India Connected Car Market Size, Share, Trends, COVID-19 Impact & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented By Platform (Android Auto, Carplay, Mirrorlink, Others), Connectivity Form Factor (Embedded, Tethered, Integrated), Application (Telematics, Ride Sharing/Hailing, Others), Hardware (Smart Antenna, Display, Electronic Control Unit, Sensors), Connectivity Technology (Cellular, Dedicated Short Range Communication) - Industry Analysis From (2025 to 2033)
India Connected Car Market Size
The global India-connected car market size is expected to reach USD 20.88 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 25.36 billion in 2025 from USD 120.04 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 21.45% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
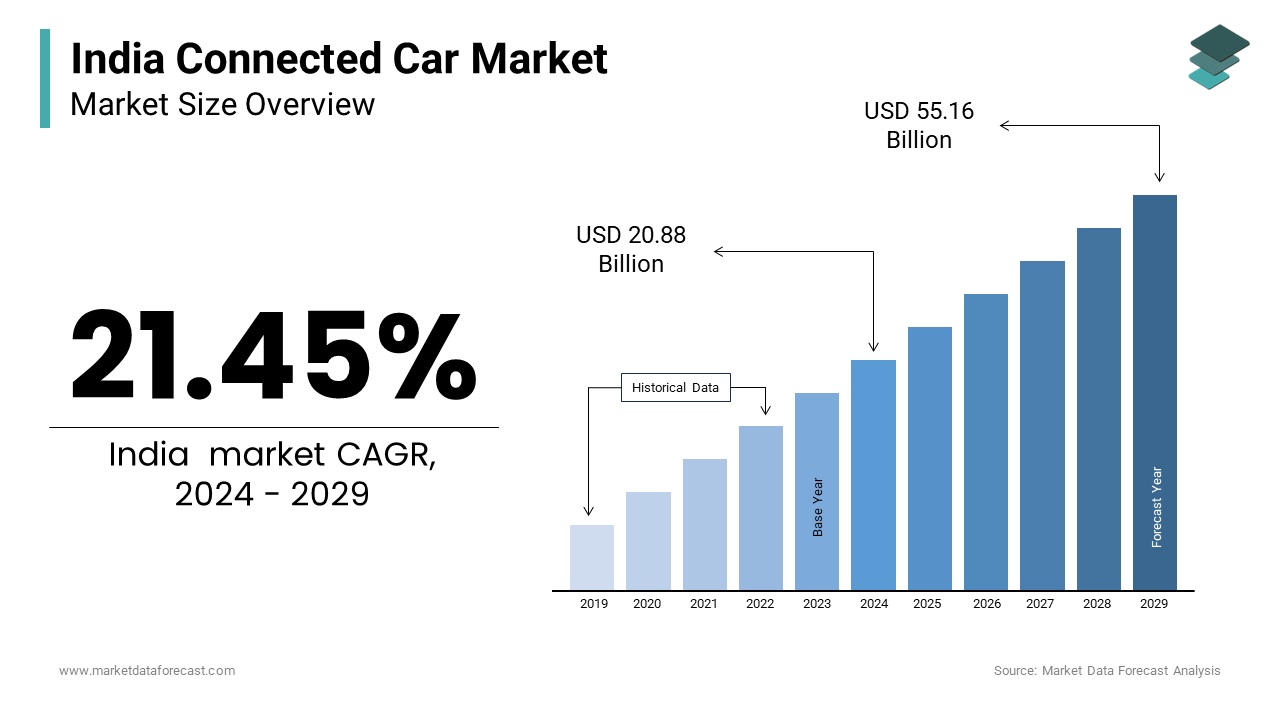
Connected cars are vehicles equipped with internet access and wireless communication systems that enable seamless interaction between the vehicle, external devices, and infrastructure. The rapid adoption of connected cars across urban and semi-urban parts of India is majorly driving the Indian market forward. The proliferation of smartphones and increasing internet penetration have created a fertile environment for integrating connectivity features such as GPS navigation, infotainment systems, and real-time diagnostics. A study by Deloitte indicates that over 60% of Indian consumers prioritize connectivity when purchasing a new vehicle, particularly in metropolitan cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore. Furthermore, government initiatives such as the Smart Cities Mission and the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme have accelerated the deployment of IoT-enabled infrastructure, fostering the growth of connected car technologies. As automakers collaborate with tech giants to develop innovative solutions, the connected car ecosystem is poised to redefine mobility in India while addressing challenges related to safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Urbanization and Demand for Smart Mobility Solutions in India
Urbanization has emerged as a pivotal driver for the connected car market in India, with cities expanding rapidly and mobility needs becoming more complex. According to the United Nations, India’s urban population is expected to reach 600 million by 2030, creating an urgent need for intelligent transportation systems. Connected cars address this demand by offering features such as real-time traffic updates, predictive maintenance, and autonomous driving capabilities. For instance, Tata Motors has introduced telematics systems in its passenger vehicles, enabling drivers to monitor fuel efficiency and receive service alerts via mobile apps. A study by McKinsey highlights that smart mobility solutions can reduce travel time by up to 25% in congested urban areas, making them highly appealing to commuters. Additionally, the rise of ride-hailing platforms like Ola and Uber has amplified the adoption of connected technologies, as these services rely on real-time data exchange to optimize routes and enhance user experience. By aligning with urbanization trends, connected cars are set to play a critical role in transforming India’s transportation landscape.
