Europe Intelligent Agriculture Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Agriculture, Application, Offering and Country (The UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Intelligent Agriculture Market Size
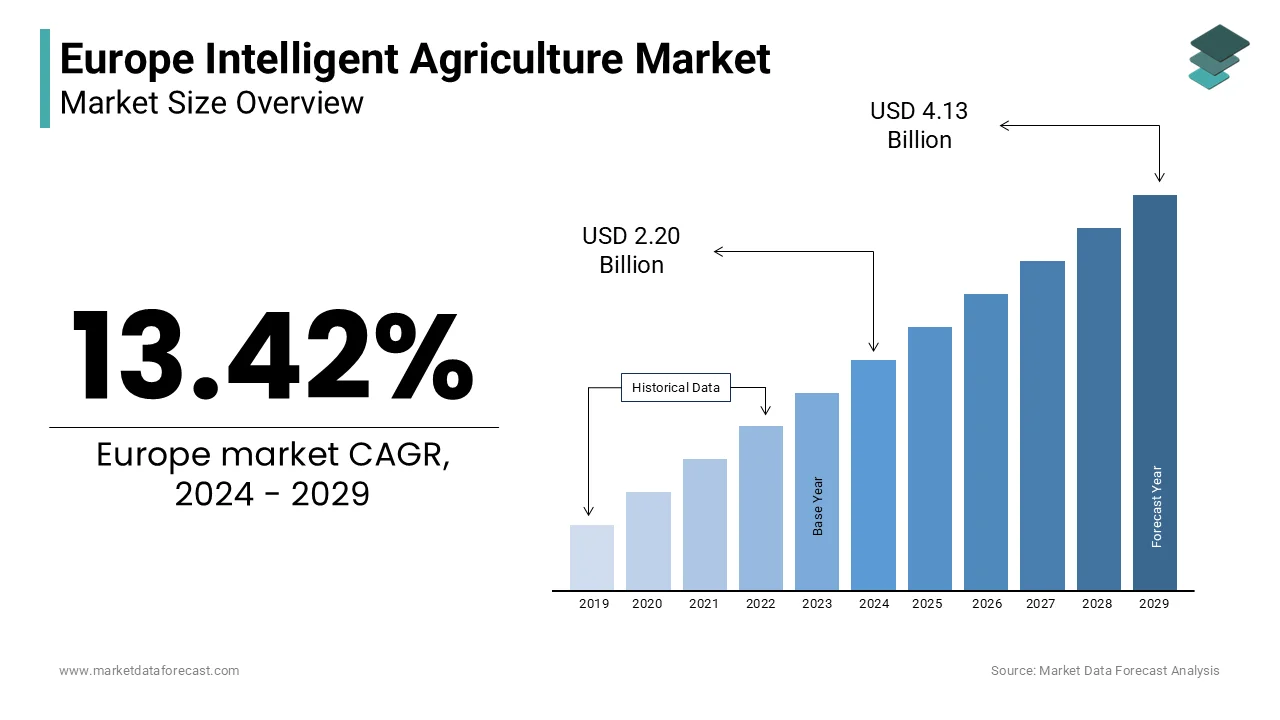
The Europe intelligent agriculture market was valued at USD 2.20 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2.50 billion in 2025 from USD 6.83 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.42% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
As Europe confronts the dual challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, sustainability in agriculture has become increasingly vital. Intelligent agriculture is emerging as a key solution, promoting sustainable practices by optimizing resource consumption, reducing carbon emissions, and improving the management of water and soil. These technologies enable farmers to efficiently manage limited resources, such as water, addressing critical issues like soil depletion and water scarcity, while simultaneously enhancing food production. As European governments push for more eco-friendly agricultural methods, intelligent agriculture offers a balanced approach, supporting productivity while meeting environmental conservation goals. This is essential to achieving long-term sustainability targets and ensuring food security across the region.
