Global Hydrogen Generator Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Source (Blue hydrogen, Gray Hydrogen, and Green Hydrogen), Technology, Application, Generation and Delivery mode, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Hydrogen Generator Market Size
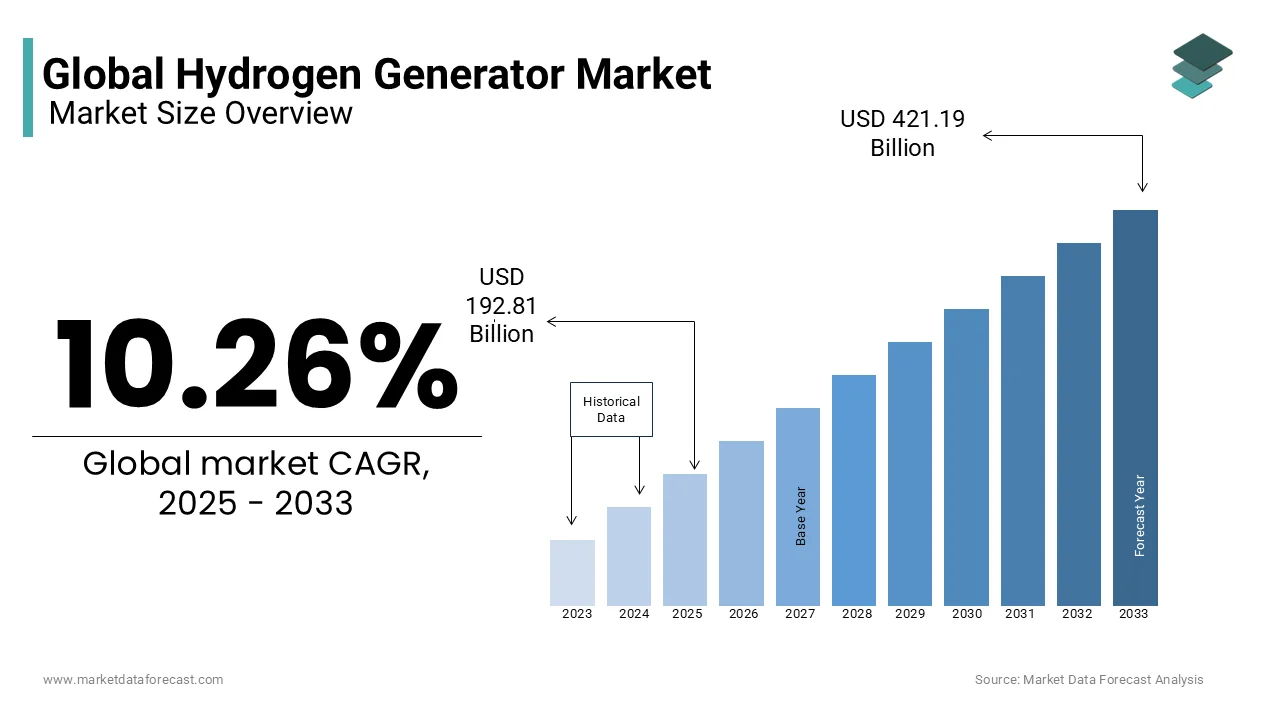
The global hydrogen generator market was valued at USD 174.87 billion in 2024. The global market is expected to reach USD 421.19 billion by 2033 from USD 192.81 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 10.26% from 2025 to 2033.
Hydrogen generators are devices engineered to produce hydrogen gas (H₂) through various technological processes, primarily electrolysis and steam methane reforming (SMR). Electrolysis involves splitting water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen using electrical energy, ideally sourced from renewables to minimize environmental impact. SMR, conversely, reacts natural gas with steam to extract hydrogen, a method prevalent in industrial applications.
In 2023, global hydrogen production reached approximately 97 million tonnes, with less than 1% classified as low-emission hydrogen. The majority of hydrogen is produced via SMR, a process that consumes about 44.5 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of natural gas per kilogram of hydrogen generated. This method is energy-intensive and contributes significantly to CO₂ emissions. Electrolysis, while offering a cleaner alternative, typically requires 50–55 kWh of electricity to produce the same amount of hydrogen, depending on the efficiency of the electrolyzer used.