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Government-led initiatives aimed at promoting digital infrastructure and sustainable mobility have significantly bolstered the connected car market in India. Under the Smart Cities Mission, the Indian government has allocated ₹2 trillion to develop 100 smart cities, emphasizing the integration of IoT and connected technologies in transportation systems. According to NITI Aayog, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication pilots in cities like Pune and Ahmedabad have demonstrated a 20% reduction in accidents and a 15% improvement in traffic flow. Furthermore, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme incentivizes the adoption of connected electric vehicles, aligning with the country’s net-zero emissions goals. A report by KPMG reveals that government subsidies have reduced the cost of connected EVs by 10%, making them more accessible to consumers. By fostering collaboration between automakers, telecom providers, and policymakers, these initiatives are paving the way for a robust connected car ecosystem in India.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Implementation Costs and Affordability Gaps
The high costs associated with developing and deploying connected car technologies pose a significant barrier to widespread adoption in India. Advanced hardware components such as smart antennas, sensors, and electronic control units require substantial investment, often increasing the overall price of vehicles. According to Frost & Sullivan, the integration of connected features can elevate the cost of a mid-range car by up to 25%, making it unaffordable for a large segment of the population. Additionally, recurring expenses related to software updates and data subscriptions further strain consumers. A survey conducted by EY reveals that over 50% of Indian buyers are unwilling to pay a premium for connectivity features, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities where disposable incomes remain low. This affordability gap limits the market’s potential, particularly among budget-conscious consumers who prioritize basic functionalities over advanced technologies.
Cybersecurity Threats and Data Privacy Concerns
As connected cars become increasingly reliant on data-driven technologies, cybersecurity threats and privacy concerns have emerged as notable restraints. The integration of IoT devices and cloud-based platforms creates vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit, potentially compromising vehicle safety and user data. According to a study by PwC, cyberattacks on connected vehicles have surged by 94% since 2020, raising alarms among manufacturers and consumers alike. Moreover, the lack of robust regulatory frameworks for data protection exacerbates these risks, leaving sensitive information exposed. A report by Deloitte highlights that 70% of Indian consumers express concerns about data breaches, deterring them from adopting connected car technologies. While automakers are investing in encryption and firewalls, the absence of standardized protocols undermines trust. Addressing these challenges is imperative to ensure the long-term viability of the connected car market in India.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is a notable opportunity for the connected car market in India. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, personalized user experiences, and enhanced safety features, aligning with evolving consumer expectations. According to Accenture, AI-driven predictive maintenance can reduce vehicle downtime by 30%, saving fleet operators millions in operational costs. For instance, Tata Motors has introduced AI-powered diagnostics in its commercial vehicles, allowing real-time monitoring of engine performance and fuel efficiency. Additionally, ML algorithms facilitate adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance, which are gaining traction among urban commuters. A study by Capgemini reveals that 65% of Indian drivers are willing to adopt AI-enabled features if they enhance convenience and safety. As automakers collaborate with tech giants like Microsoft and IBM, the convergence of AI and connected car technologies is set to redefine the future of mobility in India.
