Europe Healthcare 3D Printing Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Application (Surgical Guides, Implants, Tissue Engineering, Hearing Aids, Dental Products, Prosthetics, Others), Technology, Material, And Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest Of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Europe Healthcare 3D Printing Market Size
The Europe healthcare 3d printing market size was calculated to be USD 0.53 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 2.10 billion by 2033 from USD 0.62 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 16.45% during the forecast period.
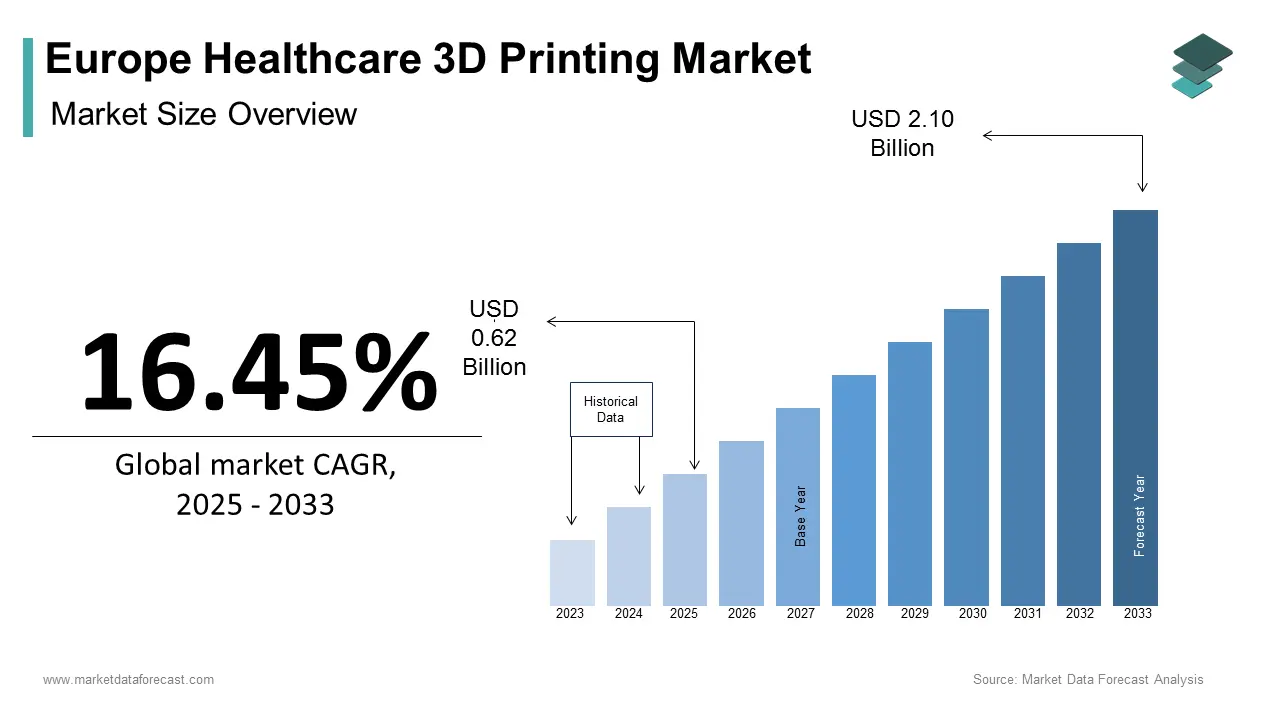
The Europe healthcare 3D printing market has emerged as a transformative force in the medical industry, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for personalized healthcare solutions. This rapid expansion is fueled by the region's robust healthcare infrastructure, high adoption rates of innovative technologies, and significant investments in research and development. Germany, France, and the UK are leading contributors to this growth, with their strong emphasis on precision medicine and regenerative therapies. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases is coupled with an aging population, has further propelled demand for customized implants and prosthetics. Additionally, regulatory support for additive manufacturing in healthcare, as per the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) that has created a conducive environment for innovation and commercialization.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for Customized Medical Solutions
The growing demand for personalized medical devices and implants is a pivotal driver of the Europe healthcare 3D printing market. 3D printing enables the creation of patient-specific implants and prosthetics, which significantly improve treatment outcomes. For instance, a study published in The Lancet revealed that 3D-printed titanium spinal implants have a success rate exceeding 95%. This capability has led to increased adoption in orthopedics and dentistry. Furthermore, the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) estimates that over 60% of new drug approvals in Europe involve personalized therapies.
