Europe Fuel Cell Technology Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Applications (Portable, Stationary, and Transport), Types, Fuel, Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Fuel Cell Technology Market Size
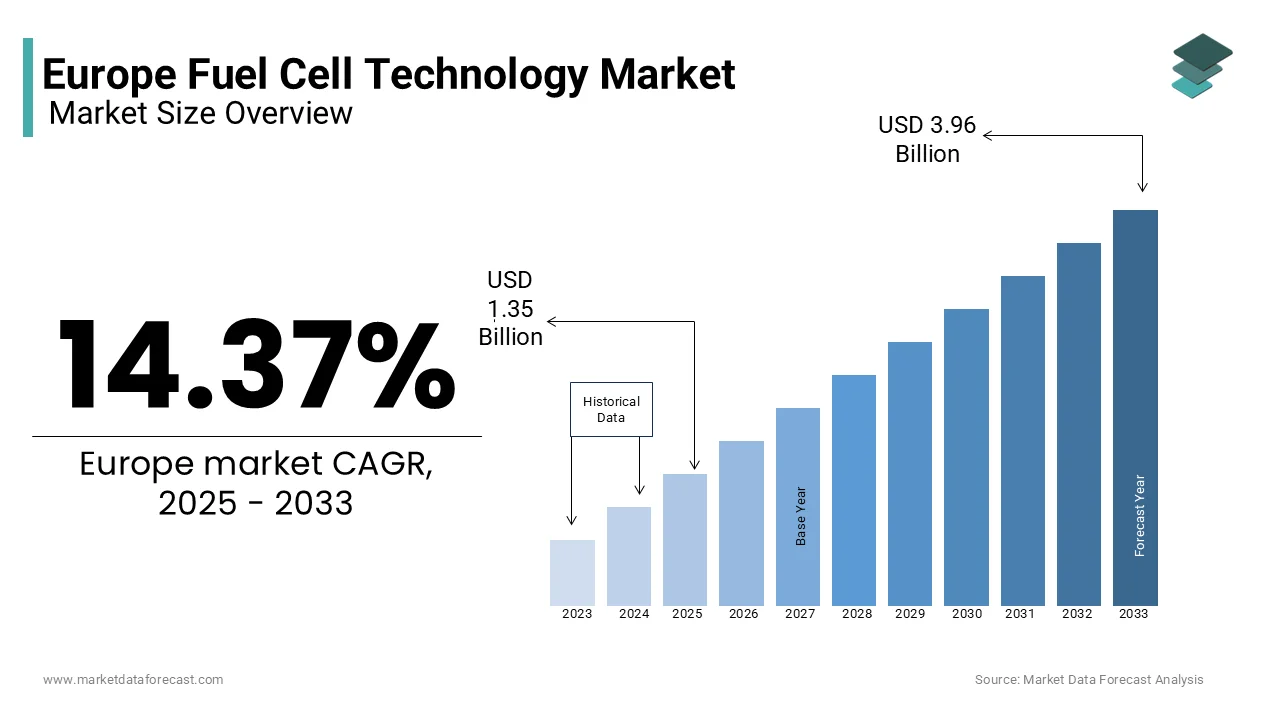
The Europe fuel cell technology market was worth USD 1.18 billion in 2024. The European market is projected to reach USD 3.96 billion by 2033 from USD 1.35 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 14.37% from 2025 to 2033.
Fuel cell technology converts chemical energy into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions and is primarily utilizing hydrogen as a fuel source. This technology is increasingly recognized for its potential to decarbonize various sectors including transportation, power generation, and industrial applications. As per the European Commission, the region is aggressively pursuing a carbon-neutral future by 2050, with fuel cells playing a pivotal role in achieving this goal. The market is characterized by advancements in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) and solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) which are being deployed across diverse applications such as portable devices, stationary power systems, and heavy-duty transport.
According to the International Energy Agency, Europe accounted for approximately 30% of global fuel cell installations in 2022 and is driven by supportive government policies and significant investments in hydrogen infrastructure. Germany, France, and the UK emerged as key contributors they collectively represent more than 60% of the regional market share. Furthermore, the European Clean Hydrogen Alliance estimates that hydrogen production capacity will reach 40 gigawatts by 2030 that creates a robust foundation for fuel cell adoption. With growing awareness of environmental sustainability and stringent emission regulations, the Europe fuel cell technology market is poised for exponential growth, underpinned by technological innovation and strategic collaborations.
MARKET DRIVERS
Government Policies Promoting Decarbonization
A critical driver propelling the Europe fuel cell technology market is the implementation of stringent government policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions. According to the European Environment Agency, the European Union has committed to cutting carbon emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. This ambitious target has led to increased adoption of fuel cell technologies and particularly in sectors such as transportation and energy generation. For instance, the EU’s Hydrogen Strategy outlines plans to install at least 40 gigawatts of renewable hydrogen electrolyzers by 2030 which fosters a conducive environment for fuel cell deployment.
