Latin America 3D Bioprinting Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Material Type, Technologies, Components, Applications and Country (Brazil, Argentina, Chile and Rest of Latin America), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Latin America 3D Bioprinting Market Size
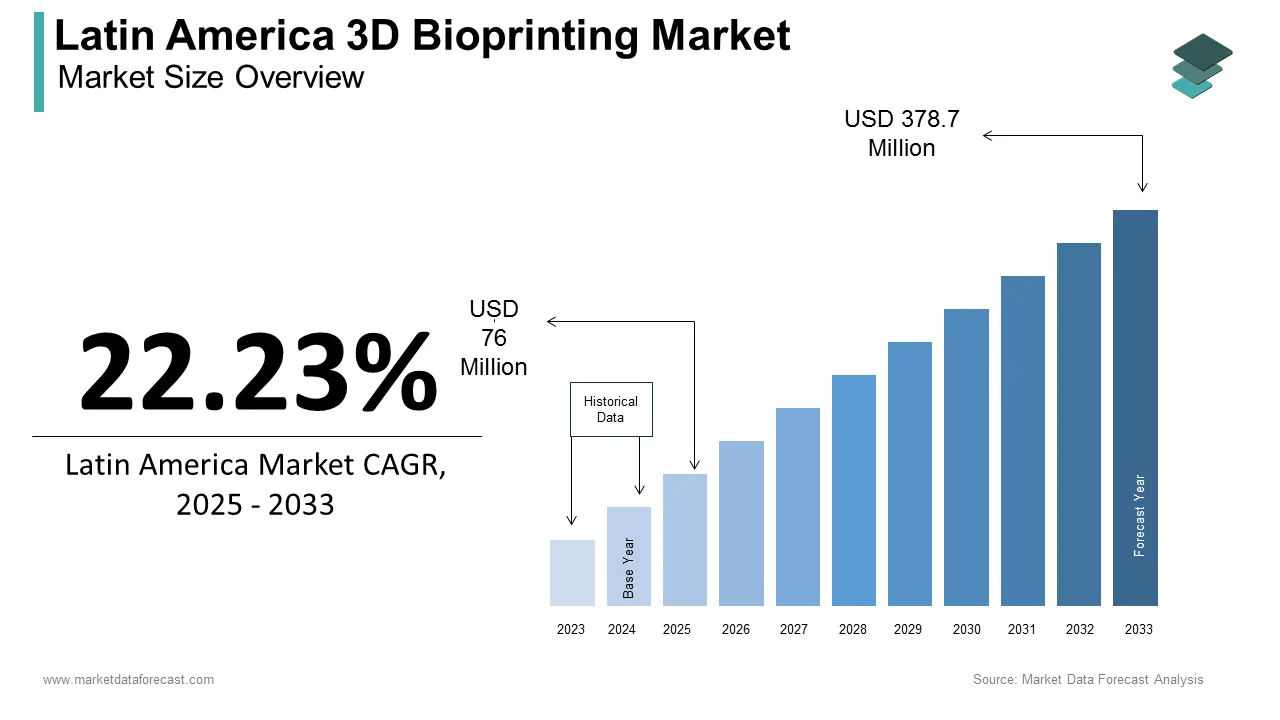
The 3D bioprinting market size in Latin America was valued at USD 62.2 million in 2024. The Latin American market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 22.23% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 378.7 million by 2033 from USD 76 million in 2025.
3D bioprinting involves using bioink materials composed of living cells to fabricate three-dimensional structures that mimic natural tissues and organs. 3D bioprinting technology is transforming medical research and patient care by enabling the development of customized treatments and enhancing the accuracy of drug discovery processes. In recent years, countries like Brazil and Mexico have emerged as key players in the region due to increased investment in healthcare infrastructure and biotechnology research. According to the Pan American Health Organization, healthcare spending in Latin America has risen significantly and enabling the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like 3D bioprinting. Additionally, Latin America is leveraging partnerships between academic institutions, governments, and private companies to drive innovation in this field.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Investment in Healthcare and Biotechnology
Governments and private enterprises in countries like Brazil and Mexico are allocating substantial resources to promote medical research and innovation. According to the Pan American Health Organization, healthcare expenditure in Latin America accounts for 8.1% of GDP on average, and a significant portion is directed toward advanced medical technologies. The Ministry of Health of Brazil has supported initiatives aimed at integrating bioprinting into research for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. These investments enable the development of 3D bioprinting infrastructure and foster collaborations between academic institutions and biopharmaceutical companies, thus driving the growth of the Latin American 3D bioprinting market.
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases in Latin America
The growing prevalence of chronic diseases in Latin America is a key factor driving the demand for 3D bioprinting in this region. According to the World Health Organization, 78% of all deaths in Latin America are attributed to non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular conditions. These diseases often require innovative treatment approaches, including tissue engineering and regenerative therapies. 3D bioprinting offers the potential to create patient-specific models for testing and therapies that can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Additionally, the rising demand for organ transplantation due to the high rates of organ failure is further accelerating the need for 3D bioprinting solutions and positioning the 3D bioprinting technology as a transformative tool in healthcare.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of 3D Bioprinting Technology
The Latin American 3D bioprinting market faces challenges due to the high costs associated with bioprinting technology. Advanced 3D bioprinters, bioinks, and associated software require significant capital investment, and these expenses limit the adoption of these technologies among smaller research institutions and hospitals. According to the Inter-American Development Bank, more than 30% of healthcare facilities in Latin America operate on constrained budgets, and these high costs make it difficult for them to allocate funds for cutting-edge technologies. Furthermore, the cost of importing bioprinting equipment and maintaining skilled personnel adds to financial barriers. These high expenses restrict the widespread implementation of 3D bioprinting across the region, particularly in economically underdeveloped areas.
