Latin America Generic Drugs Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type, Application, & Country (Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Chile & Rest of Latin America), Industry Analysis 2025 to 2033
Latin America Generic Drugs Market Size
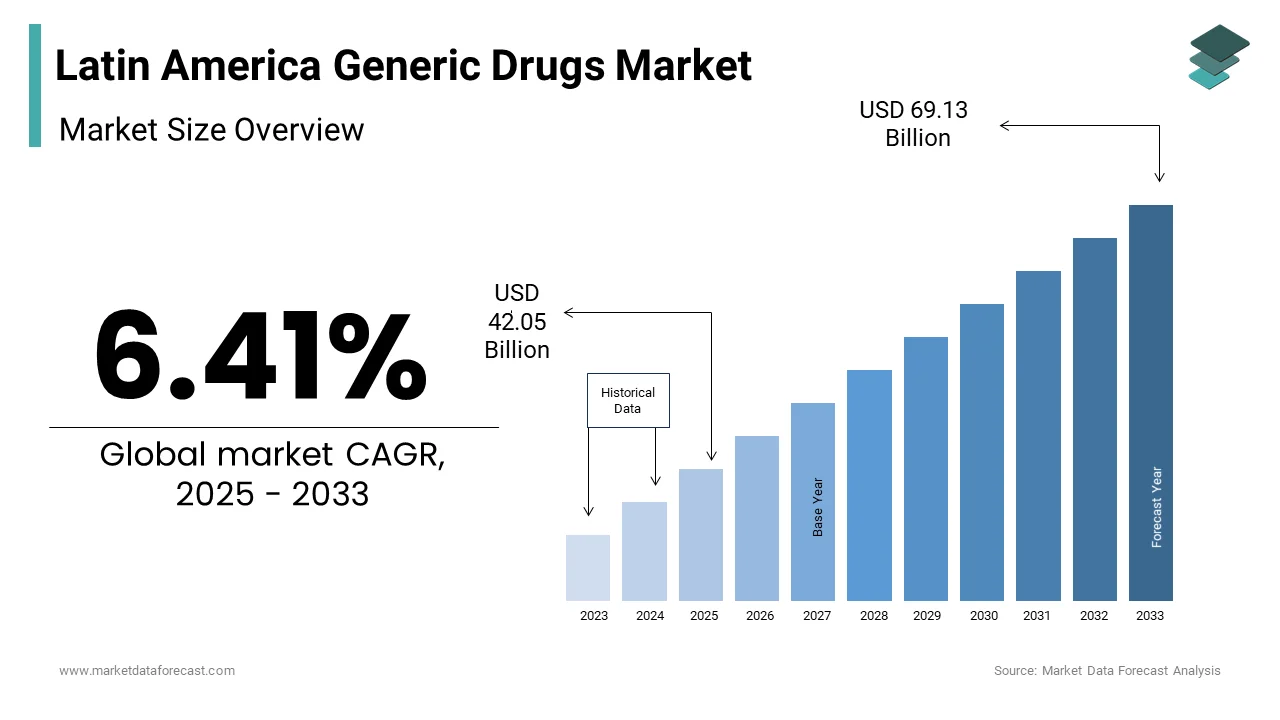
The generic drugs market size in Latin America was valued at USD 39.52 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth USD 69.13 billion by 2033 from USD 42.05 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.41% during the forecast period.
Generic drugs are bioequivalent to branded drugs in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy but are available at significantly lower costs due to the absence of research and development expenditures. These factors make them a preferred choice for healthcare systems and patients across Latin America, particularly in regions with limited healthcare budgets. The governments of Latin American countries are taking initiatives to promote the adoption of generic drugs in these countries, which is favoring regional market expansion. For instance, the National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) of Brazil regulates and encourages generic drug production to make affordable medications accessible to its population. According to the Pan American Health Organization, generic drugs account for nearly 70% of all medicines sold in Brazil. Mexico is another significant contributor to the Latin American market, and its universal health coverage programs focus on the use of generics to reduce healthcare costs. Argentina and Colombia are witnessing steady growth in generic drug penetration due to the increasing chronic disease management requirements, including diabetes and hypertension. Top of Form
MARKET DRIVERS
Cost-Effectiveness of Generic Drugs in Latin America
The affordability of generic drugs compared to branded medications is a major driver in Latin America, where healthcare budgets are often constrained. According to the data from the Pan American Health Organization, generic drugs can cost 30% to 80% less than their branded counterparts, which makes them accessible to a broader population. Generic drugs constitute nearly 70% of total pharmaceutical sales in Brazil, according to ANVISA. This confirms their affordability and widespread acceptance in this country. The cost-effectiveness of generic drugs is particularly critical in addressing chronic conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases that require long-term medication, thus reducing financial strain on both governments and individuals.
