Global Hydrogen Engine Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Type (Power Below 100KW, Power between 100kW and 300kW, and Power above 300kW), Application (Automotive, Power Generation, and Others) and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Hydrogen Engine Market Size
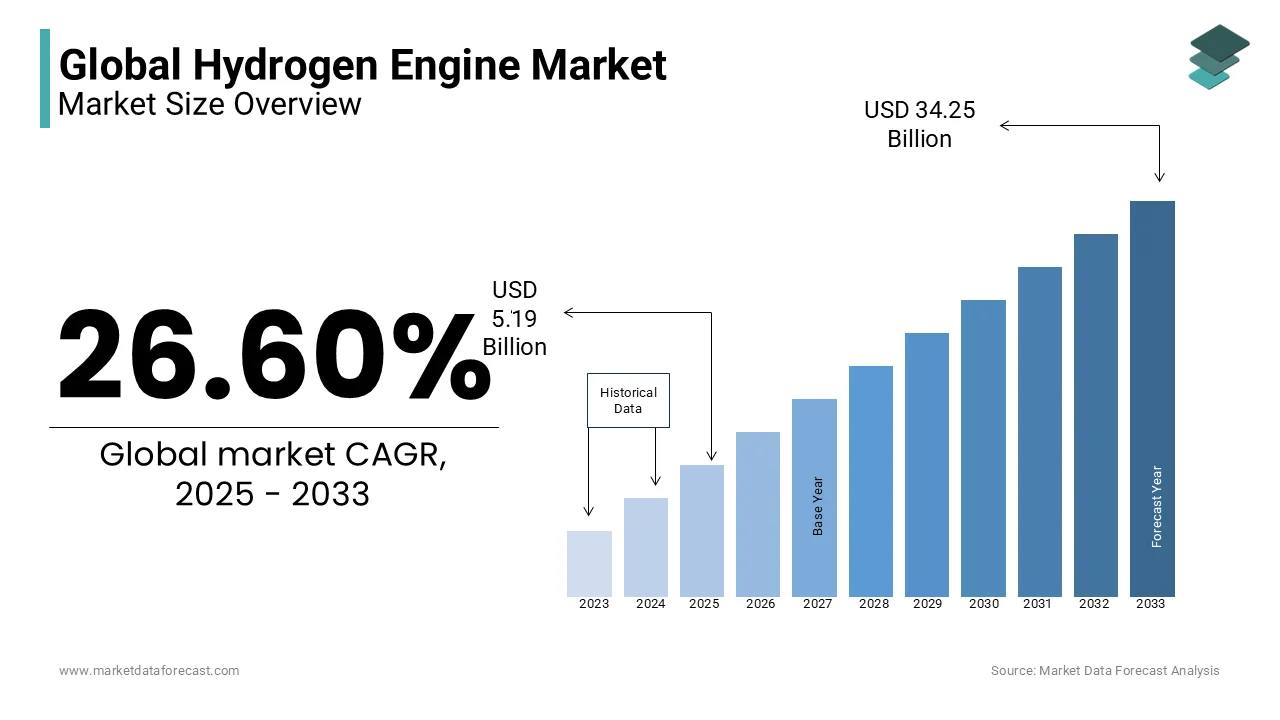
The global hydrogen engine market was worth USD 4.10 billion in 2024. The global market is projected to reach USD 34.25 billion by 2033 from USD 5.19 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 26.60% from 2025 to 2033.
Hydrogen engines, which utilize hydrogen as a fuel source, offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines (ICEs) by producing zero carbon emissions during operation. These engines are particularly attractive for heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, buses, ships, and industrial machinery, where battery-electric solutions face limitations in terms of range and energy density.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), hydrogen demand has tripled since 1975, with industrial and transportation sectors driving growth. Governments worldwide are investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, with the European Union committing €430 billion by 2030 under its Hydrogen Strategy. Similarly, Japan’s Basic Hydrogen Strategy aims to establish a hydrogen-based society by 2050. Technological advancements, such as improved fuel cell efficiency and hydrogen storage solutions are further accelerating market adoption.
MARKET DRIVERS
Decarbonization Goals and Emission Regulations
Governments worldwide are driving the adoption of hydrogen engines through stringent emission regulations and ambitious decarbonization goals. The European Union, for example, has set targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030 with hydrogen as a key energy source to meet these goals. Similarly, the United States has launched the Hydrogen Earthshot initiative by aiming to reduce the cost of clean hydrogen by 80% to $1 per kilogram by 2030. These regulations and targets create strong demand for hydrogen engine technologies as industries seek to comply and reduce carbon footprints.
