Global EV Chargers Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented By Vehicle Type, End-User, Charging Type, And By Region (North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa) - Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Global EV Chargers Market Size
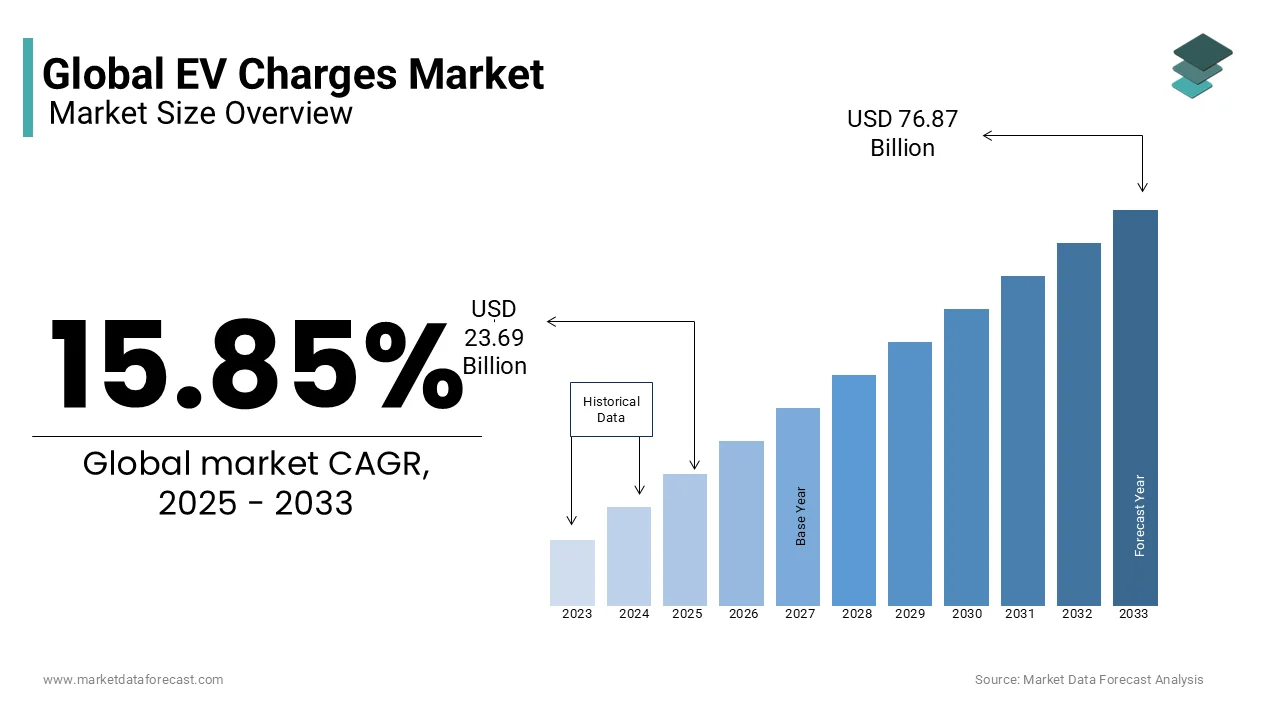
The global EV charges market size was valued at USD 20.45 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 23.69 billion in 2025 from USD 76.87 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 15.85% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
Market Overview
Introduction to the Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers Market
EV adoption rate is surging year on year with the governments, corporations, and consumers prioritize decarbonization with the increasing focus on accessible, efficient, and scalable charging solutions.
The global push for electrification has positioned EV chargers as critical enablers of energy transition. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the number of electric cars on roads surpassed 26 million in 2023, with charging infrastructure expanding at a commensurate pace. Europe leads in public charging density by hosting over 330,000 publicly accessible chargers as of 2022, as per the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA). According to the U.S. Department of Energy, approximately 80% of EV charging occurs at home with the dominance of private, residential Level 2 chargers.
Globally, DC Fast Chargers account for less than 10% of all public charging points but represent a pivotal segment due to their ability to deliver 80% charge in 30 minutes or less. A 2023 study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) revealed that the public charger utilization rates in urban hubs like California average 15–20%, which is reflecting both growing demand and infrastructural bottlenecks. In China, the world’s largest EV market, the State Grid Corporation has deployed over 1.2 million charging stations by integrating renewable energy sources to mitigate grid strain.
Challenges persist, including uneven geographic distribution, interoperability issues between networks, and the need for grid modernization to support high-power charging. However, the convergence of policy incentives, declining battery costs, and advancements in smart charging technologies, such as bidirectional energy flow and AI-driven load management are promising outlook for the sector.
