Europe Marine Diesel Engine Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Technology (Low Speed, Medium Speed, and High Speed), Application, Power, Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Marine Diesel Engine Market Size
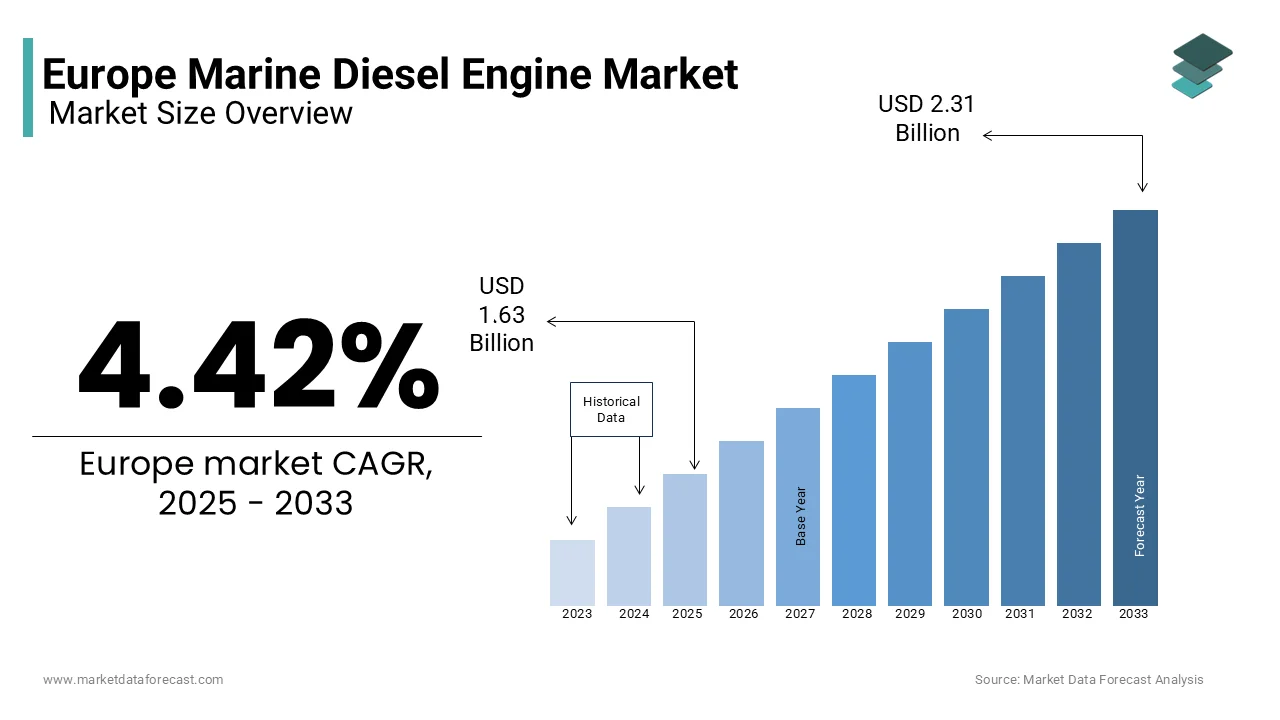
The Europe marine diesel engine market was worth USD 1.57 billion in 2024. The European market is estimated to reach USD 2.31 billion by 2033 from USD 1.63 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 4.42% from 2025 to 2033.
Marine diesel engines are internal combustion engines specifically designed for maritime applications and offer high efficiency, durability, and reliability under demanding operational conditions. According to the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA), over 90% of goods traded within Europe are transported via maritime routes, underscoring the critical role of marine diesel engines in facilitating trade and economic growth. The market is characterized by a strong emphasis on fuel efficiency, emission reductions, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations such as the International Maritime Organization’s (IMO) Tier III standards, which mandate significant cuts in sulfur oxide (SOx) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions.
The increasing demand for cleaner and more efficient propulsion systems are driving the demand for marine diesel engines. According to the reports of the Eurostat, Europe accounts for nearly 25% of global maritime trade, reinforcing the region's reliance on advanced marine technologies. Key contributors to market expansion include the rising adoption of hybrid propulsion systems, advancements in turbocharging technologies, and growing investments in retrofitting older vessels to meet environmental norms. Countries like Germany, Norway, and the Netherlands are leading adopters due to their robust shipbuilding industries and focus on sustainable shipping solutions. As Europe continues to prioritize decarbonization and energy transition, the marine diesel engine market is poised to evolve.
