Europe District Heating Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report By Heat Source (Coal, Natural Gas, Renewable, Oil & Petroleum Products, and Others), Plant Type, Application, Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe District Heating Market Size
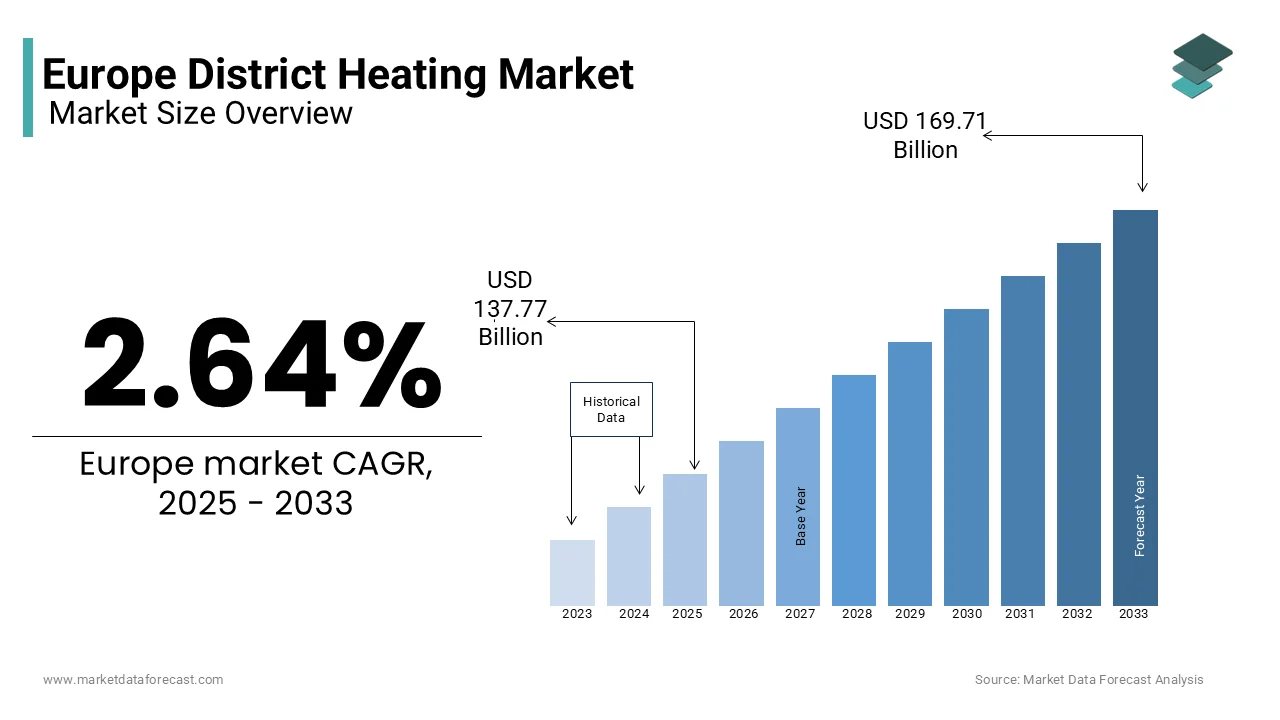
The Europe district heating market was worth USD 134.23 billion in 2024. The European market is projected to reach USD 169.71 billion by 2033 from USD 137.77 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 2.64% from 2025 to 2033.
District heating in Europe is a crucial element of the energy infrastructure of Europe and provides centralized heating solutions to residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. According to Eurostat, district heating systems supplied approximately 12% of Europe’s total heating demand in 2022, underscoring their significance in achieving energy efficiency and sustainability goals. Germany leads the market, with the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reporting that over 14% of the country’s heating needs are met through district heating networks. Denmark follows closely, where the Danish Energy Agency highlights that district heating accounts for nearly 60% of space heating in urban areas, driven by the integration of renewable energy sources. The European Commission further emphasizes that investments in modern district heating systems are projected to exceed €50 billion by 2030, supported by the EU’s commitment to carbon neutrality.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Adoption of Renewable Energy Sources in Europe
The growing integration of renewable energy sources into district heating systems is one of the major drivers of the Europe district heating market. According to the European Environment Agency, renewable energy accounted for 30% of the heat generated by district heating networks in 2022, up from 20% in 2018. Sweden leads this trend, with the Swedish Energy Agency reporting that biomass and geothermal energy now supply over 70% of the heat distributed through district heating systems in urban areas. Similarly, Denmark’s Energy Agency highlights that wind-to-heat technologies have reduced carbon emissions by 40% in Copenhagen’s district heating network. The French Ministry of Ecological Transition further notes that investments in renewable-based district heating systems have grown by 15% annually since 2020, driven by favorable government policies and subsidies. These advancements not only align with the EU’s renewable energy targets but also enhance the economic viability of district heating systems, making them indispensable for sustainable urban development.
