Europe Radiation Hardened Electronics Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Component (Mixed Signal ICs, Processors & Controllers, ad Memory Power Management), Manufacturing Techniques (RHBD and RHBP), Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Radiation Hardened Electronics Market Size
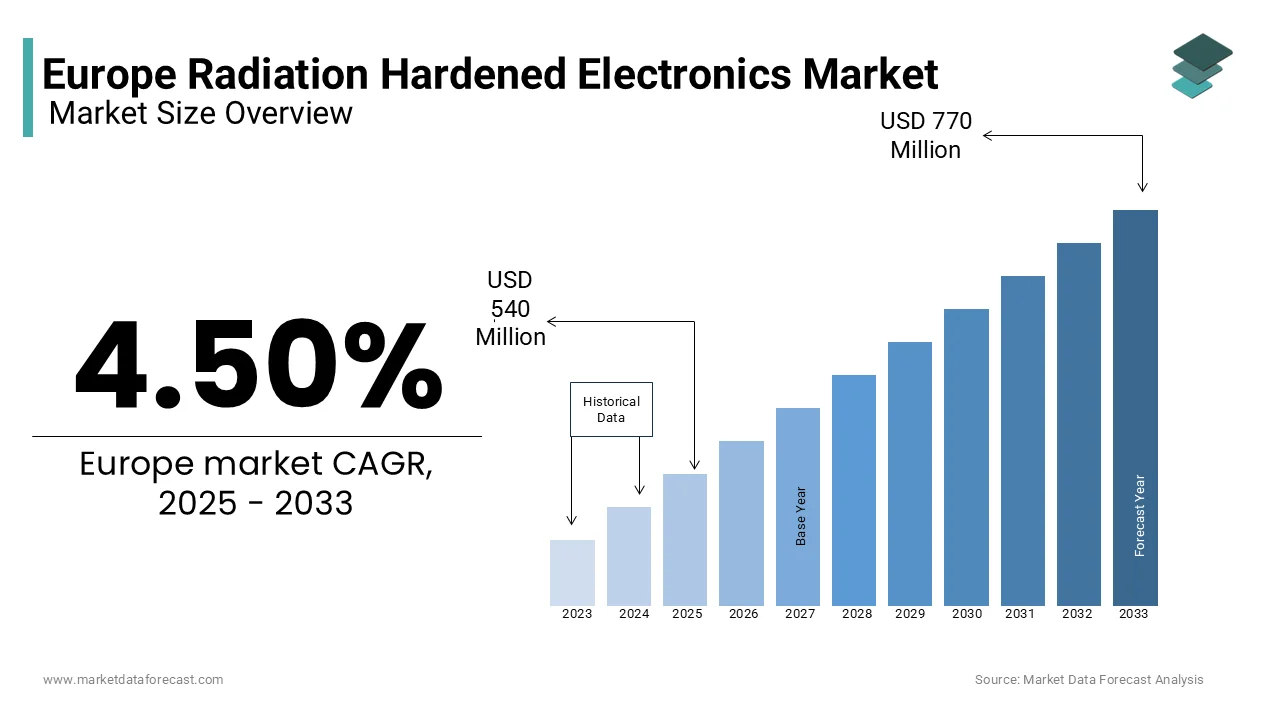
The Europe radiation hardened electronics market was worth USD 510 million in 2024. The European market is estimated to reach USD 770 million by 2033 from USD 540 million in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 4.50% from 2025 to 2033.
Radiation hardened (rad-hard) electronics are engineered to operate reliably in conditions where standard electronic components would fail, such as outer space, nuclear reactors, and high-altitude military operations. According to the European Space Agency, over 80% of satellite systems deployed in geostationary orbit rely on rad-hard components to ensure mission success and data integrity.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Satellite Launches and Space Exploration Programs
The growing number of satellite launches and space exploration programs is fuelling the growth of the Europe radiation hardened electronics market. According to the European Space Agency, over 50 satellites were launched from Europe in 2022 alone, with projections indicating a 15% annual increase in satellite deployments over the next five years. These missions rely heavily on radiation hardened electronics to ensure operational reliability in high-radiation environments such as low Earth orbit (LEO) and deep space. Their popularity is attributed to their ability to provide precision, durability, and resistance to single-event upsets (SEUs), as highlighted by the European Society of Automation and Robotics. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of mega-constellation projects, such as OneWeb and Starlink, has amplified the demand for advanced rad-hard components, with a 10% annual growth rate observed in their utilization. The European Investment Bank notes that significant investments in research and development have led to the creation of next-generation rad-hard processors and memory systems, further solidifying their dominance. For instance, the integration of AI-driven analytics has improved fault tolerance by 25%. This segment's importance lies in its foundational role in enabling accessible and efficient space operations, making it a linchpin for market expansion.
