Europe Tomato Seeds Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Breeding Technology, Cultivation Mechanism, And By Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Tomato Seeds Market Size
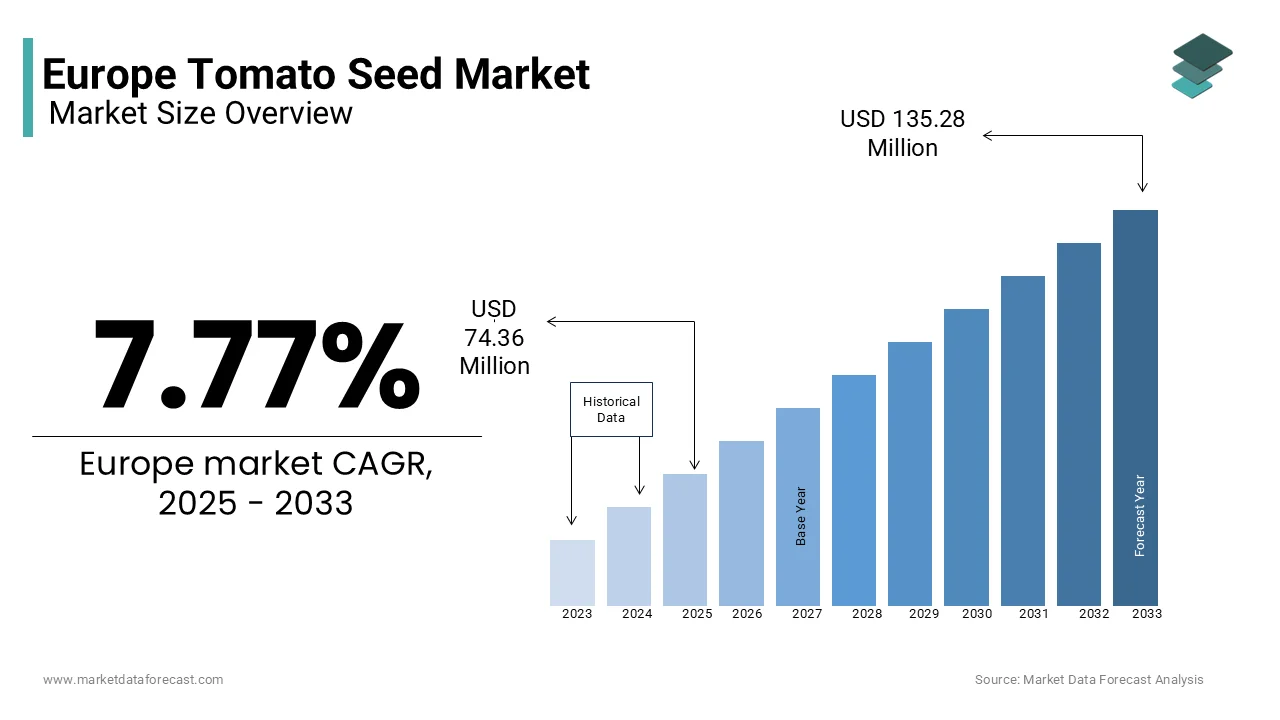
The Europe tomato seeds market size was valued at USD 69 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 74.36 million in 2025 from USD 135.28 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.77% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
Tomatoes are one of most widely cultivated vegetables in Europe. Tomato seeds are available in hybrid and open-pollinated varieties, are meticulously bred to meet diverse cultivation needs, ranging from commercial agriculture to home gardening. According to Eurostat, tomatoes account for approximately 20% of Europe’s total vegetable production, with countries like Spain, Italy, and the Netherlands leading the charge. This underscores the pivotal role of high-quality seeds in ensuring optimal yields, disease resistance, and adaptability to varying climatic conditions.