Government Policies Promoting Generics
Proactive government policies across Latin America are instrumental in driving generic drug adoption. The National Medicines Policy of Brazil focuses on the use of generics to enhance access to essential medications. According to ANVISA, the implementation of regulatory frameworks for generic drugs has significantly increased their availability and more than 8,000 registered generic products by 2022. Similarly, the Federal Commission for the Protection against Sanitary Risk (COFEPRIS) of Mexico supports the production and distribution of generics through streamlined approval processes. These policies ensure that high-quality, affordable medications are widely accessible and contribute to improved healthcare outcomes and the growth of the Latin American generic drugs market. Top of Form
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Regulatory and Approval Barriers
Complex regulatory frameworks and lengthy approval processes are major obstacles for generic drug manufacturers in Latin America. According to the Pan American Health Organization, inconsistent regulations across countries, such as Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina, result in delays in the approval and distribution of generic drugs. For instance, ANVISA in Brazil requires extensive clinical documentation for bioequivalence studies that can take several years to complete. These bureaucratic hurdles increase time-to-market for generics and discourage small and medium-sized enterprises from entering the market and limit the availability of affordable medications in the region.
Counterfeit Medicines and Quality Concerns
The prevalence of counterfeit drugs in Latin America undermines consumer trust in generic medications. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, approximately 10% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries, including Latin America, are counterfeit. This issue is exacerbated by weak enforcement of intellectual property rights and inadequate market surveillance. The lack of trust in the quality and efficacy of generic drugs can deter healthcare providers and patients from adopting them. Addressing this challenge requires stricter regulatory oversight and public awareness campaigns to ensure that generics are seen as safe, effective, and high-quality alternatives to branded drugs.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The rising burden of chronic diseases in Latin America provides an opportunity for generic drug manufacturers to address long-term treatment needs. According to the Pan American Health Organization, non-communicable diseases account for nearly 80% of deaths in Latin America and cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer being the leading causes. Generic medications offer cost-effective solutions for managing these conditions, particularly for underserved populations.
Expansion of Local Manufacturing Capabilities
The increasing focus on strengthening local pharmaceutical manufacturing in Latin America represents a key growth opportunity. Governments in countries such as Brazil and Argentina are investing in domestic production to reduce dependency on imports and ensure consistent supply. The Ministry of Health of Brazil has launched initiatives to support public-private partnerships and technology transfer agreements, boosting local manufacturing capacity. By 2022, nearly 80% of generic drugs in Brazil were produced domestically, according to ANVISA. Such developments not only enhance market resilience but also create opportunities for local players to compete effectively to ensure the availability of affordable and high-quality medications across the region.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Intellectual Property and Patent Disputes
The complexities surrounding intellectual property rights and patent laws pose challenges for generic drug manufacturers in Latin America. The Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) agreement of the World Trade Organization requires adherence to patent protection that often delays the entry of generics into the market. According to the Pan American Health Organization, extended patent periods and exclusivity rights granted to branded drugs in countries like Mexico and Brazil limit generic competition. These legal barriers prevent timely access to affordable medications and force governments and patients to rely on costlier alternatives, thus impacting public health and healthcare budgets.
Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure
Limited healthcare infrastructure in rural and low-income areas restricts the distribution and accessibility of generic drugs. As per the World Bank data, more than 30% of the Latin American population resides in rural regions, where access to healthcare facilities and pharmacies remains a challenge. For instance, logistical hurdles and supply chain inefficiencies prevent the consistent availability of essential generic medicines in countries such as Peru and Bolivia. This disparity not only affects healthcare equity but also reduces the potential reach of generic drug manufacturers in addressing the needs of underserved populations across the region.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Analysed |
By Type, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Analysed |
Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Peru and Rest of Latin America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Ranbaxy Laboratories, Ltd, Actavis., Viatris, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Par Pharmaceutical, Inc., Sandoz International GmbH, Hospira, Inc., Apotex, Inc., Pfizer Inc. and Teva Pharmaceuticals. |
SEGMENTAL INSIGHTS
By Type Insights
The branded generics segment dominated the generic drugs market in Latin America in 2024. The domination of the branded generics segment is primarily due to their affordability compared to branded drugs. Most people can quickly learn about branded generics due to the brand name rather than the chemical name, which fuels the segment growth rate. The branded generics also undergo various regulatory processes and approvals from the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA). Branded generics can be marketed by both innovators and generic companies, which is propelling segmental expansion.
The pure generic drugs segment is anticipated to have notable growth during the forecast period. Pure generic drugs are the ones known by the chemical name where the API is similar and may differ in shape, size, color, and inactive ingredients.
By Application Insights
The CNS segment held the most significant share of the regional market in 2024. The domination of the CNS segment is expected to continue during the forecast period. The growing prevalence of spinal and brain disorders worldwide enhances the demand for CNS therapeutics, escalating the segment revenue expansion. The number of treatments, surgeries, and rehabilitation is enlarging the introduction of generic drugs, leading to segment growth.
The oncology segment is projected to grow considerably during the forecast period with a notable growth rate. Various generic drugs are being adopted in oncology owing to their affordability and similar efficacy as branded drugs. These drugs do not require additional research and trials, which are the primary factors contributing to the segment growth opportunities. Generic cancer drugs provide prominent cost savings compared to branded drugs, boosting the segment's expansion.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil dominated the generic drugs market in Latin America in 2024 due to Brazil's extensive population and robust healthcare initiatives. As per the reports of the Brazilian Health Regulatory Agency (ANVISA), generic drugs accounted for nearly 70% of total pharmaceutical sales in 2024. The National Medicines Policy of Brazil prioritizes generics to enhance access to affordable medications that benefit its 214 million residents. Additionally, local manufacturing is strong in Brazil, and more than 80% of generics are produced domestically. The focus of Brazil on addressing chronic diseases such as hypertension and diabetes further contributes to the Brazilian market growth.
Mexico ranks as a leading player in the Latin American generic drugs market due to government-driven initiatives and its large consumer base. The Federal Commission for the Protection Against Sanitary Risk (COFEPRIS) facilitates the streamlined approval and production of generics, which makes them a cornerstone of public healthcare programs. According to reports from the National Institute of Public Health, generic drugs represent more than 50% of Mexico's pharmaceutical market. With over 12% of the adult population affected by diabetes, generics play a crucial role in chronic disease management.
Argentina has established itself as a prominent market for generic drugs. Favorable policies and a high prevalence of chronic diseases in Argentina are driving the growth of the generic drugs market in this country. According to the Ministry of Health, generic medications make up 45% of the national pharmaceutical market, owing to government subsidies and public awareness campaigns promoting their use. Chronic conditions such as hypertension affect nearly 35% of adults and fuel the demand for affordable generics. The pharmaceutical sector of Argentina also benefits from local production capabilities, which reduce dependency on imports and ensure consistent supply.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies playing a notable role in the Latin American generic drugs market include Ranbaxy Laboratories, Ltd., Actavis, Mylan, Inc., Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Par Pharmaceutical, Inc., Sandoz International GmbH, Hospira, Inc., Apotex, Inc., Watson Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. and Teva Pharmaceuticals.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2024, Brazil Fiocruz, a national public health foundation, announced its legal agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim. The agreement holds the deal with Fiocruz for manufacturing generic empagliflozin used to treat diabetes in Brazil's public health system.
- In 2024, Mexico's Federal Commission for Protection against Health Risks (COFEPRIS) announced the approval of its authorization for 12 new clinical trials in recent weeks, including a Phase 1 study of pediatric pneumonia treatment.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Latin American generic drugs market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Pure Generic Drugs
- Branded Generic Drugs
By Application
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)
- Cardiovascular
- Dermatology
- Oncology
- Respiratory
- Others
By Country
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Chile
- Rest of Latin America
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
