Europe Smart Building Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Solution (Security System, Safety System, and Others (Fire Door Control Systems, Others Parts, and Accessories)), Application (Residential and Commercial), Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe) Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Smart Building Market Size
The Europe smart building market was worth USD 6.29 billion in 2024. The European market is estimated to reach USD 31.02 billion by 2033 from USD 7.51 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 19.40% from 2025 to 2033.
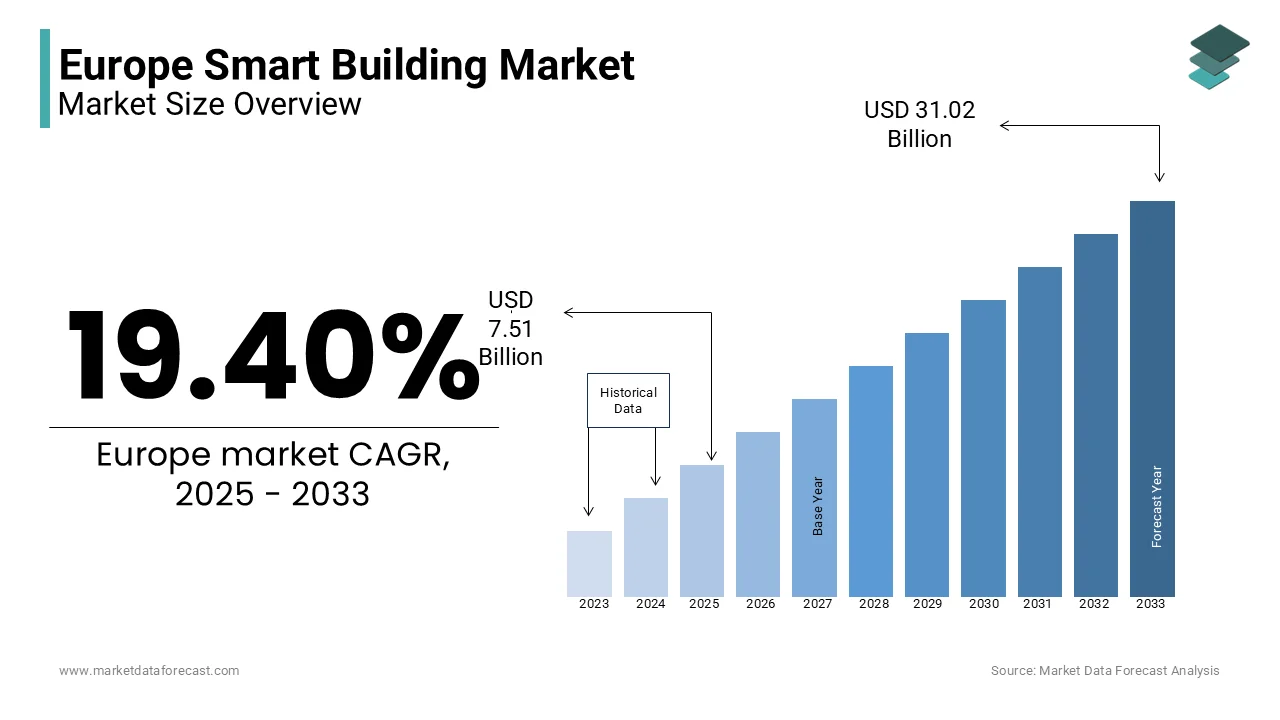
Smart buildings represent a transformative segment within the broader construction and real estate industries. Smart buildings leverage Internet of Things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics to optimize energy consumption, improve security, and streamline facility management. The Europe smart buildings market has witnessed significant growth in recent years owing to the increasing urbanization, stringent energy efficiency regulations, and the rising adoption of smart technologies. Germany, the United Kingdom, and France are leading the adoption of smart building technologies and account for more than 50% of the market share in Europe. The increasing demand for sustainable infrastructure and the rising awareness of carbon footprint reduction are propelling the European smart building market forward. As per a study by Navigant Research, smart buildings in Europe have the potential to reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, this confirms the critical role of smart buildings in achieving energy efficiency targets.
