Global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Cardiomyocytes, Hepatocytes, Neurons, Endothelia Cells and Other Cell Types), Product (Molecular And Cellular Engineering, Cellular Reprogramming, Cell Culture, Cell Differentiation and Cell Analysis), Application (Academic Research, Drug Development, Toxicity Testing and Regenerative Medicine) And Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East And Africa) – Industry Analysis, 2025 To 2033
Global Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Market Size
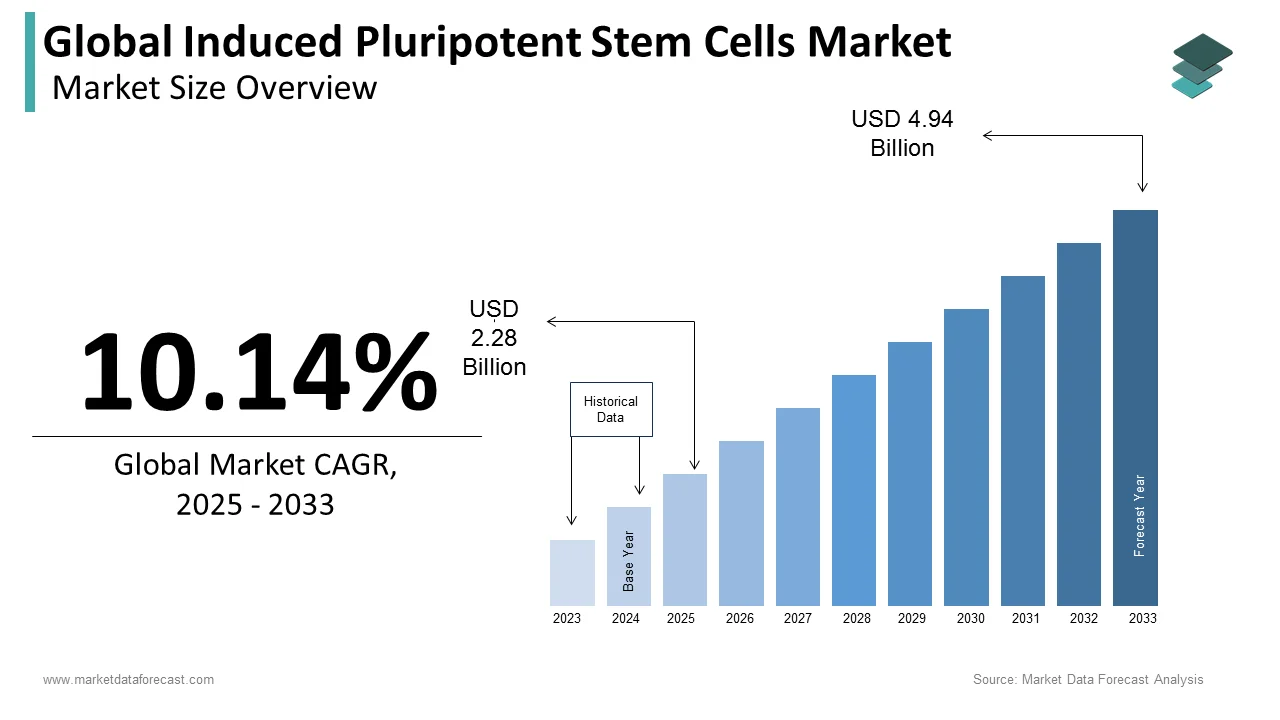
The global induced pluripotent stem cells market size was valued at USD 2.07 billion in 2024. The global market size is expected to grow from USD 2.28 billion in 2025 to USD 4.94 billion by 2033, registering a CAGR of 10.14% from 2025 to 2033.
The induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) market is growing rapidly. The growth is majorly fuelled by breakthroughs in regenerative and personalized medicine as well as drug discovery. iPSCs are adult cells that have been reprogrammed to a pluripotent state, meaning they can transform into various cell types. This unique capability makes iPSCs valuable for disease modeling, drug testing, and developing cell-based therapies. The rising investments in stem cell research, new advances in cell reprogramming technology, and an increasing demand for personalized treatments are also propelling the global market expansion. North America currently leads the market, supported by substantial R&D funding and favorable regulations, while the Asia-Pacific region is also growing fast, spurred by government support and higher healthcare spending.