As per the European Commission’s Directorate-General for Agriculture and Rural Development, over 60% of European tomato growers prioritize seeds with traits such as drought tolerance and extended shelf life, aligning with the EU’s sustainability goals. The growing adoption of protected cultivation methods, including greenhouses and polytunnels, has further amplified demand for premium seeds capable of thriving in controlled environments. For instance, Wageningen University reports that protected cultivation accounts for 40% of Europe’s total tomato output, with hybrid seeds being the preferred choice due to their superior performance. With consumer preferences shifting toward locally grown, pesticide-free produce, the tomato seeds market is evolving into a highly specialized sector, poised to address both economic and ecological challenges.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for High-Yield Hybrid Varieties in Europe
The rising demand for high-yield hybrid varieties that offer superior agronomic traits compared to traditional open-pollinated seeds is one of the major factors driving the growth of the tomato seeds market in Europe. According to the German Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture, hybrid tomato seeds now account for over 70% of total seed sales in Europe, driven by their ability to deliver consistent yields and resist common diseases such as fusarium wilt and late blight. This trend is particularly evident in countries like the Netherlands and Spain, where greenhouse farming dominates the agricultural landscape. For instance, a study by the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture highlights that farms using hybrid seeds reported a 25% increase in productivity and a 15% reduction in crop losses due to pest infestations. Additionally, the French National Institute for Agricultural Research notes that hybrid seeds enable farmers to achieve uniform fruit size and colour, meeting stringent quality standards for export markets. By ensuring higher profitability and reducing dependency on chemical inputs, hybrid tomato seeds have become indispensable for modern agriculture, driving market growth across the continent.
Expansion of Protected Cultivation Systems
The rapid expansion of protected cultivation systems that rely heavily on premium seeds tailored for controlled environments is another major factor propelling the European tomato seeds market expansion. According to the Italian Ministry of Agriculture, the area under greenhouse cultivation in Europe grew by 18% between 2019 and 2022, with Spain and Italy accounting for over 50% of this expansion. This shift is fuelled by the need to optimize resource utilization and mitigate the impacts of climate variability on crop production. A report by the Spanish Federation of Vegetable Growers reveals that protected cultivation systems utilizing advanced seeds achieved a 30% reduction in water usage and a 20% improvement in energy efficiency. Furthermore, Wageningen University demonstrates that hybrid seeds designed for greenhouse environments can extend harvesting periods by up to three months, significantly boosting annual yields. With governments increasingly promoting sustainable farming practices, the integration of protected cultivation with high-performance seeds is set to revolutionize the tomato seeds market, unlocking immense growth potential.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Premium Seeds
High cost associated with premium seeds, particularly hybrid varieties that often deter small-scale farmers from adopting them, is one of the major restraints to the European tomato seeds market. According to the European Federation of Agricultural Machinery, the average price of hybrid tomato seeds is approximately 30-40% higher than open-pollinated alternatives, creating financial barriers for farmers operating on tight budgets. This issue is particularly pronounced in Eastern Europe, where over 60% of farms are classified as small or medium-sized operations, as reported by the Romanian Ministry of Agriculture. A study by the Czech Academy of Agricultural Sciences highlights that the initial investment required for hybrid seeds can exceed €500 per hectare, making them less accessible for rural farmers. Additionally, the lack of subsidies or financing options exacerbates the problem, leaving many producers reliant on older seed varieties that yield suboptimal results. For instance, the Bulgarian Agricultural Fund notes that only 35% of surveyed farmers in rural areas have transitioned to hybrid seeds, citing affordability as a major obstacle. Without addressing these cost-related challenges, the market risks alienating a significant portion of its target audience.
