Europe Machine Translation Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Application (Automotive, Military & Defense, Electronics, IT, Healthcare, and Others), Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Machine Translation Market Size
The Europe machine translation market was worth USD 380 million in 2024. The European market is projected to reach USD 1160 million by 2033 from USD 430 million in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 13.25% from 2025 to 2033.
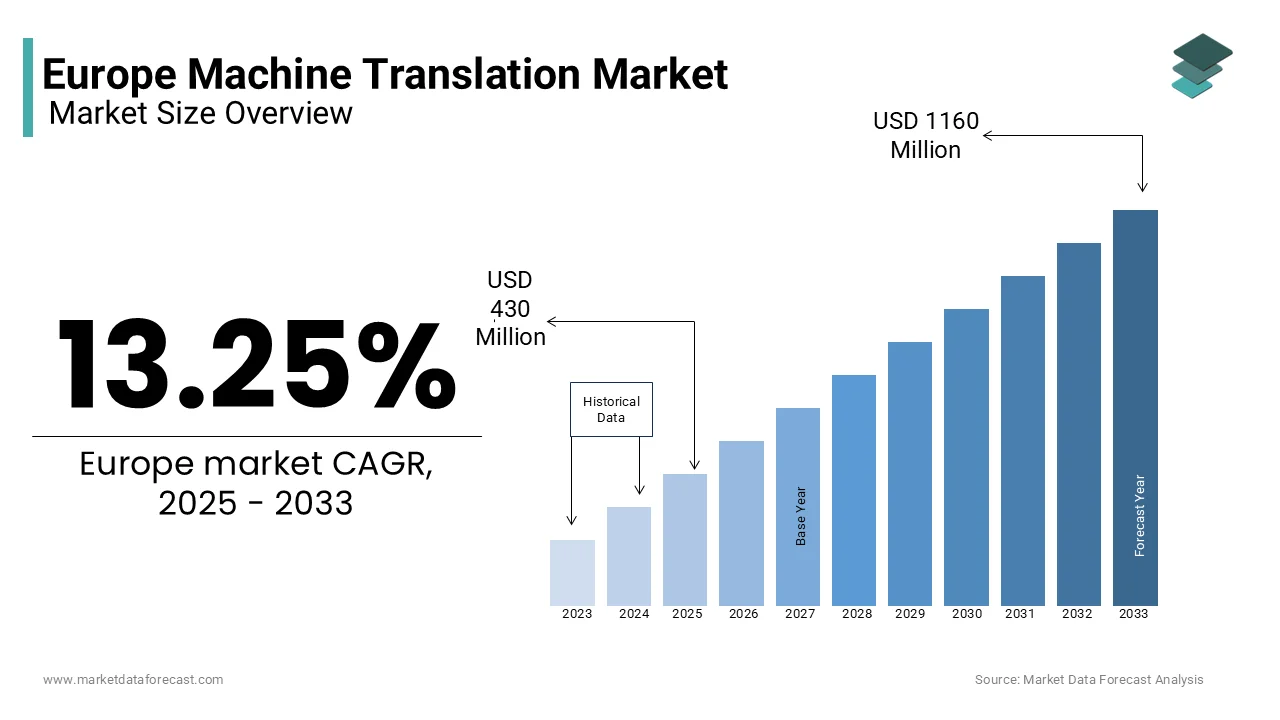
Machine translation refers to the use of advanced algorithms and neural networks to automatically translate text or speech from one language to another with minimal human intervention. In Europe, where linguistic diversity is both a cultural hallmark and a logistical challenge, machine translation technologies have become indispensable for businesses, governments, and individuals seeking seamless interaction across the continent's 24 official languages and numerous regional dialects.
As of recent reports by Eurostat, over 50% of Europeans consider language barriers a significant obstacle in accessing digital content and services, underscoring the growing demand for efficient translation solutions. The demand for machine translation services is growing rapidly in the European region due to the advancements in neural machine translation (NMT) systems that offer higher accuracy and contextual understanding compared to traditional rule-based models. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of cloud-based translation platforms, coupled with rising investments in AI research, has positioned Europe as a global leader in this domain. A report by the European Association for Machine Translation highlights that industries such as e-commerce, healthcare, and legal services are among the primary beneficiaries of these innovations, leveraging machine translation to enhance operational efficiency and customer engagement. As Europe continues to prioritize digital transformation and inclusivity, the machine translation market stands poised for sustained expansion, reshaping how language barriers are addressed in an interconnected world.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Demand for Multilingual Communication in Cross-Border Trade and E-Commerce in Europe
The European machine translation market is significantly driven by the rising need for multilingual communication in cross-border trade and e-commerce. The European Union’s Single Market enables the seamless movement of goods and services across member states, but linguistic diversity remains a challenge. Eurostat reports that over 70% of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the EU engage in cross-border trade, yet only 25% have access to professional translation services. This gap has spurred the adoption of machine translation tools, allowing businesses to localize content efficiently. The European Commission highlights that companies leveraging automated translation technologies witness a 30% increase in international sales. Additionally, the rapid growth of e-commerce has further fueled this demand.
