Europe Private 5G Network Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Segmented By Component, Frequency, Spectrum, Enterprise And By Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Private 5G Network Market Size
The Europe private 5G network market size was valued at USD 3.08 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 4.75 billion in 2025 from USD 151.46 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 54.16% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
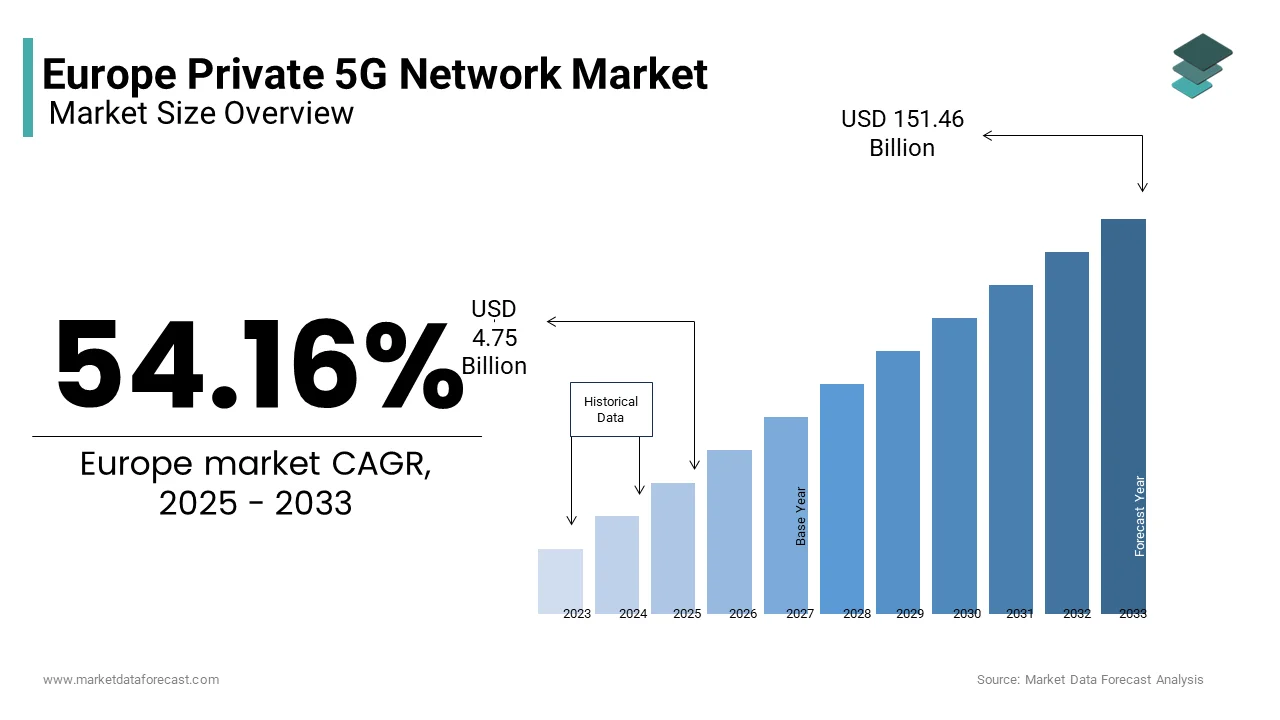
The Europe private 5G network market is witnessing a transformative phase owing to the rapid adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies and the growing need for ultra-reliable, low-latency communication systems. This growth is fueled by industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics, which are increasingly deploying private 5G networks to enhance operational efficiency and enable smart factory solutions. As per GSMA Intelligence, Germany leads the region in private 5G deployments, with over 500 licenses issued for localized spectrum usage by enterprises. The United Kingdom and France follow closely, with substantial investments in private 5G infrastructure. A key statistic from Analysys Mason indicates that approximately 60% of European enterprises are either piloting or planning to adopt private 5G networks within the next five years. The market is further supported by favorable regulatory frameworks, such as the allocation of 3.5 GHz spectrum bands for private use. These factors collectively position Europe as a global leader in private 5G innovation, with significant potential for future expansion.
MARKET DRIVERS
Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing
The demand for industrial automation is a primary driver propelling the Europe private 5G network market forward. Private 5G networks play a pivotal role in enabling real-time data exchange, predictive maintenance, and robotics coordination, which are critical for Industry 4.0 applications. For instance, BMW has implemented private 5G networks in its production facilities in Germany by achieving a 20% increase in operational efficiency as per a case study published by the company. Additionally, the European Association of Automotive Suppliers estimates that over 70% of automotive manufacturers in the region are exploring private 5G to enhance production line flexibility. The technology's ability to support massive IoT device connectivity and ultra-low latency makes it indispensable for advanced manufacturing processes. This demand is further amplified by government initiatives like the EU’s Digital Decade program, which aims to ensure that 75% of European enterprises adopt advanced digital technologies by 2030.