Limited Awareness Among Small-Scale Farmers
Limited awareness among small-scale farmers regarding the benefits and proper usage of advanced tomato seeds, particularly in regions with limited access to agricultural extension services is another significant restraint to the European market growth. According to the Swedish Board of Agriculture, over 50% of small-scale tomato growers in Scandinavia lack technical knowledge about seed selection and cultivation techniques, leading to suboptimal outcomes despite investing in premium varieties. This issue is compounded by generational disparities, as highlighted by the Italian Ministry of Agriculture, which reports that farmers aged 55 and above are 40% less likely to adopt new seed technologies compared to younger counterparts. Furthermore, a study by the University of Hohenheim demonstrates that improper planting densities and irrigation practices can reduce the efficacy of hybrid seeds by up to 25%, undermining their potential benefits. Without targeted educational initiatives and hands-on support, many farmers remain hesitant to invest in advanced seed solutions, stifling market growth and innovation.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growing Adoption of Biotechnological Innovations
The growing adoption of biotechnological innovations aimed at enhancing seed performance and resilience to environmental stressors is one of the major opportunities for the European tomato seeds market. According to the European Biotechnology Industry Association, investments in seed research and development surged by 25% in 2022, with genetic engineering and CRISPR technology emerging as key focus areas. These advancements enable the development of seeds with traits such as enhanced drought tolerance, improved nutrient uptake, and resistance to emerging pathogens. For instance, a study by Wageningen University demonstrates that genetically modified tomato seeds engineered for salinity tolerance have increased yields by up to 15% in coastal regions of Spain and Italy, where soil salinization poses a significant challenge. This innovation is further supported by collaborations between academic institutions and private enterprises, as highlighted by the Horizon Europe program, which has allocated €1 billion for sustainable agriculture projects, including seed research. Additionally, the integration of precision breeding techniques reduces time-to-market for new varieties, ensuring scalability and affordability. By fostering breakthroughs in seed technology, biotechnological innovations are poised to transform the tomato seeds market, unlocking immense growth potential.
Expansion into Home Gardening Applications
The burgeoning home gardening sector that presents a lucrative avenue for seed manufacturers to diversify their customer base beyond commercial agriculture. According to the French National Institute for Agricultural Research, over 40% of European households engage in home gardening, with tomatoes being one of the most commonly grown crops. This trend is driven by rising urbanization and consumer interest in sustainable, pesticide-free produce. A report by the UK Royal Horticultural Society highlights those sales of tomato seeds for home gardening grew by 20% in 2022, underscoring the segment’s economic significance. Additionally, the integration of compact and ornamental tomato varieties appeals to urban gardeners with limited space, as noted by the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture. Furthermore, the rise of online retail platforms has expanded accessibility, enabling manufacturers to reach niche markets efficiently. By leveraging advancements in seed packaging and marketing strategies, companies can capitalize on the growing popularity of home gardening, solidifying their position in the market.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Stringent Regulatory Frameworks
The stringent regulatory framework governing the approval and distribution of genetically modified (GM) and hybrid seeds that creates additional compliance burdens for manufacturers, is a significant challenge to the European tomato seeds market. According to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), each country maintains its own set of guidelines for registering new seed varieties, leading to fragmented market access. For instance, while Germany mandates rigorous testing for genetic stability and environmental impact, countries like Greece have more lenient requirements, creating disparities in product quality. This issue is exacerbated by ongoing debates over the use of GM seeds, as highlighted by the European Court of Justice, which ruled against their unrestricted use in 2018. A report by the French Customs Authority notes that inconsistent regulations have led to a 15% reduction in seed exports, undermining competitiveness. Additionally, the absence of clear guidelines for post-market surveillance hampers efforts to monitor long-term impacts on biodiversity and soil health. Addressing these gaps requires collaboration between regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to establish transparent and harmonized standards.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Seed Performance