Key market participants such as Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics, Takara Bio and Lonza Group are focusing on improving iPSC generation methods to enhance scalability and lower production costs. Despite these advancements, the market faces challenges such as ethical issues, high production costs, and complex regulatory requirements. However, with ongoing innovation and an increased emphasis on regenerative and personalized medicine, the iPSCs market is set for strong future growth.
MARKET TRENDS
Expansion in Drug Discovery and Toxicity Testing
The application of iPSCs in drug discovery is transforming preclinical testing by allowing for disease-specific cell modeling and toxicity screening. iPSC-derived cells have been shown to predict cardiotoxicity in new drugs with an accuracy rate of over 70%, significantly higher than traditional animal models. In 2023, nearly 45% of pharmaceutical companies integrated iPSCs into drug screening processes to improve accuracy and reduce failures in clinical trials. Additionally, it is estimated that incorporating iPSCs could cut preclinical research time by up to 20%, potentially saving millions in development costs while accelerating drug development timelines.
Advancements in Regenerative Medicine and Cell Therapies
iPSC-based therapies are also progressing in regenerative medicine, particularly in chronic disease treatment. According to recent studies, about 60% of active clinical trials involving iPSCs target neurological conditions like Parkinson’s and ALS. In 2022, the FDA approved 14 clinical trials utilizing iPSC-derived cells, a 40% increase from 2020. Moreover, patient-specific iPSC lines reduce rejection rates by 15-20%, making these therapies a promising option for personalized medicine. These advancements indicate a growing acceptance of iPSCs as a viable, scalable approach for developing regenerative and cell-based treatments.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increased Demand for Personalized Medicine
The push toward personalized medicine is a key driver of the iPSCs market, as these cells enable the creation of patient-specific cells that improve treatment outcomes. iPSCs allow for customized therapies by mimicking individual genetic conditions, leading to more effective drug responses and fewer side effects. Studies indicate that over 55% of new drug trials in 2023 incorporated personalized approaches using iPSCs. This ability to tailor treatments is gaining traction, especially in oncology and rare disease management, where iPSCs are used for patient-specific drug screening, significantly enhancing treatment precision and minimizing adverse reactions.
Advancements in Cell Reprogramming Technologies
Improvements in cell reprogramming techniques have made iPSC generation faster, safer, and more cost-effective, accelerating market growth. Traditional iPSC generation methods required viral vectors, which posed safety concerns, but new, non-integrating methods now achieve reprogramming with 98% efficiency. In 2022, innovations in CRISPR and mRNA reprogramming technology reduced reprogramming costs by nearly 30%, making iPSCs more accessible for research and therapeutic use. These advancements have spurred adoption across both academic research and commercial biotech companies, with over 65% of iPSC-related studies in 2023 employing next-generation, efficient reprogramming techniques.
Growing Focus on Disease Modeling and Drug Toxicity Testing
iPSCs are becoming essential in disease modeling and drug toxicity testing, offering a reliable alternative to animal testing. The pharmaceutical industry increasingly uses iPSCs to create human cell models for diseases such as Alzheimer’s, diabetes, and heart disease, which are difficult to replicate in animals. A 2023 survey found that 78% of pharmaceutical companies now incorporate iPSC-derived cell models for toxicity testing, significantly improving early-stage screening accuracy. This shift is reducing costly late-stage failures, potentially saving the industry billions, while aligning with ethical practices by reducing dependence on animal models.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production Costs and Complexity
The cost and complexity of generating iPSCs remain major barriers. iPSC production involves specialized equipment, reagents, and skilled labor, leading to high operational expenses. In 2022, the average cost of producing an iPSC line was approximately $10,000–$15,000, limiting accessibility for smaller labs and clinics. Additionally, the process is time-intensive, taking weeks to reprogram and differentiate cells reliably. Although advances in reprogramming methods have reduced costs, scalability remains challenging, particularly for widespread clinical and commercial applications, which constrains market expansion in lower-resource settings and smaller research institutions.