The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy reports that Germany alone invested above €9 billion in hydrogen and fuel cell projects in 2022 and thereby putting focus on the significance of policy-driven initiatives. Additionally, subsidies and tax incentives offered by governments across Europe have significantly reduced the cost barriers associated with fuel cell adoption. These measures have not only accelerated market penetration but also positioned Europe as a global leader in sustainable energy solutions. Policymakers are ensuring long-term market growth and environmental benefits by aligning fuel cell development with broader climate goals.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Efficiency
Technological breakthroughs in fuel cell design and materials have emerged as another major driver for the Europe fuel cell technology market. According to the Joint Research Centre, advancements in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) have improved their efficiency by over 20% in the past five years which is making them more viable for commercial applications. These innovations have reduced the reliance on expensive platinum catalysts, consequently lowering production costs and enhancing scalability.
The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission highlights that solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) now achieve energy conversion efficiencies exceeding 60% and surpasses traditional combustion-based systems. Such improvements are particularly impactful in stationary power applications where reliability and efficiency are paramount. Furthermore, collaborative research initiatives such as the EU-funded HyCARE project are exploring novel storage solutions to address hydrogen supply chain challenges. These technological strides are not only expanding the scope of fuel cell applications but also attracting significant private sector investment and further bolstering market growth.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs and Infrastructure Limitations
High initial investment required for both fuel cell systems and supporting infrastructure is one of the primary restraints hindering the Europe fuel cell technology market. According to the European Investment Bank, the cost of installing hydrogen refueling stations ranges between €1 million and €2 million per station that poses a great financial barrier. This expense is compounded by the limited availability of hydrogen production and distribution networks which currently cover only a fraction of the continent. The UK Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy estimates that less than 5% of Europe’s energy infrastructure is currently equipped to handle hydrogen and draws attention to the scale of the challenge.
Moreover, the upfront cost of fuel cell systems remains prohibitively high for many end-users, despite ongoing efforts to reduce manufacturing expenses. For example, the cost of PEMFC systems for automotive applications averages €40,000 per unit deters extensive consumer adoption. While economies of scale and technological advancements are expected to mitigate these costs over time, the current financial burden continues to impede market expansion. Addressing these infrastructure and cost-related issues is crucial for unlocking the full potential of fuel cell technology in Europe.
Public Awareness and Acceptance Challenges
The lack of public awareness and acceptance of fuel cell technology is another major restraint for the Europe fuel cell technology which limits its adoption across various sectors. According to Eurobarometer, a survey conducted by the European Commission, less than 30% of Europeans are familiar with hydrogen fuel cells and their benefits. This knowledge gap often leads to misconceptions about safety, efficiency, and environmental impact further complicates market penetration efforts.
The Italian Ministry of Ecological Transition notes that public skepticism is particularly pronounced in rural areas, where access to information about emerging technologies is limited. Additionally, resistance from traditional energy stakeholders who view fuel cells as a threat to established business models, exacerbates the challenge. For instance, lobbying efforts by fossil fuel industries have delayed the implementation of several hydrogen-focused initiatives in Eastern Europe. Bridging this awareness gap through targeted education campaigns and transparent communication is essential to overcoming societal barriers and fostering greater acceptance of fuel cell technology.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
Its integration with renewable energy systems is a promising opportunity for the Europe fuel cell technology market and enables the creation of hybrid solutions that enhance energy efficiency and grid stability. According to the European Association for Storage of Energy, renewable energy sources accounted for 38% of the EU’s electricity generation in 2022, highlighting the growing need for effective energy storage and management solutions. Fuel cells and in that particularly solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) can store excess energy generated from wind and solar farms which is converting it into hydrogen for later use.
The Spanish Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving emphasizes that such hybrid systems could reduce energy losses by up to 40% and addresses one of the key limitations of intermittent renewable sources. Furthermore, the Netherlands Enterprise Agency reports that integrating fuel cells with offshore wind farms could generate an additional 10 gigawatts of clean energy by 2030. This synergy not only enhances the viability of renewable energy projects but also creates new revenue streams for fuel cell manufacturers. By capitalizing on this opportunity, Europe can accelerate its transition to a sustainable energy ecosystem while strengthening energy security.
Expansion into Emerging Markets and Applications
The expansion of fuel cell technology into emerging markets and applications such as maritime transport and data centers presents potential opportunity for the growth of the Europe fuel cell technology. According to the European Maritime Safety Agency, the shipping industry accounts for approximately 13% of Europe’s total greenhouse gas emissions and this presents a lucrative opportunity for fuel cell adoption. Hydrogen-powered vessels equipped with PEMFC systems offer a zero-emission alternative to conventional marine engines which aligns with the International Maritime Organization’s decarbonization targets.