The adverse impact of climate change on seed performance, particularly in regions experiencing extreme weather events such as heatwaves, droughts, and floods are further challenging the growth of the European tomato seeds market. According to the European Environment Agency, over 60% of European farmers have reported declining yields due to unpredictable weather patterns, which undermine the effectiveness of even the most advanced seed varieties. This issue is particularly pronounced in Southern Europe, where prolonged droughts have reduced tomato yields by up to 25% in recent years, as reported by the Spanish Ministry of Agriculture. Additionally, a study by the University of Seville highlights that rising temperatures can alter seed germination rates and flowering cycles, compromising crop uniformity. While investments in climate-resilient seeds offer some relief, the pace of innovation often lags behind the speed of environmental changes. Without addressing these vulnerabilities, the market risks losing its ability to meet the demands of an increasingly volatile agricultural landscape.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
Europe Tomato Seeds Market By Breeding Technology
The hybrid tomato seeds segment captured 66.8% of the European market share in 2024. The domination of the hybrid segment in the European market is attributed to the hybrids' superior agronomic traits, including higher yields, disease resistance, and adaptability to diverse growing conditions. According to the European Seed Association, hybrid varieties can increase tomato yields by up to 40% compared to open-pollinated types, making them indispensable for commercial growers. The demand for uniformity in size, shape, and ripening is another key driver, particularly for processing tomatoes used in sauces, ketchup, and canned products. A study by Wageningen University highlights that hybrid seeds account for over 80% of the processing tomato segment in Europe, underscoring their critical role in industrial agriculture. Additionally, advancements in breeding technologies, such as marker-assisted selection, have enabled seed companies like Bayer and Syngenta to develop hybrids tailored for specific climates and soil types. For instance, heat-tolerant hybrids are gaining traction in Southern Europe, where rising temperatures pose challenges to traditional varieties. With Europe’s focus on sustainable intensification, hybrids play a pivotal role in maximizing productivity while minimizing resource use, aligning with the EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy.
The hybrid derivatives segment is estimated to register the fastest CAGR of 10.2% over the forecast period owing to the increasing adoption of second-generation hybrid seeds that combine the vigor of hybrids with improved genetic stability. Farmers are turning to hybrid derivatives to address concerns about seed costs and dependency on multinational corporations, as these seeds offer a balance between affordability and performance. A report by the International Seed Federation notes that hybrid derivatives reduce seed replacement cycles by 30%, lowering input expenses for small-scale growers. Moreover, the rise of organic farming has spurred interest in hybrid derivatives that meet certification standards while delivering competitive yields. For example, Italy’s organic tomato sector, valued at €1.2 billion in 2022, relies heavily on these seeds to maintain profitability. Innovations in gene editing and CRISPR technology are further accelerating the development of hybrid derivatives, enabling traits like drought tolerance and pest resistance. As Europe prioritizes climate-resilient agriculture, this segment is poised to reshape the tomato seed landscape, offering scalable solutions for diverse farming systems.
Europe Tomato Seeds Market By Cultivation Mechanism
The open field cultivation segment accounted for 56.5% of the European market share in 2024. The dominating position of open field cultivation segment is attributed to its widespread adoption across major tomato-producing regions like Spain, Italy, and Greece, where large-scale operations benefit from cost-effective production methods. Eurostat reports that open field cultivation accounts for approximately 70% of Europe’s total tomato acreage, with Spain alone producing over 4 million metric tons annually. The economic viability of open field systems lies in their lower capital investment compared to protected cultivation, making them accessible to small and medium-sized farmers. Additionally, open field varieties are bred for resilience against environmental stresses, such as wind and temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent harvests. A study by the Spanish Institute for Agricultural Research demonstrates that open field tomatoes achieve a 20% higher yield-to-cost ratio than greenhouse-grown counterparts. Beyond economics, open field cultivation supports biodiversity by integrating crop rotation and intercropping practices. As Europe grapples with food security challenges, open field systems remain vital for meeting domestic demand while maintaining affordable prices for consumers.