Technological Advancements in the European Intelligent Agriculture Market
AI and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing European agriculture by enabling predictive analytics and decision-making systems that enhance farm productivity. In 2023, the adoption of AI in European farming grew by 28%, with applications spanning crop yield prediction, pest management, and precision farming. Leading companies like Trimble Inc. and Deere & Company are developing AI-driven platforms that analyze large datasets from IoT devices, drones, and weather stations, helping farmers make data-informed decisions. For instance, Deere’s AI-powered FarmSight™ technology provides real-time crop yield predictions with up to 95% accuracy. Moreover, ML algorithms are being employed to fine-tune irrigation schedules and detect early signs of crop diseases, resulting in a 30% reduction in water usage and a 20% decrease in pesticide application across Europe, contributing significantly to sustainable farming.
IoT and Sensors
The adoption of IoT and sensor technologies has grown rapidly within European agriculture. Eurostat reports that over 1.2 million farms implemented IoT-based monitoring systems in 2023, representing a 35% year-on-year increase. IoT sensors provide real-time data on key metrics such as soil moisture and crop health, allowing farmers to make data-driven decisions regarding irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. For example, in Spain, smart irrigation systems using IoT sensors have reduced water usage by 25% in arid regions like Andalusia. In the Netherlands, IoT-enabled greenhouses are boosting crop yields by 15%. By 2029, IoT systems are projected to account for 40% of the intelligent agriculture market, with companies such as Bosch and Yara International driving innovation in this space.
Drones and UAVs
Drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are becoming integral to precision agriculture across Europe. The Global Drone Market Report projects a 15% increase in drone adoption for farming by 2025. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras and sensors provide detailed aerial imagery, enabling farmers to monitor crop health, assess soil conditions, and detect pests or diseases early. As of 2023, more than 30% of large-scale farms in France and Germany were using drones for precision farming. Drones are also being used to spray pesticides, reducing chemical usage by 10% in certain areas. Companies such as DJI and Parrot are leading this market, with drone adoption expected to grow at a CAGR of 12% by 2029.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are reshaping the agricultural landscape in Europe, addressing labor shortages and rising input costs. A 2023 report by Agri-Tech East highlighted a 22% increase in the adoption of robotic technologies across European farms. Autonomous tractors, robotic harvesters, and weeding robots are gaining traction, especially in countries like the Netherlands, Germany, and France. French company Naïo Technologies has developed a robotic weeder that reduces labor costs by 30% and improves efficiency by 25%. Meanwhile, John Deere’s AutoTrac™ autonomous tractors are being deployed on over 10,000 European farms. By 2029, it is projected that 35% of farms will incorporate robotic machinery, enhancing productivity and reducing dependency on manual labor.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for Food Security in Europe
With Europe’s population expected to exceed 748 million by 2024, ensuring food security is becoming increasingly critical. The United Nations estimates that global food production must increase by 70% by 2050 to meet demand. In Europe, intelligent agriculture is key to addressing this challenge by boosting yields while conserving resources. Precision farming techniques, for instance, have reduced fertilizer usage by 30% and increased crop yields by up to 20%. To support this shift, European nations are heavily investing in smart technologies; Germany alone allocated €400 million in 2023 to foster digital farming solutions. The European Union’s Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is also promoting technological integration to ensure long-term food sustainability in the Europe intelligent agriculture market.