The primary consumers of hydrogen are the refining and industrial sectors. In 2023, oil refineries utilized approximately 40 million tonnes of hydrogen, primarily for hydrocracking processes that convert heavy petroleum fractions into lighter, more valuable products. Industrial applications accounted for about 54 million tonnes, with significant usage in ammonia production for fertilizers (34 million tonnes), methanol synthesis (15 million tonnes), and the manufacture of direct reduced iron (5 million tonnes), essential for steelmaking.
MARKET DRIVERS
Technological Advancements Reducing Production Costs
Recent technological innovations have significantly decreased the cost of hydrogen production, particularly through electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global average levelized cost of hydrogen production from renewable electricity is projected to fall to approximately USD 2-9 per kilogram by 2030, which is about half of today's value. This reduction is primarily due to declining costs of renewable energy and the scaling up of hydrogen production technologies. Such cost reductions enhance the economic feasibility of hydrogen generators by making them more attractive for various applications across industries.
Government Policies and Financial Incentives
Governments worldwide are implementing policies and financial incentives to promote the adoption of clean hydrogen technologies. In the United States, the Department of Energy (DOE) released an updated Hydrogen Program Plan in December 2024, outlining strategic, high-impact areas for research, development, demonstration, and deployment of clean hydrogen technologies. This plan aims to facilitate large-scale production and utilization of clean hydrogen, thereby accelerating the transition to a hydrogen-based economy. Such governmental support is crucial in driving the growth of the hydrogen generator market by fostering innovation and providing financial incentives for adoption
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production Costs
The production of hydrogen, especially through electrolysis, remains economically challenging. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, as of 2024, the cost of producing low-carbon hydrogen via electrolysis is estimated at $5 to $7 per kilogram, excluding tax credits. This high cost is primarily due to elevated electricity prices, installation expenses, and capital costs. In contrast, hydrogen produced from natural gas with carbon capture (reformation-based methods) is comparatively less expensive, ranging from $1.8 to $2.2 per kilogram. These financial disparities pose significant barriers to the widespread adoption of hydrogen generators, as industries may find it economically unfeasible to transition from traditional energy sources to hydrogen-based systems.
Insufficient Infrastructure Development
The current infrastructure for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is underdeveloped, hindering the market's growth. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, need for substantial advancements in hydrogen infrastructure to facilitate large-scale adoption. This includes developing efficient storage solutions by expanding transmission and distribution networks, and establishing reliable delivery and dispensing systems. The lack of a comprehensive infrastructure not only escalates the costs associated with hydrogen utilization but also raises concerns about the reliability and safety of its supply chain. Addressing these infrastructural challenges requires coordinated efforts and significant investments from both public and private sectors to create a robust hydrogen economy.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Industrial Applications
The hydrogen generator market is poised to capitalize on the increasing demand for clean energy solutions in industrial sectors. As per U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), industrial applications, such as ammonia production, methanol synthesis, and steel manufacturing, are significant consumers of hydrogen. The adoption of hydrogen as a cleaner alternative is gaining momentum as industries strive to reduce carbon emissions. The DOE's updated "Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Clean Hydrogen" report shows that the United States is on track to achieve 7 to 9 million metric tons per annum of clean hydrogen production capacity by 2030, driven by industrial sector demand. This trend presents substantial growth opportunities for hydrogen generator manufacturers to supply the necessary technology for industrial decarbonization.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of hydrogen production with renewable energy sources offers a promising avenue for market expansion. The DOE's "Pathways to Commercial Liftoff: Clean Hydrogen" report emphasizes that advancements in electrolyzer technologies, coupled with decreasing costs of renewable energy, are making green hydrogen more economically viable. The report projects that the United States is on track to reach 7 to 9 million metric tons per annum of clean hydrogen production capacity by 2030, facilitated by renewable energy integration. This development not only enhances energy storage capabilities but also provides a sustainable solution for sectors aiming to transition to low-carbon energy systems, thereby creating significant opportunities for the hydrogen generator market.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Environmental Concerns
The production of hydrogen, particularly through methods like steam methane reforming (SMR), raises significant environmental concerns. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, SMR is the most common method for hydrogen production, but it results in substantial carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions, contributing to climate change. Additionally, hydrogen itself, when released into the atmosphere, can act as an indirect greenhouse gas by extending the atmospheric lifetime of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This factor leverages the importance of developing and implementing cleaner hydrogen production technologies to mitigate environmental impacts.