Emphasis on Digital Transformation and AI Adoption in Public Sector Institutions
The rising focus on digital transformation and AI adoption within public sector institutions is further booting the growth of the European machine translation market. Governments across Europe are investing heavily in AI-powered technologies to enhance operational efficiency and citizen engagement. The European Commission’s Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI) reveals that public administration services utilizing machine translation have improved accessibility by 40%, benefiting non-native speakers and marginalized communities. Moreover, the EU’s Horizon Europe program has allocated over €1 billion to support AI and language technology research, fostering innovation in neural machine translation systems. According to a study by the European Parliament, the integration of machine translation in legislative processes has reduced document processing times by up to 60%. These advancements highlight the critical role of machine translation in achieving inclusive governance and efficient public service delivery, thereby propelling market growth across the continent.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Concerns Over Data Privacy and Security in Machine Translation
One of the major restraints of the European machine translation market is the growing concern over data privacy and security. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), enforced by the European Union, imposes stringent rules on how personal data is processed and stored, creating challenges for machine translation providers. According to a report by the European Data Protection Board, over 60% of businesses using cloud-based translation tools face compliance issues due to the transfer of sensitive data across borders. Additionally, Eurostat highlights that 45% of EU citizens express concerns about the confidentiality of their translated content, particularly in sectors like healthcare and legal services. These apprehensions hinder the widespread adoption of machine translation technologies, as organizations fear potential breaches and regulatory penalties. A study by the European Commission further reveals that non-compliance with GDPR can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, discouraging smaller enterprises from investing in these solutions.
Limitations in Translation Accuracy for Low-Resource Languages
Another significant restraint is the limited accuracy of machine translation systems for low-resource languages, which are often underrepresented in training datasets. The European Parliament reports that while machine translation performs well for widely spoken languages like English, French, and German, it struggles with regional and minority languages such as Basque, Gaelic, and Sami. This limitation creates disparities in access to digital services for speakers of these languages. According to Eurostat, approximately 10% of the EU population speaks a regional or minority language, yet only 3% of machine translation research funding is allocated to developing models for these languages. Furthermore, a study by the European Association for Machine Translation highlights that translation errors for low-resource languages can exceed 30%, leading to mistrust among users. These gaps in linguistic inclusivity pose a significant barrier to the broader adoption of machine translation technologies across Europe.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Machine Translation in the Healthcare Sector
A significant opportunity for the European machine translation market lies in its potential to revolutionize communication within the healthcare sector. The European Commission highlights that over 50 million EU citizens face language barriers when accessing healthcare services, particularly in cross-border medical treatments and emergency situations. Machine translation can bridge this gap by enabling real-time translation of medical records, patient consultations, and pharmaceutical instructions. According to Eurostat, the healthcare sector accounts for 10% of the EU’s GDP, with digital health solutions projected to grow by 12% annually through 2030. A report by the European Health Parliament emphasizes that integrating machine translation into telemedicine platforms could enhance accessibility for non-native speakers, reducing miscommunication errors by up to 40%. As Europe prioritizes digital health transformation under initiatives like the EU4Health program, machine translation providers have a unique opportunity to cater to this underserved yet critical domain.
Integration with Emerging Technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and IoT
Another promising opportunity is the integration of machine translation with emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT). The European Patent Office reports that patent applications for AI-driven AR and IoT solutions have surged by 35% over the past five years, signaling rapid technological convergence. Machine translation can enhance these technologies by providing real-time multilingual support in applications like smart tourism, industrial maintenance, and consumer electronics. For instance, a study by the European Travel Commission reveals that 70% of tourists prefer multilingual guidance, which AR-enabled translation devices can deliver seamlessly. Additionally, the European Commission estimates that the IoT market in Europe will reach €250 billion by 2025, creating a fertile ground for machine translation innovations. By embedding translation capabilities into IoT devices and AR platforms, businesses can unlock new revenue streams while addressing Europe’s linguistic diversity in cutting-edge ways.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Ethical Concerns and Bias in Machine Translation Algorithms
One of the major challenges facing the European machine translation market is the issue of ethical concerns and algorithmic bias. The European Union Agency for Fundamental Rights highlights that biased translations can perpetuate stereotypes and discrimination, particularly against minority groups. For instance, a study by the European Commission found that machine translation systems exhibit gender bias in 20% of cases, often misrepresenting pronouns or professional roles. This challenge is exacerbated by the lack of diverse training datasets, which fail to adequately represent Europe’s linguistic and cultural diversity. Eurostat reports that over 60 million EU citizens speak regional or minority languages, yet these languages are underrepresented in AI models, leading to mistranslations and eroded trust. Furthermore, the European Parliament warns that unchecked biases in machine translation could violate anti-discrimination laws, potentially resulting in legal repercussions for businesses and developers.
