Europe Light Commercial vehicles (LCVs) Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented By Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type And By Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe) - Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Light Commercial Vehicles Market Size
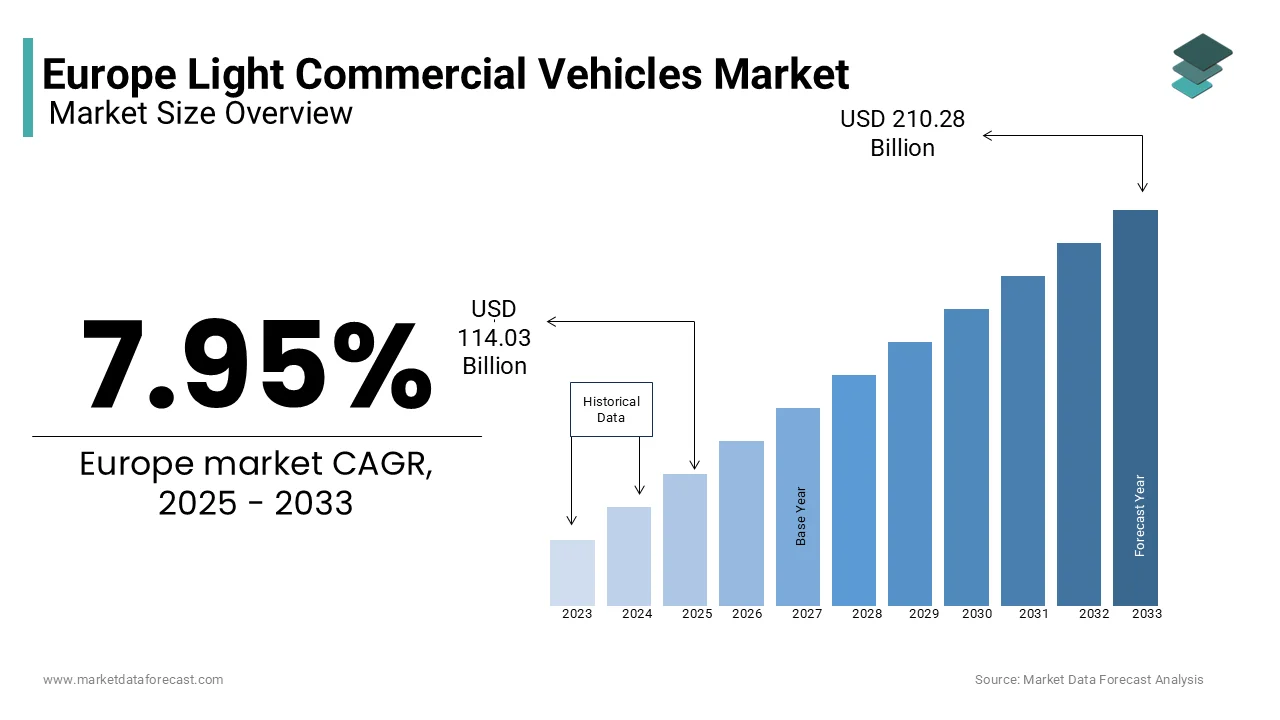
The Europe light commercial vehicle market size was valued at USD 105.63 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 114.03 billion in 2025 from USD 210.28 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.95 % during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The Europe Light commercial vehicles (LCVs) are typically defined as vehicles with a gross vehicle weight of up to 3.5 tonnes, are widely used for urban deliveries, construction, and service operations. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA), the LCV market accounted for approximately 20% of total vehicle sales in Europe in 2022, reflecting its economic significance. The growing emphasis on e-commerce and last-mile delivery has further amplified demand, with countries like Germany and France witnessing a 15% annual increase in LCV registrations, as reported by the French Ministry of Transport.
As per the International Energy Agency (IEA), over 60% of European LCVs are now being manufactured with advanced fuel-efficient technologies, including hybrid and electric powertrains, aligning with the EU’s stringent emissions regulations. This shift is supported by government incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies for low-emission vehicles, which have accelerated adoption rates. For instance, the UK Department for Transport highlights that electric LCV sales grew by 40% in 2022 alone. With urbanization and sustainability goals driving innovation, the LCV market is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping Europe’s future mobility landscape.