High Water Consumption
Hydrogen production processes, especially electrolysis, require significant water inputs. The U.S. Department of Energy's studies have shown that producing hydrogen via electrolysis consumes approximately 9 liters of water per kilogram of hydrogen produced. In regions facing water scarcity, this level of water consumption could exacerbate existing water stress, posing challenges for the sustainable scaling of hydrogen production. Therefore, addressing water usage through technological innovations and resource management is crucial for the hydrogen generator market's growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
10.26% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Source, Technology, Application, Generation and Delivery Mode, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ALFA LAVAL (Sweden), Kelvion Holding GmbH (Germany), Danfoss (Denmark), Exchanger Industries Limited (Canada), Mersen (France), API Heat Transfer (US), Boyd (US), H. Güntner (UK) Limited (Germany), Johnson Controls (Ireland), Xylem (US), Wabtec Corporation (US), SPX FLOW (US), LU-VE S.p.A. (Italy), Lennox International Inc. (US), and Modine Manufacturing Company (US). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By source Insights
The grey hydrogen dominated the hydrogen generator market with 59.1% of the total share in 2024 owing to its cost-effectiveness, primarily produced via steam methane reforming using natural gas. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, natural gas prices significantly influence grey hydrogen's affordability, with production costs averaging $1-$2 per kilogram. Despite its environmental drawbacks, emitting about 9-12 kg of CO2 per kg of hydrogen, grey hydrogen remains integral due to established infrastructure and scalability, making it a transitional solution until cleaner alternatives scale up.
The green hydrogen is anticipated to witness a significant CAGR 54.7% during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is fueled by plummeting renewable energy costs, with solar and wind prices dropping by over 80% since 2010, as stated by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Governments worldwide are accelerating green hydrogen adoption; for instance, the European Union aims to install 40 gigawatts of electrolyzers by 2030. Green hydrogen’s importance lies in its potential to decarbonize industries, with the Hydrogen Council estimating it could reduce global emissions by 34 million metric tons annually by 2030. Its zero-emission profile positions it as a cornerstone for achieving net-zero goals.
By Technology Insights
The steam Methane Reforming (SMR) dominated the hydrogen generator market and held 40.1% of share in 2024. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, SMR produces hydrogen at $1–2 per kilogram, significantly lower than other methods. Its widespread adoption supports industries like ammonia production and refining, which consume over 55 million tons of hydrogen annually. Despite its reliance on fossil fuels, SMR remains pivotal due to its scalability and reliability in meeting industrial hydrogen demands.
The electrolysis segment is likely to witness a fastest CAGR of 14.2% during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is driven by the global push for green hydrogen, produced via renewable-powered electrolyzers. The Hydrogen Council projects that electrolyzer capacity could reach 850 GW by 2030, up from just 0.3 GW in 2020. Governments like the European Union are investing heavily, committing €470 billion to hydrogen infrastructure by 2050. Electrolysis aligns with net-zero goals by enabling decarbonization in sectors such as steel and transportation.
By Application Insights
The petroleum refinery segment was the largest by occupying 35.1% of the hydrogen generator market share in 2024. This dominance is due to the critical role of hydrogen in hydrocracking and desulfurization processes, which are essential for producing cleaner fuels. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), refineries consume nearly 5% of global hydrogen production annually. This segment's importance lies in its ability to meet regulatory standards while supporting the transition to cleaner energy sources.
The power generation segment is likely to experience a fastest CAGR of 8.2% during the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cells for clean energy production and grid stabilization. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, hydrogen-based power systems can reduce carbon emissions by up to 30% compared to conventional fossil fuel technologies. Hydrogen's role in decarbonizing power sectors becomes pivotal as countries aim to achieve net-zero emissions. Investments in green hydrogen projects, such as the $8 billion allocated under the U.S. Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, further accelerate this trend.