Government Initiatives and Policies
Government initiatives are critical to advancing intelligent agriculture in Europe. The European Green Deal, introduced in 2020, aims to position Europe as the first climate-neutral continent by 2050, with agriculture playing a central role. The Farm to Fork Strategy, part of the Green Deal, promotes the adoption of smart technologies to reduce the environmental impact of agriculture while maintaining productivity. In 2023, France launched a €500 million initiative to advance smart farming, with an emphasis on sustainability and precision agriculture. Similarly, Germany’s Digital Farming 2030 initiative provides subsidies for IoT sensors and autonomous machinery, helping farmers adopt digital solutions. As of 2023, 45% of EU farmers utilized digital technologies, a figure expected to rise to 60% by 2026, positioning Europe as a global leader in intelligent agriculture.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability is an increasingly urgent priority, especially as Europe moves towards achieving the targets set by the Paris Agreement. According to a 2022 report by the European Environment Agency (EEA), agriculture accounts for nearly 10% of the continent’s greenhouse gas emissions. To address this, intelligent agriculture technologies are being adopted to optimize resource use and minimize environmental impact. For instance, smart irrigation systems have reduced water consumption by 25% in drought-prone areas such as Spain and Italy. Precision farming, which relies on data-driven approaches, can decrease pesticide use by up to 30%, mitigating the flow of harmful chemicals into the environment. In the Netherlands, the rise of vertical farming has led to a 90% reduction in water usage compared to traditional farming methods. With continued investment in sustainable agriculture, the market for eco-friendly farming technologies is expected to see substantial growth.
Labor Shortages and Rising Input Costs
Labor shortages are becoming a significant challenge for the European agricultural sector, with the European Commission reporting that 60% of farms face workforce shortages, particularly for manual labor. Additionally, input costs, including fertilizers, seeds, and machinery, have risen by 15% over the past year, as noted by Eurostat. Intelligent agriculture offers solutions through automation and robotics. Autonomous tractors, which are widely used in Germany and the Netherlands, can reduce the need for manual labor by up to 40% while increasing productivity by 20%. Robotic harvesters, such as those developed by Agrobot, are gaining popularity, particularly in the fruit and vegetable farming sectors, which are most affected by labor shortages. By 2025, it is anticipated that 50% of European farms will employ some form of automation to control labor costs and maintain profitability.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment
The high initial investment required for adopting intelligent agriculture technologies remains a significant barrier, particularly for small and medium-sized farms. McKinsey & Company reports that implementing advanced systems such as drones, AI-driven platforms, and IoT devices can cost between €50,000 and €100,000 per farm. This financial burden has proven prohibitive for many, with nearly 70% of European farmers citing cost as the primary reason for delaying smart farming adoption in 2023. While government subsidies such as Germany’s €200 million funding initiative for digital farming that help offset these costs, ongoing operational expenses for maintaining and updating software and hardware further challenge profitability, particularly in less developed regions of Europe.
Lack of Awareness and Technical Knowledge
Despite the availability of intelligent agriculture technologies, a lack of awareness and technical knowledge continues to slow widespread adoption. A 2023 survey conducted by Agri-Tech East revealed that 45% of European farmers are unfamiliar with how to integrate digital technologies into their operations. This knowledge gap is especially pronounced in rural areas and among older generations, where traditional farming methods prevail. Additionally, many farmers lack access to the technical training necessary to operate advanced systems such as AI-driven platforms or IoT-based sensors. Without adequate support and education, the perceived complexity of these technologies may deter farmers from adopting them, even when subsidies are available. While educational programs in countries like France and the UK are addressing this gap, further efforts are necessary to ensure broader understanding and implementation across Europe.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The increasing reliance on IoT sensors, drones, and cloud-based platforms in intelligent agriculture raises concerns about data privacy and security. According to a 2023 Accenture study, 35% of European farmers are hesitant to adopt smart farming solutions due to fears of data breaches or misuse. The European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on data collection and usage, creating further uncertainty about how farm data is stored and shared. Additionally, the lack of industry-wide standards for data protection increases the risk of cyberattacks, with agricultural data breaches rising by 12% between 2022 and 2023. To build trust, companies must prioritize robust encryption methods and transparent data governance policies. Addressing these concerns will be critical to ensuring long-term growth in the intelligent agriculture market.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of 5G and Internet Connectivity
The rollout of 5G technology is expected to significantly impact the Europe Intelligent Agriculture Market by enhancing internet connectivity in rural areas. Ericsson’s Mobility Report projects that 90% of Europe will have 5G coverage by 2025, providing the high-speed, reliable connections necessary for real-time data transfer between IoT sensors, drones, and autonomous machinery. This connectivity expansion is particularly vital for regions in Eastern Europe, where internet infrastructure has historically lagged. In 2023, Vodafone launched a 5G-enabled smart farming pilot project in Hungary, allowing real-time monitoring of soil moisture and crop health through IoT devices. As 5G networks expand, the Europe intelligent agriculture market is likely to register promising growth during the forecast period, with connectivity improvements accelerating the adoption of digital farming solutions across the continent.
