Europe Smart Windows Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Technology (Electrochromic Technology, Pdlc, Spd, and Photochromic), Application (Architectural And Construction, Transportation, Automotive, Aircraft, Marine, Consumer Goods, and Power Generation), Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Smart Windows Market Size
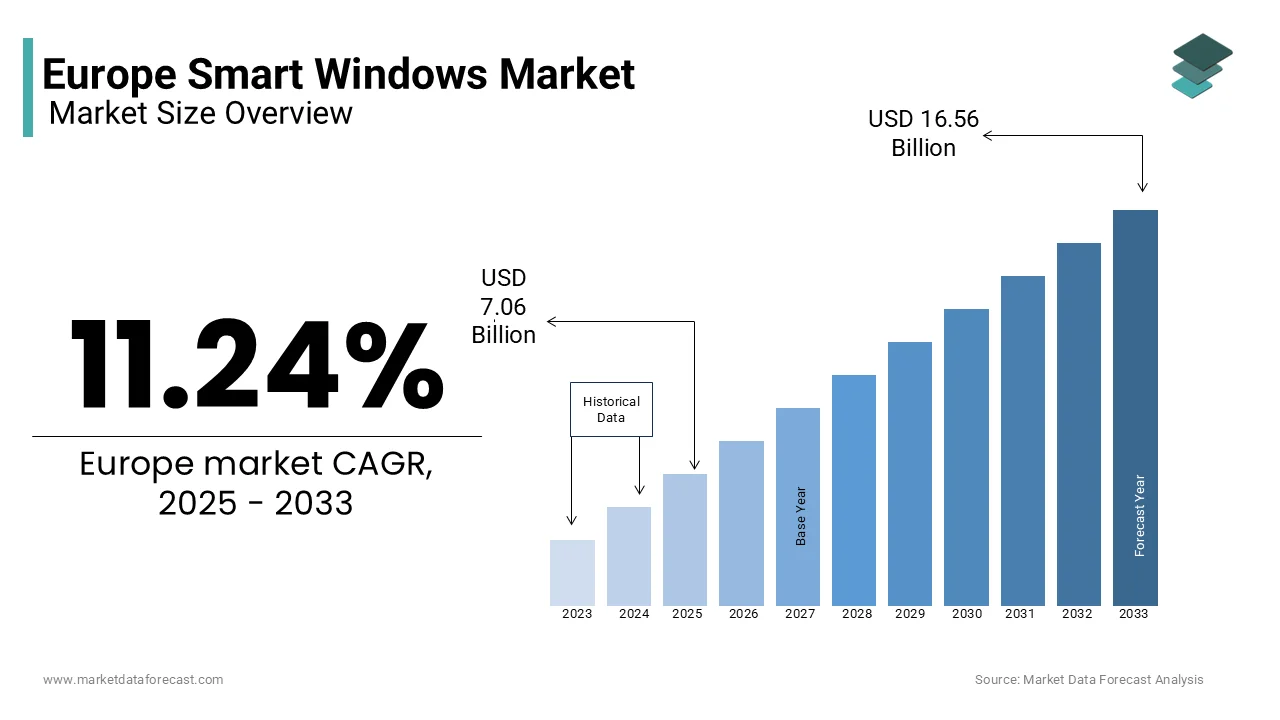
The Europe smart windows market was worth USD 6.35 billion in 2024. The European market is projected to reach USD 16.56 billion by 2033 from USD 7.06 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.24% from 2025 to 2033.
Smart windows are also known as dynamic or switchable windows. These are advanced glazing systems capable of altering their properties in response to external stimuli such as light, heat, or electrical signals. These windows utilize cutting-edge technologies like electrochromic, thermochromic, photochromic, and suspended particle devices (SPDs) to regulate light transmission, enhance thermal insulation, and reduce energy consumption.
The European Union has set ambitious targets under its Green Deal initiative, mandating a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030. This has catalyzed demand for energy-efficient building solutions, with smart windows playing a pivotal role. According to the International Energy Agency, buildings account for approximately 40% of Europe’s total energy consumption, making them a critical focus area for sustainability efforts. In 2022, the European glass industry reported that over 60% of new commercial buildings incorporated smart window technologies, reflecting their growing popularity. Countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands are leading adopters, supported by robust investments in green infrastructure. Furthermore, advancements in IoT integration have enabled smart windows to synchronize with building management systems, enhancing occupant comfort and operational efficiency.