By Generation and Delivery Mode Insights
The captive hydrogen generation segment dominated the market by capturing 50.2% of the global hydrogen generator market share in 2024. This mode involves on-site hydrogen production for direct industrial use, particularly in refining and ammonia synthesis. Its dominance stems from cost efficiency and reliability by minimizing transportation expenses. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, captive models reduce hydrogen delivery costs by up to 30% by making them indispensable for energy-intensive industries. With over 75 million tons of hydrogen produced annually for industrial applications, captive systems ensure consistent supply.
The merchant hydrogen delivery is the fastest-growing segment with a projected CAGR of 6.8% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by rising demand for clean hydrogen in mobility and power sectors, where centralized production and distribution are more feasible. The Hydrogen Council studies have shown that merchant hydrogen could supply up to 15% of global energy needs by 2050. Governments like the European Union are investing heavily in hydrogen pipelines and storage infrastructure by aiming to expand merchant networks. According to the IEA, global investments in hydrogen infrastructure exceeded $10 billion in 2022 by emphasizing its importance in scaling green hydrogen adoption. Merchant models enable scalable, flexible supply chains, driving their rapid expansion.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific led the hydrogen generator market with 45.1% of the global share in 2024. This dominance is driven by China, Japan, and South Korea, which are aggressively investing in hydrogen technologies. China alone accounts for over 30% of global hydrogen production, primarily for industrial use, while Japan’s Green Growth Strategy targets 20 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2050. According to the Asian Development Bank, the region’s hydrogen investments exceeded $50 billion in 2022.
Europe hydrogen generator market is likely to experience a fastest CAGR of 7.2% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by stringent EU climate policies, including the European Green Deal, which mandates a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. Germany and France are leading investments, with the European Commission allocating €470 billion for hydrogen projects by 2030. According to the IEA, Europe aims to produce 10 million tons of renewable hydrogen annually by 2030. The region’s focus on green hydrogen, coupled with robust funding and policy frameworks, which positions it as a global leader in clean energy innovation.
North America is expected to grow steadily, driven by U.S. Department of Energy initiatives like the Hydrogen Shot program, targeting $1 per kilogram of clean hydrogen by 2030. Latin America shows promise due to its abundant renewable resources, with Chile aiming for 5 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2030. The Middle East and Africa are leveraging their solar potential, with Saudi Arabia’s NEOM project aiming to produce 650 tons of green hydrogen daily. These regions collectively represent a $30 billion investment opportunity by 2030, as per the Hydrogen Council, underscoring their strategic importance in the global hydrogen economy.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global hydrogen generator market include Linde plc (Ireland), ENGIE (France), Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. (US), Saudi Arabian Oil Co. (Saudi Arabia), Iwatani Corporation (Japan), Air Liquide (France), Orsted A/S (Germany), Equinor ASA (Norway), Shell plc (UK), Chevron Corporation (US), Exxon Mobil Corporation (US), BP p.l.c. (UK), Petroliam Nasional Berhad (PETRONAS) (Malaysia), Siemens (Germany), Hiringa Energy Limited (New Zealand), Messer Group (Germany), Uniper SE (Germany), Iberdrola, S.A. (Spain), BayoTech (US), and HyGear (the Netherlands).
Top 3 Players in the Market
Linde plc (Ireland)
Linde plc is a global leader in the hydrogen generator market, renowned for its cutting-edge technologies and extensive infrastructure. The company specializes in both traditional and renewable hydrogen production methods, including electrolysis and steam methane reforming. Linde has established itself as a pioneer in green hydrogen, actively participating in large-scale projects such as collaborations to build advanced electrolyzers. Its commitment to sustainability and innovation has positioned it as a key player in the global hydrogen economy, enabling cleaner energy solutions across industries.
Air Liquide (France)
Air Liquide is another dominant force in the hydrogen generator market, leveraging its expertise in industrial gases to drive hydrogen adoption worldwide. The company operates an extensive network of hydrogen refueling stations and is deeply involved in initiatives to scale low-carbon hydrogen production. Air Liquide’s participation in international alliances and its focus on renewable energy integration expands its dedication to decarbonization. By advancing hydrogen technologies and infrastructure, Air Liquide plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable energy systems globally.
Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. (US)
Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. is a major contributor to the hydrogen generator market, with a strong emphasis on developing innovative hydrogen solutions. The company is at the forefront of large-scale green hydrogen projects, including landmark initiatives aimed at producing renewable hydrogen using solar and wind energy. Air Products’ advancements in hydrogen liquefaction and storage have enhanced the efficiency of hydrogen supply chains.
Top Strategies Used by the Key Market Participants
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Leading companies like Linde plc and Air Liquide have forged strategic alliances with technology providers, governments, and research institutions to accelerate hydrogen innovation. For instance, partnerships with electrolyzer manufacturers such as ITM Power enable these firms to integrate advanced technologies into their operations. Collaborations also extend to joint ventures for large-scale projects, such as Air Products’ involvement in the NEOM green hydrogen project, which demonstrates how shared expertise and resources can drive market’s growth.
Investments in Green Hydrogen Projects
To align with global decarbonization targets, key players are heavily investing in green hydrogen production. Companies like ENGIE and Orsted A/S are developing renewable-powered electrolysis plants, ensuring a sustainable and scalable supply of hydrogen. These investments not only position them as leaders in clean energy but also help reduce reliance on fossil fuel-based hydrogen production methods.
Expansion of Refueling Infrastructure
Companies such as Shell plc and Iwatani Corporation are focusing on building extensive hydrogen refueling networks to support the adoption of fuel cell vehicles. By expanding infrastructure, these firms address one of the primary barriers to hydrogen mobility, fostering greater consumer confidence and market penetration.
Research and Development (R&D)
Continuous R&D is a cornerstone strategy for firms like Siemens and Messer Group, which are innovating in areas such as hydrogen storage, liquefaction, and transportation. Advancements in these fields improve efficiency and reduce costs, making hydrogen more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Policy Advocacy and Government Engagement
Players like Equinor ASA and Chevron Corporation actively engage with policymakers to shape hydrogen-friendly regulations and secure funding for projects. Their involvement in initiatives like the European Clean Hydrogen Alliance ensures alignment with government priorities while unlocking financial incentives.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The hydrogen generator market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the growing global emphasis on decarbonization and the transition to sustainable energy systems. Key players such as Linde plc, Air Liquide, and Air Products and Chemicals, Inc. dominate the landscape, leveraging their technological expertise, extensive infrastructure, and strategic investments to maintain its dominance. These companies are increasingly focusing on green hydrogen projects, aligning with international climate goals and capitalizing on government incentives to scale renewable energy solutions.
Emerging competitors, including regional firms like Hiringa Energy Limited and BayoTech, are also gaining traction by targeting niche markets and offering innovative, modular hydrogen generation systems. This diversification has intensified competition, pushing established players to innovate and expand their offerings. Collaborations and partnerships have become a critical strategy, with firms joining forces to develop large-scale projects and share risks associated with high-capital investments.
Geographically, Europe and Asia-Pacific are hotbeds of competition due to favorable policies and substantial funding for hydrogen initiatives. North America is also witnessing rising rivalry as companies vie for federal grants under programs like the U.S. Department of Energy’s Hydrogen Shot. The competitive dynamics are further shaped by the race to reduce production costs and improve efficiency, particularly in electrolysis technologies. As demand for hydrogen grows across industries such as transportation, refining, and power generation, companies are under pressure to differentiate themselves through sustainability commitments, technological advancements, and scalable solutions, ensuring their position in this rapidly evolving market.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In July 2021, Linde Engineering announced the construction of the world’s largest PEM electrolyzer for green hydrogen production in Leuna, Germany. This project is anticipated to significantly enhance Linde's capacity to produce renewable hydrogen while addressing the global challenge of climate change. The electrolyzer, with a capacity of 24 MW, will be built, owned, and operated by Linde, underscoring its commitment to advancing sustainable energy solutions.