Growing Demand for Organic and Sustainable Farming
The demand for organic and sustainably produced food is accelerating rapidly across Europe. According to Euromonitor International, the European organic food market reached €45 billion in 2023, marking a 10% year-on-year increase. Heightened consumer awareness about the environmental impact of conventional farming is driving the shift towards sustainable agricultural practices. Intelligent agriculture technologies, such as precision farming and smart irrigation, are playing a pivotal role in supporting organic farming by minimizing chemical inputs and optimizing resource use. For instance, drip irrigation systems, which reduce water usage by 30%, are widely adopted on organic farms in Spain and Italy. Furthermore, the European Union’s Farm to Fork Strategy, which targets a 25% increase in organic farming by 2030, is fueling demand for smart farming solutions. Consequently, the market for sustainable and organic farming technologies is expected to witness robust growth in the coming years.
Emergence of Agritech Startups in Europe
The agritech ecosystem in Europe is thriving, with startups driving innovation and advancing intelligent agriculture technologies. In 2023, European agritech startups raised over €2 billion in venture funding, a 15% increase from the previous year, according to AgFunder. The United Kingdom and the Netherlands are at the forefront of this trend, with companies developing AI-driven analytics, drone technology, and IoT-based farming solutions. UK-based Hummingbird Technologies, for example, leverages AI and satellite imagery to deliver precision farming insights, while Farmers Edge, a Canadian startup with a strong European presence, offers cloud-based farm management platforms. The rise of agritech startups is intensifying competition, providing farmers with cutting-edge technologies at competitive prices. With venture capital continuing to flow into this space, the startup landscape is expected to further accelerate the adoption of intelligent agriculture across Europe.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Emerging markets in Eastern Europe, including Poland, Romania, and Hungary, are experiencing rapid agricultural modernization, presenting significant growth opportunities for the Europe Intelligent Agriculture Market. Eurostat reports that agricultural productivity in these regions increased by 12% between 2020 and 2023, driven by the adoption of precision farming and IoT-based technologies. Governments in these countries are investing heavily in smart farming solutions to address challenges such as labor shortages and climate change. In Poland, for example, the government has allocated over €200 million to support digital farming initiatives, while Romania is focusing on smart irrigation systems to mitigate water scarcity. These emerging markets offer lucrative expansion opportunities for European agritech companies looking to broaden their reach.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fragmented Market
The European intelligent agriculture market is highly fragmented, with more than 300 companies offering a diverse range of technologies and solutions, according to a 2023 Agriculture Market Research report. This fragmentation presents challenges for farmers, who often struggle to integrate multiple systems from different providers into a cohesive farming operation. For instance, a farmer may use separate platforms for precision irrigation, crop health monitoring, and livestock management, leading to compatibility issues and increased operational complexity. Additionally, the lack of standardization across software and hardware solutions further complicates adoption. Many farmers, particularly in smaller or less developed regions, are hesitant to invest in systems that may not be fully interoperable. To address this, industry leaders like John Deere and AGCO are working to develop more comprehensive, integrated solutions that streamline operations and improve user experience across the farming ecosystem.