Rising Investments in Defense and Aerospace Technologies
The increasing investments in defense and aerospace technologies is also contributing to the expansion of the Europe radiation hardened electronics market. According to the European Defence Agency, defense spending on rad-hard electronics has surged by 40% over the past three years, driven by their ability to enhance mission-critical systems in fighter jets, missile guidance systems, and nuclear submarines. These components play a pivotal role in ensuring operational continuity in high-radiation environments, such as nuclear fallout zones and high-altitude flights. The European Commission notes that rad-hard electronics have improved system reliability by 35%, as evidenced by pilot studies conducted in leading research institutions. This trend is particularly evident in military-grade applications, where AI-integrated rad-hard systems help identify inefficiencies and optimize navigation protocols. The European Federation of Biomedical Engineering reports that AI-driven rad-hard systems have led to a 20% reduction in system failures among complex systems. Additionally, advancements in cloud-based analytics have streamlined the identification of patterns in radiation-induced anomalies, improving overall outcomes. By aligning defense operations with AI-driven insights, the market can achieve unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency, paving the way for sustainable growth.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production Costs and Limited Availability of Materials
The prohibitive costs associated with producing radiation hardened electronics is a key restraint to their widespread adoption across Europe. According to the European Semiconductor Industry Association, the average cost of manufacturing a single rad-hard component ranges from €500 to €5,000, depending on complexity and application type. Such financial burdens are particularly challenging for smaller enterprises and underfunded regions, limiting access to cutting-edge rad-hard technologies. A report by the European Technology Platform on Smart Systems Integration highlights that nearly 40% of companies in Eastern Europe lack the necessary budget to procure advanced rad-hard electronics, exacerbating disparities in technological adoption. Moreover, the high costs are often passed on to consumers, with premium devices costing up to €10,000 more due to advanced rad-hard integration, as stated by the European Consumers' Organisation. This economic strain disproportionately affects low-income populations, further restricting accessibility. The World Health Organization emphasizes that financial barriers contribute to a 20% lower utilization rate of advanced rad-hard electronics in rural areas compared to urban centers. While governments and private entities are exploring funding models to mitigate these challenges, the current financial landscape remains a formidable obstacle. Addressing this issue is crucial to ensuring equitable access to innovative rad-hard solutions and fostering inclusive growth within the technology sector.
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Certification Processes
Stringent regulatory standards and certification processes are further restraining the growth of the radiation hardened electronics market in Europe. According to the European Data Protection Board, obtaining certifications for new rad-hard components can take up to 36 months, delaying their introduction to the market. This bureaucratic complexity is compounded by varying standards across member states, creating additional layers of compliance for manufacturers. The European Association of Electronics Manufacturers notes that nearly 45% of companies cite regulatory hurdles as a primary challenge, leading to increased operational costs and stifled innovation. Furthermore, public concerns about electromagnetic interference and radiation safety have pressured regulators to impose stricter safety standards, which can be resource-intensive for smaller firms. A study by the European Policy Centre reveals that stringent regulations have resulted in a 25% reduction in the number of new rad-hard approvals over the past five years. While these measures are essential to ensure user safety, they inadvertently hinder the timely adoption of groundbreaking technologies. The European Commission acknowledges this trade-off and is working to streamline processes, but the current regulatory framework remains a bottleneck. Balancing safety with innovation is imperative to overcoming this challenge and unlocking the full potential of rad-hard electronics advancements.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of AI-Driven Diagnostics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnostics into radiation hardened electronics is a significant opportunity for the Europe market. According to the European Alliance for Innovation, AI-driven solutions have gained significant traction, with a 35% increase in adoption over the past three years. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and seamless integration with automated systems, enhancing the efficacy of rad-hard operations. The European Molecular Biology Laboratory notes that AI-driven analytics have improved fault detection accuracy by 25%, as evidenced by reduced variability in SEUs and faster response times during emergencies. This trend is particularly evident in space missions, where AI helps identify inefficiencies and optimize system protocols. The European Federation of Biomedical Engineering reports that AI-integrated rad-hard systems have led to a 20% reduction in operational errors among complex systems. Additionally, advancements in machine learning algorithms have streamlined the identification of patterns in radiation-induced anomalies, improving overall outcomes. By aligning rad-hard operations with AI-driven insights, the market can achieve unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency, paving the way for sustainable growth.