Government Policies Supporting Energy Efficiency and Decarbonization
Stringent government policies aimed at improving energy efficiency and reducing carbon emissions is further boosting the expansion of the district heating market in Europe. According to the European Commission, member states are mandated to achieve a 32.5% improvement in energy efficiency by 2030, accelerating investments in district heating infrastructure. Germany’s Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reports that €10 billion was allocated to upgrade existing district heating networks in 2022, supported by tax incentives and feed-in tariffs. Similarly, the UK’s Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy highlights that district heating projects received £5 billion in funding under the Green Heat Network Fund, creating a robust pipeline for manufacturers and operators. The Italian Ministry of Ecological Transition further emphasizes that compliance with EU directives has led to a 25% increase in the adoption of low-carbon heating solutions. These policy frameworks not only ensure long-term market stability but also foster innovation and technological advancements in district heating systems.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs and Infrastructure Upgrades
The substantial initial investment costs and the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades is majorly restraining the growth of the district heating market in Europe. According to Eurostat, the average cost of constructing a new district heating network ranges between €5 million and €10 million per kilometer, depending on urban density and technology. The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reports that upgrading aging infrastructure in major cities has delayed project timelines by up to two years, increasing overall costs by 30%. Similarly, the French Ministry of Economy and Finance highlights that logistical challenges, such as land acquisition and permitting processes, often lead to cost overruns, particularly in densely populated areas. The European Commission further notes that smaller municipalities face difficulties securing financing for district heating projects, limiting their scalability. These financial and technical barriers hinder the widespread adoption of district heating systems, especially in regions with weaker economic conditions, threatening the market’s growth trajectory.
Public Perception and Awareness Barriers
Limited public awareness and misconceptions about district heating systems is another notable restraint for the European district heating market. According to the European Social Survey, only 40% of Europeans are familiar with district heating as a sustainable heating solution, compared to 70% for solar and wind energy. The Austrian Environmental Agency reports that public protests halted the construction of two large-scale district heating projects in Austria in 2022 due to unfounded concerns about environmental impacts. Similarly, the Irish Environmental Protection Agency highlights that misinformation campaigns have stalled district heating initiatives in rural Ireland, despite their potential to address energy poverty. The European Commission further emphasizes that inadequate educational campaigns fail to communicate the benefits of district heating, such as its role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting circular economies. Bridging this awareness gap requires targeted outreach programs and transparent communication strategies to foster public trust and acceptance.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Smart Grid Technologies and Digitalization
The integration of smart grid technologies and digitalization is a notable opportunity for the district heating market in Europe. According to the European Technology Platform for the Electricity Network of the Future (ETIP SNET), investments in smart district heating systems are projected to exceed €20 billion by 2030, driven by the need for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Denmark leads this trend, with the Danish Energy Agency reporting that smart meters and IoT-enabled sensors have improved energy efficiency by 25% in Copenhagen’s district heating network. Similarly, Sweden’s Energy Markets Inspectorate highlights that digital twin technologies enable operators to optimize heat distribution, reducing energy losses by 15%. The French Ministry of Science and Innovation further notes that machine learning algorithms integrated into district heating systems have reduced operational costs by 20%, aligning with sustainability goals. These advancements not only improve operational reliability but also create lucrative opportunities for manufacturers to capitalize on emerging innovations.
Urbanization and Increasing Demand for Sustainable Heating Solutions
The rapid pace of urbanization and the increasing demand for sustainable heating solutions is another significant opportunity for the district heating market in Europe. According to Eurostat, urban populations in Europe are expected to grow by 15% by 2030, creating a robust pipeline for district heating projects. France leads this trend, with the French Ministry of Ecological Transition reporting that district heating systems are being expanded to meet the heating needs of over 5 million new urban residents. Similarly, the Netherlands’ Ministry of Economic Affairs highlights that investments in district heating infrastructure have grown by 20% annually, driven by the government’s focus on reducing energy poverty. The European Commission further emphasizes that cross-border collaborations, such as the North Sea Energy Cooperation, are expected to unlock €10 billion in investments by 2030. These initiatives not only support Europe’s energy security but also position district heating systems as a critical enabler of sustainable urban development.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Competition from Decentralized Heating Solutions
The growing competition from decentralized heating solutions is a formidable challenge for the district heating market in Europe. According to the European Commission, individual heat pumps and solar thermal systems accounted for 40% of new heating installations in 2022, diverting investments away from centralized district heating networks. The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reports that funding for decentralized solutions exceeded €20 billion in 2022, compared to €10 billion for district heating systems. Similarly, the Spanish Ministry of Ecological Transition highlights that hybrid energy systems, which combine multiple heating technologies, create additional barriers for district heating systems. The French Ministry of Science and Innovation further notes that consumer preferences for greater control over energy consumption have led to a 10% decline in district heating subscriptions in urban areas. This competitive landscape necessitates strategic positioning and enhanced advocacy to secure the market’s place in Europe’s evolving energy ecosystem.