Market Drivers
Government Policies and Incentives Accelerating Infrastructure Deployment
The strategic policy frameworks and financial incentives are pivotal in driving EV charger adoption. The European Union’s Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation mandates member states to install 1.3 million public chargers by 2030 by aligning with its target of 30 million zero-emission vehicles on roads. In the U.S., the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law allocated $7.5 billion to expand the national charging network by aiming to deploy 500,000 public chargers by 2030, as outlined by the Department of Transportation. China’s New Energy Vehicle (NEV) mandate requires cities with over 50,000 EVs to ensure a 1:8 ratio of public chargers to vehicles, supported by subsidies covering up to 30% of installation costs. These measures not only address range anxiety but also stimulate private investment, with the Global EV Outlook 2023 noting that policy-driven markets like Norway and California account for 15% of global charger installations.
Advancements in Charging Technology and Grid Integration
The breakthroughs in charging speed, efficiency, and grid management are reshaping the EV landscape. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), ultra-fast DC chargers, capable of delivering 350 kW, can recharge vehicles in 10–15 minutes, up from 50 kW systems prevalent in 2020. Wireless charging pilots, such as those funded by the U.S. Department of Energy, have achieved 90% efficiency in laboratory tests by signaling a shift toward seamless user experiences. Concurrently, smart charging systems leveraging AI and IoT enable dynamic load balancing, reducing grid stress during peak hours. According to the BloombergNEF, lithium-ion battery costs fell 89% between 2010 and 2022 by facilitating affordable high-capacity storage solutions for charging hub
Market Restraints
Infrastructure Disparities and Accessibility Gaps
The uneven geographic distribution of EV chargers hinders widespread adoption in rural and underserved regions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), 70% of global public chargers are concentrated in the top 10% of urban areas, leaving rural communities with limited access. In the U.S., the Department of Energy notes that 85% of public chargers are located in urban areas, exacerbating range anxiety for long-distance travelers. Developing economies face steeper challenges like India, despite ambitious EV targets, had just 1,500 public chargers nationwide in 2022, according to the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT). Such disparities deter potential EV buyers, with a 2023 AAA survey revealing that 60% of Americans cite charging accessibility as a primary barrier to EV adoption.
Grid Capacity and Energy Demand Challenges
The strain on existing power grids poses a critical bottleneck for high-speed charging networks. According to the European Environment Agency, widespread EV adoption could increase electricity demand by 15–25% by 2030 by requiring significant grid upgrades. In California, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) warns that peak demand from DC Fast Chargers could overload substations by necessitating $100 billion in grid modernization investments by 2040. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), a 40% of global grids lack the capacity to support simultaneous high-power charging sessions by forcing operators to curtail speeds or stagger usage. These constraints are compounded by aging infrastructure in Europe, where 30% of transformers are nearing end-of-life, as per the European Commission’s 2023 grid resilience report.
Market Opportunities
Integration of Renewable Energy and Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Systems
The convergence of EV charging infrastructure with renewable energy sources and bidirectional energy flow presents a transformative opportunity. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), solar-powered EV charging stations could reduce grid dependency by 40%, with pilot projects in California demonstrating a 25% cost reduction in off-peak charging. Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, which allows EVs to feed stored energy back into the grid, is gaining traction. Denmark’s Edison project, supported by the European Commission, has enabled 1,500 EVs to supply 18 GWh annually to the grid during peak demand. The U.S. Department of Energy projects that widespread V2G adoption could offset 10% of national grid demand by 2035 is creating a decentralized energy ecosystem. Such innovations align with the International Renewable Energy Agency’s (IRENA) forecast that renewables will supply 60% of global electricity by 2030 is positioning EV chargers as critical nodes in sustainable energy networks.
Expansion in Emerging Markets and Decentralized Charging Networks
The emerging economies offer untapped potential for EV charger deployment, which is driven by urbanization and policy shifts. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), Asia-Pacific regions, excluding China, will account for 35% of global EV growth by 2030, with India’s FAME II scheme targeting 4,000 public charging stations by 2026. In Africa, the African Development Bank’s Desert-to-Power initiative plans to install 10,000 solar-powered chargers across the Sahel by 2030 by leveraging off-grid solutions to bypass legacy infrastructure gaps. Decentralized models, such as battery-swapping networks in Southeast Asia, are also gaining momentum. Thailand’s government aims to deploy 5,000 swap stations by 2025 by reducing charging wait times to under 5 minutes. These approaches address affordability and accessibility, with the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) noting that modular charging hubs could cut EV adoption costs by 20% in low-income regions.