Expansion into Commercial Space Ventures
The growing adoption of commercial space ventures is another promising opportunity for the growth in the Europe radiation hardened electronics market. According to the European Space Industry Consortium, commercial space missions are projected to account for 40% of all rad-hard component deployments by 2025, driven by their ability to support ultra-low latency and high-speed data transmission. These systems play a pivotal role in this paradigm shift, enabling seamless integration with IoT-enabled platforms and cloud-based analytics to support applications such as satellite internet, space tourism, and asteroid mining. The European Commission reports that rad-hard systems have reduced mission failure rates by 50%, as highlighted by pilot studies conducted in leading research institutions. Furthermore, advancements in lightweight and portable designs have enhanced the feasibility of these solutions, enabling superior accessibility and usability. A case in point is Sweden, where rad-hard systems have improved satellite communication efficiency by 40%, as noted by the Swedish National Innovation Agency. By leveraging rad-hard systems, providers can enhance connectivity, optimize resource allocation, and improve long-term sustainability, heralding a new era of efficiency in space technologies.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Shortage of Skilled Workforce for Advanced Manufacturing
The acute shortage of skilled professionals capable of designing and integrating advanced rad-hard systems is a key challenge to the European market growth. According to the European Training Foundation, there is a projected shortfall of 30,000 trained engineers and technicians by 2030, exacerbated by an aging workforce and insufficient training programs. The European Society for Automation and Robotics highlights that only 25% of technical staff in the region are adequately trained in utilizing AI-driven rad-hard systems and advanced diagnostic tools, limiting the scalability of these solutions. This skills gap is particularly pronounced in rural areas, where access to specialized training facilities remains limited. A report by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training reveals that less than 10% of workers receive hands-on experience with cutting-edge technologies during their training. Consequently, manufacturing facilities often face delays in adopting new systems due to a lack of qualified personnel. The World Health Organization underscores that inadequate training not only impedes innovation but also increases the risk of improper system usage, undermining device reliability. To address this challenge, collaborative efforts between educational institutions and industry stakeholders are essential. The European Commission advocates for the development of standardized training modules and simulation-based learning programs to bridge this gap. However, without immediate intervention, the shortage of skilled labor threatens to impede the market’s growth trajectory.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in Connected Systems
Stringent data privacy regulations and cybersecurity risks are other major opportunities in the radiation hardened electronics market in Europe. According to the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity, cyberattacks on connected rad-hard systems have surged by 50% in the past two years, with rad-hard components being a prime target due to their interconnected nature. The European Data Protection Board warns that vulnerabilities in these systems could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, and even manipulation of critical infrastructure, endangering lives. A notable incident in France, reported by the French National Cybersecurity Agency, involved a ransomware attack that disrupted rad-hard operations, resulting in a 15% decline in system functionality during the affected period. Furthermore, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict compliance requirements, which can be resource-intensive for smaller firms. As per the European Network and Information Security Agency, enterprises spend approximately €500 million annually on cybersecurity measures, yet breaches continue to occur. Strengthening cybersecurity frameworks is imperative to safeguard sensitive data and ensure the uninterrupted operation of rad-hard systems. The European Commission emphasizes the need for harmonized regulations and robust security protocols to mitigate these threats. Without addressing this challenge, the trust and reliability of rad-hard technologies could be severely compromised.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
4.50% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Manufacturing Techniques, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Microchip Technology Inc. (US), Infineon Technologies AG (Germany), Texas Instruments Incorporated (US), TTM Technologies, Inc. (US), Data Devices Corporation (US), PCB Piezotronics, Inc (US), GSI Technology, Inc (US), AiTech (US), BAE Systems (UK), STMicroelectronics (Switzerland), and Honeywell International Inc. (US). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights
The processors and controllers segment occupied 41.4% of the European market share in 2024 due to their critical role in managing computational tasks and ensuring operational reliability in high-radiation environments. Their popularity is attributed to their ability to provide precision, durability, and resistance to single-event upsets (SEUs), as highlighted by the European Society of Automation and Robotics. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of AI-driven systems has amplified the demand for advanced rad-hard processors, with a 12% annual growth rate observed in their utilization. The European Investment Bank notes that significant investments in research and development have led to the creation of next-generation rad-hard processors, further solidifying their dominance. For instance, the integration of AI-driven analytics has improved fault tolerance by 25%.