The Swedish Energy Agency highlights that the global demand for fuel cell-powered ships is projected to grow substantially between 2023 and 2030. Similarly, the rise of hyperscale data centers in Europe has created a demand for reliable and sustainable power solutions. Fuel cells provide uninterrupted power supply while reducing carbon footprints and are making them an attractive option for tech giants like Google and Microsoft. By diversifying into these untapped sectors, the Europe fuel cell technology market can unlock new growth avenues and reinforce its leadership in clean energy innovation
MARKET CHALLENGES
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Material Scarcity
Supply chain vulnerability and particularly concerning critical materials such as platinum and rare earth elements is a pressing challenge the Europe fuel cell technology market faces. According to the European Raw Materials Alliance, Europe relies heavily on imports for over 90% of its platinum requirements which are essential for manufacturing proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). This dependency exposes the market to geopolitical risks and price volatility and is undermining long-term stability.
The Czech Ministry of Industry and Trade reports that disruptions in the global supply chain during the COVID-19 pandemic caused a 25% increase in material costs, significantly impacting fuel cell production timelines. Moreover, the scarcity of rare earth elements, such as lanthanum and cerium used in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) constitutes additional challenges. Efforts to develop alternative materials and recycling technologies are underway, but progress remains slow. Addressing these supply chain vulnerabilities is imperative to ensure the resilience and competitiveness of the Europe fuel cell technology market.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Policy Fragmentation
Regulatory uncertainty and policy fragmentation across European countries hinder the harmonized development of fuel cell technology is additionally obstructing the development of this market in Europe. According to the European Policy Centre, inconsistent national policies regarding hydrogen production, distribution, and usage create barriers to cross-border collaboration and market integration. For instance, while Germany has implemented comprehensive hydrogen strategies, countries like Romania and Bulgaria lag behind due to limited resources and political will.
The Danish Energy Agency notes that this lack of coordination has resulted in fragmented hydrogen infrastructure with only 20% of planned projects reaching completion. Furthermore, the absence of standardized regulations for fuel cell safety and performance complicates compliance for manufacturers operating in multiple jurisdictions. Overcoming these challenges requires greater alignment among EU member states and the establishment of unified frameworks to facilitate seamless market growth and innovation.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
14.37% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Applications, Types, Fuel, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
AFC Energy (U.K.), Heliocentris (Germany), Topsoe (Denmark), Genport SRL (Italy), SFC Energy (Germany), Ceres Power (U.K.), AFC Energy (U.K.), Topsoe (Denmark), Ceres Power (U.K.), and SFC Energy (Germany). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Applications Insights
The Stationary applications segment dominated the Europe fuel cell technology market by capturing 55.8% of the total market share in 2024. This segment includes residential and commercial power generation, backup power systems, and grid stabilization solutions. The prominence of stationary applications can be attributed to their ability to provide reliable and efficient energy and particularly in regions with unstable electricity grids. Furthermore, the German Federal Network Agency notes that stationary fuel cells achieved an average efficiency of 65% which is surpassing traditional energy systems. Additionally, the growing emphasis on decentralized energy solutions has fueled demand for stationary fuel cells with over 10,000 units installed across Europe in 2022. These systems not only reduce carbon emissions but also offer significant cost savings in the long term makes them an attractive option for businesses and households alike.
On the other hand, the transport applications segment appears the fastest-growing category with a CAGR of 22% between 2025 and 2033. This progress is caused by the increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) in the commercial and public transport sectors. Countries like France and the UK have introduced mandates requiring 30% of new buses to be zero-emission by 2025, propelling demand for FCVs. Also, the French National Hydrogen Council stresses that over 500 hydrogen-powered buses were operational in Europe by the end of 2022 with projections indicating a tenfold increase by 2030. The versatility of fuel cells in powering heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and trains, further amplifies their importance. This rapid expansion underscores the critical role of transport applications in shaping the future of Europe’s fuel cell technology market
By Types Insights
The Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) segment gained the top spot and accounted for 45.8% of the Europe fuel cell technology market in 2024. Their high efficiency, compact design, and suitability for a wide range of applications including automotive and portable power systems contributes to the dominance of this segment. Moreover, the UK Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Association notes that PEMFCs achieved an average efficiency of 60% which is making them ideal for transportation applications. Additionally, advancements in membrane technology have reduced production costs by 15% over the past three years and further boosts adoption rates. With over 5,000 PEMFC systems installed in Europe in 2022, this segment continues to lead the market due to its versatility and proven performance.
The Solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) segment became the quickest expanding category and is expected to move ahead with a CAGR of 25.6% from 2025 to 2033 due to their superior energy conversion efficiency, which exceeds 65%, and their ability to operate on multiple fuel types including natural gas and biogas. In addition, the Italian National Agency for New Technologies brings to light that SOFCs are increasingly being adopted for stationary power applications, with over 2,000 units deployed across Europe in 2022. Their compatibility with renewable energy systems and potential for large-scale industrial use further accelerates their adoption. This rapid expansion positions SOFCs as a key driver of innovation in the Europe fuel cell technology market.
By Fuel Insights
The Hydrogen segment commanded the Europe fuel cell technology market in 2024 by capturing 60.4% of the total market share in 2024. Its prevalence is driven by its clean-burning properties and compatibility with PEMFCs and SOFCs. Further, the French Ministry of Ecological Transition reports that hydrogen production capacity in Europe reached 2.5 million tons in 2022, with projections indicating a doubling by 2030. The widespread adoption of hydrogen is further supported by government initiatives, such as the EU’s Hydrogen Strategy which aims to establish a robust hydrogen economy. This segment’s leadership underscores its critical role in decarbonizing Europe’s energy landscape.
Whereas, the Anaerobic digester gas segment rapidly advanced having an estimated CAGR of 30.1% over the forecast period. This rise is because of its renewable nature and ability to support circular economy principles. Also, the Dutch Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management shows that over 500 anaerobic digestion plants are operational in Europe is producing biogas for fuel cell applications. The integration of anaerobic digester gas with SOFCs offers a sustainable solution for waste management and energy generation and is driving its rapid adoption. This segment’s expansion reflects Europe’s commitment to innovative and eco-friendly energy solutions.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany led the Europe fuel cell technology market by capturing 25.1% of the total market share in 2024. Its dominance is driven by robust government policies, substantial investments in hydrogen infrastructure, and a thriving automotive industry. The German Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Association reports that the country invested over €9 billion in hydrogen projects in 2022, establishing itself as a global leader in fuel cell innovation. With over 200 hydrogen refueling stations operational, Germany’s commitment to decarbonization underscores its pivotal role in the regional market.
France grew considerably and is predicted to register a CAGR of 14.5% during the forecast period. The country’s focus on renewable energy integration and hydrogen-powered public transport has fueled demand for fuel cell technology. The French National Hydrogen Council points out that France aims to deploy 500 hydrogen-powered buses by 2025 and is reinforcing its rule in sustainable mobility. Additionally, investments in SOFC systems for stationary applications have strengthened its market position.
The UK accounts for a major portionof the market share which is attributed to ambitious hydrogen strategies and strong private sector participation. The UK Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy reports that the country plans to produce 5 gigawatts of low-carbon hydrogen by 2030 and is driving fuel cell adoption across various sectors. This strategic focus positions the UK as a key contributor to Europe’s fuel cell technology market.
Italy is an attractive market for fuel cell technology in Europe. The country’s emphasis on renewable energy and industrial decarbonization has spurred fuel cell adoption. The Italian National Agency for New Technologies notes that Italy has installed over 1,000 fuel cell systems for residential and industrial use, highlighting its growing influence in the regional market.
Spain captures a of the market share, according to the Spanish Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving. Its leadership is driven by investments in renewable energy and hydrogen production. The Spanish Ministry for the Ecological Transition reports that Spain aims to install 4 gigawatts of renewable hydrogen capacity by 2030 and is showing its commitment to advancing fuel cell technology.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe fuel cell technology market include AFC Energy (U.K.), Heliocentris (Germany), Topsoe (Denmark), Genport SRL (Italy), SFC Energy (Germany), Ceres Power (U.K.), AFC Energy (U.K.), Topsoe (Denmark), Ceres Power (U.K.), and SFC Energy (Germany).
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe fuel cell technology market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Applications
- Portable
- Stationary
- Transport
By Types
- PEMFC
- DMFC
- PAFC
- SOFC
- MCFC
By Fuel
- Hydrogen
- Natural Gas
- Methanol
- Anaerobic Digester Gas
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the Europe fuel cell technology market?
The growth is primarily driven by increasing government initiatives for clean energy, advancements in hydrogen fuel infrastructure, and rising demand for zero-emission transportation solutions.
Which industries are adopting fuel cell technology in Europe?
Key industries include automotive, aerospace, power generation, marine, and industrial manufacturing, with significant adoption in hydrogen-powered vehicles and backup power solutions.
How is the automotive sector utilizing fuel cell technology in Europe?
The automotive sector is investing in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) for passenger cars, buses, and trucks, with growing support from infrastructure development and fleet adoption programs.
What is the future outlook for the fuel cell technology market in Europe?
The market is expected to expand with increased investments in hydrogen production, improved fuel cell efficiency, and wider adoption across industries, driven by stricter emissions regulations and sustainability goals.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]