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Hurdles
Environmental concerns and stringent regulatory requirements is another major challenge for the district heating market in Europe. According to the European Environment Agency, the installation of new district heating networks can disrupt local ecosystems, leading to opposition from environmental groups. The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency reports that environmental impact assessments delayed the construction of two large-scale projects in 2022 due to concerns about soil contamination and water usage. Similarly, Ireland’s Marine Institute highlights that regulatory bottlenecks have stalled district heating initiatives in coastal regions, despite their potential to enhance energy security. The European Commission further emphasizes that compliance with EU-wide directives, such as the Emissions Trading System (ETS), requires significant adjustments, adding to operational complexities. While these regulations aim to protect biodiversity, they often prolong project timelines and increase costs, discouraging new entrants and slowing overall market growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
2.64% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Heat Source, Plant Type, Application, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
General Electric (U.S.), Engie (France), Dall Energy (Denmark), Helen Group (Finland), Uniper (Germany), FVB Energy Inc. (Canada), Statkraft (Norway), Alfa Laval (Sweden), Danfoss Group (Denmark), Veolia (France), and Ramboll (Denmark). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Heat Source Insights
The natural gas segment occupied 45.8% of the European market share in 2024. The leading position of natural gas segment in the European market is attributed to its availability, affordability, and lower carbon emissions compared to coal and oil. Germany leads this trend, with the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reporting that natural gas supplies over 50% of the heat generated by district heating systems in urban areas. Similarly, Italy’s Ministry of Ecological Transition highlights that natural gas-based systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 30%, aligning with decarbonization goals. Their importance lies in their ability to provide reliable and efficient heating solutions while supporting the transition to renewable energy. With investments in gas infrastructure set to grow, natural gas will remain a preferred heat source for district heating systems.
The renewable energy segment is expected to expand at a CAGR of 6.1% over the forecast period. The rising adoption of biomass, geothermal, and wind-to-heat technologies is primarily fuelling the growth of the renewable energy segment in the European market. Sweden leads this trend, with the Swedish Energy Agency reporting that renewables account for over 70% of the heat supplied through district heating networks. Similarly, Denmark’s Energy Agency highlights that wind-to-heat systems have reduced carbon emissions by 40% in Copenhagen. The European Commission further notes that investments in renewable-based systems are projected to reach €30 billion by 2030, driven by the EU’s renewable energy targets. Their ability to align with sustainability goals underscores their importance in achieving carbon neutrality.
By Plant Type Insights
The combined heat and power (CHP) segment led the market by occupying 46.4% of the European market share in 2024. The leading position of CHP segment in the European market is attributed to its superior efficiency in generating both heat and electricity, making it ideal for urban applications. Denmark leads this trend, with the Danish Energy Agency reporting that CHP plants supply over 60% of the heat distributed through district heating networks. Similarly, Germany’s Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action highlights that CHP systems reduce energy losses by 25%, enhancing their economic viability. Their importance lies in their ability to optimize resource utilization while ensuring reliable performance. With investments in CHP infrastructure set to expand, this segment will remain a cornerstone of the market.
The heat pumps segment is predicted to register a CAGR of 8.2% over the forecast period due to their ability to harness renewable energy sources, such as geothermal and air, for heating applications. Sweden leads this trend, with the Swedish Energy Agency reporting that heat pumps have improved energy efficiency by 30% in urban districts. Similarly, France’s Ministry of Ecological Transition highlights that investments in heat pump technologies have grown by 20% annually, driven by government subsidies. According to the European Investment Bank, investments in heat pump systems are considerably growing due to the focus of the European Union on sustainable heating solutions. Their ability to reduce carbon emissions underscores their importance in achieving climate goals.