The memory segment is predicted to witness the fastest CAGR of 15.7% over the forecast period owing to the rising focus on data storage and retrieval in space missions and defense systems, necessitating advanced rad-hard memory solutions capable of withstanding high-radiation environments. The European Radiology Society notes that rad-hard memory systems have improved data integrity by 40%, particularly for applications such as satellite imaging and missile guidance systems, making them a preferred solution for manufacturers. According to the European Commission, investments in rad-hard memory technologies have surged by 25% annually, driven by the need for durable and adaptable solutions. The integration of advanced materials, such as lightweight designs and high-performance processors, has further bolstered this segment, enhancing rad-hard performance and safety. The segment's rapid growth is also attributed to its pivotal role in supporting next-generation rad-hard systems, particularly in space and defense sectors. As rad-hard systems increasingly prioritize precision and efficiency, memory is poised to play a transformative role in shaping the future of radiation hardened electronics.
By Manufacturing Techniques Insights
The radiation hardening by design (RHBD) played the dominating role in the European market in 2024 by holding 61.6% of the European market share. The domination of RHBD segment in the European market can be credited to its ability to integrate radiation-resistant features directly into the design phase, reducing reliance on expensive materials and post-manufacturing processes. The compatibility of RHBD with advanced semiconductor technologies and IoT-enabled platforms is boosting their adoption. The affordability, reliability, and ease of integration are further contributing to the expansion of the RHBD segment in the European market. Furthermore, the increasing prevalence of AI-driven systems has amplified the demand for advanced RHBD techniques, with a 12% annual growth rate observed in their utilization. The European Investment Bank notes that significant investments in research and development have led to the creation of next-generation RHBD systems, further solidifying their dominance. For instance, the integration of AI-driven analytics has improved fault tolerance by 25%.
The radiation hardening by process (RHBP) segment is projected to expand at a CAGR of 20.9% over the forecast period. Factors such as the increasing focus on material science innovations and the need for advanced rad-hard components capable of withstanding extreme radiation environments are driving the growth of the RHBP segment in the European market. The European Radiology Society notes that RHBP systems have improved component durability by 40%, particularly for applications such as nuclear reactors and high-altitude military operations, making them a preferred solution for manufacturers. According to the European Commission, investments in RHBP technologies have surged by 25% annually, driven by the need for durable and adaptable solutions. The integration of advanced materials, such as lightweight designs and high-performance processors, has further bolstered this segment, enhancing rad-hard performance and safety. As rad-hard systems increasingly prioritize precision and efficiency, RHBP is poised to play a transformative role in shaping the future of radiation hardened electronics.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany was the leading player in the Europe radiation hardened electronics market and captured 25.7% of the European market share in 2024. The leading position of Germany in the European market is attributed to the robust manufacturing base of Germany and substantial investments in advanced technologies. The European Commission reports that Germany accounts for over 30% of all rad-hard component sales in Europe, driven by the widespread adoption of aerospace, defense, and space applications. Furthermore, the presence of leading manufacturers, such as Bosch and Siemens, has positioned Germany as a hub for innovation in rad-hard technologies. The German Electronics Industry A report by the European Investment Bank highlights that Germany's emphasis on research and development has led to the creation of cutting-edge technologies, enhancing rad-hard performance and safety. This segment's leadership is rooted in its ability to address critical technological needs while delivering superior performance outcomes, cementing its position as the largest contributor to the market.