- In February 2025, Air Liquide announced a series of major investments aimed at supporting European decarbonization efforts in collaboration with TotalEnergies. This strategic move is anticipated to accelerate the development of low-carbon hydrogen production facilities across Europe. By leveraging its expertise in industrial gases and clean energy technologies, Air Liquide aims to strengthen its position as a key player in the transition to a sustainable energy future while fostering partnerships that drive large-scale decarbonization initiatives.
- In July 2021, NEOM announced a landmark $7 billion investment in the NEOM Green Hydrogen Project in Saudi Arabia, developed in partnership with Air Products and ACWA Power. This initiative is set to become the world’s largest green hydrogen production facility, powered entirely by renewable energy. With an expected output of 650 tons of hydrogen per day, the project aims to supply carbon-free hydrogen for global markets, supporting decarbonization efforts across industries.
- In November 2021, ENGIE achieved a significant milestone in its Australian renewable hydrogen project with Yara International, following the approval of an ARENA (Australian Renewable Energy Agency) grant. This project aims to construct a 100 MW green hydrogen plant to produce renewable ammonia, supporting the decarbonization of agriculture and energy sectors. By integrating renewable energy into hydrogen production, ENGIE and Yara are paving the way for sustainable ammonia use in fertilizers and beyond.
- In May 2023, Shell announced the expansion of its hydrogen refueling network in Europe, adding 50 new stations across Germany and the Netherlands. This initiative is part of Shell's broader strategy to support the adoption of fuel cell vehicles and strengthen its position in the clean mobility sector. By expanding its hydrogen infrastructure, Shell aims to address one of the key barriers to hydrogen vehicle adoption—limited refueling availability—while advancing its commitment to renewable energy solutions. This move escalates Shell's dedication to fostering sustainable transportation and positioning itself as a leader in the transition to low-carbon energy systems.
- In August 2022, Equinor announced that its H2H Saltend project in the UK was selected as one of the first projects to receive funding under the UK government’s Hydrogen Business Model. This initiative aims to produce large-scale blue hydrogen to decarbonize industrial clusters in the Humber region. By integrating carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology, the project seeks to reduce emissions while providing clean energy for industrial use.
- In February 2023, Siemens Energy announced the development of its next-generation electrolyzer technology with the establishment of a gigawatt-scale factory for electrolyzer production. This initiative is designed to enhance the efficiency and scalability of green hydrogen production, supporting global decarbonization efforts. By ramping up manufacturing capabilities, Siemens Energy aims to meet the growing demand for renewable hydrogen solutions while driving down costs.
- In March 2022, Orsted announced a partnership with Maersk to supply green hydrogen for the shipping industry. This collaboration aims to decarbonize maritime operations by replacing fossil fuels with renewable hydrogen-based solutions. The project expands Orsted’s commitment to driving innovation in clean energy and supporting hard-to-abate sectors like shipping. By leveraging its expertise in renewable energy production, Orsted is positioned to play a pivotal role in advancing sustainable practices within the global shipping industry, further promoting its importance in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- In October 2022, Chevron Corporation invested in Acme Group’s green hydrogen and ammonia project in India. This investment is expected to mark Chevron’s entry into the renewable hydrogen space in Asia-Pacific and diversify its energy portfolio.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global hydrogen generator market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Source
- Blue hydrogen
- Gray Hydrogen
- Green Hydrogen
By Technology
- Steam Methane Reforming (SMR)
- Partial Oxidation (POX)
- Auto Thermal Reforming (ATR)
- Coal Gasification
- Electrolysis
By Application
- Petroleum Refinery
- Transportation
- Ammonia Production
- Methanol Production
- Power Generation
- Others
By Generation and Delivery Mode
- Captive
- Merchant
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the global hydrogen generator market?
Increasing demand for clean energy, government incentives, and advancements in hydrogen production technology are key growth drivers.
Which industries use hydrogen generators the most?
Hydrogen generators are widely used in energy, transportation, chemical manufacturing, and industrial sectors for clean fuel and industrial applications.
What role does hydrogen play in the future of transportation?
Hydrogen fuel cells are gaining traction in electric vehicles, buses, and trains, offering longer ranges and faster refueling compared to batteries.
What is the future outlook for the hydrogen generator market?
Growing investments, technological advancements, and global decarbonization efforts are expected to drive significant market expansion in the coming years.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]