Expansion into Rural and Semi-Urban Markets
The untapped potential of rural and semi-urban markets offers a lucrative opportunity for the connected car industry in India. With over 65% of the population residing in non-metro areas, there is a growing appetite for affordable yet technologically advanced vehicles. According to CRISIL, rural automotive sales grew by 15% in 2022, driven by improved infrastructure and rising incomes. Automakers are tailoring their offerings to cater to this demographic, introducing entry-level connected features such as GPS navigation and infotainment systems. For example, Maruti Suzuki’s “Smartplay” system has gained traction in tier-2 cities, offering essential connectivity at a competitive price point. Furthermore, the expansion of 4G networks into rural regions facilitates seamless integration of telematics and IoT solutions. As connectivity becomes more accessible, rural markets are poised to emerge as a key growth driver for the connected car ecosystem in India.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fragmented Regulatory Landscape
The absence of a unified regulatory framework poses a significant challenge to the development of the connected car market in India. While global standards for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication and data privacy are being established, India lags behind in implementing cohesive policies. According to Boston Consulting Group, the lack of clarity on spectrum allocation for V2X technologies has delayed the rollout of smart mobility solutions in metropolitan areas. Additionally, discrepancies in state-level regulations complicate compliance for automakers operating across multiple regions. A study by Roland Berger highlights that fragmented policies hinder collaboration between stakeholders, including OEMs, telecom providers, and government agencies. Without standardized guidelines, the scalability of connected car technologies remains constrained, impeding progress toward a fully integrated mobility ecosystem.
Limited Awareness and Consumer Education
Despite the rapid advancement of connected car technologies, limited awareness among consumers remains a persistent challenge in India. Many potential buyers are unfamiliar with the benefits and functionalities of connected features, leading to skepticism and hesitation. According to NielsenIQ, only 35% of Indian consumers possess a clear understanding of how connected car systems operate, with misconceptions about complexity and usability deterring adoption. Furthermore, the lack of educational campaigns exacerbates this issue, particularly in rural areas where exposure to cutting-edge technologies is minimal. A survey by Deloitte indicates that enhancing consumer awareness could increase adoption rates by up to 40%. To bridge this gap, automakers must invest in targeted marketing strategies and hands-on demonstrations to demystify connected car technologies. Overcoming this challenge is crucial to unlocking the market’s full potential.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
21.45% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Application, Platform, Connectivity Form Factor, Hardware, Connectivity Technology, and region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, and Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Honda Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, Hyundai Motors, General Motors (U.S.), Ford Motor Company (U.S.), Audi (Germany), BMW (Germany), Mahindra and Mahindra (India), Tata Motors (India), and Maruti Suzuki India (India), and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
India Connected Car Market By Application
The telematics segment held 50.5% of the Indian market share in 2024 due to its ability to enhance fleet management and improve road safety. According to NITI Aayog, telematics systems have reduced fuel consumption by 20% and maintenance costs by 15% for commercial fleets. Platforms like Fleetx and Safetrax leverage real-time data analytics to monitor vehicle performance, driver behavior, and route optimization, benefiting logistics companies. The growing emphasis on smart transportation has further propelled adoption, with the Indian government mandating telematics for public buses under the Smart Cities Mission. A study by Frost & Sullivan reveals that telematics-enabled vehicles account for 60% of new commercial vehicle sales, underscoring their importance. By fostering efficiency and sustainability, telematics remains a cornerstone of the connected car ecosystem.
The ride sharing and hailing segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 18.7% over the forecast period owing to the rapid urbanization and proliferation of app-based mobility services. Ola and Uber have integrated connected car technologies to enhance user experience, offering features like real-time tracking and cashless payments. According to a report by RedSeer Consulting, ride-hailing platforms facilitated over 1 billion trips in 2022, with connected cars accounting for 30% of the fleet. The integration of AI-driven safety features, such as driver fatigue monitoring, has further boosted consumer confidence. Additionally, government incentives for shared mobility align with sustainability goals, as shared rides reduce carbon emissions by 25%. As urban mobility evolves, ride sharing/hailing is poised to transform the connected car market by prioritizing convenience and eco-friendliness.