Technological Advancements and Cost Efficiency
Technological innovations in 3D printing have significantly reduced production costs while enhancing precision and scalability. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, additive manufacturing can reduce production costs by up to 50% compared to traditional methods. This cost efficiency has encouraged widespread adoption in healthcare facilities across Europe. For example, hospitals in Germany and France have integrated 3D printing for surgical planning is reducing operation times by an average of 20%, as per data from the European Society of Radiology. Moreover, advancements in bioprinting have opened new avenues for tissue engineering, with researchers at the University of Maastricht successfully creating 3D-printed liver tissues in 2022. These developments not only enhance patient care but also position Europe as a leader in cutting-edge medical technologies.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs
One of the primary barriers to the adoption of 3D printing in healthcare is the substantial initial investment required for equipment and infrastructure. The financial burden is particularly challenging for smaller healthcare institutions and startups is limiting their ability to integrate 3D printing into their operations. Additionally, the European Association of Hospital Managers notes that maintenance and operational costs for these systems can exceed €50,000 annually that further straining budgets. While larger hospitals in countries like Germany and the UK have managed to adopt these technologies, smaller facilities in Eastern Europe often struggle to justify the expense. This economic disparity creates uneven adoption rates across the region by hindering overall market growth.
Regulatory and Ethical Concerns
The regulatory hurdles and ethical considerations pose significant challenges to the Europe healthcare 3D printing market. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) mandates stringent testing and approval processes for 3D-printed medical devices, which can delay market entry. According to Deloitte, obtaining regulatory clearance for a single 3D-printed implant can take up to two years, discouraging innovation. Ethical concerns surrounding bioprinting, such as the creation of synthetic organs, also spark debates among policymakers and stakeholders. A survey conducted by the European Bioethics Forum revealed that 65% of respondents expressed apprehension about the long-term implications of bioprinting. These factors create uncertainty for manufacturers and healthcare providers that is slowing the pace of adoption and commercialization in the region.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Bioprinting Applications
Bioprinting represents a groundbreaking opportunity for the Europe healthcare 3D printing market, with immense potential in regenerative medicine and organ transplantation. Researchers at the University of Edinburgh successfully developed 3D-printed skin grafts in 2022 by demonstrating the feasibility of using bioprinting for burn treatments. Similarly, advancements in stem cell technology have enabled the creation of functional tissues, such as cartilage and heart valves is offering hope for patients with degenerative conditions. The European Union’s Horizon Europe program has allocated over €2 billion for biotechnology research that is further accelerating innovation. These developments position Europe as a hub for pioneering bioprinting applications is creating lucrative opportunities for market players.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with 3D printing is poised to revolutionize healthcare delivery in Europe. According to PwC, AI-driven 3D printing solutions could save the European healthcare system up to €100 billion annually by 2030. AI algorithms can optimize design processes, predict material behavior, and enhance precision in printing complex structures. For instance, Siemens Healthineers collaborated with a German university in 2023 to develop an AI-powered 3D printing system for creating patient-specific stents by reducing production time by 40%. Furthermore, the European Commission’s Digital Innovation Hubs initiative supports the adoption of AI in healthcare by fostering collaboration between tech companies and medical institutions. This synergy not only improves patient outcomes but also opens new revenue streams for stakeholders in the 3D printing ecosystem.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Limited Skilled Workforce
The shortage of skilled professionals proficient in both healthcare and 3D printing technologies poses a significant challenge to the Europe healthcare 3D printing market. According to a report by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP), the demand for specialized technicians in additive manufacturing is expected to grow by 30% by 2025. However, educational programs addressing this intersection remain limited is leaving a gap in expertise. For instance, a survey conducted by the European Additive Manufacturing Users Group revealed that 70% of healthcare institutions face difficulties in finding qualified personnel to operate and maintain 3D printing systems. This lack of trained professionals hampers the efficient implementation of 3D printing solutions in rural areas where access to advanced training is minimal. Addressing this challenge requires collaborative efforts between academia, industry, and government bodies to develop comprehensive training programs.
