africa's energy storage capacity is expected to grow significantly, with lead-acid batteries playing a crucial role in off-grid and backup power solutions. Additionally, the region's mining activities are expanding, contributing to both local consumption and export of lead resources.
North America remains a key player in the lead market, primarily driven by secondary lead production. According to the U.S. Geological Survey, the United States produced approximately 270,000 metric tons of lead in 2023, with secondary lead accounting for the majority of supply. The region’s stringent environmental policies have led to the closure of primary lead smelting facilities, increasing reliance on recycled lead from used batteries and industrial waste. The demand for lead-acid batteries in the automotive and backup power sectors remains strong, ensuring continued consumption. However, regulatory pressures from agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) on lead-based products may impact long-term market growth.
Europe is witnessing a gradual decline in consumption due to stringent environmental policies and the push for alternative energy storage solutions. The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) has proposed restrictions on lead use in ammunition and other applications, further reducing demand. Despite this, the region remains a leader in lead recycling, with over 85% of lead-acid batteries being collected and processed under the European Union’s Battery Directive. The push towards circular economy practices ensures a stable supply of secondary lead, supporting existing industries such as automotive and power backup solutions. However, with increasing regulations on lead-based products, the market is expected to shrink in certain applications.
Latin America holds a steady position in the global lead market and is primarily due to high mining activity in countries like Mexico and Peru. The U.S. Geological Survey reported that Peru produced 250,000 metric tons of lead in 2023, making it one of the top global producers. Mexico also plays a significant role in lead exports to North America and other regions. The demand for lead-acid batteries in the region continues to grow, driven by the automotive, industrial, and telecommunications sectors. However, fluctuations in mining regulations and environmental policies may impact long-term production. As Latin America invests in mineral resource development, its role in global lead supply is expected to remain stable.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Glencore (Switzerland/UK), Doe Run (USA), Hindustan Zinc (India), Teck Resources Limited (Canada), BHP Billiton (Australia/UK), Canada Metal North America Ltd (Canada), East Penn Manufacturing Company (USA), Johnson Controls (USA), M. A. Metal Corporation (Turkey), Nyrstar (Belgium) are playing dominating role in the global lead market.
The global lead market is characterized by intense competition among key players, primarily driven by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integration. Major companies like Glencore, Hindustan Zinc Limited (HZL), and Korea Zinc Co., Ltd. dominate the market, leveraging their vast mining and refining capabilities to maintain a stronghold. The competition is influenced by the demand for lead in industries such as battery manufacturing, construction, and radiation shielding.
One of the primary competitive factors is cost efficiency in production. Companies with access to rich lead reserves and advanced refining technologies gain an edge by lowering production costs while meeting stringent environmental regulations. Technological innovation plays a crucial role, as firms that adopt sustainable smelting techniques and invest in recycling initiatives improve profitability and market positioning.
Geopolitical factors, including trade restrictions and environmental policies, also impact competition. Stringent government regulations in countries like the U.S. and China influence mining operations and trade dynamics. Additionally, supply chain disruptions due to global economic fluctuations and geopolitical tensions affect pricing and availability.
STRATEGIES USED BY THE MARKET PLAYERS
Technological Innovation and Process Optimization
Companies like Glencore and Korea Zinc Co., Ltd. focus on technological advancements to enhance operational efficiency and reduce environmental impact. By investing in state-of-the-art smelting technologies and process improvements, these firms aim to increase production capacity, lower costs, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. For instance, adopting advanced smelting methods allows for better energy efficiency and reduced emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Vertical Integration and Diversification
Hindustan Zinc Limited (HZL) employs a strategy of vertical integration, managing operations from mining to smelting and refining. This approach ensures control over the supply chain, enhances product quality, and improves cost efficiency. Additionally, diversifying into related sectors, such as the production of critical minerals and exploration of acquisition opportunities in Southeast Asia, enables companies to mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Strategic Partnerships and Market Expansion
Forming strategic partnerships and expanding into new markets are crucial strategies for maintaining a competitive edge. For example, Korea Zinc has engaged in preliminary discussions with U.S. entities to supply antimony, aiming to establish long-term contracts and strengthen its presence in the U.S. market. Such collaborations not only open new revenue streams but also enhance the company's global footprint and resilience against regional market volatility.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Glencore plc
Glencore plc, headquartered in Baar, Switzerland, is one of the world's largest diversified natural resource companies. Founded in 1974, Glencore has evolved from a trading company into a major producer and marketer of commodities, including significant operations in lead production. The company engages in the production, refinement, processing, storage, transport, and marketing of metals and minerals, energy products, and agricultural products. Glencore's extensive global operations and integrated supply chain contribute substantially to the global lead supply.
Hindustan Zinc Limited (HZL)
Hindustan Zinc Limited, a subsidiary of Vedanta Limited, is India's largest and the world's second-largest integrated producer of zinc-lead. Headquartered in Udaipur, Rajasthan, HZL operates fully integrated zinc-lead businesses, including five lead-zinc mines and multiple smelting facilities. The company's operations comprise lead-zinc mines, hydrometallurgical zinc smelters, lead smelters, pyro-metallurgical lead-zinc smelter, as well as sulphuric acid and captive power plants in northwest India. With a total reserve and resource base of 456.3 million tonnes and an average zinc-lead grade of 6.8%, HZL has a mine life exceeding 25 years. The company holds around a 75% market share in India's primary zinc industry and is also the third-largest silver producer globally.
Korea Zinc Co., Ltd.
Established in 1974 and headquartered in Seoul, South Korea, Korea Zinc Co., Ltd. is a leading non-ferrous metal smelting company. The company specializes in the production and sale of non-ferrous metals, including zinc, lead, gold, silver, copper, and sulfuric acid. Korea Zinc's operations are integral to various industries, such as construction, automotive, electronics, and technology. The company's commitment to technological advancement and sustainable development positions it as a pivotal player in the global non-ferrous metal sector.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
-
In February 2025, environmental advocacy groups, including the Global Legal Action Network and the London Mining Network, initiated a legal test case against the London Metal Exchange (LME). This lawsuit alleges that the LME could be complicit in money laundering by permitting the trading of metals sourced from the Grasberg mine in Indonesia’s Papua region. The case seeks to compel the LME to disclose any knowledge of environmental crimes associated with the mine and suspend trading of Grasberg-derived products until environmental practices improve.
-
In February 2025, the U.S. government imposed additional tariffs on imports from major trading partners, including China, Canada, and Mexico. A 10% tariff was applied to imports from China, while a 25% tariff was levied on goods from Canada and Mexico, with a temporary 30-day suspension for the latter two countries. In response, China imposed export restrictions on five critical metals—tungsten, tellurium, bismuth, indium, and molybdenum—requiring licenses for their export. These regulatory changes are expected to significantly impact global supply chains in the mining and refining sectors.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global lead market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on isotope, application, and region.
By Isotope
- Lead-204
- Lead-207
- Lead-208
- Lead-206
- Others
By Application
- Ammunition
- Batteries
- Construction
- Electronics
- Marine
- Plumbing
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the current size of the global lead market?
As of 2024, the global lead market was valued at approximately USD 22.25 billion.
2. What factors are driving the growth of the lead market?
Key drivers include advancements in lead recycling technologies, increasing demand for lead-acid batteries in automotive and energy storage applications, and rapid urbanization leading to infrastructure development.
3. Which regions are the largest producers and consumers of lead?
China is the leading producer of lead, with an output of 1.9 million metric tons in 2023. The Asia-Pacific region, including countries like China, Japan, and India, dominates global lead consumption due to their burgeoning automotive and construction industries.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]