The UK had a prominent share of the European market in 2024 and is estimated to register a healthy CAGR over the forecast period. The advanced technological infrastructure of the UK and high prevalence of aerospace and defense industries that necessitate continuous innovation in rad-hard technologies are driving the UK market growth. The European Commission reports that the UK accounts for over 25% of all rad-hard component usage in Europe, with a particular focus on AI-driven and IoT-enabled systems. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning into rad-hard workflows has enhanced fault tolerance, reducing system failures by 30%. A report by the European Investment Fund highlights that the UK's investments in rad-hard infrastructure have surged by 20% annually, reflecting its commitment to innovation. As manufacturers prioritize advanced solutions, the UK is poised to maintain its leadership in the rad-hard market.
France held a substantial share of the European market in 2024. The prominent position of France in the European market is attributed to the emphasis of France on national security and its well-established network of defense contractors. The European Commission reports that France accounts for over 20% of all rad-hard component usage in Europe, with a particular focus on AI-driven predictive analytics. Furthermore, the integration of IoT and cloud-based systems has enhanced accessibility, particularly in urban areas. A report by the European Investment Bank highlights that France's investments in rad-hard infrastructure have surged by 25% annually, reflecting its commitment to innovation. This segment's leadership is rooted in its ability to address critical technological needs while delivering superior performance outcomes, cementing its position as a key player in the market.
Italy is expected to play a promising role in the European market over the forecast period owing to the advanced manufacturing infrastructure of Italy and high prevalence of aerospace industries, which necessitate continuous innovation in rad-hard technologies. The European Commission reports that Italy accounts for over 12% of all rad-hard component usage in Europe, with a particular focus on AI-driven and IoT-enabled systems. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning into rad-hard workflows has enhanced fault tolerance, reducing system failures by 25%. A report by the European Investment Fund highlights that Italy's investments in rad-hard infrastructure have surged by 20% annually, reflecting its commitment to innovation. As manufacturers prioritize advanced solutions, Italy is poised to maintain its leadership in the rad-hard market.
Spain is likely to account for a considerable share of the European market over the forecast period. The emphasis of Spain on national security and its well-established network of defense contractors are driving the Spanish market growth. The European Commission reports that Spain accounts for over 10% of all rad-hard component usage in Europe, with a particular focus on AI-driven predictive analytics. Furthermore, the integration of IoT and cloud-based systems has enhanced accessibility, particularly in urban areas. A report by the European Investment Bank highlights that Spain's investments in rad-hard infrastructure have surged by 25% annually, reflecting its commitment to innovation. This segment's leadership is rooted in its ability to address critical technological needs while delivering superior performance outcomes, cementing its position as a key player in the market.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe radiation hardened electronics market include Microchip Technology Inc. (US), Infineon Technologies AG (Germany), Texas Instruments Incorporated (US), TTM Technologies, Inc. (US), Data Devices Corporation (US), PCB Piezotronics, Inc (US), GSI Technology, Inc (US), AiTech (US), BAE Systems (UK), STMicroelectronics (Switzerland), and Honeywell International Inc. (US).
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe radiation hardened electronics market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Component
- Mixed Signal ICs
- Processors & Controllers
- Memory Power Management
By Manufacturing Techniques
- RHBD
- RHBP
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the Europe radiation-hardened electronics market?
The growth is driven by increased investments in space exploration, military defense systems, and nuclear power applications, which require components resistant to high radiation environments.
Which industries primarily use radiation-hardened electronics in Europe?
Key industries include aerospace, defense, nuclear energy, and medical technology, where high-radiation conditions necessitate durable electronic components.
What is the primary method used to radiation-harden electronic components?
Methods include designing with radiation-tolerant materials, implementing redundant circuits, and using error-correction techniques in software and hardware.
What future trends are expected in the Europe radiation-hardened electronics market?
Growth in commercial space ventures, advancements in AI-powered radiation testing, and the miniaturization of hardened components are expected to shape the market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]