By Application Insights
The residential segment dominated the market in Europe by holding 60.9% of the European market share in 2024. The leading position of residential segment in the European market is attributed to the concentration of urban populations and the need for affordable heating solutions. Germany leads this trend, with the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action reporting that district heating systems supply heat to over 10 million households. Similarly, Denmark’s Energy Agency highlights that residential applications reduce energy costs by 20%, enhancing their economic benefits. Their importance lies in their ability to address energy poverty while ensuring reliable heating solutions. With urbanization set to increase, residential applications will remain a cornerstone of the market.
The commercial segment is another major segment and is expected to witness a CAGR of 10.12% over the forecast period. Factors such as the increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions in office buildings, shopping malls, and hospitals is majorly driving the growth of the commercial segment in the European market. France leads this trend, with the French Ministry of Ecological Transition reporting that district heating systems have reduced energy consumption by 25% in commercial buildings. Similarly, the Netherlands’ Ministry of Economic Affairs highlights that investments in commercial applications have grown by 15% annually, driven by government incentives. According to the European Investment Bank, investments in commercial heating solutions are projected to grow substantially in the next few years owing to the EU’s focus on sustainable urban development. Their ability to enhance energy efficiency underscores their importance in achieving operational sustainability.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany held the leading position in the European district heating market in 2024 by holding a 25.8% of the European market share. The extensive urban infrastructure and strong policy support of Germany, with over €10 billion allocated to upgrade existing networks, are driving the domination of Germany in the European market. Germany’s investments in natural gas and renewable-based systems have reduced carbon emissions by 30%, underscoring their importance. The German government further notes that the district heating sector contributes €5 billion annually to the economy. Its leadership is reinforced by adherence to stringent environmental standards. With ambitious decarbonization targets, Germany will continue to shape the market’s trajectory.
Denmark held the second largest share of the European district heating market in 2024 and is likely to hold a promising position in the European market over the forecast period. The pioneering role of Denmark in renewable energy integration, with district heating accounting for 60% of urban heating needs, is primarily driving the Denmark market growth. The agency highlights that wind-to-heat technologies have reduced emissions by 40%, enhancing sustainability. Denmark’s government further emphasizes that investments in district heating infrastructure will reach €5 billion by 2030. Denmark’s focus on innovation positions it as a key market contributor.
Sweden is anticipated to account for a notable share of the European district heating market over the forecast period. The prominent position of Sweden in the European market is driven by its reliance on biomass and geothermal energy, supplying over 70% of district heating needs. Sweden’s investments in heat pumps have improved energy efficiency by 30%, enhancing economic viability. The Swedish government further notes that the district heating sector contributes €3 billion annually to the economy. Sweden’s focus on sustainability reinforces its regional importance.
France is expected to witness a healthy CAGR in the European market over the forecast period. The focus of France on reducing energy poverty, with district heating systems supplying heat to over 5 million urban residents is boosting the French market growth. The investments of France in smart grid technologies have optimized energy distribution, enhancing operational efficiency. France’s strategic initiatives reinforce its regional importance.
Italy is predicted to account for a considerable share of the European district heating market over the forecast period. The growing adoption of Italy of natural gas-based systems that reduce emissions by 30% is primarily boosting the Italian market growth. Italy’s investments in renewable energy integration have grown by 15% annually, driven by government subsidies. Italy’s focus on sustainability positions it as a key player in advancing district heating solutions.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the Europe district heating market include General Electric (U.S.), Engie (France), Dall Energy (Denmark), Helen Group (Finland), Uniper (Germany), FVB Energy Inc. (Canada), Statkraft (Norway), Alfa Laval (Sweden), Danfoss Group (Denmark), Veolia (France), and Ramboll (Denmark).
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe district heating market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Heat Source
- Coal
- Natural Gas
- Renewable
- Oil & Petroleum Products
- Others
By Plant Type
- Boiler
- CHP
- Heat Pump
- Heat Accumulators
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the Europe district heating market?
The growth of the Europe district heating market is driven by increasing urbanization, government initiatives for carbon neutrality, and the transition to renewable energy sources such as biomass, geothermal, and waste heat recovery.
What are the main energy sources used in Europe’s district heating systems?
Europe’s district heating systems primarily use biomass, geothermal energy, waste heat, natural gas, and, increasingly, large-scale heat pumps and solar thermal energy.
How are European governments supporting district heating development?
Governments in Europe support district heating through subsidies, tax incentives, renewable energy mandates, and funding for research and infrastructure modernization.
What is the future outlook for the Europe district heating market?
The future of the Europe district heating market is positive, with increasing investments in renewable energy integration, modernization projects, and supportive government policies driving expansion.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]