Limited Skilled Workforce and Technical Expertise
A shortage of skilled professionals trained in 3D bioprinting technology is another major restraint in the Latin American market. The implementation of bioprinting requires expertise in areas such as biomedical engineering, software development, and tissue engineering, which remain underdeveloped in the region. As per the World Bank, less than 1% of the labor force in Latin America is employed in research and development, which confirms a limited pool of professionals capable of operating bioprinting systems. This skills gap hampers the efficient adoption and utilization of the technology and slows progress in 3D bioprinting research and its integration into clinical applications across Latin America.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Research and Development Initiatives
The increasing focus on research and development (R&D) in biotechnology and healthcare presents significant opportunities for the 3D bioprinting market in Latin America. According to the Ministry of Science of Brazil, Technology and Innovations reported a 10% annual growth in R&D investments in 2022 and more than $3 billion allocated to healthcare innovations. Mexico is also advancing in this domain with the National Council for Science and Technology funding programs to enhance tissue engineering and regenerative medicine capabilities. According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization, Latin America contributes approximately 2.5% of global R&D expenditures, with a growing focus on bioprinting technologies. These investments create an ecosystem that supports advancements in 3D bioprinting applications across academia and industry.
Rising Demand for Personalized Medicine
The demand for personalized medicine in Latin America is rapidly growing due to the high prevalence of chronic and non-communicable diseases. According to the World Health Organization, non-communicable diseases account for 78% of deaths in the region, which highlights the need for tailored treatment solutions. In Brazil alone, more than 16 million people live with diabetes and the demand for customized treatment options is also on the rise. According to the Inter-American Development Bank, the increasing middle-class population is driving investments in advanced healthcare solutions. The ability of 3D bioprinting to create patient-specific tissue models and organ replacements positions it as a transformative tool in delivering personalized healthcare across the region.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory and Ethical Challenges
Many countries in Latin America lack comprehensive frameworks for approving bio-printed tissues and organs for clinical use. According to the Pan American Health Organization, less than 40% of Latin American nations have fully established biotechnology regulations to create uncertainty for investors and researchers. Additionally, ethical concerns around the creation of bioprinted human tissues raise debates about compliance with international medical standards. These regulatory gaps and ethical complexities hinder the commercialization and clinical application of 3D bioprinting technology in the region and limit the market expansion in Latin America.
Insufficient Infrastructure and Funding for Innovation
Limited infrastructure and inadequate funding for advanced research are major challenges for the 3D bioprinting market in Latin America. While some nations like Brazil and Mexico have robust biotechnology sectors, smaller economies often struggle with underdeveloped research facilities and insufficient investment. According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization, Latin America allocates only 0.6% of its GDP to R&D on average, which is significantly below the global average of 1.7%. This lack of funding limits access to state-of-the-art equipment and resources necessary for 3D bioprinting advancements. Consequently, the ability of Latin America to compete on a global scale and develop cutting-edge solutions is constrained by these infrastructural deficits.
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Material Type
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil dominates the 3D bioprinting market in Latin America due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and significant investment in biotechnology. As per the reports of the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovations, Brazil allocated over $3 billion to healthcare R&D in 2022 to focus on regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. Brazil hosts prominent research institutions, such as the University of São Paulo, that collaborate with global firms on bioprinting technologies. Additionally, as per the World Health Organization, the prevalence of chronic diseases is high in Brazil, and diabetes is a chronic disease that affects 16 million people in Brazil. This patient population is driving the need for innovative treatment solutions and further strengthening Brazil's position in the Latin American market.
Argentina is a promising player in the Latin America 3D bioprinting market. The National Agency for the Promotion of Research, Technological Development, and Innovation has boosted funding for advanced medical technologies, including bioprinting. According to the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, Argentina increased its R&D expenditure by 20% between 2019 and 2022 to focus on applications like drug testing and tissue engineering.
Chile is emerging as a key market for 3D bioprinting in Latin America. The Chilean Economic Development Agency actively supports biotechnology innovation and allocated $500 million in 2021 to healthcare-related R&D. The healthcare system of Chile, which is recognized for its efficiency in the region, increasingly integrates bioprinting for medical research and personalized medicine. According to reports from the World Bank, Chile has one of the highest healthcare expenditures in Latin America, at 9.3% of GDP, and this is enabling the adoption of advanced technologies. With a growing demand for organ transplantation and regenerative treatments, Chile plays a vital role in advancing the regional bioprinting market.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies playing a dominating role in the Latin America 3D Bioprinting Market covered in this report are 3Dynamic Systems Ltd., Organovo Holdings, Inc., CELLINK, Bio3D Technologies, Advanced Solutions, Inc., EnvisionTEC GmbH, Ourobotics, 3D Bioprinting Solutions, BioBots, Inc., Poietis, Cyfuse Biomedical K.K., Aerotech, Inc., GeSIM, Nano3D Biosciences, Inc., regenHU Ltd, and GeSIM.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This market research report on the Latin America 3D bioprinting market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Material Type
- Living Cells
- Hydrogels
- Extracellular Matrices
- Others
By Technologies
- Micro Extrusion Bioprinting
- Magnetic Levitation
- Inkjet-Based
- Syringe-Based
- Laser-Based
- Others
By Components
- 3D Bioprinters
- Biomaterials
- Scaffolds
By Country
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