MARKET DRIVERS
Surge in E-Commerce and Last-Mile Delivery in Europe
The rapid expansion of e-commerce is a significant driver propelling the European light commercial vehicle market, as businesses increasingly rely on LCVs for efficient last-mile delivery. According to the European E-Commerce Association, online retail sales in Europe reached €800 billion in 2022, representing a 20% year-on-year growth. This surge has created a pressing need for reliable and versatile LCVs capable of navigating urban environments while meeting strict emission standards. A study by the German Federal Ministry of Transport highlights that urban delivery fleets expanded by 25% in major cities like Berlin and Munich, driven by the proliferation of e-commerce platforms. Additionally, the French Ministry of Transport reports that over 70% of urban delivery vehicles are now LCVs, underscoring their indispensability. By enabling faster and more sustainable logistics, LCVs have become a cornerstone of modern commerce, driving market growth across the continent.
Stringent Emissions Regulations and Adoption of Electric LCVs
The implementation of stringent emissions regulations that have catalysed the adoption of electric and hybrid LCVs are further boosting the expansion of the European light commercial vehicle market. According to the European Environment Agency, the transportation sector accounts for approximately 25% of Europe’s total greenhouse gas emissions, prompting policymakers to enforce stricter limits on CO2 emissions from vehicles. A report by the UK Department for Transport reveals that electric LCV sales surged by 40% in 2022, driven by government subsidies and tax incentives aimed at promoting low-emission alternatives. For instance, companies like DHL and UPS have committed to electrifying 50% of their delivery fleets by 2025, as highlighted by the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure. Additionally, advancements in battery technology have reduced costs by 30%, making electric LCVs more accessible for small and medium-sized enterprises. By aligning with sustainability goals, these innovations are propelling the market forward.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs of Electric LCVs
One of the primary restraints hindering the growth of the European light commercial vehicle market is the high initial cost of electric LCVs, which often deter small and medium-sized enterprises from adopting them. According to the German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs, the average price of an electric LCV is approximately 40% higher than its diesel counterpart, creating financial barriers for businesses operating on tight budgets. This issue is particularly pronounced in Eastern Europe, where over 60% of SMEs lack access to financing options or subsidies, as reported by the Czech Ministry of Industry and Trade. A study by the Italian National Institute of Statistics highlights that only 25% of surveyed businesses in rural areas have transitioned to electric LCVs, citing affordability as a major obstacle. Additionally, the lack of widespread charging infrastructure exacerbates the problem, leaving many operators reliant on traditional fuel-powered vehicles. Without addressing these cost-related challenges, the market risks alienating a significant portion of its target audience, stifling broader adoption.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
Limited availability of charging infrastructure, particularly in rural and suburban areas that undermines the practicality of electric LCVs for long-distance and regional operations is further impeding the growth of the European market. According to the European Alternative Fuels Observatory, over 70% of public charging stations are concentrated in urban centers, leaving peripheral regions underserved. This disparity is particularly evident in countries like Spain and Italy, where rural electrification projects lag behind, as noted by the Spanish Ministry of Ecological Transition. A report by the French National Institute for Transport Research highlights that 45% of surveyed fleet operators cited insufficient charging networks as a barrier to adopting electric LCVs. Furthermore, the absence of standardized payment systems and interoperability between charging providers complicates usage, deterring potential buyers. While urban areas benefit from robust infrastructure, rural businesses face significant hurdles, limiting the scalability of electric LCV adoption and constraining market growth.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Autonomous Driving Technologies
A promising opportunity for the European light commercial vehicle market lies in the integration of autonomous driving technologies, which promise to revolutionize logistics and reduce operational costs. According to the European Commission’s Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport, over 50% of urban delivery routes could be automated by 2030, driven by advancements in AI and sensor technologies. A study by the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure highlights that autonomous LCVs can reduce labour costs by up to 30%, making them an attractive option for businesses seeking efficiency gains. This trend is further bolstered by pilot projects in cities like Amsterdam and Stockholm, where autonomous delivery vehicles have demonstrated a 25% improvement in route optimization, as reported by the Swedish Transport Administration. Additionally, partnerships between automakers and tech companies are accelerating innovation, ensuring scalability and affordability. By bridging the gap between technology and logistics, autonomous LCVs are set to transform the market, unlocking immense growth potential.