Regulatory Barriers
Regulatory hurdles remain a major obstacle to the adoption of intelligent agriculture technologies in Europe. The agricultural sector is subject to stringent regulations on environmental protection, food safety, and data privacy, all of which can limit the deployment of new technologies. For example, the European General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on data collection and usage, making it challenging for companies to implement data-driven farming solutions without violating privacy laws. Additionally, the use of drones and autonomous machinery is tightly regulated in countries like France and Germany, where airspace restrictions and rules on data collection are particularly stringent. A 2023 report by the European Commission highlighted that over 30% of farmers identified regulatory issues as a major barrier to adopting smart farming technologies. Close collaboration between industry stakeholders and policymakers is essential to navigate these regulatory frameworks while fostering innovation.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
13.42% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Agriculture, Application, Offering and By Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ohn Deere, AGCO Corporation, Trimble Inc., Kubota Corporation, and European GNSS Agency (GSA). etc |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Agriculture Type Insights
The precision farming segment remains the largest segment in the European intelligent agriculture market, holding a 36.6% market share in 2023. Precision farming’s ability to optimize resource use, including water and fertilizers, makes it a highly efficient solution, particularly in water-scarce regions such as Spain and Italy. The smart greenhouses segment is the fastest-growing, with a projected CAGR of 10.68% from 2024 to 2029. This growth is driven by the rise of vertical farming and climate-controlled agriculture, particularly in countries like the Netherlands and Denmark.
By Offering Insights
In 2023, hardware was the dominant offering, accounting for 58.7% of the market share, fueled by increasing demand for IoT-based devices, drones, and autonomous machinery. The software segment, however, is anticipated to grow the fastest, with a forecasted CAGR of 12.44% from 2024 to 2029. AI-based farm management platforms and predictive analytics tools are gaining traction across Europe as farmers adopt more digital solutions for improving agricultural efficiency.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Germany is the largest market for precision farming in Europe, holding 31.8% of the region's intelligent agriculture market share in 2023. The country has established a robust digital farming ecosystem, with over 60% of farms utilizing precision farming technologies, including GPS-guided tractors and AI-powered field management platforms. Germany's Digital Farming 2030 initiative is expected to further accelerate growth, with the government allocating over €400 million towards developing smart farming infrastructure. Additionally, Germany leads in autonomous machinery adoption, with autonomous tractor usage increasing by 20% between 2022 and 2023. Key players like John Deere and Fendt are at the forefront of innovation in this space, making Germany a hub for agricultural technology.
France is another key player in the European intelligent agriculture market, particularly in livestock monitoring and smart irrigation solutions. In 2023, the French government introduced a €500 million funding package to support the digital transformation of its agricultural sector, focusing on sustainability and efficiency. Over 45% of French livestock farms have adopted IoT-based monitoring systems, enabling real-time animal health and behavior tracking. Additionally, smart irrigation technologies have helped farmers reduce water consumption by 25% while increasing crop yields by 15% over the past two years, particularly in regions like Provence and the Loire Valley.
The Netherlands is a global leader in smart greenhouse technologies and vertical farming. With limited arable land, the country has embraced controlled-environment agriculture to maximize crop production. In 2023, the Netherlands accounted for 30% of Europe’s smart greenhouse market, according to Agriculture Market Insights. Dutch farmers are increasingly adopting fully automated greenhouse systems that utilize IoT sensors, AI-driven climate controls, and hydroponics, resulting in a 90% reduction in water usage compared to traditional methods, according to Wageningen University. Dutch companies such as Priva and Philips are at the forefront of these advancements, driving innovation in climate-controlled agriculture.
The United Kingdom is rapidly becoming a hub for agritech startups and digital farming solutions. In 2023, UK agritech startups raised over £400 million in funding, making it one of Europe’s fastest-growing markets for digital agriculture, according to Tech Nation. The UK government’s Agri-Tech Strategy has played a crucial role in fostering innovation, supporting startups that develop AI-driven farm management platforms, drone technology, and IoT-based monitoring systems. Companies such as Small Robot Company and Hummingbird Technologies are leading the way in autonomous machinery and precision farming analytics. AgFunder reports that 35% of UK farms are now using AI-based decision-support systems to optimize crop management.
