Global Integrated Pest Management Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented By Pest Type (Weeds, Invertebrates, Pathogens, And Vertebrates), Control Method (Biological Control, Chemical Control, Cultural Controls, Mechanical & Physical Controls And Other Control Method), Application (Agriculture, Commercial Buildings, Industrial, Residential, And Others), By Region (North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa) - Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Global Integrated Pest Management Market Size
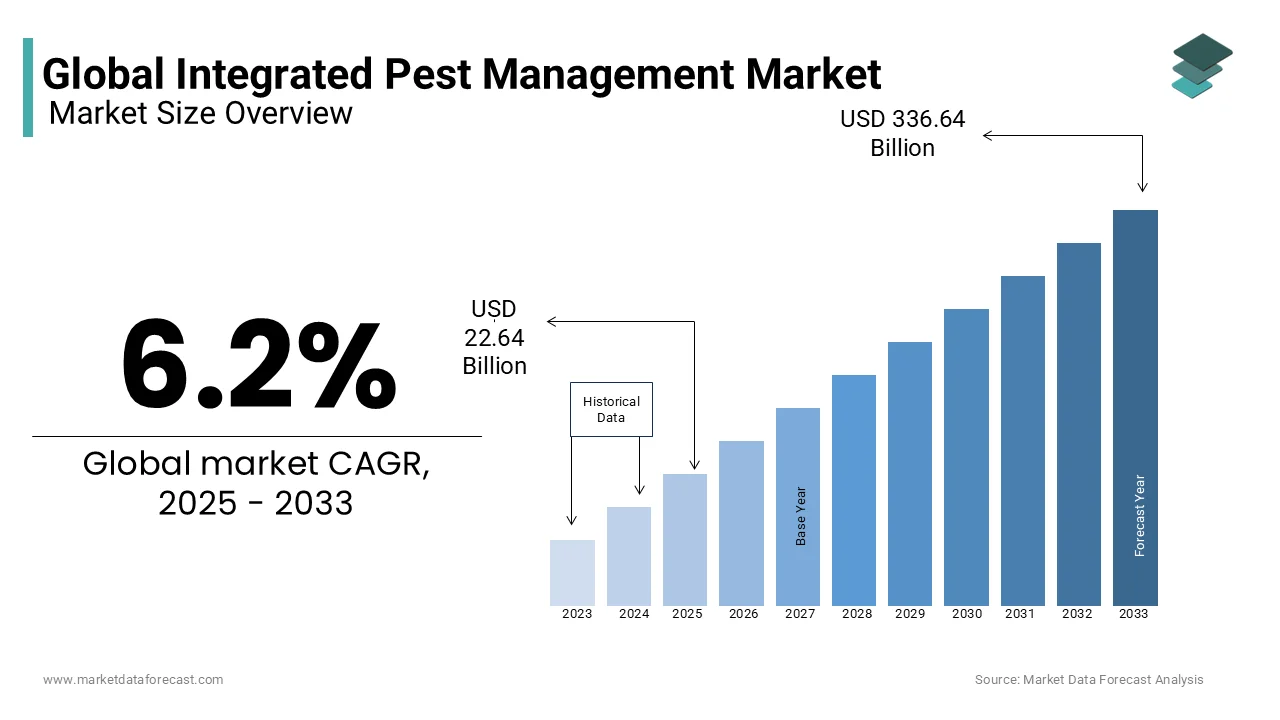
The global integrated pest management market was valued at USD 21.32 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 22.64 billion in 2025 from USD 336.64 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2025 to 2033.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a holistic and sustainable approach to pest control by blending biological, chemical, cultural, and mechanical methods to minimize crop damage while safeguarding environmental health. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), IPM strategies have been adopted in over 100 countries by reducing pesticide use by up to 50% in some regions. This approach is gaining traction as global agricultural production faces mounting challenges, including pest resistance, climate change, and biodiversity loss. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, pests cause annual crop losses exceeding $200 billion with the critical need for effective management solutions. IPM not only addresses these issues but also aligns with regulatory frameworks promoting eco-friendly practices. Europe and North America are leading adopters by stringent environmental policies and consumer demand for sustainably grown produce. The role of IPM in ensuring food security while preserving ecosystems becomes increasingly indispensable as the global population approaches 9.7 billion by 2050.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Concerns Over Environmental Degradation
The escalating concerns over environmental degradation caused by conventional pest control methods are propelling the adoption of integrated pest management (IPM). The United Nations Environment Programme estimates that excessive pesticide use contributes to the contamination of 40% of global water bodies, endangering aquatic ecosystems. IPM offers a sustainable alternative by reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and promoting natural pest control mechanisms. For instance, according to the European Commission, IPM adoption has lowered pesticide-related emissions by 30% by aligning with regional sustainability goals. As per the World Health Organization, pesticide exposure causes over 200,000 deaths annually that emphasizing the urgent need for safer alternatives. Farmers in regions like Scandinavia and Canada have embraced IPM, achieving a 40% reduction in chemical inputs while maintaining crop yields.