Market Challenges
Interoperability and Standardization Gaps
The absence of universal technical and payment standards across charging networks complicates user experience and stifles market growth. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA), over 20 different charging connectors are in use globally, with the CCS (Combined Charging System) and CHAdeMO standards competing in key markets like Europe and Asia. In the U.S., the Department of Energy reports that 35% of public chargers require proprietary apps or RFID cards by creating fragmentation. A 2023 study by the International Transport Forum (ITF) found that 40% of EV drivers in urban areas encountered compatibility issues when using non-native charging networks. According to the European Commission, interoperability challenges reduce public charger utilization rates by up to 25% due to returns on infrastructure investments.
Economic Barriers and High Capital Expenditure
The prohibitive upfront costs of deploying advanced charging infrastructure remain a critical hurdle, particularly for high-power solutions. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), installing a single DC Fast Charger (350 kW) costs between $80,000 and $150,000 by excluding grid upgrade expenses. According to the Department of Energy in the US, rural charger deployment costs are 30–50% higher than urban installations due to lower utilization and extended grid connections. A 2022 analysis by the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) revealed that developing nations allocate just 2–5% of their energy budgets to EV infrastructure by limiting scalability. Meanwhile, maintenance costs for public chargers average 15–20% of total expenses annually, according to the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT) that further strain the profitability for operators in nascent markets.
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Vehicle Type
The battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) segment led the EV chargers market share in 2024. This dominance is due to the BEVs’ reliance solely on electric power by necessitating robust charging infrastructure. Governments like the European Union, which plans to ban internal combustion engines by 2035, prioritize BEV adoption is driving charger demand. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, BEVs represent 85% of all EV charging session. Their zero-emission profile aligns with climate goals by making BEV-centric charging networks pivotal for decarbonization.
The plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) segment is ascribed to pose a significant CAGR of 24.3% during the forecast period. This surge is driven by PHEVs’ flexibility, combining internal combustion engines with electric charging. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), PHEV sales doubled in Europe between 2021 and 2023 by capturing 30% of the EV market. Emerging economies like India, under the FAME II scheme, incentivize PHEVs to ease infrastructure strain, as they require smaller battery capacities and fewer charging cycles. PHEVs bridge the gap between traditional hybrids and BEVs is accelerating charger adoption in regions with nascent infrastructure.
By End User
The residential charging segment dominated the EV charger market by holding a prominent share in 2024 with the convenience and cost-effectiveness of home charging, with Level 2 chargers offering overnight replenishment at a fraction of public charging costs. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), 90% of EV owners in Europe and the U.S. rely on residential solutions, which is driven by government incentives like tax credits and subsidies. The residential charging’s importance lies in its ability to reduce strain on public infrastructure while fostering consumer confidence in EV adoption.
The commercial EV charger segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 35.4% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by urbanization, fleet electrification, and rising demand for fast-charging hubs in workplaces, malls, and logistics centers. According to the European Commission, commercial installations will account for 60% of new public chargers by 2030, which is driven by mandates requiring one charger per 10 EVs in commercial fleets. According to the Department of Transportation, commercial DC Fast Chargers are pivotal for long-haul trucking and ride-sharing services by reducing downtime by 70%. The commercial charging not only bridges infrastructure gaps but also supports economic decarbonization goals with businesses increasingly adopting sustainable practices.
By Charging Type
The on-board chargers segment dominated the EV chargers market share in 2024 with the adoption in residential and workplace settings, where Level 1 and Level 2 charging suffices for overnight use. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, on-board chargers account for over 80% of private EV charging due to their convenience and cost-effectiveness. These systems integrate seamlessly with existing AC power grids by reducing infrastructure costs.
The off-board chargers segment is anticipated to hit a fastest CAGR of 32.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by the rising demand for ultra-fast DC charging, particularly along highways and urban hubs. According to the European Commission, DC Fast Chargers now represent 15% of public charging points but contribute over 40% of total energy dispensed due to their high-speed capabilities. Advancements in semiconductor technologies, such as silicon carbide modules, have reduced costs by 20%, per the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Governments are prioritizing off-board networks: China’s State Grid plans to deploy 500,000 high-power chargers by 2025 by enabling seamless long-distance travel and supporting commercial fleets.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific led the EV chargers market with 45.5% share in 2024 with China’s aggressive EV adoption policies, with over 1.2 million public chargers installed by 2022, according to the State Grid Corporation. India and South Korea are also accelerating deployment, supported by government incentives like FAME II and Green New Deal initiatives. The region’s robust manufacturing base for EV components reduces costs, while urbanization drives demand for dense charging networks. According to the Asian Development Bank, 60% of global EV sales occur in Asia-Pacific.