MARKET DRIVERS
Stringent Energy Efficiency Regulations
The European smart windows market is significantly driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable building practices. The European Commission’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive mandates that all new buildings must be nearly zero-energy by 2030, creating a robust demand for innovative solutions like smart windows. According to the International Energy Agency, buildings account for 40% of Europe’s total energy consumption, with heating and cooling being the largest contributors. Smart windows, which can reduce energy usage by up to 20%, as reported by the European Environment Agency, are becoming indispensable in meeting these targets. Additionally, the EU Green Deal’s goal of achieving a 55% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 has accelerated investments in energy-efficient technologies. These regulatory frameworks not only incentivize adoption but also position smart windows as a key enabler of Europe’s sustainability agenda.
Rising Demand for Smart Building Technologies
The growing trend toward smart building technologies is another major driver propelling the European smart windows market forward. The European Investment Bank stated that investments in smart infrastructure exceeded €20 billion in 2022, with smart windows playing a critical role in enhancing building automation and occupant comfort. A report by Eurostat reveals that over 60% of urban households in Europe prioritize energy-efficient and technologically advanced living spaces, driving demand for IoT-integrated smart windows. These windows offer dynamic control over light and heat transmission, improving indoor environments while reducing operational costs. Furthermore, the World Health Organization emphasizes that improved indoor air quality and thermal comfort directly impact occupant well-being, making smart windows an attractive solution for modern urban dwellings. As Europe continues its shift toward smart cities, the integration of such technologies is expected to grow exponentially.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs and Limited Awareness
A major restraint to the European smart windows market is the high initial cost associated with these advanced glazing systems. The European Commission’s Joint Research Centre reports that smart windows can be up to 300% more expensive than traditional glazing solutions, making them less accessible for small-scale projects or residential applications. For instance, electrochromic windows, a popular variant, cost approximately €1,000 per square meter, deterring widespread adoption. Additionally, limited awareness about the long-term benefits of smart windows hampers market growth. A 2022 survey by Eurostat revealed that only 25% of European households are familiar with energy-efficient window technologies, bringing into light a significant knowledge gap. This lack of understanding, coupled with budget constraints, particularly in Eastern Europe, restricts market penetration. Without targeted subsidies or incentives, the affordability barrier will continue to challenge market expansion.
Technical Limitations and Installation Challenges
Another important issue is the technical limitations and installation challenges associated with smart windows. The European Environment Agency revealed that issues such as slow switching speeds, limited color options, and durability concerns hinder their adoption in diverse climatic conditions. For example, thermochromic windows often struggle to maintain consistent performance in extreme temperatures, limiting their applicability in regions like Scandinavia. Furthermore, the complexity of integrating smart windows with existing building management systems poses additional hurdles. According to the International Energy Agency, retrofitting older buildings with smart windows can increase installation costs by up to 40%, discouraging property owners from upgrading. These technical and logistical barriers, combined with the need for specialized expertise during installation, create significant obstacles for broader market acceptance across Europe.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growing Urbanization and Smart City Initiatives
The rapid pace of urbanization and the proliferation of smart city initiatives across Europe present a significant opportunity for the European smart windows market. The European Commission projects that urban areas will house over 80% of the continent’s population by 2050, driving demand for energy-efficient and technologically advanced building solutions. Smart windows, which enhance energy savings and improve indoor comfort, align perfectly with these urban development goals. According to Eurostat, investments in smart city infrastructure reached €30 billion in 2022, with a focus on sustainable technologies. For instance, cities like Amsterdam and Stockholm are integrating smart windows into public buildings to reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. This trend is further supported by EU funding programs like Horizon Europe, which allocate €10 billion annually to green urban innovations, creating a fertile ground for smart window adoption.