MARKET DRIVERS
Government Regulations and Sustainability Initiatives in Europe
The stringent regulatory framework of European Union is a primary driver of the Europe smart building market. The Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD), revised in 2024, mandates that all new buildings in the EU must be nearly zero-energy by 2030, with public buildings required to meet this standard by 2027. According to the European Commission, buildings account for 40% of the EU’s total energy consumption and 36% of greenhouse gas emissions. Smart building technologies, such as energy management systems and IoT-enabled devices, are critical in achieving these targets. The European Environment Agency reports that smart buildings can reduce energy use by up to 30%, making them indispensable for compliance with EU climate goals.
Technological Advancements and IoT Adoption
The rapid advancement of IoT and AI technologies is significantly propelling the smart building market in Europe. The European Commission’s Digital Strategy highlights that IoT adoption in buildings is expected to grow by 20% annually, driven by the need for efficient energy management and operational optimization. Smart sensors, connected lighting, and HVAC systems are becoming increasingly prevalent. These technologies enable real-time monitoring and automation, reducing operational costs by up to 15%, according to the International Energy Agency. This technological evolution is fostering the development of smarter, more sustainable urban infrastructure across Europe.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary restraints of the European smart building market is the significant upfront capital required for implementing advanced technologies. According to the European Commission, retrofitting existing buildings with smart systems can cost between €100 and €300 per square meter, depending on the level of integration. For large-scale commercial or residential projects, these costs can escalate rapidly, posing a barrier for many stakeholders. The International Energy Agency highlights that while smart buildings offer long-term savings, the initial investment often deters small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and property owners with limited financial resources. This financial hurdle slows down the widespread adoption of smart building solutions across Europe.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Concerns
The increasing reliance on IoT and connected devices in smart buildings raises significant data privacy and cybersecurity challenges. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) reports that cyberattacks on IoT devices have increased by 300%, with smart buildings being a vulnerable target due to their interconnected systems. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on data handling, adding complexity to the deployment of smart technologies. According to a study by the European Data Protection Board, 65% of businesses cite data security as a major concern when adopting IoT solutions. These challenges hinder the market’s growth by creating reluctance among potential adopters.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
The European smart building market is poised to benefit significantly from the integration of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines, with smart technologies. The European Commission’s Renewable Energy Directive aims for a 32% share of renewable energy in the EU’s total energy consumption by 2030. Smart buildings can optimize energy usage by storing excess renewable energy and redistributing it during peak demand. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, buildings equipped with smart energy management systems can increase renewable energy efficiency by up to 25%. This synergy between smart technologies and renewables presents a substantial opportunity for market growth, particularly in countries like Germany and Spain, where renewable energy adoption is high.
Rising Demand for Energy-Efficient Retrofits
The growing emphasis on retrofitting existing buildings to meet energy efficiency standards offers a significant opportunity for the smart building market. The European Commission estimates that 75% of the EU’s building stock is energy-inefficient, representing a vast potential for upgrades. The Renovation Wave Strategy aims to double annual energy renovation rates by 2030, targeting 35 million buildings. Smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled HVAC systems and energy monitoring tools, are critical for achieving these goals. According to the European Environment Agency, energy-efficient retrofits can reduce energy consumption by up to 60% in older buildings. This trend is driving demand for smart building solutions, particularly in urban areas with aging infrastructure.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Interoperability and Standardization Issues
A major challenge in the European smart building market is the lack of interoperability and standardization among various smart technologies and systems. The European Commission highlights that the absence of unified protocols often leads to compatibility issues, hindering seamless integration of devices from different manufacturers. According to a report by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute, nearly 40% of smart building projects face delays or increased costs due to interoperability challenges. This fragmentation not only complicates implementation but also limits the scalability of smart building solutions. Addressing these issues is critical for ensuring the efficient functioning of smart ecosystems and maximizing their potential across Europe.