India Connected Car Market By Platform
The android auto segment had the leading share of 45.4% in the Indian market in 2024 owing to its compatibility with a wide range of Android smartphones, which dominate the Indian mobile market. Android devices account for over 90% of smartphone sales in India, making Android Auto the preferred choice for seamless integration. Its user-friendly interface and support for regional languages enhance accessibility, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities. Furthermore, partnerships with local automakers like Mahindra and Hyundai have expanded its reach, with over 1.5 million vehicles equipped with Android Auto in 2022. The platform’s emphasis on navigation, music streaming, and voice commands aligns with consumer preferences, as highlighted by a study from TechARC. By bridging the gap between smartphones and vehicles, Android Auto plays a pivotal role in democratizing connected car technologies across diverse demographics.
The integrated systems segment is predicted to progress at a CAGR of 22.3% over the forecast period owing to the increasing demand for all-in-one solutions that combine hardware and software seamlessly. Tata Consultancy Services notes that integrated systems reduce dependency on external devices, offering a streamlined user experience. For instance, Tata Motors’ Nexon EV features an embedded infotainment system with real-time traffic updates and remote diagnostics, appealing to tech-savvy consumers. Additionally, the rise of electric vehicles has amplified adoption, as integrated systems optimize battery management and energy efficiency. A report by EY highlights that integrated platforms can enhance vehicle resale value by 15%, further incentivizing manufacturers to invest in this segment. As consumer expectations evolve, integrated systems are set to redefine the connected car landscape by delivering unparalleled convenience and functionality.
India Connected Car Market By Connectivity Form Factor
The embedded form is predicted to be the most essential and fastest-growing form factor for connected cars in India during the foreseen period. One of the key drivers burgeoning the embedded segment is the surge in demand for infotainment and navigation services in vehicles in India. The Indian government has also started implementing several mandates for connected services.
India Connected Car Market By Hardware
The sensors segment occupied 35.8% of the European market share in 2024. The demand for radar and LiDAR sensors has surged by 40% in 2022, driven by the rise of ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems). Bosch, a leading supplier, has developed sensors capable of detecting obstacles within milliseconds, enhancing road safety. Additionally, the integration of IoT-enabled sensors facilitates real-time data collection, optimizing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. A study by Deloitte highlights that sensor-equipped vehicles can lower accident rates by 30%, underscoring their importance. As automakers prioritize innovation, sensors remain indispensable for advancing the connected car ecosystem.
The smart antennas segment is expected to expand at a CAGR of 25.6% during the forecast period due to their ability to support multiple connectivity technologies, including 5G and V2X communication. The deployment of smart antennas in connected cars has increased by 50% since 2020, enabling seamless data exchange and enhanced navigation. Companies like Harman and Continental have pioneered multi-band antennas that improve signal strength and reduce latency. Furthermore, the advent of autonomous vehicles has amplified demand, as smart antennas facilitate real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure. A report by PwC highlights that smart antennas can reduce connectivity disruptions by 40%, ensuring uninterrupted performance. As connectivity becomes paramount, smart antennas are set to revolutionize the hardware landscape.
India Connected Car Market By Connectivity Technology
The cellular technology segment occupied 60.7% of the Indian market share in 2024 owing to its widespread availability and compatibility with existing infrastructure. According to Ericsson, India’s 4G network coverage exceeds 90%, providing a robust foundation for cellular-based connected car solutions. Platforms like Jio’s IoT ecosystem have enabled automakers to integrate telematics and infotainment systems seamlessly. Additionally, the rollout of 5G networks is expected to enhance data transfer speeds by 10 times, facilitating real-time applications such as remote diagnostics and over-the-air updates. A study by KPMG highlights that cellular connectivity reduces implementation costs by 25% compared to DSRC, making it a cost-effective choice. As urban centers embrace smart mobility, cellular technology remains central to the connected car ecosystem.
The dedicated short range communication (DSRC) segment is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 28.4% over the forecast period due to its reliability in vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication. According to NITI Aayog, DSRC systems have demonstrated a 30% improvement in traffic flow and a 20% reduction in accidents during pilot projects. Tata Motors has integrated DSRC in its commercial vehicles to enable real-time hazard alerts and collision avoidance. Furthermore, the technology’s low latency and high security make it ideal for autonomous driving applications. A report by Accenture highlights that DSRC can enhance road safety by 40%, positioning it as a game-changer for the connected car market. As smart city initiatives gain momentum, DSRC is set to play a transformative role.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
India's connected vehicle market is predicted to point out a double-digit rate of growth in the foreseen years. Consumers in this nation are increasingly emphasizing in-car technology instead of the worth or engine performance when it involves buying a car, and 40% are willing to vary brands for better connectivity.