Intellectual Property Concerns
Intellectual property (IP) issues present another obstacle for the Europe healthcare 3D printing market, particularly concerning the replication of patented medical devices. According to the European Patent Office, the number of IP disputes related to 3D printing has risen by 40% over the past five years. Unauthorized reproduction of medical devices not only undermines innovation but also raises safety concerns. A case study by the European Health Law Association have revealed that counterfeit 3D-printed dental implants led to a 25% increase in post-surgical complications in 2022. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of 3D printing makes it difficult to enforce IP laws, complicating legal frameworks. These challenges deter manufacturers from investing in new technologies is slowing market progress and stifling creativity.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
16.45% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Application, Technology, Material, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, and Czech Republic |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Stratasys Ltd., 3D Systems Corporation, Materialise NV, EnvisionTEC GmbH, Renishaw plc, EOS GmbH, Arcam AB, Prodways, 3T Additive Manufacturing Ltd., Carbon Inc., Formlabs, CELLINK GLOBAL, Anatomics Pty Ltd., SLM Solutions, FIT AG, and Wacker Chemie AG |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Application Insights
The medical implants segment dominated the Europe healthcare 3D printing market by holding a share of 35.9% in 2024. The growth of the segment is attributed to the increasing prevalence of orthopedic disorders, with arthritis affecting over 100 million Europeans, according to the European Alliance for Access to Safe Medicines. 3D printing allows for the creation of patient-specific implants, such as hip and knee replacements, which offer superior fit and functionality. For instance, a study by the University of Zurich demonstrated that 3D-printed titanium implants achieved a 98% success rate in spinal surgeries. Additionally, government initiatives like Germany’s “Innovative Medicine” program promote the use of additive manufacturing in implant production.
The tissue engineering segment is expected to grow with a CAGR of 22.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by advancements in bioprinting, enabling the creation of functional tissues for drug testing and regenerative therapies. For example, researchers at the Karolinska Institute in Sweden successfully printed human liver tissue in 2023 by paving the way for organ transplants. The European Union’s Horizon Europe program has invested €500 million in bioprinting research, accelerating innovation. Moreover, the rising demand for alternatives to animal testing, as mandated by the EU’s REACH regulations, has increased the adoption of 3D-printed tissues in pharmaceutical development by propelling this segment’s rapid expansion.
By Technology Insights
The laser sintering segment was the largest and held 40.3% of the Europe healthcare 3D printing market share in 2024. This technology is widely used for producing durable and precise medical devices, such as orthopedic implants and dental prosthetics. According to a study by the Fraunhofer Institute, laser sintering reduces material waste by up to 70% is making it a cost-effective solution. Its ability to work with metals and polymers has made it indispensable in healthcare applications. For instance, in 2023, a French hospital utilized laser sintering to produce custom cranial implants, reducing surgery time by 30%. Government funding for sustainable manufacturing practices has further bolstered the adoption of laser sintering.
The jetting technology segment is ascribed to hit a CAGR of 25.3% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is attributed to its versatility in producing multi-material and multi-color prototypes, ideal for surgical planning and education. According to a report by the Royal College of Surgeons, jetting technology has reduced preoperative planning errors by 25%. Additionally, its compatibility with biological materials has expanded its use in bioprinting, with researchers at the University of Cambridge successfully printing vascular networks in 2023. The European Commission’s funding for digital innovation hubs has accelerated the adoption of jetting technology is positioning it as a key driver of future growth.
By Material Insights
The polymers segment was accounted in holding 50.1% of the Europe healthcare 3D printing materials market share in 2024. Their versatility, biocompatibility, and cost-effectiveness make them ideal for producing medical devices, such as surgical guides and dental aligners. According to a study by the Technical University of Munich, polymer-based implants have shown a 95% success rate in reconstructive surgeries. The EU’s Green Deal initiative promotes the use of recyclable polymers, further boosting their adoption. For instance, in 2023, a Dutch hospital adopted biodegradable polymers for pediatric implants is reducing environmental impact while ensuring patient safety.
The biological cells segment is likely to register a CAGR of 28.4% from 2025 to 2033. Advances in bioprinting have enabled the creation of functional tissues, such as skin and cartilage is addressing unmet medical needs. According to a report by the University of Oxford, 3D-printed biological cells reduced recovery times by 40% in wound healing trials. The European Commission’s investment in biofabrication research has accelerated innovation, positioning biological cells as a transformative force in regenerative medicine.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany led the Europe healthcare 3D printing market with 25.4% of share in 2024 owing to its robust healthcare infrastructure and strong emphasis on R&D. For instance, the Fraunhofer Institute collaborates with hospitals to develop 3D-printed implants, enhancing patient outcomes. Government initiatives, such as the “Future of Health” program, allocate €1 billion annually to additive manufacturing, fostering innovation.