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
The iPSCs market is restricted by ethical and regulatory hurdles, especially concerning cell sourcing and genetic manipulation. While iPSCs sidestep many ethical issues tied to embryonic stem cells, regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA still impose rigorous standards to ensure safety and efficacy. In 2023, only around 20% of iPSC-based therapies seeking approval progressed to clinical trials due to stringent preclinical data requirements. Furthermore, ethical concerns about gene editing and reprogramming persist, particularly around unintended mutations or tumorigenicity, which raises barriers for clinical adoption and commercialization.
Risk of Tumorigenicity in iPSC Applications
A critical challenge with iPSCs is the risk of tumor formation, as reprogramming cells to a pluripotent state can lead to genomic instability. Studies have shown that iPSCs sometimes develop mutations during reprogramming, increasing the risk of tumorigenicity when these cells are used in therapeutic applications. Research in 2022 highlighted that up to 15% of iPSC-derived cells exhibited mutations that could lead to uncontrolled cell growth. This risk imposes a substantial obstacle in clinical settings, as regulators demand extensive safety validations, extending the timeline and costs of developing iPSC-based therapies.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expanding Applications in Neurological Disease Treatment
The potential for iPSCs in treating neurological diseases presents a significant opportunity. iPSCs can be differentiated into neurons, enabling new therapies and drug screening for conditions like Parkinson’s, ALS, and Alzheimer’s. According to recent studies, over 40% of active clinical trials involving iPSCs are focused on neurological diseases. This application is promising for the 50 million people worldwide affected by neurodegenerative diseases, for whom limited treatment options currently exist. As research advances, iPSC-derived therapies offer a scalable and targeted approach, opening new markets in neurotherapy and regenerative neurology.
Growing Interest in Cardiovascular Disease Research
Cardiovascular disease research with iPSCs is a rapidly growing area, as iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (heart cells) allow for precise modeling of heart disease and the testing of cardiotoxicity in new drugs. The American Heart Association notes that cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, affecting nearly 18 million people annually. iPSCs offer a patient-specific, ethical alternative to animal models, with studies reporting predictive accuracy rates above 75% for drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Increased funding and demand for better cardiovascular treatments are driving interest, creating a substantial opportunity for iPSC applications in cardiac research.
Rising Demand for Biobanking of iPSCs
The demand for iPSC biobanking is growing, with more institutions establishing biobanks for disease-specific and patient-derived iPSC lines. Biobanking offers long-term storage and availability of diverse iPSC lines, facilitating research across genetic backgrounds and disease models. In 2023, global investments in iPSC biobanks increased by 35%, reflecting their value in personalized medicine and population-wide studies. By preserving these cell lines, biobanks enable faster, more accessible research on genetic disorders and drug testing. This trend provides an opportunity for biobanking companies and research institutions to support large-scale studies and accelerate iPSC-driven innovations in medicine.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Genomic Instability and Tumorigenic Potential
A significant challenge for iPSCs is genomic instability, which raises concerns about their safety in clinical applications. Reprogramming cells to a pluripotent state can lead to genetic mutations and abnormalities that increase the risk of tumor formation. Studies report that up to 15% of iPSC lines carry mutations that could result in tumorigenicity, particularly in long-term therapies. Regulatory agencies require extensive safety data, extending development timelines and costs. Addressing this challenge requires ongoing innovation in reprogramming methods to minimize mutations and rigorous screening processes to ensure only stable iPSCs are used clinically.
Scalability and High Production Costs
The high cost and complexity of producing iPSCs limit their scalability, posing a barrier to widespread adoption. Each iPSC line requires precise reprogramming, differentiation, and validation processes, which are labor-intensive and expensive. The average cost per iPSC line is around USD 10,000 to USD 15,000, restricting accessibility for smaller research institutions and limiting large-scale therapeutic applications. Despite advancements, the scalability of iPSC production remains a challenge. Automation and improved efficiency in cell production may help lower costs, but current limitations prevent iPSCs from becoming a broadly available tool in both research and clinical use.