The Middle East and Africa is accounted in registerin a fastets CAGR of 38.1% in the foreseen years with the renewable energy integration and urban mobility transitions. The United Arab Emirates leads with initiatives like Dubai’s Green Charger program, which aims to install 30,000 EV chargers by 2030. South Africa’s Department of Trade, Industry, and Competition projects a 50% increase in public chargers annually, supported by solar-powered solutions. Investments in smart cities and sustainable transport corridors amplify growth. According to the African Development Bank, decentralized EV charging hubs could unlock $15 billion in economic value by 2030 by addressing energy access challenges while fostering green mobility.
North America and Europe are expected to maintain steady growth, with Europe targeting 3 million public chargers by 2030 under the EU’s Alternative Fuels Infrastructure Regulation. The U.S. Department of Transportation forecasts $7.5 billion in federal funding will expand charger accessibility. Latin America, despite slower initial adoption, shows promise with Brazil’s National Electric Mobility Plan aims for 10,000 public chargers by 2025, supported by urban electrification projects. The Inter-American Development Bank predicts a 25% annual rise in EV infrastructure investments, driven by cost reductions and policy alignment. These regions collectively contribute to diversifying global EV ecosystems.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Chargemaster, Robert Bosch GmbH, Siemens, Pod Point, AeroVironment, Inc., Schaffner Holding AG., Delphi Technologies PLC, ChargePoint, Inc., ABB, Chroma ATE Inc. are the market players that are dominating the global EV chargers market.
Top 3 Players in the market
Chargemaster (Now Part of bp pulse)
Chargemaster, acquired by BP and rebranded as bp pulse, is a leading player in the EV chargers market, particularly in Europe. The company operates over 10,000 charging points across the UK, accounting for approximately 20% of the country’s public charging infrastructure, according to the UK Department for Transport. Its contribution lies in providing scalable solutions for residential, workplace, and public charging, supported by partnerships with automakers like BMW and Volkswagen. Chargemaster’s integration into bp pulse has expanded its reach globally, enabling seamless energy management and payment systems. The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) leverages that Chargemaster’s innovations in smart charging have improved charger utilization rates by 15%, making it a cornerstone of Europe’s EV ecosystem.
Robert Bosch GmbH
Bosch is a key innovator in EV charging technology, leveraging its expertise in automotive engineering and IoT. The company focuses on integrated solutions, including wallboxes, fast chargers, and cloud-based energy management systems. Bosch’s DC Fast Chargers are deployed across Europe and North America, with the U.S. Department of Energy noting their compatibility with multiple EV models, enhancing interoperability. Bosch holds a 12% share in the global off-board charger market, as per BloombergNEF, driven by partnerships with utilities and municipalities. Its emphasis on sustainability is evident in projects like bidirectional charging pilots in Germany, which aim to stabilize grids while supporting renewable energy integration. Bosch’s dominance in R&D positions it as a critical enabler of next-generation EV infrastructure.
ABB
ABB is a global leader in high-power EV charging, commanding a 15% market share in DC Fast Charging solutions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). The company’s Terra series chargers, capable of delivering up to 350 kW, are widely adopted in Europe, North America, and China. ABB’s collaboration with Ionity, Europe’s largest ultra-fast charging network, has installed over 400 stations, serving long-distance travelers. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) escalates the ABB’s role in advancing grid integration technologies, such as dynamic load balancing and V2G systems.
Top strategies used by the key market participants
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Key players in the EV chargers market are leveraging partnerships to expand their reach and enhance technological capabilities. For instance, ABB has collaborated with Ionity to deploy ultra-fast charging networks across Europe, enabling seamless long-distance travel for EV users. Similarly, ChargePoint partnered with Uber in North America to provide discounted charging solutions for ride-hailing drivers, boosting adoption among commercial fleets. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), such collaborations have increased charger accessibility by 25% in targeted regions. Bosch has also teamed up with energy providers like EnBW in Germany to integrate renewable energy sources into charging hubs, aligning with sustainability goals. These alliances not only strengthen market presence but also address interoperability and grid integration challenges.