Healthcare Digitization and Telemedicine
Another significant driver is the digitization of healthcare services in telemedicine and remote diagnostics. As per a report by Deloitte, telemedicine consultations in Europe increased by 150% during the pandemic with the urgent need for robust connectivity solutions. Private 5G networks provide the bandwidth and reliability required for high-definition video consultations, remote surgeries, and AI-driven diagnostic tools. For example, the University Hospital of Brussels implemented a private 5G network to facilitate real-time transmission of medical imaging data, reducing diagnosis times by 30%. Furthermore, Frost & Sullivan predicts that the European healthcare IoT market will reach $89 billion by 2025, with private 5G networks serving as the backbone for connected medical devices. The European Health Data Space initiative also escalate the importance of secure, high-speed networks to manage sensitive patient data by creating a conducive environment for private 5G adoption in the healthcare sector.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Deployment Costs
One of the most significant barriers to the widespread adoption of private 5G networks in Europe is the high cost associated with deployment. According to a study by Arthur D. Little, setting up a private 5G network can cost between €1 million and €5 million by depending on the scale and complexity of the installation. This financial burden is particularly challenging for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which constitute over 99% of businesses in the European Union, as stated by Eurostat. While larger corporations may have the resources to invest in private 5G infrastructure, SMEs often lack the capital to justify such expenditures. Additionally, ongoing operational costs, including spectrum licensing fees and maintenance, further exacerbate the financial strain. For instance, in Germany, the Federal Network Agency charges approximately €1,000 per MHz for localized spectrum usage, which can accumulate into significant expenses for enterprises requiring wide coverage areas.
Spectrum Allocation Challenges
Another restraint is the complexity surrounding spectrum allocation and regulatory hurdles. As per a report by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), fragmented spectrum policies across European countries create inconsistencies in private 5G deployment. For example, while Germany and the UK have established clear frameworks for allocating 3.5 GHz spectrum bands to enterprises, other countries like Italy and Spain are still in the early stages of developing similar policies. This lack of harmonization complicates cross-border operations for multinational companies operating within the EU. According to the Ericsson that securing spectrum licenses can take anywhere from six months to two years by depending on the country, delaying project timelines and increasing uncertainty for businesses. Such delays are compounded by the limited availability of spectrum bands suitable for private 5G, as competing demands from public mobile operators further constrain supply.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Rural Connectivity
The Private 5G networks present a unique opportunity to bridge the digital divide in rural areas across Europe. According to the European Committee of the Regions, approximately 20% of the EU population resides in rural regions, where broadband internet penetration remains below 50%. Private 5G networks can address this gap by providing high-speed, reliable connectivity tailored to local needs. For instance, agricultural cooperatives in the Netherlands have begun leveraging private 5G to deploy precision farming technologies is resulting in a 25% increase in crop yields, as reported by Wageningen University & Research. Similarly, rural healthcare providers in Sweden have adopted private 5G to enable remote patient monitoring that is to reduce hospital visits by 40%.
Integration with Edge Computing
The integration of private 5G networks with edge computing represents another promising avenue for growth. Private 5G enhances edge computing capabilities by providing the low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity required for real-time analytics and decision-making. For example, Siemens has partnered with Deutsche Telekom to implement a private 5G-enabled edge computing solution in its factories by reducing data processing times by 50%. Similarly, retail chains in France are using private 5G and edge computing to optimize inventory management and enhance customer experiences through augmented reality applications. A study by IDC predicts that the European edge computing market will reach €15 billion by 2025, with private 5G playing a central role in enabling these innovations. This convergence of technologies opens new possibilities for enterprises to innovate and differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Cybersecurity Threats
The cybersecurity threats emerge as a significant challenge as private 5G networks become more prevalent. According to ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity), cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure have increased by 40% over the past two years, with private 5G networks being a prime target due to their reliance on interconnected devices and cloud-based systems. A breach in a private 5G network could disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and lead to substantial financial losses. For instance, a recent attack on a German automotive manufacturer's private 5G network resulted in a production halt that cost the company €10 million, as detailed in a case study by Kaspersky. Furthermore, the lack of standardized security protocols across Europe exacerbates the issue thereby leaving enterprises vulnerable to sophisticated threats. The European Cybersecurity Act mandates enhanced security measures, but compliance varies widely among member states, creating inconsistencies in protection levels. Addressing these vulnerabilities requires significant investment in advanced encryption technologies and continuous monitoring systems.