Advancements in IoT and Building Automation Integration
The integration of smart windows with IoT and building automation systems offers another promising opportunity for market growth. Tas per the European Investment Bank, IoT-enabled technologies in buildings are expected to grow at a rapidpace through 2030, driven by the need for enhanced operational efficiency. Smart windows equipped with sensors and connectivity features can dynamically adjust light and heat transmission based on real-time data, optimizing energy usage. The International Energy Agency reports that such integrations can reduce HVAC-related energy costs by up to 25%, making them highly attractive for commercial spaces. Furthermore, advancements in AI-driven analytics enable predictive maintenance and performance monitoring, enhancing user experience. With the European Union mandating smart-ready buildings under its Green Deal, the demand for IoT-compatible smart windows is set to surge, unlocking new avenues for innovation and market expansion.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Limited Standardization and Interoperability Issues
A substantial challenge impacting the European smart windows market is the lack of standardization and interoperability with existing building systems. According to the European Committee for Standardization (CEN), the absence of unified protocols for integrating smart windows with building management systems creates compatibility issues, particularly in retrofit projects. According to a 2022 report by the International Energy Agency, nearly 40% of smart window installations face delays due to integration complexities, leading to increased costs and reduced adoption rates. Furthermore, the European Commission notes that fragmented regulations across member states complicate compliance, hindering cross-border market expansion. This lack of harmonization not only affects scalability but also limits consumer confidence in adopting these technologies. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts to establish industry-wide standards, ensuring seamless integration and broader acceptance.
Environmental Concerns Related to Manufacturing Processes
An additional major hurdle is the environmental impact associated with the manufacturing processes of smart windows. The European Environment Agency reports that the production of electrochromic and thermochromic materials involves energy-intensive procedures and the use of rare earth elements, contributing to a carbon footprint that undermines their sustainability claims. For instance, the extraction and processing of tungsten oxide, a key component in electrochromic windows, generate approximately 15 kg of CO2 per square meter of glass produced. Additionally, Eurostat data reveals that over 60% of consumers prioritize eco-friendly products, making it imperative for manufacturers to adopt greener practices. However, transitioning to sustainable manufacturing methods requires substantial investment, which many small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) struggle to afford. Balancing innovation with environmental responsibility remains a critical hurdle for the market.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
11.24% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, Application, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Saint-Gobain Group (France), Ravenwindow (US), Ppg Industries, Inc. (US), Kinestral Technologies, Inc. (US), Gentex Corporation (US), Merck Kgaa (Germany), Pleotint, Llc (US), E-Chromic Technologies, Inc. (US), Chromogenic Ab (Sweden), Agc, Inc. (Japan), Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd (Japan), Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd (Japan), Innovative Glass Corporation (US), Glasnovations Ltd. (UK), Heliotrope Technologies (US), Sage Electrochromics, Inc. (US), Scienstry (US), Stellaris (US), View Inc. (US), And Vista Window Company (US). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Technology Insights
The electrochromic technology segment commanded the European smart windows market and captured a 45.6% share in 2024 owing to its energy-saving capabilities are reducing HVAC costs by up to 20%, as showcased by the International Energy Agency and is strengthening the position of this segment in the market. Electrochromic windows are widely adopted in commercial buildings, with over 60% of new constructions in Germany and France incorporating this technology. Their ability to dynamically adjust tint levels using electrical signals ensures optimal light and heat control, aligning with EU Green Deal targets. The European Environment Agency notes that electrochromic windows can cut carbon emissions by 15%, making them indispensable for sustainable urban development.

The Suspended Particle Device (SPD) technology segment is likely to experience the fastest CAGR of 8% during the forecast period due to its superior light modulation properties, ideal for high-end automotive and aviation applications. The European Investment Bank stated that SPD-based smart windows reduce glare and improve passenger comfort, driving demand in luxury vehicles and aircraft. Additionally, advancements in nanotechnology have lowered production costs by 25%, making SPD more accessible. With an estimated market value of €300 million in 2023, SPD technology is pivotal for industries prioritizing aesthetics and performance. Its rapid adoption underscores its role in enhancing energy efficiency and user experience across diverse sectors.
By Application Insights
The Architectural and Construction segment dominated the European smart windows market and held a 40.7% share in 2024. EU regulations mandating energy-efficient buildings, with smart windows reducing HVAC energy usage by up to 25%, according to the International Energy Agency, is driving the growth of the segment in the global market. Over 60% of new commercial buildings in Europe now integrate smart glazing solutions, particularly in Germany and France. These windows enhance thermal insulation, improve occupant comfort, and align with the EU Green Deal’s goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. Their critical role in sustainable urban development makes them indispensable for modern construction.