India's connected vehicle market is predicted to register a double-digit growth rate in the coming years. Consumers in the country are increasingly emphasizing in-car technology and engine performance, but less on worth to some extent, and 40% are willing to vary brands for better connectivity. Also, it holds a strong place in the heavy vehicles market worldwide because it is the third-largest maker in this category, 2nd biggest producer of buses, and the largest manufacturer of tractors. Besides this, multiple policies and initiatives by the Indian government, like the scrappage policy, the Automotive Mission Plan 2026, and the production-linked incentive scheme, are projected to place this market as the world leader in four and two-wheelers. Moreover, there was a rising influx of cumulative equity FDI of around 35.65 billion dollars between April 2000 and December 2023. And it is on the right course to establish itself as the largest electric vehicle industry by 2030, with overall investment prospects of more than 200 billion dollars in the coming 8 to 10 years. Furthermore, buyers are also purchasing cars with built-in internet and other connected features. Companies like BYD and Morris Garages are actively launching internet-based SUVs and mini-SUVs. Additionally, the country has also registered growth in luxury cars in recent years. For example, 1340 premium cars were sold by BMW in January 2024, which made it the highest in the category. At the same time, Mercedes-Benz was able to sell 1333 cars. Therefore, considering all the factors, the India-connected car market will thrive in the future.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Honda Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, Hyundai Motors, General Motors (U.S.), Ford Motor Company (U.S.), Audi (Germany), BMW (Germany), Mahindra and Mahindra (India), Tata Motors (India) and Maruti Suzuki India (India) are some of the major key players involved in the India-connected car market.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THIS MARKET
- The $20.7 billion Mahindra Group and US car major Ford Motor Company on Wednesday signed two definitive agreements on gearing and connected car solutions to secure their ongoing strategic alliance discussion in India that began in late 2017.
- Electric vehicles, petrol engines, and connected vehicles are going to be among the key technology focus areas for Mahindra & Mahindra in the wake of adjusting business landscape, the corporation has said.
- Tata Elxsi, the planning and technology services firm, a Tata group company, has introduced a partnership with Tata Motors to build a unified, connected vehicle platform that will power the Nexon EV range of electric cars.
- Motors and Microsoft India have announced a strategic agreement to redefine connected and personalized driving experiences for Indian consumers. Tata Motors will leverage Microsoft's connected vehicle technologies that compile AI (AI), advanced machine learning, and therefore the Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities on the regional hyper-scale Azure cloud to traverse the digital and physical worlds and make a highly personalized, smart and safer driving experience across the digital life of a vehicle owner.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the India connected car market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on the application, platform, connectivity form factor, hardware, connectivity technology, and region.
By Application
- Telematics
- Ridesharing/Hailing
- Others (OTA Updates, Safety & Security, Autonomous Driving)
By Platform
- Android Auto
- Carplay
- Mirrorlink
- Others
By Connectivity Form Factor
- Embedded
- Tethered
- Integrated
By Hardware
- Smart Antenna
- Display
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
- Sensors
By Connectivity Technology
- Cellular
- Dedicated Short Range Communication (DSRC)
Frequently Asked Questions
what is the current size of the connected market in India?
The connected car market in India is estimated to be worth USD 17.19 billion in 2023.
Which regions in India show the highest adoption of connected car technology?
Southern India, particularly Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, has witnessed significant adoption due to the presence of technology hubs and urban development.
What percentage of the Indian automotive market is comprised of connected vehicles?
Currently, connected vehicles constitute approximately 40% of the overall automotive market in India.
What is the expected growth rate of the connected car market in South India over the next five years?
The expected growth rate of CAGR is 21.45% during the forecast period 2023 to 2028.
who are the key market players involved in the connected market in India?
Honda Motor Company, Toyota Motor Corporation, Hyundai Motors, General Motors (U.S.), Ford Motor Company (U.S.), Audi (Germany), BMW (Germany), Mahindra and Mahindra (India), Tata Motors (India), Maruti Suzuki India (India).
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 1200
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]