MARKET DRIVERS
Stringent Environmental Regulations
One of the primary drivers of the Europe marine diesel engine market is the implementation of stringent environmental regulations aimed at reducing emissions from maritime activities. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has mandated that all vessels operating in designated Emission Control Areas (ECAs) must comply with sulfur oxide (SOx) emission limits of 0.1%, as outlined in its Tier III standards. According to the European Environment Agency, these regulations have led to a 30% reduction in SOx emissions from European shipping between 2015 and 2022. This regulatory push has accelerated the adoption of advanced marine diesel engines equipped with exhaust gas cleaning systems or running on low-sulfur fuels. The European Commission highlights that over 70% of European shipowners have invested in compliant engines to avoid penalties and ensure operational continuity. These regulations are driving innovation and creating demand for cleaner, more efficient marine diesel technologies.
Rising Demand for Fuel-Efficient Propulsion Systems
Another significant driver is the growing demand for fuel-efficient propulsion systems, driven by volatile fuel prices and the need to reduce operational costs. Eurostat reports that marine fuel costs account for approximately 50% of total shipping expenses, making fuel efficiency a top priority for ship operators. Advances in marine diesel engine technology, such as turbocharging and common rail fuel injection systems, have improved fuel efficiency by up to 15%, according to the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA). Additionally, hybrid propulsion systems, which combine diesel engines with electric motors, are gaining traction, particularly in Norway and Sweden, where they are used in over 20% of new vessel builds. The International Energy Agency (IEA) emphasizes that these innovations not only reduce fuel consumption but also align with Europe’s decarbonization goals. As industries prioritize cost savings and sustainability, the demand for advanced marine diesel engines continues to grow.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of Compliance with Environmental Regulations
One major restraint in the Europe marine diesel engine market is the high cost associated with compliance to increasingly stringent environmental regulations. Retrofitting existing vessels or purchasing new engines that meet International Maritime Organization (IMO) Tier III standards can be prohibitively expensive. According to the European Commission, retrofitting a single vessel with exhaust gas cleaning systems or switching to low-sulfur fuels can cost between USD 1 million and USD 5 million, depending on the ship's size and engine type. Eurostat highlights that small and medium-sized shipping companies, which account for over 40% of Europe’s maritime fleet, often struggle to afford these upgrades. This financial burden is further exacerbated by fluctuating fuel prices, which have increased by 20% since 2020. As a result, many operators delay investments in compliant engines, slowing market growth despite regulatory pressures.
Limited Availability of Alternative Technologies
Another significant restraint is the limited availability and maturity of alternative propulsion technologies, which creates uncertainty for the marine diesel engine market. While hybrid and electric propulsion systems are gaining attention, their adoption remains constrained by technological and infrastructural limitations. The European Environment Agency notes that battery-powered vessels currently account for less than 5% of Europe’s total fleet, primarily due to restricted energy storage capacity and long charging times. Additionally, the European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) reports that hydrogen fuel cell technology, though promising, is still in its nascent stages, with only a handful of pilot projects underway. These alternatives lack the scalability and reliability of traditional diesel engines, leaving shipowners hesitant to transition fully. This slow development of viable substitutes prolongs dependency on marine diesel engines, even as industries seek sustainable solutions.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth in Hybrid and Dual-Fuel Engine Technologies
A significant opportunity in the Europe marine diesel engine market lies in the growing adoption of hybrid and dual-fuel engine technologies, driven by the need for cleaner and more efficient propulsion systems. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) reports that hybrid propulsion systems are expected to account for 15% of new vessel builds by 2030, reflecting a shift toward sustainable shipping solutions. Dual-fuel engines, which can operate on both conventional fuels and liquefied natural gas (LNG), have already gained traction, with Eurostat estimating that LNG-powered vessels now represent 10% of Europe’s maritime fleet. These technologies reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 25% compared to traditional diesel engines, aligning with the European Green Deal’s decarbonization goals. The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that investments in LNG infrastructure across Europe have grown by 30% since 2018, further supporting this transition. As industries prioritize sustainability, hybrid and dual-fuel engines present lucrative opportunities for market expansion.