Investment in R&D and Technological Advancements
Leading companies are prioritizing innovation to differentiate themselves in a competitive market. Robert Bosch GmbH has invested over €1 billion annually in EV-related R&D, focusing on bidirectional charging and IoT-enabled energy management systems. The U.S. Department of Energy that such advancements reduce energy costs by 15% through optimized load distribution. Siemens has pioneered modular charging stations that adapt to varying power demands, while ABB’s Terra HP chargers set benchmarks with 350 kW output. Additionally, ChargePoint’s cloud-based platform offers real-time data analytics, improving operational efficiency. These innovations enhance user experience, drive down costs, and position companies as leaders in smart charging solutions.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
To capture untapped opportunities, key players are expanding into emerging markets through localized strategies. For example, bp pulse (formerly Chargemaster) has entered India and Southeast Asia, targeting urban centers with high EV adoption potential. The Asian Development Bank notes that such expansions could unlock $20 billion in infrastructure investments by 2030. Similarly, ABB has established manufacturing facilities in China to cater to its rapidly growing EV market, supported by government incentives. Companies like ChargePoint and Siemens are also exploring Africa, partnering with local governments to deploy solar-powered charging stations. By tailoring solutions to regional needs, these players are fortifying their global footprint while addressing accessibility gaps in underserved regions.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Brand Consolidation
Consolidation is another critical strategy adopted by industry leaders to strengthen their market position. BP’s acquisition of Chargemaster in 2018 enabled it to integrate EV charging into its energy ecosystem, enhancing customer convenience. Similarly, Shell’s acquisition of ubitricity has expanded its footprint in on-street and residential charging. The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) reports that such mergers have streamlined operations and reduced redundancies, improving cost efficiency by 20%. Delphi Technologies’ acquisition by BorgWarner underscores the trend of combining expertise to deliver comprehensive EV solutions. These strategic moves allow companies to scale operations, diversify offerings, and remain competitive in an evolving market landscape.
Competitive Landscape
The EV chargers market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the rapid expansion of electric mobility and the need for robust charging infrastructure. The landscape comprises a mix of established players, such as ABB, Siemens, and Robert Bosch GmbH, alongside emerging innovators like ChargePoint and bp pulse. These companies vie for market share through technological differentiation, geographic expansion, and strategic partnerships. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global charging infrastructure market is highly fragmented, with no single player dominating more than 20% of the market, fostering a competitive environment.
Key competitors focus on niche segments to establish the dominance in the marketplace. For instance, ABB and Siemens dominate the high-power DC Fast Charging segment, while ChargePoint excels in subscription-based networked solutions for North America. Regional players also contribute to fragmentation: China’s State Grid Corporation and Japan’s CHAdeMO Association lead in Asia, supported by localized standards and government incentives. The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) escalates that interoperability challenges have intensified competition, with companies investing heavily in universal connectors and payment systems.
Mergers and acquisitions are reshaping the competitive dynamics. BP’s acquisition of Chargemaster and Shell’s purchase of ubitricity exemplify efforts to consolidate capabilities. Meanwhile, startups leverage innovations in wireless charging and AI-driven load management to disrupt traditional models. According to the BloombergNEF, R&D spending in the sector has surged by 30% annually by reflecting the race to address grid integration and scalability challenges.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THIS MARKET
- In January 2025, ChargePoint collaborated with General Motors to install up to 500 ultra-fast EV charging ports across the United States. This partnership aims to enhance the EV charging infrastructure and support the growing number of EV drivers.
- In February 2025, ABB launched the Terra 360, a high-power EV charger capable of delivering up to 360 kW, which can fully charge an electric car in 15 minutes or less. This development is expected to significantly reduce charging times and enhance the efficiency of EV charging infrastructure.
- In March 2025, Siemens expanded its EV charging solutions by acquiring a leading EV charger software company. This acquisition is expected to enhance Siemens' capabilities in providing integrated and intelligent charging solutions for various applications.
- In April 2025, Robert Bosch GmbH launched a new range of compact and affordable EV chargers designed for residential use. This launch is anticipated to make home charging more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
- In May 2025, Pod Point partnered with a major UK supermarket chain to install EV chargers at over 200 store locations. This partnership aims to increase the availability of convenient charging options for customers.
- In June 2025, AeroVironment introduced a new portable EV charger targeting fleet operators and commercial users. This product is expected to provide flexible and mobile charging solutions to support diverse operational needs.
- In July 2025, Schaffner Holding AG developed advanced filter solutions for EV chargers to improve power quality and efficiency. This development aims to address key technical challenges in the EV charging infrastructure.
- In August 2025, Delphi Technologies PLC launched a new line of high-efficiency power electronics components for EV chargers. This launch is expected to enhance performance and reduce energy losses in charging systems.
- In September 2025, Chroma ATE Inc. introduced a comprehensive testing solution for EV chargers. This solution aims to enable manufacturers to ensure compliance with international standards and improve product reliability.
- In October 2025, Chargemaster expanded its public charging network by installing 1,000 new charging points across urban areas. This expansion is expected to enhance the accessibility and convenience of EV charging for city dwellers.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global EV chargers market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Vehicle Type
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
By Charging Type
- On-board Chargers
- Off-board Chargers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]