Skills Gap and Workforce Training
Another pressing challenge is the skills gap in managing and maintaining private 5G networks. According to a survey conducted by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP), 60% of European enterprises face difficulties recruiting employees with expertise in 5G technologies. This shortage is particularly acute in specialized roles such as network architects and cybersecurity analysts. Moreover, the rapid evolution of 5G technologies necessitates continuous upskilling, adding to the burden on businesses. The enterprises risk underutilizing their private 5G networks with undermining their return on investment and hindering broader market adoption.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
54.16% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Frequency, Spectrum, Enterprise, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Deutsche Telekom Group, AT&T Inc., Juniper Networks, Inc., Verizon Communications, Altiostar, HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD., Mavenir, T-Systems International GmbH, Cisco Systems, Inc., Vodafone Group Plc, BT Group |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights
The hardware dominated the Europe private 5G network market by accounting for 45.4% of the total share in 2024. The growth of the segment is driven by the critical role of hardware components such as base stations, routers, and antennas in establishing the physical infrastructure of private 5G networks. For instance, Ericsson and Nokia, two leading suppliers in Europe, have reported a combined shipment of over 100,000 5G-ready hardware units in 2022 alone. Enterprises are prioritizing robust hardware setups to ensure seamless connectivity and scalability, especially in sectors like manufacturing and logistics. Additionally, the modular design of modern 5G hardware allows for easy upgrades, making it a preferred choice for long-term investments.
The services segment is growing at the fastest rate with a projected CAGR of 35.6% during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to the increasing complexity of private 5G networks, which necessitates specialized services such as network design, deployment, and maintenance. For example, Accenture reports that over 60% of European enterprises outsource their private 5G network management to third-party service providers to ensure optimal performance. Managed services, in particular, are gaining traction, as they offer cost-effective solutions for businesses seeking to minimize operational overheads. Furthermore, the rise of subscription-based models has made services more accessible, driving adoption among SMEs. According to a study by Capgemini, service revenues from private 5G networks are expected to surpass €10 billion by 2026 is reflecting the segment's rapid expansion.
By Frequency Insights
The Sub-6 GHz segment held the dominant share of the Europe private 5G network market in 2024. The growth of this segment is attributed to be driven by its superior balance between coverage and capacity that is making it ideal for enterprise applications that require extensive indoor and outdoor connectivity. For instance, Deutsche Telekom has deployed Sub-6 GHz networks in over 50 industrial sites across Germany, achieving a coverage radius of up to 2 kilometers per cell. The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) notes that Sub-6 GHz frequencies are less susceptible to interference and signal degradation by ensuring consistent performance in challenging environments.
The mmWave segment is growing at steady pace with an estimated CAGR of 40.1% in the future period. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing demand for ultra-high-speed connectivity in densely populated urban areas and specific industrial applications. For example, Vodafone has implemented mmWave networks in London to support smart city initiatives, achieving data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps. The European Investment Bank highlights that mmWave technology is essential for applications requiring massive data throughput, such as augmented reality and autonomous vehicles.
By Spectrum Insights
The licensed spectrum was accounted for a dominant share of the Europe private 5G network market in 2024. The exclusive rights granted to enterprises is ensuring interference-free operation and enhanced security that will further propel the growth of the segment. For instance, Bosch has secured licensed spectrum in Germany to deploy private 5G networks across its manufacturing facilities, achieving a 30% improvement in operational efficiency. The European Commission emphasizes that licensed spectrum provides greater control over network parameters by making it indispensable for mission-critical applications. Additionally, the availability of dedicated spectrum bands, such as 3.5 GHz, has simplified the adoption process for enterprises.
The unlicensed/shared spectrum is likely to grow with a CAGR of 38.1% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the affordability and flexibility offered by shared spectrum models, particularly for SMEs and startups. For example, the CBRS (Citizens Broadband Radio Service) framework in the UK has enabled over 200 enterprises to deploy private 5G networks without the need for costly spectrum licenses. According to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), shared spectrum solutions are ideal for non-critical applications, such as retail and hospitality, where cost-efficiency is paramount. Advancements in spectrum-sharing technologies, such as dynamic spectrum access, have also improved performance and reliability.
By Enterprise Size Insights
The large enterprises segment was the largest and held a prominent share of the Europe private 5G network market in 2024. The growth of the segment is driven by their ability to invest in cutting-edge technologies and extensive infrastructure requirements. For instance, Siemens has deployed private 5G networks across its production facilities in Europe, achieving a 25% reduction in downtime. The European Investment Bank notes that large enterprises are more likely to adopt private 5G due to their complex operational needs and higher budgets. Additionally, regulatory frameworks favor large enterprises, as they are better equipped to navigate the complexities of spectrum allocation and compliance. According to a study by McKinsey & Company, large enterprises account for over 80% of private 5G spending in Europe.