Expansion into Shared Mobility and Subscription Models
The burgeoning shared mobility sector that presents a lucrative avenue for LCV manufacturers to diversify their revenue streams beyond traditional sales is another promising opportunity in the European market. According to the UK Department for Transport, over 40% of businesses in Europe are exploring subscription-based models for fleet management, driven by the flexibility and cost-effectiveness they offer. A report by the French Ministry of Economy highlights that shared LCV services grew by 20% in 2022, underscoring the segment’s economic significance. The rise of urban consolidation centers further accelerates adoption, as highlighted by the Italian Ministry of Transport, which notes a 30% annual increase in collaborative logistics projects. Additionally, the integration of digital platforms enables seamless booking and tracking, enhancing user experience. By leveraging advancements in shared mobility and subscription models, companies can capitalize on the growing demand for flexible transportation solutions, solidifying their position in the market.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Supply Chain Disruptions and Semiconductor Shortages
A significant challenge facing the European light commercial vehicle market is the ongoing supply chain disruptions and semiconductor shortages, which have severely impacted production timelines and delivery schedules. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA), global semiconductor shortages led to a 15% decline in LCV production in 2022, affecting manufacturers across the continent. This issue is particularly pronounced in Germany, where over 60% of automotive plants experienced delays due to component shortages, as reported by the German Federal Ministry of Economic Affairs. A study by the French National Institute for Transport Research highlights that 40% of surveyed businesses faced extended lead times for new vehicle orders, undermining their ability to meet rising demand. Additionally, the rising costs of raw materials, such as steel and aluminum, have increased production expenses by 20%, further straining profitability. Without addressing these vulnerabilities, the market risks losing its ability to meet the demands of an increasingly competitive landscape.
Consumer Scepticism Toward Electric LCVs
Consumer scepticism regarding the performance and reliability of electric LCVs, particularly in terms of range anxiety and charging convenience is further challenging the growth of the European market. According to the European Consumer Organisation (BEUC), over 50% of potential buyers express concerns about the limited driving range of electric LCVs, which averages 200 kilometres per charge, as highlighted by the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure. This perception is exacerbated by inconsistent charging speeds and network availability, particularly in rural areas. A report by the Italian National Institute of Statistics notes that only 35% of surveyed businesses have fully transitioned to electric fleets, citing uncertainty about long-term viability. Additionally, the absence of universally accepted benchmarks for battery lifespan and performance undermines trust in product efficacy. Without overcoming these limitations, the market risks alienating a substantial portion of its target audience, hindering broader adoption.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Vehicle Type
The vans segment had staggering 71.4% of the European light commercial vehicle market share in 2024. The leading position of vans segment in the European market driven by their versatility and adaptability to a wide range of applications, from last-mile delivery to mobile workshops. The rise of e-commerce has been a significant driver, with companies like Amazon and DHL expanding their logistics fleets to meet surging online shopping demands. According to the European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA), van sales in Europe grew by 15% in 2022 alone, driven by urbanization and the need for efficient intra-city transportation. Additionally, vans are favored for their lower operational costs compared to larger trucks, making them ideal for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). A study by Frost & Sullivan highlights that SMEs account for 60% of van purchases in Europe, underscoring their critical role in supporting local economies. Furthermore, advancements in technology, such as connectivity features and driver-assistance systems, have enhanced the appeal of modern vans. For instance, Mercedes-Benz’s Sprinter model incorporates IoT-enabled fleet management tools, reducing downtime by 20%. With cities implementing stricter emission regulations, lightweight and fuel-efficient vans remain indispensable for sustainable urban logistics.