Regulatory and Ethical Hurdles
iPSC research faces strict regulatory scrutiny, as safety and ethical concerns persist, especially around cell reprogramming and potential genetic editing. While iPSCs avoid many ethical issues tied to embryonic stem cells, concerns remain regarding the unintended consequences of genetic manipulation. For instance, regulators like the FDA require extensive preclinical data to address the risk of mutations and other adverse effects, leading to approval rates below 25% for iPSC-based therapies. These regulatory and ethical requirements add time and complexity to clinical approvals, slowing the path to commercialization and increasing research costs for developers.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
10.14% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Product, Application and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Ncardia, Takara Bio Inc., ATCC, Creative Bioarray, Bio-Techne, PeproTech Inc., Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., Addgene, Plasticell, System Biosciences LLC., Axol Bioscience Ltd., Genecopoeia Inc., Waisman Biomanufacturing, Corning Inc., Lonza, Merck KGaA, BlueRock Therapeutics, Gentarget Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., PromoCell GmbH, InvivoGen, ID Pharma Co. Ltd., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Megakaryon Corp., Applied StemCell, Applied Biological Materials Inc. (ABM), Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Qiagen, Reprocell Inc., ScienCell Research Laboratories, StemCell Technologies, Alstem, Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc., Fate Therapeutics, Allele Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals Inc., Newcells Biotech and Promega Corp. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The neurons segment dominated the market and accounted for 36.3% of the global market share in 2023. iPSC-derived neurons are in high demand for neurological disease modeling and drug testing, especially for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and ALS. The prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases has increased, affecting over 50 million people worldwide, with Alzheimer’s alone impacting around 6 million people in the United States. These cells provide an invaluable model for studying complex neurological disorders and testing new neurotherapeutics without invasive procedures. Additionally, iPSC-derived neurons enable personalized medicine approaches, allowing researchers to study patient-specific cellular responses and improve treatment precision. Given the rising prevalence of neurological conditions and the demand for effective therapies, neurons continue to lead the iPSC market.

The cardiomyocytes segment is the fastest-growing segment and is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 16.6% over the forecast period. Cardiovascular research and drug toxicity testing are driving the rapid expansion of iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death globally, accounting for nearly 18 million deaths each year, and they represent a significant area for therapeutic development. iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes enable researchers to model heart diseases and test new cardiovascular drugs more accurately by predicting potential cardiotoxicity and efficacy in human-like models. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly rely on these cells to reduce late-stage drug development failures, as traditional animal models often fail to replicate human cardiac responses. This segment’s rapid growth reflects the urgent need for innovative CVD treatments and safer drug development practices.
By Product Insights
The cellular reprogramming segment was the largest segment in the induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) market and had 33.7% of the global market share in 2023. Cellular reprogramming is central to iPSC technology, as it involves converting adult cells back to a pluripotent state, enabling them to differentiate into various cell types. This process is essential for creating iPSCs, which serve as the foundation for applications in disease modeling, drug discovery, and regenerative medicine. In recent years, advancements in reprogramming methods have increased efficiency and reduced costs, making it more accessible for laboratories and biotech companies. Reprogramming remains a crucial step for iPSC production and is fundamental to generating reliable cell models for research. The segment’s dominance is driven by ongoing innovations and increased demand for high-quality reprogramming processes across pharmaceutical and academic research settings.
The cell differentiation segment is growing the fastest CAGR of 18.14% over the forecast period. Cell differentiation technology is critical for producing specific cell types from iPSCs, such as neurons, cardiomyocytes, and hepatocytes, which are used in targeted disease modeling and therapeutic research. The ability to direct iPSCs to differentiate into specific cell lineages is vital for applications in personalized medicine and regenerative therapies. Recent studies highlight the expanding role of iPSC-derived differentiated cells in preclinical research, especially for testing drugs’ effects on human cell types without invasive procedures. The high demand for differentiated cells in diverse applications from organoid research to toxicity testing is accelerating growth in this segment.