Expansion of Retrofitting Services for Existing Vessels
Another major opportunity is the increasing demand for retrofitting services aimed at upgrading existing vessels to comply with environmental regulations. According to the European Commission, over 70% of Europe’s current maritime fleet consists of older vessels that require modifications to meet IMO Tier III standards. Retrofitting solutions, such as installing exhaust gas cleaning systems or switching to low-sulfur fuels, have become a cost-effective alternative to purchasing new engines. The European Environment Agency estimates that retrofitting projects could generate a market value of USD 2 billion annually by 2025. Furthermore, advancements in modular retrofit kits have reduced installation times by up to 40%, making them more accessible for small and medium-sized operators. This trend is particularly prominent in countries like Norway and Germany, where government subsidies cover up to 50% of retrofitting costs, encouraging widespread adoption. Retrofitting not only extends vessel lifespans but also supports Europe’s broader sustainability objectives.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Transition to Alternative Fuels
A significant challenge for the Europe marine diesel engine market is the transition to alternative fuels, which is hindered by inadequate infrastructure and technological uncertainties. The European Environment Agency highlights that while liquefied natural gas (LNG) and hydrogen are emerging as viable alternatives, only 2% of European ports currently have LNG bunkering facilities, limiting widespread adoption. Additionally, hydrogen fuel cell technology, though promising, faces challenges due to the lack of large-scale production and storage solutions. Eurostat reports that less than 1% of Europe’s maritime fleet uses hydrogen or other zero-carbon fuels, primarily due to high costs and safety concerns. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) emphasizes that building the necessary infrastructure could take over a decade, creating uncertainty for shipowners and engine manufacturers. This slow progress in developing alternative fuel ecosystems poses a significant barrier to reducing reliance on traditional marine diesel engines.
Economic Pressures from Rising Fuel Costs and Inflation
Another major challenge is the economic pressure caused by rising fuel costs and inflation, which strain the budgets of shipping companies and delay investments in advanced marine diesel technologies. Eurostat data reveals that marine fuel prices surged by 40% between 2020 and 2022, driven by geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions. The European Commission notes that small and medium-sized shipping operators, which account for over 40% of the fleet, are particularly vulnerable to these cost fluctuations. Additionally, inflation has increased the costs of raw materials used in engine manufacturing, such as steel and aluminum, by up to 25%, according to the European Central Bank. These financial pressures force operators to prioritize short-term survival over long-term sustainability, slowing the adoption of energy-efficient engines. As economic instability persists, balancing affordability with regulatory compliance remains a critical challenge for the marine diesel engine market.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
4.42% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, Application, Power, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
AB Volvo, Anglo Belgian, Caterpillar, Cummins, Daihatsu Diesel, Deere & Company, DEUTZ, Hyundai, IHI Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, MAN Energy Solutions, Rolls-Royce, Scania, Siemens, STX Heavy Industries, Wartsila, Yanmar, and Yuchai International. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Technology Insights
The low-speed segment held the major share of 60.2% in the European market in 2024. The growth of the low-speed segment is driven by their unmatched fuel efficiency and ability to operate on heavy fuel oil (HFO). These engines, operating below 100 RPM, are ideal for large commercial vessels like container ships and tankers, which account for over 70% of global maritime trade, according to the International Maritime Organization (IMO). Their compatibility with exhaust gas cleaning systems ensures compliance with stringent emission regulations, making them indispensable for deep-sea shipping. As Europe prioritizes sustainability, low-speed engines remain critical for balancing efficiency and environmental compliance.
The medium-speed segment is predicted to witness a CAGR of 10.4% over the forecast period owing to their adaptability to alternative fuels like liquefied natural gas (LNG) and integration into hybrid propulsion systems. As per the European Environment Agency, medium-speed engines are increasingly adopted in ferries and offshore vessels, where versatility and moderate power output are essential. Their compact design and improved fuel efficiency, enhanced by advancements in turbocharging, make them ideal for regional shipping. As Europe accelerates its transition to sustainable maritime solutions, medium-speed engines play a pivotal role in bridging traditional and green technologies.
By Application Insights
The merchant vessels ruled the market by accounting for the largest share of the European market in 2024. The growing usage of merchant vessels in global trade, with container vessels, tankers, and bulk carriers accounting for the majority of maritime activity, is one of the key factors boosting the domination of merchant vessels segment in the European market. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) highlights that container vessels alone represent 30% of the merchant fleet, relying on low-speed engines for fuel efficiency and high torque during long-distance operations. Merchant vessels transport over 90% of Europe’s trade volume, according to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), making them indispensable to the economy. Their importance lies in supporting international logistics while adopting cleaner technologies to meet emission regulations, ensuring sustainability in global supply chains.
The offshore segment is anticipated to progress at a prominent CAGR of 8.8% over the forecast period due to the increased investments in offshore wind energy and oil exploration. The European Environment Agency notes a 15% rise in offshore support vessels since 2020, supported by hybrid propulsion systems that reduce emissions by up to 20%. Floating production units and drilling rigs are also adopting advanced engines for compliance with environmental standards. As Europe expands its offshore energy infrastructure, this segment is vital for integrating renewable energy and enhancing maritime innovation.
By Power Insights
The > 20,000 HP segment captured the leading share of 45.4% of the European marine diesel engine market in 2024 due to its increased use in large merchant vessels like container ships and tankers that handle over 70% of Europe’s maritime trade. These high-power engines, primarily low-speed designs, offer unmatched fuel efficiency, achieving up to 15% higher savings than smaller engines. Their ability to operate on heavy fuel oil (HFO) and integrate with emission-reducing technologies ensures compliance with environmental regulations. As global trade grows, these engines remain critical for deep-sea logistics, providing reliability and torque essential for long-distance operations.