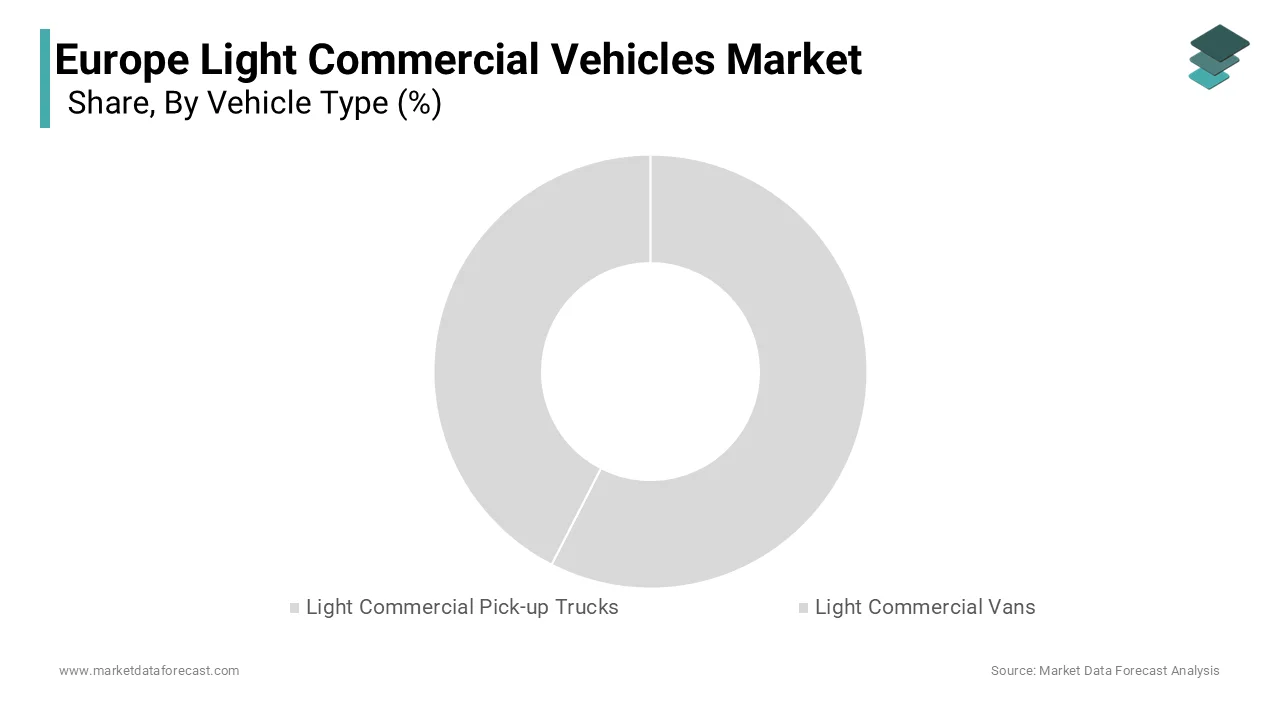
The pickups segment is predicted to register the fastest CAGR of 8.12% over the forecast period due to the increasing demand for rugged, multi-purpose vehicles capable of handling both urban and rural terrains. The agricultural sector, particularly in Eastern Europe, has embraced pickups for their durability and payload capacity. A case study by the Polish Automotive Industry Association reveals that pickup sales in Poland surged by 40% between 2020 and 2022, driven by subsidies for farmers upgrading to modern vehicles. Additionally, the growing popularity of adventure tourism has spurred private buyers to invest in pickups for recreational use. Ford’s Ranger, for example, saw a 25% increase in sales across Scandinavia due to its off-road capabilities. Governments are also incentivizing the adoption of dual-purpose vehicles to support rural development; Germany offers tax breaks for businesses purchasing pickups for agricultural or construction purposes. As Europe diversifies its vehicle needs, pickups are emerging as a bridge between commercial utility and personal leisure, offering unique opportunities for manufacturers to innovate and expand their portfolios.