Rising Demand for Organic and Sustainably Grown Produce
The rising demand for organic and sustainably grown produce is another significant driver boosting the integrated pest management market. Consumers are increasingly prioritizing products free from synthetic chemicals, which is driving farmers to adopt IPM strategies that align with organic certification standards. For example, India’s Ministry of Agriculture states that organic farming initiatives supported by IPM have increased by 25% annually since 2018 in states like Sikkim and Kerala. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, IPM adoption has enabled American farmers to access premium markets, with organic produce fetching prices 20-30% higher than conventionally grown crops.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Implementation Costs and Complexity
High implementation costs and complexity pose significant barriers to the widespread adoption of integrated pest management (IPM) for small-scale farmers. As per the International Finance Corporation, transitioning to IPM systems can increase initial operational costs by 20-30% due to investments in training, monitoring tools, and biological control agents. In developing regions like Sub-Saharan Africa, where profit margins are already thin, this financial burden often proves prohibitive. According to the African Development Bank, less than 15% of smallholder farmers in rural areas utilize advanced pest management techniques due to cost constraints. Moreover, the lack of standardized training programs exacerbates the problem by leaving many farmers reliant on trial-and-error methods. Their reach remains insufficient to meet the growing demand for sustainable farming solutions by hindering broader market penetration.
Limited Awareness Among End-Users
Limited awareness among end-users about the benefits and proper implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) acts as another major restraint. A survey conducted by the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research found that only 30% of farmers in Latin America are familiar with the principles of IPM. This knowledge gap often results in improper application, undermining its effectiveness. For instance, incorrect timing or dosage of biological control agents can lead to pest resurgence, negating the intended benefits. According to the African Soil Health Consortium, extension services, which aim to educate farmers on sustainable practices, remain underfunded in many rural areas. Additionally, misinformation spread through unverified sources exacerbates the problem, deterring potential users. The full potential of IPM cannot be realized by limiting its adoption in underserved agricultural communities.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Emerging markets present untapped potential for the integrated pest management (IPM) market by increasing agricultural investments and supportive government policies. According to the Asian Development Bank, agricultural output in South Asia and Southeast Asia is projected to grow by 4% annually over the next decade by creating robust demand for sustainable pest control solutions. For example, India’s Ministry of Agriculture has launched initiatives to promote IPM adoption by aiming to combat soil degradation and reduce pesticide dependency. According to the International Trade Centre, trade agreements and reduced tariffs are facilitating the entry of foreign suppliers into these regions.
Integration with Precision Agriculture Technologies
The integration of integrated pest management (IPM) with precision agriculture technologies offers immense potential to enhance farming efficiency and sustainability. IPM complements this ecosystem by providing real-time data on pest populations and crop health, enabling targeted interventions that minimize resource wastage. A study by the American Society of Agronomy reveals that combining IPM with precision technologies can increase pest control efficiency by 25%. Countries like Germany and Canada have invested heavily in smart farming solutions by driving demand for complementary practices like IPM. This synergy between advanced technologies and innovative agricultural inputs escalates the transformative potential of precision agriculture in reshaping the pest management market by offering scalable solutions for a greener future.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Resistance Development Among Pests
Resistance development among pests poses a significant challenge to the effectiveness of integrated pest management (IPM) by threatening its long-term viability. The International Plant Protection Convention reports that over 600 pest species have developed resistance to commonly used pesticides by rendering traditional control methods ineffective. For instance, the fall armyworm, a devastating pest in sub-Saharan Africa, has shown resistance to multiple chemical treatments, causing annual crop losses exceeding $13 billion. According to the European AgriTech Association, even biological control agents face diminishing efficacy as pests adapt to new threats. Addressing this issue requires continuous innovation and diversification of control strategies, which can be costly and time-consuming. Without proactive measures, the rise of resistant pest populations could undermine the progress achieved through IPM by urgent action to preserve its impact.
Fragmented Regulatory Frameworks Across Regions
Fragmented regulatory frameworks across regions complicate the implementation and standardization of integrated pest management (IPM) practices by creating additional hurdles for market players. The European Chemicals Agency mandates rigorous testing of all pest control methods, including biological agents, to ensure minimal ecological impact. However, inconsistencies in regulatory standards across countries create additional barriers. For example, while the European Union enforces strict guidelines, some developing nations lack clear frameworks by leading to fragmented market dynamics. According to the Pesticide Action Network, approximately 40% of new agricultural inputs face delays during the regulatory approval phase, impacting their commercial viability. Furthermore, disparities in labeling and certification requirements hinder cross-border trade by limiting the scalability of IPM solutions. Streamlining processes and harmonizing regulations are essential to facilitate faster adoption and market expansion.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
6.2% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Pest Type, Control Method, Application, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
IPM Pest Control, SGS SA, MB Integrated Pest Control, BASF SE, Advanced Integrated Pest Management, Bayer CropScience LP, Ecolab Inc, IPM Technologies Pty Ltd, Integrated Pest Management Solution (IPMS India) and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The weeds segment dominated the integrated pest management (IPM) market by capturing 45.2% of share in 2024 due to their ability to compete with crops for nutrients, water, and sunlight by causing significant yield losses. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, weeds account for nearly 30% of global crop losses by intensifying demand for effective management solutions. For instance, herbicide-resistant weeds affect over 100 million acres globally by prompting farmers to adopt IPM strategies like crop rotation and mechanical removal.