By Application Insights
The academic research segment led the market and captured 42.1% of the worldwide market share in 2023. Academic institutions and research laboratories are the primary users of iPSCs, as these cells offer vast potential for basic and applied research in understanding disease mechanisms, cellular behavior, and genetic functions. iPSCs provide a unique platform to study rare diseases and perform functional genomics, enabling researchers to model diseases and explore personalized medicine applications without relying on animal models. Over 65% of published studies involving iPSCs originate from academic institutions, which reflects the heavy reliance on iPSCs for groundbreaking research. Increased government funding and grants for stem cell research further support this segment’s dominance, as iPSCs remain essential for exploring new frontiers in biomedical science.
The regenerative medicine segment is the fastest-growing segment in the iPSCs market and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 22.7% over the forecast period. iPSCs have transformative potential in regenerative medicine, where they can generate patient-specific cells for tissue repair and organ regeneration. iPSC-derived therapies are particularly promising for chronic and degenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s, heart disease, and spinal cord injuries, where traditional treatments are limited. In 2022, over 30 clinical trials involving iPSC-based regenerative therapies were underway, representing a 40% increase from previous years. Demand for iPSCs in regenerative applications is growing as healthcare systems look for solutions to address aging populations and chronic disease prevalence, making this a rapidly advancing area with significant clinical and commercial potential.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America dominated the iPSCs market by accounting for 38.1% of the global market share in 2023. The leadership of North America in the global iPSCs market is driven by significant investment in stem cell research, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and strong R&D funding from both the public and private sectors. The U.S. dominates this region, home to key players such as Thermo Fisher Scientific and Bristol-Myers Squibb and is the origin of nearly 50% of global iPSC clinical trials. The region is expected to maintain its lead due to ongoing investment in regenerative and personalized medicine.
Europe was the second-largest region and captured 24.8% of the global iPSCs market share in 2023. Europe has a strong research base in stem cell technology, with notable activity in countries like Germany, the U.K., and France, which lead in iPSC research and innovation. The European Union’s supportive policies, such as Horizon Europe’s funding for advanced research, are contributing to the market’s growth. Future expansion is likely, particularly with Europe’s focus on sustainable biotechnology and increased funding for regenerative medicine, positioning the region as a critical hub for iPSC research and applications.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the iPSCs market and is predicted to showcase a CAGR of 24.9% over the forecast period. The growth of the market in the Asia-Pacific is fueled by rising healthcare expenditures, expanding research capabilities and supportive government policies in countries like Japan, China, and South Korea. Japan, an early leader in iPSC research, was the first country to commercialize iPSC-derived treatments and continues to invest heavily in stem cell technologies. China is also rapidly advancing, with increasing R&D investment and collaborations. With a strong focus on innovative therapies and a growing biopharma industry, Asia-Pacific is poised to increase its market share significantly over the next decade.
The iPSC market in Latin America is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. The growth of the Latin America is primarily driven by Brazil and Mexico, where healthcare modernization and stem cell research initiatives are on the rise. However, limited funding and less-developed research infrastructure compared to North America and Europe hinder faster growth. Despite these challenges, growing interest in regenerative medicine and cell-based research offers opportunities for expansion. Government initiatives to improve biotechnology capabilities are expected to drive future growth in this region.
The iPSC market in the Middle East and Africa is nascent, with development concentrated in countries like the United Arab Emirates and South Africa. Limited resources, infrastructure, and funding constrain market growth. However, governments in the region are increasingly investing in medical research and healthcare advancements, creating potential for future expansion. Increased collaboration with international research organizations and a growing focus on advanced therapeutics may gradually enhance the region’s position in the iPSC market.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies that play a promising role in the global induced pluripotent stem cells market include Ncardia, Takara Bio Inc., ATCC, Creative Bioarray, Bio-Techne, PeproTech Inc., Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., Addgene, Plasticell, System Biosciences LLC., Axol Bioscience Ltd., Genecopoeia Inc., Waisman Biomanufacturing, Corning Inc., Lonza, Merck KGaA, BlueRock Therapeutics, Gentarget Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., PromoCell GmbH, InvivoGen, ID Pharma Co. Ltd., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Megakaryon Corp., Applied StemCell, Applied Biological Materials Inc. (ABM), Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Qiagen, Reprocell Inc., ScienCell Research Laboratories, StemCell Technologies, Alstem, Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc., Fate Therapeutics, Allele Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals Inc., Newcells Biotech and Promega Corp.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2024, Takara Bio Inc. introduced its Shasta Single-Cell System, a high-throughput single-cell next-generation sequencing platform aimed at advancing biomarker discovery and drug development. This system offers scalable solutions for oncology and precision medicine research.