By Propulsion Type
The internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles segment ruled the market by holding 81.8% of the European market share in 2024. The dominance of ICE segment in the European market is attributed to their established infrastructure, affordability, and widespread availability. Diesel-powered ICE vehicles, in particular, remain popular among fleet operators due to their high torque output and fuel efficiency, which are crucial for heavy-duty tasks. The International Energy Agency notes that diesel engines power over 90% of commercial fleets in Europe, reflecting their entrenched position in the market. Additionally, the existing network of fueling stations ensures minimal disruptions for businesses reliant on consistent vehicle performance. However, the importance of ICE vehicles extends beyond economics; they serve as a transitional backbone while alternative propulsion technologies mature. For instance, ACEA reports that ICE vehicles still outperform hybrids and EVs in terms of upfront costs, making them accessible to budget-constrained buyers. Despite regulatory pressures to phase out fossil fuels, ICE vehicles remain vital for maintaining operational continuity in sectors like construction and logistics.
The electric vehicles (EVs) segment is predicted to register the highest CAGR of 22.3% over the forecast period owing to the stringent emissions regulations and ambitious climate goals set by the European Union. The EU’s target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030 has accelerated investments in EV technology, with manufacturers like Renault and Volkswagen launching dedicated electric LCV models. A report by McKinsey & Company states that EV adoption in Europe’s commercial sector grew by 150% between 2020 and 2022, supported by government incentives such as tax exemptions and subsidies. For example, France offers up to €9,000 in grants for businesses purchasing electric vans, boosting sales by 30%. Moreover, advancements in battery technology have addressed key concerns like range anxiety; Tesla’s upcoming electric truck boasts a range of 500 kilometers on a single charge. Urban areas are also driving EV adoption through low-emission zones and congestion charges, making them the preferred choice for last-mile delivery. As Europe transitions to a carbon-neutral economy, EVs are poised to redefine the commercial vehicle landscape, offering sustainable solutions without compromising performance.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Germany dominated the European LCV market by accounting for 22.7% of European market share in 2024. The dominating position of Germany in European market is driven by the robust logistics sector of Germany that spans over 3 million businesses and generates €250 billion annually. According to the Fraunhofer Institute, German companies spend approximately €10 billion annually on LCVs, reflecting their commitment to innovation. The prominence of Germany in European market is further reinforced by its strong regulatory framework and investment in research.
France is likely to account for a significant share of the European LCV market over the forecast period. The extensive urbanization and e-commerce boom of France create a fertile ground for LCV adoption, which is primarily boosting the French market growth. According to Eurostat, France’s LCV registrations grew by 12% in 2022, driven by government incentives for low-emission vehicles. A study by INRAE highlights that over 70% of urban delivery fleets in France utilize LCVs, underscoring their economic benefits.
The UK is a notable market for light commercial vehicles in Europe. The focus of the UK on sustainable logistics and last-mile delivery is one of the major factors propelling the UK market growth. According to the British Vehicle Rental and Leasing Association, electric LCV sales grew by 40% in 2022, driven by tax breaks and subsidies. The strategic investments of the UK in charging infrastructure enhance adoption is also aiding the UK LCV market expansion.
Italy is predicted to account for a substantial share of the European light commercial vehicles market over the forecast period owing to its extensive small and medium-sized enterprises. According to Coldiretti, over 60% of businesses in Italy rely on LCVs for urban deliveries, ensuring premium quality service. The country’s Mediterranean climate and rich biodiversity make it ideal for logistics applications, reinforcing its leadership position.
Spain is projected to witness a prominent CAGR over the forecast period in the European LVC market due to expertise in urban logistics. According to the Spanish Federation of Transport Businesses, LCV usage in urban areas grew by 20% in 2022, driven by e-commerce expansion. Additionally, Spain’s focus on sustainability ensures continued market growth.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe light commercial vehicles market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Vehicle Type
- Commercial Vehicles
- Light Commercial Pick-up Trucks
- Light Commercial Vans
By Propulsion Type
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
- BEV
- FCEV
- HEV
- PHEV
- ICE
- Fuel Categories
- CNG
- Diesel
- Gasoline
- LPG
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]