High Development Costs and Resource Intensity for Advanced Models
Another significant challenge is the high development costs and resource intensity associated with creating advanced machine translation models. The European Investment Bank notes that developing state-of-the-art neural machine translation systems requires substantial investment in computational infrastructure and skilled personnel, with costs often exceeding €10 million per project. Additionally, the European Commission’s Horizon Europe program emphasizes that training large-scale AI models consumes significant energy, contributing to environmental concerns. A report by Eurostat reveals that only 25% of European SMEs have the financial capacity to adopt cutting-edge translation technologies, leaving smaller players at a competitive disadvantage. Moreover, the European Association for Machine Translation highlights that maintaining and updating these systems to ensure accuracy and relevance further escalates operational expenses. These financial and resource barriers limit innovation and hinder the widespread adoption of machine translation solutions across Europe.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
13.25% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Application, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
AppTek, Cloudwords Inc., IBM Corporation, Lighthouse IP, Lingo24 Limited, Lingotek, Lionbridge Technologies, LLC, RWS Holdings plc, Pangeanic, PROMT, RTX, Smart Communications, SYSTRAN, and Welocalize. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Application Insights
The IT segment held the leading share of 28.8% of the European market in 2024. The dominating position of IT segment in the European market is due to the growing reliance of IT industry on multilingual solutions for software localization, technical documentation, and customer support. According to Eurostat, 70% of IT companies use machine translation to enhance global competitiveness, as the EU’s IT market contributes 8% to the region’s GDP. The rise of cloud-based platforms and real-time communication tools has further driven adoption.
The healthcare is predicted to exhibit a CAGR of 14.2% over the forecast period owing to the increasing need for multilingual patient care and telemedicine services. According to Eurostat, hospitals using machine translation have reduced medical errors by 40%, improving patient outcomes. With over 50 million EU citizens facing language barriers in healthcare, machine translation ensures equitable access to services. The European Commission notes that digital health solutions, including machine translation, are growing at 12% annually, driven by cross-border treatments and remote consultations. This rapid expansion highlights the segment’s importance in addressing linguistic diversity and enhancing healthcare inclusivity across Europe.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany played the dominating role in the European market by accounting for 29.4% of the European market share in 2024. The robust industrial base of Germany, particularly in automotive and manufacturing sectors, where multilingual communication is critical is one of the major factors driving the German market growth. The German government’s Digital Strategy 2025 has accelerated AI adoption, including machine translation, with investments exceeding €3 billion annually. Eurostat highlights that over 60% of German SMEs utilize machine translation to enhance cross-border trade, which accounts for 47% of the nation’s GDP. Furthermore, Germany’s emphasis on research and development, supported by institutions like the Fraunhofer Society, fosters innovation in neural machine translation. This strategic focus positions Germany as a leader in driving technological advancements and addressing linguistic diversity across Europe.
France is predicted to account for a prominent share of the European machine translation market over the forecast period owing to its strong presence in the IT and healthcare sectors, where machine translation enhances localization and patient care. The French government’s AI for Humanity initiative has allocated €1.5 billion to AI research, including language technologies. According to Eurostat, France’s digital economy contributes 12% to its GDP, with machine translation playing a pivotal role in global e-commerce and tourism. Additionally, the European Commission highlights that France’s commitment to fostering startups in AI has led to a 30% increase in machine translation patents over the past five years, solidifying its position as a key innovator in this domain.
The UK is projected to hold a notable position in the European market during the forecast period due to the dominance of the UK in the financial services and media industries, where real-time translation is essential for global operations. The UK government’s National AI Strategy emphasizes linguistic technologies, with annual investments exceeding £1 billion. Eurostat notes that the UK’s digital sector contributes 8% to its GDP, with machine translation enabling seamless cross-border communication for businesses. Furthermore, the British Standards Institution highlights that the UK’s expertise in cloud computing and AI integration has reduced translation costs by 25%, making it a hub for scalable and innovative solutions. This strategic focus ensures the UK remains a frontrunner in advancing machine translation capabilities across Europe.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe machine translation market include AppTek, Cloudwords Inc., IBM Corporation, Lighthouse IP, Lingo24 Limited, Lingotek, Lionbridge Technologies, LLC, RWS Holdings plc, Pangeanic, PROMT, RTX, Smart Communications, SYSTRAN, and Welocalize.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe machine translation market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Application
- Automotive
- Military & Defense
- Electronics
- IT
- Healthcare
- Others
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the Europe machine translation market?
The increasing demand for real-time translation in business, government, and technology sectors, along with advancements in AI and neural machine translation, is driving market growth.
Which industries are the biggest users of machine translation in Europe?
Key industries include e-commerce, healthcare, IT, legal services, and travel & tourism, where rapid and accurate multilingual communication is essential.
What is the future outlook for the Europe machine translation market?
The market is expected to see continuous advancements in AI-driven translation quality, greater industry-specific customization, and wider integration with business applications.
How does machine translation compare to human translation in Europe?
While machine translation is faster and cost-effective, human translation is still preferred for legal, literary, and highly specialized content due to its superior accuracy and cultural nuance.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]