- In April 2024, Bio-Techne announced the launch of a CRISPR-Cas9-enabled iPSC line designed to enhance the accuracy of gene editing in drug discovery and disease modeling. This advancement is expected to support oncology and genetic disorder research.
- In March 2024, Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc. expanded its GMP-compliant iPSC manufacturing capabilities in the United States, strengthening its position as a leader in clinical-grade iPSC production for regenerative medicine and cell therapy.
- In May 2024, Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a comprehensive iPSC differentiation kit tailored for cardiac and neurological cell types, meeting the growing demand for disease-specific iPSC models in drug testing.
- In June 2024, Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc. entered into a partnership with Newcells Biotech to co-develop iPSC-derived organoid models for kidney disease. This collaboration aims to enhance the development of treatments targeting renal pathologies.
- In July 2024, Lonza opened a new stem cell research and bioproduction facility in Switzerland, focusing on high-volume iPSC culture and differentiation capabilities. This investment supports the scaling of regenerative medicine research across Europe.
- In August 2024, Creative Bioarray released an advanced iPSC culture medium specifically designed to improve reprogramming efficiency and cell viability, targeting researchers in personalized medicine and cell therapy.
- In September 2024, Allele Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals Inc. introduced a cost-effective non-viral iPSC reprogramming kit, reducing the risk of gene insertional mutagenesis and making reprogramming safer for clinical applications.
- In October 2024, Applied StemCell received FDA clearance for its iPSC-derived therapeutic product for Parkinson’s disease, marking a milestone for iPSC-based treatments in neurological disorders.
- In November 2024, StemCell Technologies announced the expansion of its iPSC biobanking services, providing researchers with access to a diverse collection of patient-specific iPSC lines for drug screening and disease modeling across multiple therapeutic areas.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This report on the global induced pluripotent stem cells market is segmented and sub-segmented into type, product, application and region.
By Type
- Cardiomyocytes
- Hepatocytes
- Neurons
- Endothelia Cells
- Other Cell Types
By Product
- Molecular and Cellular Engineering
- Cellular Reprogramming
- Cell Culture
- Cell Differentiation
- Cell Analysis
By Application
- Academic Research
- Drug Development
- Toxicity Testing
- Regenerative Medicine
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East And Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the induced pluripotent stem cells market?
The global induced pluripotent stem cells market was worth USD 2.07 billion in 2024 and is expected to become as big as 4.94 billion by 2033.
What is the CAGR of the induced pluripotent stem cells market?
The global induced pluripotent stem cells market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 10.14% from 2025 to 2033.
Which segment by type had the major share of the induced pluripotent stem cells market in 2023?
Based on type, the neurons segment occupied a share of 36.3% of the global market in 2023.
Who are the major players in the induced pluripotent stem cells market?
Ncardia, Takara Bio Inc., ATCC, Creative Bioarray, Bio-Techne, PeproTech Inc., Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc., Addgene, Plasticell, System Biosciences LLC., Axol Bioscience Ltd., Genecopoeia Inc., Waisman Biomanufacturing, Corning Inc., Lonza, Merck KGaA, BlueRock Therapeutics, Gentarget Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., PromoCell GmbH, InvivoGen, ID Pharma Co. Ltd., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Megakaryon Corp., Applied StemCell, Applied Biological Materials Inc. (ABM), Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Qiagen, Reprocell Inc., ScienCell Research Laboratories, StemCell Technologies, Alstem, Fujifilm Cellular Dynamics Inc., Fate Therapeutics, Allele Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals Inc., Newcells Biotech and Promega Corp are currently playing the leading role in the induced pluripotent stem cells market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