The Automotive segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 9.3% during the forecast period. The increasing demand for advanced glazing in luxury vehicles, where smart windows reduce glare and heat while enhancing aesthetics, fuelled the growth of this segment. The European Automobile Manufacturers Association notes that over 20% of high-end cars now feature electrochromic or SPD-based windows. Advancements in lightweight materials have reduced integration costs by 15%, boosting adoption. With an estimated market value of €300 million in 2023, automotive smart windows play a vital role in improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions, aligning with Europe’s sustainability goals and driving rapid market expansion.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany led the European smart windows market with a 22.9% share in 2024. The growth of the German market is driven by stringent energy efficiency regulations, such as the Energy Saving Ordinance, which mandates the integration of sustainable technologies in buildings. The German Construction Industry Federation revealed that over 70% of new commercial buildings in Germany incorporate smart windows to meet carbon neutrality goals. Additionally, Germany’s robust R&D ecosystem fosters innovation, with companies investing heavily in electrochromic and SPD technologies. The country’s emphasis on retrofitting aging infrastructure further accelerates adoption and is making it a hub for smart window deployment across Europe.

France held the second-largest position with an 18.2% market share in 2024. France has strong focus on sustainable urban development, supported by the "Plan Bâtiment Durable," which promotes energy-efficient solutions as well as the progress of the segment. Eurostat reports that France allocates 11% of its GDP to construction and infrastructure, propelling demand for smart windows in both residential and commercial sectors. Furthermore, the French government’s incentives for green building certifications, such as HQE, have boosted adoption. With over 60% of urban households prioritizing eco-friendly living spaces, France remains a key player in advancing smart window technologies.
Sweden ranks third and is progressing at a notable rate in the regional market. The commitment of Sweden to achieving net-zero emissions by 2045 is driving investments in energy-efficient building solutions, which is contributing to the market expansion in this country. Sweden’s cold climate makes smart windows particularly attractive, as they reduce heating costs by up to 30%, according to the International Energy Agency. Additionally, Stockholm’s smart city initiatives prioritize sustainable technologies, creating a strong demand for electrochromic and photochromic windows. The Swedish government’s subsidies for renewable energy projects further encourage adoption, strengthening Sweden’s position as a leader in innovative and eco-conscious building practices.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe smart windows market include Saint-Gobain Group (France), Ravenwindow (US), Ppg Industries, Inc. (US), Kinestral Technologies, Inc. (US), Gentex Corporation (US), Merck Kgaa (Germany), Pleotint, Llc (US), E-Chromic Technologies, Inc. (US), Chromogenic Ab (Sweden), Agc, Inc. (Japan), Hitachi Chemical Co., Ltd (Japan), Nippon Sheet Glass Co., Ltd (Japan), Innovative Glass Corporation (US), Glasnovations Ltd. (UK), Heliotrope Technologies (US), Sage Electrochromics, Inc. (US), Scienstry (US), Stellaris (US), View Inc. (US), And Vista Window Company (US).
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe smart windows market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Technology
- Electrochromic Technology
- Pdlc
- Spd
- Photochromic
By Application
- Architectural And Construction
- Transportation
- Automotive
- Aircraft
- Marine
- Consumer Goods
- Power Generation
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the demand for smart windows in Europe?
The demand is primarily driven by energy efficiency regulations, government incentives for green buildings, and growing adoption of sustainable construction materials in commercial and residential sectors.
What are the key technologies used in European smart windows?
The key technologies include electrochromic glass, thermochromic glass, liquid crystal glass, and suspended particle devices (SPD), each offering different ways to control light and heat transmission.
How do smart windows help reduce energy consumption in European buildings?
Smart windows reduce energy consumption by optimizing daylight usage, minimizing heat gain or loss, and decreasing the need for artificial lighting and HVAC systems, leading to lower electricity costs.
What future trends are expected in the European smart windows market?
Future trends include advancements in AI-driven window automation, integration with IoT-based building management systems, increased affordability, and wider adoption in residential buildings.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]