Heavy-Duty Vehicle Electrification
Hydrogen engines are increasingly favored for heavy-duty vehicles where electric battery technology faces limitations in range and refueling times. Hydrogen engines offer rapid refueling with times comparable to traditional fuel engines, and can support longer driving ranges essential for sectors like freight trucking and public transport. Studies suggest hydrogen-fueled trucks can have ranges up to 700-800 km per refuel, an advantage over battery-electric options. The shift to hydrogen engines for commercial fleets with transportation contributing over 20% of global emissions plays a crucial role in addressing climate goals.
Investments in Hydrogen Production and Infrastructure
The hydrogen engine market is bolstered by growing investments in hydrogen production technologies by including green hydrogen derived from renewable energy. Major energy companies and governments are investing billions into production plants and infrastructure to bring down hydrogen costs and improve supply stability. For instance, Europe’s Hydrogen Strategy envisions up to €470 billion invested by 2050 to build a robust hydrogen economy. The availability and affordability of hydrogen will improve by making hydrogen engines a more viable and attractive option across industries.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production and Storage Costs
Hydrogen production, particularly green hydrogen from renewable sources, remains expensive, making hydrogen engines less economically competitive. Producing green hydrogen currently costs between $3 to $6 per kilogram when compared to conventional fuels at under $2 per gallon. Additionally, hydrogen storage requires high-pressure tanks or cryogenic conditions by adding complexity and cost. The infrastructure to store and transport hydrogen is limited, and scaling it would require substantial investment. The high expenses associated with hydrogen production and storage pose a significant restraint to widespread adoption in the hydrogen engine market.
Limited Refueling Infrastructure
A lack of widespread hydrogen refueling stations restricts hydrogen engine adoption, especially in the automotive and heavy-duty vehicle sectors. As of 2023, there are fewer than 1,000 hydrogen refueling stations globally, primarily concentrated in specific regions like Japan, South Korea, and select European countries. Expanding this infrastructure is costly and requires government and industry collaboration. The lack of refueling options limits the practical range and appeal of hydrogen-powered vehicles, especially for long-haul transportation by creating a major barrier to market growth and limiting hydrogen engine deployment in areas without strong infrastructure investment.
Competition with Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) have gained considerable momentum, especially in the light-duty automotive sector, where they are more efficient and supported by extensive charging networks. BEVs benefit from falling battery costs and government incentives by creating strong competition for hydrogen-powered vehicles. The overall energy efficiency of BEV is up to 90% in converting electricity to power which surpasses that of hydrogen engines. As a result, hydrogen engines are often relegated to niche applications in heavy-duty sectors. The strong market presence of BEVs challenges hydrogen engine adoption, especially as BEV technology and infrastructure continue to improve rapidly.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Industrial and Marine Sectors
The industrial and marine sectors present untapped opportunities for hydrogen engines, where long operational hours and high energy demands favor hydrogen’s energy density. The maritime industry, which emits about 2.5% of global CO₂, is exploring hydrogen engines as a cleaner propulsion alternative to traditional heavy fuels. In industrial settings, hydrogen engines can power machinery with high energy needs, reducing dependence on fossil fuels. By capitalizing on hydrogen’s quick refueling and robust power, hydrogen engines can fulfill stringent emission regulations, in shipping, where decarbonization efforts align with hydrogen’s strengths.
Technological Advancements in Fuel Cell Efficiency
Ongoing advancements in fuel cell technology create opportunities to make hydrogen engines more viable across various applications. Emerging solid oxide and proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells have demonstrated higher durability and energy efficiency, making them ideal for hydrogen engines. Fuel cells now achieve efficiencies of 60% or more in electric energy conversion with improvements in materials like graphene-enhanced catalysts that reduce precious metal requirements. Hydrogen engines can become competitive for sectors like transportation and power generation to boost their market appeal.
Government Incentives and Carbon Credits
Governments worldwide are introducing incentives and carbon credits to promote hydrogen as part of their decarbonization strategies. In the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act offers substantial subsidies and tax credits for clean hydrogen production which can lower costs for hydrogen engine applications. The European Union’s Hydrogen Strategy includes funding initiatives that support hydrogen infrastructure and usage in transport. Carbon credit systems also reward companies for adopting low-emission technologies like hydrogen engines. Such policies make hydrogen engines financially attractive by offsetting production costs and providing an economic edge for companies prioritizing sustainability.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Energy Efficiency and Storage Challenges
Hydrogen engines face significant energy efficiency losses during production, storage, and utilization. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, producing hydrogen through electrolysis has an efficiency of only 60–70%, and when used in fuel cells, the overall efficiency drops to around 30–40%. Additionally, storing hydrogen requires high-pressure tanks or cryogenic temperatures, which are energy-intensive and costly. For example, liquid hydrogen storage requires temperatures as low as -253°C is leading to energy losses during the liquefaction process. These inefficiencies make hydrogen engines less competitive compared to battery-electric alternatives, which have higher energy efficiency rates of 80–90%.