Italy and Spain are pioneers in adopting intelligent agriculture for fruit and vineyard farming. According to Eurostat, precision farming adoption in vineyards grew by 18% in 2023, particularly in regions like Tuscany and La Rioja. Italy has implemented smart irrigation systems that have reduced water usage by 30% in drought-prone areas, while Spain has employed IoT-based solutions to monitor soil health and weather conditions in real time. Both countries are utilizing drone technologies for crop monitoring and pest control, helping to increase fruit yields by 10-15%. Government initiatives, such as Italy’s National Recovery Plan and Spain’s Strategic Plan for Sustainable Agriculture, continue to support the adoption of smart farming technologies.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Prominent players in the European intelligent agriculture market include John Deere, AGCO Corporation, Trimble Inc., Kubota Corporation, and European GNSS Agency (GSA). The hardware segment is led by John Deere, which holds a 25% share of the European market for autonomous tractors and GPS-guided systems as of 2023. Similarly, Trimble Inc. has captured a significant share of the software segment, driven by its AI-powered farm management systems that integrate real-time data from IoT devices and sensors.
The market is also witnessing an influx of agritech startups disrupting traditional farming methods. For example, Small Robot Company, a UK-based startup, is developing small, autonomous robots that can precisely monitor and manage crops, reducing pesticide use by 95%. In 2023, the company secured £10 million in funding, signaling growing investor interest in intelligent agriculture solutions. Startups are expected to account for 20% of the market share by 2029, intensifying competition in the industry.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THIS MARKET
- In 2022, John Deere acquired Bear Flag Robotics, expanding its portfolio of autonomous farming solutions and increasing its European market share by 5% in 2023. AGCO Corporation also bolstered its precision farming technology offerings with the acquisition of Precision Planting LLC.
- in 2023, Trimble Inc. partnered with Horsch Maschinen GmbH, a German agricultural machinery manufacturer, to develop fully automated planting and harvesting systems. These partnerships are expected to deliver integrated solutions to farmers, helping overcome operational challenges.
- Kubota Corporation launched its AI-powered autonomous tractors in 2023, leading to a 20% increase in sales across Europe. Similarly, AGCO Corporation introduced the IoT-based Fendt Connect platform, enabling farmers to remotely monitor and manage machinery.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the europe intelligent agriculture agriculture market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Agriculture Type
- Livestock Monitoring
- Precision Farming
- Smart Greenhouses
- Fish Farming
- Others
By Application
- Livestock Monitoring Applications
- Feeding Management
- Heat Stress Management
- Milk Harvesting
- Breeding Management
- Animal Comfort Management
- Behaviour Monitoring & Management
- Others
- Precision Farming Applications
- Yield Monitoring
- Field Mapping
- Crop Scouting
- Weather Tracking & Forecasting
- Irrigation Management
- Inventory Management
- Farm Labor Management
- Financial Management
- Others
- Fish Farming Applications
- Fish Tracking & Fleet Navigation
- Feeding Management
- Water Quality Management
- Others
- Smart Greenhouse Applications
- Hvac Management
- Yield Monitoring
- Water & Fertilizer Management
- Others
By Offering
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is intelligent agriculture in Europe?
It's the use of smart technologies like IoT, AI, drones, and sensors to improve farming efficiency, sustainability, and yields.
What’s driving the growth of intelligent agriculture in Europe?
Demand for food security, labor shortages, climate change, and strong EU support for digital farming.
Which countries lead in adopting intelligent agriculture tech?
Germany, the Netherlands, and France are leading due to advanced infrastructure and high-tech farming initiatives.
What are the main technologies used?
Precision farming tools, autonomous tractors, satellite mapping, smart irrigation systems, and crop-monitoring drones.
What challenges does the market face?
High initial investment costs, a lack of digital skills among farmers, and data privacy concerns.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]