The pathogens segment is anticipated to register a CAGR of 9.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by the increasing prevalence of fungal and bacterial diseases by climate change and globalization. According to the European AgriTech Association, fungal pathogens cause annual crop losses exceeding $200 billion by driving demand for bio-based IPM solutions. For example, neem oil-based formulations are gaining popularity due to their antifungal properties and environmental safety.
By Control Type
The biological control dominated the integrated pest management (IPM) market with a 40.4% of share in 2024 due to its eco-friendly nature and ability to target specific pests without harming beneficial organisms. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, biological control agents, such as ladybugs and parasitic wasps, have reduced pest populations by 30% in organic farming systems. Additionally, their compatibility with organic certification standards makes them a preferred choice for sustainably grown produce.
The cultural control segment is likely to grow with a CAGR of 10.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by its cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation in small-scale farming operations. According to the India’s Ministry of Agriculture, cultural practices, such as crop rotation and intercropping that have gained traction in rural areas, where access to advanced technologies is limited.
By Application
The agriculture segment dominated the integrated pest management (IPM) market and held a 55.3% of share in 2024 due to its ability to address pest-related challenges in large-scale farming operations by ensuring food security and economic stability. The Canadian Greenhouse Conference reports that IPM adoption has increased crop yields by 20% by making it a critical tool for modern agriculture.
The commercial buildings segment is likely to experience a CAGR of 12.5% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the rising demand for pest-free environments in offices, retail spaces, and hospitality sectors. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, IPM adoption in commercial buildings has reduced pest-related complaints by 40% by improving tenant satisfaction and operational efficiency.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America led the global integrated pest management (IPM) market with a 35.3% share in 2024. The region's dominance is attributed to its advanced agricultural practices and stringent environmental regulations. For instance, California’s agricultural sector, valued at $50 billion in 2022, prioritizes sustainable pest control solutions.
Europe integrated pest management market growth is likely to grow with a CAGR of 15.4% during the forecast period. The European Union’s REACH regulation promotes the use of eco-friendly pest control methods, fostering market growth. Germany is the largest adopter and acounts for 30% of regional sales. The European Commission reports that IPM adoption has reduced pesticide usage by 30% by achieving sustainability targets.
Asia Pacific is likely to have steady growth pace in the next coming years with the rapid urbanization and population growth drive demand for sustainable pest management solutions. China and India collectively account for 60% of regional consumption. Government initiatives promoting organic farming further accelerate market expansion.
Latin America’s tropical climate necessitates efficient pest control solutions is increasing IPM demand is elevating the growth of the market. The Middle East and Africa region’s arid conditions amplify the need for sustainable pest management with South Africa leading adoption. Investments in agricultural infrastructure are expected to drive future growth with untapped potential.Top of Form
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
IPM Pest Control, SGS SA, MB Integrated Pest Control, BASF SE, Advanced Integrated Pest Management, Bayer CropScience LP, Ecolab Inc, IPM Technologies Pty Ltd, Integrated Pest Management Solution (IPMS India). are the market players dominate the global Integrated pest management market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global integrated pest management market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Pest Type
- Weeds
- Invertebrates
- Pathogens
- Vertebrates
By Control Method
- Cultural Controls
- Mechanical & Physical Controls
- Biological Control
- Chemical Control
- Control Method
By Application
- Agriculture
- Commercial buildings
- Industrial, Residential
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How is Integrated Pest Management (IPM) different from traditional pest control?
IPM focuses on sustainable, eco-friendly methods like biological control, habitat manipulation, and resistant crop varieties, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides.
What are the main factors driving the growth of the global IPM market?
Increasing environmental concerns, stringent pesticide regulations, rising demand for organic farming, and advancements in biopesticides and precision agriculture.
Which industries widely adopt Integrated Pest Management solutions?
Agriculture, horticulture, forestry, residential and commercial pest control, and public health sectors benefit significantly from IPM practices.
Which regions lead the global IPM market?
North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific dominate the market, with strong adoption in the U.S., Canada, Germany, France, China, and India due to supportive government policies.
Who are the key players in the IPM market?
Major companies include BASF SE, Bayer CropScience, Syngenta, Corteva Agriscience, and Marrone Bio Innovations, leading in biopesticide and pest management innovations.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]