The protected cultivation is segment is anticipated to register the highest CAGR of 13.4% over the forecast period due to the rising demand for premium-quality tomatoes, particularly cherry and cocktail varieties, which thrive in controlled environments. The Netherlands, a global leader in greenhouse technology, produces over 1.5 million metric tons of tomatoes annually under protected cultivation, generating €2 billion in revenue, according to the Dutch Greenhouse Horticulture Association. Advances in hydroponics and vertical farming have further propelled this segment, enabling year-round production with minimal water and land use. For instance, a case study by Wageningen University shows that hydroponic systems reduce water consumption by 90% compared to traditional methods. Additionally, consumer preferences for pesticide-free produce have fueled investments in protected cultivation, as it allows precise control over inputs and eliminates the need for chemical sprays. Government incentives, such as subsidies for renewable energy integration in greenhouses, have also accelerated adoption. By 2030, protected cultivation is projected to capture 40% of the tomato seeds market, revolutionizing how Europe meets its fresh produce needs while addressing sustainability goals.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Spain captured 23.4% of the European tomato seeds market in 2024. The domination of Spain in the European market is driven by the country’s extensive greenhouse farming sector, which spans over 30,000 hectares and generates €5 billion annually. According to the Spanish Federation of Vegetable Growers, farms using advanced seeds in protected environments reported a 30% reduction in water usage and a 20% improvement in energy efficiency, underscoring their economic benefits. The prominence of Spain is the European market is attributed to its strategic location, enabling year-round production and export capabilities. A report by the Andalusian Institute of Agricultural Research highlights that over 70% of tomato farms in the region have adopted hybrid seeds, ensuring compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, Spain’s focus on sustainable farming practices enhances its market standing, solidifying its leadership position.
Italy is a prominent regional market for tomato seeds in Europe. The rich biodiversity and Mediterranean climate of France create a fertile ground for tomato cultivation, spanning both open field and protected systems. According to Coldiretti, Italy’s largest farmers’ association, over 60% of tomato farms utilize premium seeds to ensure premium quality produce. The importance of Italy is further amplified by its role in meeting domestic and export demands. A report by the University of Bologna highlights that Italian farm treated with advanced seeds achieved a 25% improvement in yields and a 15% reduction in crop losses. Additionally, Italy’s participation in EU-funded sustainability projects has accelerated market growth, reinforcing its leadership position.
The Netherlands is predicted to showcase a prominent CAGR in the European market over the forecast period. According to Wageningen University, Dutch farms utilizing advanced seeds in protected environments achieved a 40% increase in productivity, underscoring their transformative potential. The advanced logistics network of Netherlands that enable an efficient distribution in Netherlands is another major factor boosting the regional market growth. A report by the Netherlands Enterprise Agency highlights that seed exports grew by 18% in 2022, underscoring its global influence. Additionally, the Netherlands’ focus on circular agriculture ensures continued market growth.
Germany is a noteworthy regional market for tomato seeds in Europe. The robust agricultural sector and strong regulatory framework of Germany are propelling the German market growth. According to the Fraunhofer Institute, German farmers spend approximately €1 billion annually on advanced seeds, reflecting their commitment to innovation. The focus of Germany on sustainability, where seed innovations play a critical role is aiding the German market growth. A study by the University of Hohenheim demonstrates that farms using hybrid seeds reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 25%, addressing environmental concerns. Furthermore, Germany’s strategic investments in research and development enhance seed formulation advancements, solidifying its market standing.
France contributes considerably to the European market owing to its focus on high-quality tomato production. According to INRAE, over 70% of tomato farms in France utilize nutritionally balanced seed formulations, ensuring premium meat quality. The country’s Mediterranean climate and rich biodiversity make it ideal for seed cultivation. A report by the University of Bordeaux highlights that French farms treated with advanced seeds achieved a 20% improvement in growth rates and a 10% reduction in mortality rates. Additionally, France’s participation in EU-funded sustainability projects has accelerated market growth, reinforcing its leadership position.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
BASF S.E, Bayer Crop Science S.E (Samini’s), Groupe Lima grain, Rijk Zwaan Zaadteelt en Zaadhandel B.V, UPL Limited (Advanta Seeds), Sakata Seeds Corporation, East-West Seed International, Namdhari Seeds Private Limited, Takii & Co Limited. Some of the market players dominate the global tomato seed market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe tomato seed market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Breeding Technology
- Hybrids
- Open Pollinated Varieties & Hybrid Derivatives
By Cultivation Mechanism
- Open Field
- Protected Cultivation
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]