Safety Concerns and Public Perception
Hydrogen is highly flammable and requires stringent safety measures for storage, transportation, and usage. While hydrogen engines are designed with advanced safety features, public perception remains a challenge due to incidents like the 2019 explosion at a hydrogen refueling station in Norway. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), safety regulations for hydrogen infrastructure are still evolving is creating uncertainty for investors and consumers. Moreover, the lack of awareness about hydrogen's safety protocols and benefits further slows adoption. Building public trust through education and transparent safety standards is crucial for the market's growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
26.60% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Toyota Motor Corporation, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., BMW Group, Hyundai Motor Company, Cummins Inc., MAN Truck & Bus SE, Volvo Group, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Suzuki Motor Corporation, and Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The Power Above 300kWsegment held 45% of total share in the hydrogen engine market. This dominance is attributed to the segment's application in heavy-duty vehicles and industrial machinery, which require high power outputs. This dominance is driven by its critical role in heavy-duty applications, such as commercial trucks, buses, ships, and industrial machinery, where high power output is essential. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), heavy-duty vehicles contribute to over 40% of global CO2 emissions from the transportation sector, making hydrogen engines a vital solution for decarbonization. Governments and industries are investing heavily in this segment, with the European Union’s Hydrogen Strategy aiming to deploy 60,000 hydrogen-powered trucks by 2030. The segment’s importance lies in its ability to provide zero-emission solutions for industries that are difficult to electrify, ensuring a sustainable transition to clean energy.
Conversely, the Power Below 100kW segment is experiencing the fastest growth, with a projected CAGR of 10.39% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by its versatility in medium-duty applications, such as delivery trucks, municipal vehicles, and regional trains. According to the Hydrogen Council, the demand for medium-duty hydrogen engines is rising due to their optimal balance between power and efficiency by making them ideal for urban and regional logistics. Additionally, the segment benefits from lower infrastructure costs compared to high-power engines, enabling faster adoption. For instance, countries like Japan and South Korea are investing in hydrogen-powered delivery fleets to reduce urban emissions. The segment’s importance lies in its ability to bridge the gap between low-power and high-power applications, driving the hydrogen economy forward.
By Application Insights
In the global hydrogen internal combustion engine (ICE) market, the Automotive segment holds the largest share. This dominance is driven by the automotive industry's pursuit of sustainable and low-emission alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. Hydrogen ICEs offer a viable solution, especially for heavy-duty vehicles such as trucks and buses, where battery-electric options may face limitations due to weight and range constraints. Major truck manufacturers, including Volvo and MAN, are developing hydrogen-powered combustion engines as a low-cost with faster alternative to move away from diesel and toward zero emissions.
The Power Generation segment is experiencing the fastest growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.39% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by the global shift towards renewable energy sources and the need for flexible, low-emission power generation solutions. Hydrogen ICEs can be integrated into existing power infrastructure, providing a reliable and cleaner alternative to conventional fossil-fuel-based generators. Their ability to operate on hydrogen as a clean fuel which makes them an attractive option for reducing greenhouse gas emissions in the power sector.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America holds major share of the global hydrogen engine market with, 35% in 2024, driven by strong government support and technological advancements. The U.S. is the leading country, contributing over 80% of the regional market share, with initiatives like the Hydrogen Shot program aiming to reduce green hydrogen costs to 1perkilogram by 2030. According to the U.S.Department of Energy, the region is investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, withover 1perkilogram by 2030 where 9.5 billion is allocated under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10-12% from 2025 to 2033, fueled by the adoption of hydrogen-powered trucks and buses. Canada is also emerging as a key player, focusing on hydrogen production from renewable sources.

Europe is expected to grow significantly, due to supported by investments in hydrogen-powered trains, trucks, and industrial applications. The region’s dominance is driven by ambitious policies like the European Green Deal and the EU Hydrogen Strategy, which aim to install 40 GW of electrolyzers by 2030. Germany is the largest market by contributing over 25% of the regional share, followed by France and the Netherlands. According to the European Commission, the region has allocated €430 billion for hydrogen projects by making it a hub for innovation and deployment. The focus on decarbonizing heavy industries and transportation is driving the region’s growth.
The Asia-Pacific region is growing at higher rate with a CAGR of 15-18% projected from 2025 to 2033. Rapid industrialization and government initiatives are the factors propelling the growth rate of the market in this region. China is the largest contributor with 50% of the regional share with its Hydrogen Energy Industry Development Plan aiming to deploy 1 million hydrogen-powered vehicles by 2035. Japan and South Korea are also key players by focusing on hydrogen-powered public transport and fuel cell technology. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Asia-Pacific is investing heavily in hydrogen infrastructure, with Japan alone committing $3.4 billion to hydrogen projects. The region’s growth is fueled by the need to reduce air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.