The 5,001 - 10,000 HP segment is estimated to expand at a CAGR of 9.3% over the forecast period due to the increasing demand for medium-sized vessels like ferries and offshore support ships that benefit from hybrid propulsion systems reducing emissions. The European Environment Agency highlights their adaptability to alternative fuels like LNG, enhancing sustainability. Advancements in turbocharging improve fuel efficiency by 10%, making them ideal for regional shipping. As Europe prioritizes greener maritime solutions, this segment bridges traditional power needs with innovative, eco-friendly technologies, driving its rapid expansion.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany dominated the marine diesel engine market in Europe by holding 26.2% of the European market share in 2024. The robust shipbuilding industry and strong emphasis on innovation of Germany, with companies like MAN Energy Solutions and MTU playing pivotal roles in engine manufacturing are driving the German market growth. Eurostat highlights that Germany accounts for over 20% of Europe’s maritime trade, driving demand for advanced marine diesel engines. The European Environment Agency notes that Germany’s focus on sustainability has accelerated the adoption of hybrid and low-emission engines, particularly in inland waterways and short-sea shipping. Additionally, government incentives for retrofitting older vessels have bolstered market growth, solidifying Germany’s leadership in both production and adoption of cutting-edge marine technologies.
Norway is a promising regional segment for marine diesel engines in Europe and is likely to hold a substantial share of the European market over the forecast period. The commitment of Norway to green shipping solutions, including hybrid and electric propulsion systems that align with its goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2030, is propelling the marine diesel engine market growth in Norway. The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that Norway has invested heavily in LNG-powered vessels, with over 30% of its fleet now utilizing cleaner fuels. Norway’s extensive coastline and reliance on maritime transport for trade further amplify demand for efficient engines. Additionally, government subsidies for sustainable technologies, such as hydrogen fuel cells, have positioned Norway as a pioneer in eco-friendly marine innovations, setting benchmarks for other European nations.
Italy is another leading market for marine diesel engines in Europe and is expected to witness a prominent CAGR during the forecast period. The growth of the Italian market in Europe is attributed to its thriving shipbuilding sector, which specializes in luxury yachts, cruise ships, and commercial vessels. The European Maritime Safety Agency (EMSA) reports that Italy contributes approximately 18% of Europe’s shipbuilding output, creating significant demand for high-performance marine diesel engines. The country’s strategic location along the Mediterranean Sea enhances its role in regional trade, boosting the need for reliable propulsion systems. Furthermore, Italy’s adoption of hybrid engines in ferries and passenger vessels, supported by EU funding for green initiatives, underscores its commitment to sustainability. This blend of industrial expertise and environmental focus cements Italy’s position as a key player in the marine diesel engine market.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe marine diesel engine market include AB Volvo, Anglo Belgian, Caterpillar, Cummins, Daihatsu Diesel, Deere & Company, DEUTZ, Hyundai, IHI Corporation, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, MAN Energy Solutions, Rolls-Royce, Scania, Siemens, STX Heavy Industries, Wartsila, Yanmar, and Yuchai International.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe marine diesel engine market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Technology
- Low Speed
- Medium Speed
- High Speed
By Application
- Merchant
- Container Vessels
- Tankers
- Bulk Carriers
- Gas Carriers
- RO-RO
- Others
- Offshore
- Drilling RIGS & Ships
- Anchor Handling Vessels
- Offshore Support Vessels
- Floating Production Units
- Platform Supply Vessels
- Cruise & Ferry
- Cruise Vessels
- Passenger Vessels
- Passenger/Cargo Vessels
- Others
- Navy
- Others
By Power
- 1,000 HP
- 1,000 - 5,000 HP
- 5,001 - 10,000 HP
- 10,001 - 20,000 HP
- > 20,000 HP
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors driving the Europe marine diesel engine market?
The market is primarily driven by increasing maritime trade, growing demand for fuel-efficient engines, and stringent environmental regulations pushing for cleaner diesel technologies.
What are the primary applications of marine diesel engines in Europe?
These engines are widely used in cargo ships, tankers, passenger vessels, ferries, and naval ships across European waters.
What technological advancements are shaping the marine diesel engine market in Europe?
Innovations such as electronic fuel injection, turbocharging, and exhaust after-treatment systems are enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing emissions.
What is the future outlook for the Europe marine diesel engine market?
The market is expected to see continued demand due to the expansion of maritime trade, advancements in engine efficiency, and the gradual transition toward eco-friendly propulsion systems.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]