Skilled Workforce Shortage
The rapid adoption of smart building technologies has outpaced the availability of a skilled workforce capable of designing, installing, and maintaining these systems. The European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training estimates that by 2025, there will be a shortage of over 1.8 million professionals in the construction and technology sectors with expertise in smart building solutions. This skills gap poses a significant barrier to market growth, as inadequate training and knowledge can lead to suboptimal implementation and operational inefficiencies. Bridging this gap through targeted education and training programs is essential for the sustainable expansion of the smart building market in Europe.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
19.40% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Solution, Application and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Novoferm GmbH (Germany), Bosch GmbH (Germany), GEZE GmbH (Germany), Johnson Controls (Ireland), Hormann (Germany), Schüco International (Germany), ZKTeco Europe, S.L. (Spain), Dormakaba (Switzerland), SALTO (Spain), SimonsVoss (Germany), Schneider Electric (France), ABB (Switzerland), and Honeywell International Inc. (U.S.) are some of the major players in the European smart building market. |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany dominated the European smart building market in 2023. The domination of Germany in European market is primarily attributed to its strong emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability, driven by the country’s Energiewende (energy transition) policy. The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy reports that smart buildings play a pivotal role in achieving the national target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030. Germany’s advanced manufacturing sector and high adoption of IoT technologies further bolster its leadership. According to the German Energy Agency, over 30% of new buildings in Germany are equipped with smart energy management systems, making it a frontrunner in integrating renewable energy and smart technologies.
The UK is another key regional market for smart buildings in Europe. The growth of the UK market is attributed to the stringent building regulations and a strong focus on reducing carbon emissions. The Future Homes Standard of the UK government mandates that all new homes must produce 75-80% lower carbon emissions by 2025. A report by the UK Green Building Council highlights that smart technologies are integral to meeting these targets, with over 40% of commercial buildings in the UK already incorporating IoT-enabled systems. The country’s robust technology sector and significant investments in smart infrastructure further solidify its leading position in the market.
France is likely to play an integral role in the European smart building market. The ambitious environmental policies and the Energy Transition for Green Growth Act are driving the French smart building market growth. The French Environment and Energy Management Agency states that smart buildings are critical for achieving the nation’s goal of reducing energy consumption by 20% by 2030. France’s focus on retrofitting older buildings with smart technologies has also contributed to its leadership. According to the French Ministry of Ecological Transition, nearly 25% of building renovations in France now include smart systems, positioning the country as a leader in sustainable urban development and energy-efficient infrastructure.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Novoferm GmbH (Germany), Bosch GmbH (Germany), GEZE GmbH (Germany), Johnson Controls (Ireland), Hormann (Germany), Schüco International (Germany), ZKTeco Europe, S.L. (Spain), Dormakaba (Switzerland), SALTO (Spain), SimonsVoss (Germany), Schneider Electric (France), ABB (Switzerland), and Honeywell International Inc. (U.S.) are some of the major players in the European smart building market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe smart building market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Solution
- Security System
- Access Control System
- Smart Door Lock
- Biometric Door Locks
- Smart Card Door Locks
- Electric Strike Door Locks
- Others (Keypad Door Lock)
- Safety System
- Others (Fire Door Control Systems, Others Parts, and Accessories)
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Hotel
- Healthcare
- Retail
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key drivers of growth in the Europe Smart Building Market?
The market is driven by increasing energy efficiency regulations, advancements in smart technology, rising adoption of IoT, and growing demand for enhanced security and automation in buildings.
Which industries are benefiting the most from smart building solutions in Europe?
The commercial real estate sector, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, data centers, and industrial plants benefit the most due to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
What are the latest trends in the Europe Smart Building Market?
Emerging trends include AI-driven building automation, digital twins for real-time building simulations, smart HVAC optimization, and blockchain for secure data transactions in smart buildings.
What is the future outlook for the Europe Smart Building Market?
The market is expected to expand significantly as urbanization increases, 5G adoption accelerates, and businesses focus on reducing carbon footprints through smart energy solutions.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]