Latin America region is expected to grow at a noteworthy pace, driven by investments in renewable energy and hydrogen infrastructure. Brazil is the leading country with contributing over 40% of the regional share, with its National Hydrogen program focusing on green hydrogen production. Chile is emerging as a key player, leveraging its vast solar and wind resources to produce green hydrogen. According to the Inter-American Development Bank, Latin America could become a major exporter of green hydrogen, with projects like Chile’s HyEx aiming to produce 160,000 tons of hydrogen annually by 2025. The region’s growth is supported by its abundant renewable energy resources and increasing focus on decarbonization.
The Middle East and Africa region is expected to grow with its vast renewable energy potential and strategic investments in hydrogen infrastructure. The UAE and Saudi Arabia are the leading countries, with Saudi Arabia’s NEOM Green Hydrogen Project aiming to produce 1.2 million tons of green hydrogen annually by 2026. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the Middle East could supply 10% of global hydrogen demand by 2050. South Africa is also emerging as a key player by focusing on hydrogen production from renewable sources. The region’s growth is supported by its commitment to diversifying energy exports and reducing carbon emissions.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Toyota Motor Corporation, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., BMW Group, Hyundai Motor Company, Cummins Inc., MAN Truck & Bus SE, Volvo Group, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Suzuki Motor Corporation, and Yamaha Motor Co., Ltd. are some of the major players in the global hydrogen market.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In September 2024, Toyota Motor Corporation, a leader in automotive innovation, expanded its collaboration with BMW Group to develop hydrogen fuel cell technology. Purpose: This partnership is expected to standardize components, reduce costs, and enhance hydrogen vehicle infrastructure.
- In August 2024, BMW Group, a premium automobile manufacturer, announced plans to launch its first hydrogen-powered vehicle by 2028 in partnership with Toyota. Purpose: This move aims to diversify BMW's zero-emission vehicle portfolio and leverage hydrogen technology for sustainable mobility.
- In June 2024, Wärtsilä Corporation, a leader in smart energy technologies, launched the world’s first large-scale, 100% hydrogen-ready engine power plant. Purpose: This initiative is anticipated to support net-zero power systems and advance hydrogen use in power generation.
- In May 2024, MAN Energy Solutions, known for large-bore diesel engines, signed a contract with Karpowership to deliver 48 dual-fuel engines for their fleet. Purpose: This deal is set to enhance the sustainability and flexibility of maritime power solutions.
- In April 2024, Hyundai Motor Company announced plans to offer 21 electric vehicle models by 2030, including hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Purpose: This expansion is intended to increase Hyundai’s global EV sales and boost its investments in hydrogen fuel cell technology.
- In March 2024, Plug Power Inc., a hydrogen fuel-cell company, reported a 31% increase in operating cash flows, partially from heightened electrolyzer sales. Purpose: This financial improvement is aimed at supporting the company’s growth in hydrogen infrastructure.
- In February 2024, Kohler Energy, an energy solutions provider, announced a new hydrogen KDI engine and its first hydrogen fuel cell power system. Purpose: This launch is expected to broaden Kohler’s clean energy portfolio and accelerate its clean energy initiatives.
- In January 2024, ZeroAvia, focused on zero-emission aviation, successfully conducted a 10-minute flight of its Dornier 228 with a hydrogen-electric powertrain. Purpose: This test flight supports ZeroAvia’s development of hydrogen-electric systems for regional aircraft.
- In December 2023, Honda Motor Co., Ltd. started producing a new hydrogen fuel cell system co-developed with General Motors. Purpose: This production is expected to enhance Honda’s capabilities in hydrogen technology and expand its fuel cell vehicle lineup.
- In November 2023, Uniper, a German utility company, announced a slowdown of its €8 billion investment in greener fuels due to lower-than-expected hydrogen demand. Purpose: This adjustment aims to realign Uniper’s strategy with current market demand for hydrogen.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global hydrogen engine market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Power Below 100KW
- Power between 100kW and 300kW
- Power above 300kW
By Application
- Automotive
- Power Generation
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the global hydrogen engine market?
The increasing demand for clean energy solutions, government incentives for hydrogen-based technologies, and advancements in hydrogen storage and distribution are the key drivers of the hydrogen engine market.
Which industries are adopting hydrogen engines the most?
The automotive, aerospace, marine, and heavy machinery industries are the primary adopters of hydrogen engines due to their focus on reducing carbon emissions and achieving sustainability goals.
How does hydrogen engine technology compare to battery-electric vehicles?
Hydrogen engines offer longer refueling times, higher energy density, and suitability for heavy-duty applications, whereas battery-electric vehicles have lower operational costs and a more developed charging infrastructure.
What is the future outlook for the hydrogen engine market?
The hydrogen engine market is expected to grow steadily as technology advances, infrastructure expands, and global regulations push for cleaner transportation solutions.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]