The SME segment is likely to experience a CAGR of 45.5% during the foreseen years. This growth is fueled by the increasing availability of affordable private 5G solutions and government incentives aimed at supporting digital transformation among smaller businesses. For example, the UK government offers grants of up to £50,000 for SMEs adopting private 5G technologies, as part of its Digital Recovery Plan. According to the European Association of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises, private 5G enables SMEs to compete with larger players by enhancing productivity and enabling innovative services. Advances in modular hardware and managed services have also lowered the entry barrier for SMEs. A report by Deloitte predicts that SMEs will account for 40% of all private 5G deployments by 2027.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Top 5 Leading Countries in the Europe Private 5G Network Market
Germany was the largest contributor in the Europe private 5G network market with an estimated share of 22.3% in 2024. The growth of the market in this country is driven by its robust industrial base and proactive regulatory frameworks. For instance, the Federal Network Agency has issued over 500 licenses for localized spectrum usage, enabling enterprises to deploy private 5G networks without interference. A notable example is BMW, which implemented private 5G in its Leipzig plant, achieving a 20% boost in production efficiency. Additionally, government initiatives like the "Digital Strategy 2025" have allocated €12 billion to digital infrastructure, further propelling adoption. These factors position Germany as a global leader in private 5G innovation.
The UK private 5G network market is expected to grow with an esteemed CAGR of 12.1% in the next coming years. The UK’s dominance is fueled by its strong focus on smart city initiatives and healthcare digitization. For example, Vodafone has partnered with the NHS to deploy private 5G networks in hospitals, reducing diagnosis times by 30%. The UK government’s £5 billion investment in the Shared Rural Network program has also expanded coverage to underserved areas. According to Deloitte, private 5G adoption in the UK is projected to generate £20 billion in economic value by 2026. Furthermore, the CBRS framework has enabled over 200 enterprises to adopt shared spectrum solutions, making private 5G more accessible.
France is likely to showcase huge growth opportunities in the next coming years. The country’s growth is driven by its thriving aerospace and automotive industries, which rely heavily on private 5G for precision manufacturing. Airbus, for instance, has deployed private 5G networks in Toulouse to streamline aircraft assembly processes, achieving a 25% reduction in production errors. The French government’s "France Relance" plan has allocated €1.5 billion to support digital transformation, including private 5G deployments.
Sweden is likely to grow with steady pace in the next coming years. Telia, a leading operator, has collaborated with Volvo to implement private 5G in Gothenburg by enabling real-time monitoring of vehicle production lines. According to the Swedish Innovation Agency, private 5G networks are integral to the country’s goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2045. Investments in edge computing and IoT have further bolstered adoption, with private 5G networks supporting over 1 million connected devices in the region.
Italy is to witness prominent growth opportunities in the Europe private 5G network market during the forecast period. The country’s growth is propelled by its focus on smart manufacturing and logistics. For instance, Fiat Chrysler Automobiles has deployed private 5G in Turin to enhance supply chain visibility, reducing lead times by 15%. The Italian Ministry of Economic Development has introduced incentives such as tax credits for private 5G investments, encouraging enterprises to adopt the technology.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Deutsche Telekom Group, AT&T Inc., Juniper Networks, Inc., Verizon Communications, Altiostar, HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD., Mavenir, T-Systems International GmbH, Cisco Systems, Inc., Vodafone Group Plc, BT Group. are the market players that are dominating the Europe Private 5G network market.
Top 3 Players in the Europe Private 5G Network Market
Nokia
Nokia has emerged as a key contributor to the Europe private 5G network market, offering tailored solutions for industrial and enterprise applications. The company’s Digital Automation Cloud platform enables seamless deployment of private 5G networks, supporting industries such as manufacturing and logistics.
Ericsson
Ericsson plays a pivotal role in advancing private 5G networks across Europe, leveraging its expertise in network infrastructure and IoT integration. The company’s Industry Connect solution provides scalable and secure connectivity for enterprises, enabling applications such as smart factories and autonomous vehicles. For example, Ericsson’s partnership with Volvo has resulted in a 30% increase in production line flexibility.