France is more likely to hit a fastest CAGR of 7.6% during the forecast period. According to the French National Academy of Medicine, 3D printing has reduced surgical complications by 30%. The government’s investment in digital health platforms has accelerated adoption, with Paris-based startups leading in bioprinting innovations.
The UK healthcare 3D printing market is attributed in having significant growth with its advanced healthcare system and strong academic-industry collaborations. A study by Imperial College London revealed that 3D-printed prosthetics improved mobility by 50%.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Stratasys Ltd.
Stratasys is a pioneer in 3D printing solutions, offering advanced technologies for healthcare applications. The company’s PolyJet and FDM systems are widely used for creating anatomical models and surgical tools. Stratasys collaborates with European hospitals to enhance patient care through customized solutions.
3D Systems Corporation
3D Systems provides end-to-end 3D printing solutions, focusing on precision and scalability. Its Figure 4 platform is instrumental in producing dental devices and orthopedic implants. The company’s commitment to sustainability aligns with Europe’s Green Deal objectives.
EOS GmbH
EOS specializes in industrial-grade 3D printing, catering to the healthcare sector’s demanding requirements. Its metal 3D printing systems are used for producing high-performance implants. EOS’s partnerships with European research institutions drive innovation in additive manufacturing.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY PLAYERS
Strategic Collaborations
Players collaborate with hospitals and universities to co-develop innovative solutions. For example, Stratasys partnered with a German university to advance bioprinting applications.
Product Diversification
Companies expand their product portfolios to address diverse healthcare needs. 3D Systems introduced new materials compatible with biological cells by enhancing its offerings.
Sustainability Initiatives
Firms focus on eco-friendly practices, such as recycling materials. EOS launched a program to reuse metal powders is aligning with EU sustainability goals.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players of the Europe healthcare 3D printing market include Stratasys Ltd., 3D Systems Corporation, Materialise NV, EnvisionTEC GmbH, Renishaw plc, EOS GmbH, Arcam AB, Prodways, 3T Additive Manufacturing Ltd., Carbon Inc., Formlabs, CELLINK GLOBAL, Anatomics Pty Ltd., SLM Solutions, FIT AG, Wacker Chemie AG
The Europe healthcare 3D printing market is highly competitive, characterized by intense rivalry among established players and emerging startups. Companies differentiate themselves through technological innovation, strategic partnerships, and customer-centric solutions. The presence of regulatory frameworks ensures high-quality standards, fostering trust among stakeholders. Market leaders invest heavily in R&D to maintain their edge, while smaller firms leverage niche applications to gain traction. The fragmented nature of the market encourages mergers and acquisitions, consolidating market share.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2024, Stratasys acquired a UK-based bioprinting startup to enhance its regenerative medicine portfolio.
- In May 2024, 3D Systems launched a new polymer material for dental applications, improving durability by 30%.
- In June 2024, EOS partnered with a French hospital to develop 3D-printed spinal implants, reducing recovery times by 25%.
- In July 2024, Materialise introduced AI-driven software for optimizing 3D printing designs, increasing efficiency by 40%.
- In August 2024, GE Additive collaborated with a German research institute to advance metal 3D printing for orthopedics.
DETAILED SEGMENTATION OF EUROPE HEALTHCARE 3D PRINTING MARKET INCLUDED IN THIS REPORT
This research report on the Europe Healthcare 3D Printing Market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on application, technology, material, & region.
By Application
- Surgical Guides
- Implants
- Tissue Engineering
- Hearing Aids
- Dental Products
- Prosthetics
- Others
By Technology
- Laser Beam Melting
- Electron Beam Melting
- Photopolymerization
- Droplet Deposition/Extrusion-Based Technologies
- Three-Dimensional Printing (3DP) / Binder Jetting
- Others
By Material
- Polymers
- Biological Cells
By Region
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is driving the growth of the healthcare 3D printing market in Europe?
Key drivers include rising demand for personalized healthcare, technological advancements, reduced production costs, and increasing investments in healthcare innovation and research.
2. Who are the leading players in the Europe healthcare 3D printing market?
Some key players are Stratasys Ltd., 3D Systems, Materialise NV, EnvisionTEC GmbH, Renishaw plc, EOS GmbH, and CELLINK.
3. How is the market regulated in Europe?
The market is governed under the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR), which sets strict standards for safety, performance, and documentation for 3D-printed medical products.
4. Which European countries are leading in healthcare 3D printing?
Germany, the UK, France, and the Netherlands are among the leaders due to strong R&D infrastructure and healthcare innovation.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