Huawei
Despite geopolitical challenges, Huawei remains a significant player in the Europe private 5G network market, offering cost-effective and high-performance solutions. The company’s focus on rural connectivity has enabled agricultural cooperatives in regions like the Netherlands to adopt precision farming technologies, boosting crop yields by 25%. Huawei’s innovations in spectrum optimization and energy-efficient hardware have also contributed to its global reputation. With over 1,000 private 5G projects worldwide, Huawei continues to shape the future of enterprise connectivity.
Top Strategies Used By Key Market Participants
Partnerships and Collaborations
Key players in the Europe private 5G network market are increasingly forming strategic partnerships to expand their reach and enhance service offerings. For example, Nokia has collaborated with Siemens to integrate private 5G with industrial automation systems, enabling seamless data exchange and predictive maintenance. Such alliances allow companies to leverage complementary expertise and deliver end-to-end solutions tailored to enterprise needs.
Investment in R&D
Companies are prioritizing research and development to innovate cutting-edge technologies that address specific industry challenges. Ericsson, for instance, has invested over €5 billion in developing advanced beamforming and spectrum-sharing solutions, which are critical for optimizing private 5G performance. These investments ensure that players remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Focus on Sustainability
Sustainability has become a core strategy for key participants, aligning with Europe’s green agenda. Huawei has introduced energy-efficient hardware and modular designs that reduce carbon footprints, appealing to environmentally conscious enterprises. This approach not only enhances brand reputation but also positions companies as leaders in sustainable innovation.
Competition Overview In The Europe Private 5G Network Market
The Europe private 5G network market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the presence of global giants such as Nokia, Ericsson, and Huawei, alongside regional players like Deutsche Telekom and Vodafone. According to ABI Research, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 35% through 2028, fueled by increasing demand for ultra-reliable, low-latency communication systems. This growth has intensified rivalry among vendors striving to capture market share through differentiated offerings. For instance, Nokia focuses on industrial automation, while Ericsson emphasizes IoT integration and edge computing. Meanwhile, Huawei competes on cost-effectiveness and scalability, targeting SMEs and rural enterprises. Regional operators like Vodafone leverage their extensive customer base to offer managed services, further complicating the competitive landscape. Government policies, such as spectrum allocation frameworks, also play a pivotal role in shaping competition, as they determine accessibility and affordability for enterprises. As the market matures, companies are adopting aggressive pricing strategies and investing heavily in R&D to maintain their edge is creating a dynamic and highly competitive environment.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THIS MARKET
- In April 2024, Nokia announced a partnership with Siemens to integrate private 5G with industrial automation systems. This collaboration aims to enable real-time data exchange and predictive maintenance, enhancing operational efficiency for manufacturing enterprises.
- In June 2023, Ericsson launched its Industry Connect platform in Sweden, empowering enterprises to deploy private 5G networks for smart factory applications. This initiative has already supported over 50 industrial sites across Europe.
- In February 2023, Huawei unveiled its RuralStar Pro solution in Italy, targeting agricultural cooperatives with affordable private 5G networks. The solution has improved crop yields by 25%, driving adoption in rural areas.
- In September 2022, Vodafone introduced a managed services portfolio in the UK, offering end-to-end private 5G solutions for healthcare providers. This move has reduced hospital operational costs by 15%, strengthening Vodafone’s market presence.
- In December 2021, Deutsche Telekom secured a €1 billion investment to expand its private 5G infrastructure in Germany. The project focuses on enabling smart city initiatives, positioning the company as a leader in urban connectivity solutions.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe private 5G network market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Component
- Hardware
- Radio Access Network
- Core Network
- Backhaul & Transport
- Software
- Services
- Installation & Integration
- Data Services
- Support & Maintenance
By Frequency
- Sub-6 GHz
- mmWave
By Spectrum
- Licensed
- Unlicensed/Shared
By Enterprise Size
-
- Small & Medium Enterprises
- Large Enterprises
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key drivers behind the growth of private 5G networks in Europe?
This FAQ explores the major factors propelling adoption—like industrial automation, government digitalization efforts, smart cities, and data sovereignty concerns.
Which industries in Europe are leading the adoption of private 5G networks and why?
Here, the focus is on verticals such as manufacturing, logistics, automotive, and healthcare, examining specific use cases and advantages.
How do European regulations and spectrum policies impact the deployment of private 5G networks?
This addresses the role of EU and national regulators, spectrum availability (like shared/local licenses), and the influence of GDPR on network architecture.
What are the major challenges and risks associated with implementing private 5G networks in Europe?
A look at barriers such as high initial costs, integration complexity, security concerns, and the skills gap in managing 5G infrastructures.
Who are the key players in the European private 5G market ecosystem, and what partnerships are shaping the landscape?
Covers major telecom providers, infrastructure vendors, and technology partners, as well as notable collaborations and pilot projects across Europe.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]