Europe Biodiesel Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Feedstock (Vegetable Oil and Animal Fats), Application (Fuel, Power Generation, and Others), Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Europe Biodiesel Market Size
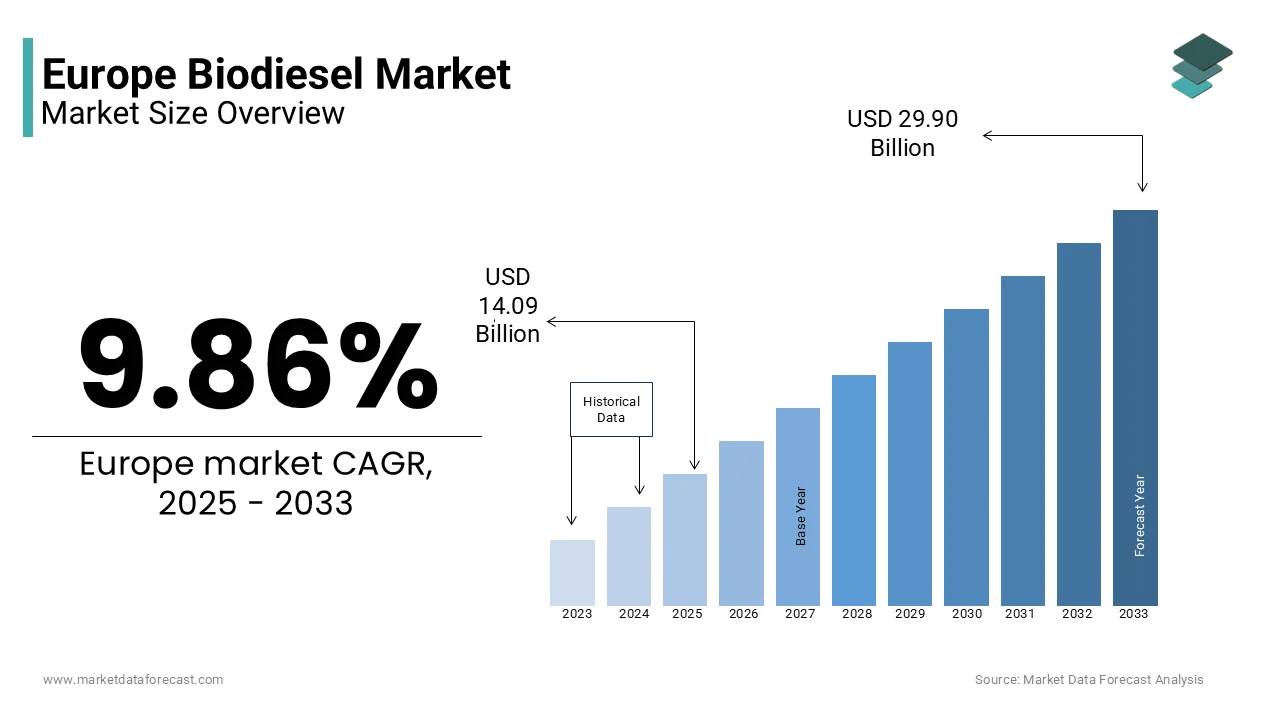
The Europe biodiesel market was worth USD 12.83 billion in 2024. The European market is projected to reach USD 29.90 billion by 2033 from USD 14.09 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 9.86% from 2025 to 2033.
Biodiesel is a renewable fuel derived primarily from vegetable oils, animal fats, and recycled cooking oils, serves as a cleaner alternative to conventional fossil diesel. It is widely utilized in transportation, heating, and industrial applications, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on non-renewable energy sources. Germany, France, and Italy emerging as key contributors to the European market. The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) mandates that by 2030, at least 32% of the EU’s energy consumption must come from renewable sources, driving substantial investments in biodiesel production. According to the European Biodiesel Board, the region produced over 14 million metric tons of biodiesel in 2022, accounting for nearly 40% of global output. This dominance is underpinned by favorable policies, such as tax incentives and blending mandates, which require a minimum biodiesel content in conventional diesel.
MARKET DRIVERS
Regulatory Frameworks and Policy Mandates in Europe
The European biodiesel market is significantly propelled by stringent regulatory frameworks and policy mandates aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The European Union’s Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) sets a binding target for member states to achieve a 32% share of renewable energy by 2030, as outlined by the European Commission. This directive enforces blending mandates, requiring that transportation fuels contain a minimum biodiesel content, which has driven consistent demand across the region. For instance, Germany implemented a mandate for a 6.7% biofuel blend in diesel, while France targets a 7% blend by 2024, according to the French Ministry of Ecological Transition. These policies have catalyzed investments in biodiesel production, with the EU accounting for over 40% of global output in 2022. Such regulatory support not only ensures compliance but also fosters innovation in sustainable fuel technologies, reinforcing Europe’s leadership in renewable energy adoption.
Growing Emphasis on Decarbonization and Sustainability
The escalating focus on decarbonization and sustainability serves as another major driver for the European biodiesel market. The European Environment Agency highlights that the transportation sector contributes approximately 25% of the EU’s total greenhouse gas emissions, prompting urgent action to adopt cleaner alternatives. Biodiesel, with its potential to reduce lifecycle emissions by up to 80% compared to fossil diesel, has emerged as a key solution. The International Energy Agency reports that Europe’s biodiesel consumption reached 18 million metric tons in 2022, reflecting a steady annual growth rate of 4.5%. Furthermore, initiatives like the European Green Deal emphasize phasing out fossil fuels, encouraging industries to transition toward renewable energy sources. This shift is bolstered by consumer awareness and corporate commitments to net-zero goals, creating a robust demand for biodiesel as a sustainable energy option.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Feedstock Availability and Supply Chain Challenges
One of the primary restraints in the European biodiesel market is the limited availability of sustainable feedstock, which poses a significant challenge to scaling production. The European Commission highlights that nearly 60% of biodiesel in Europe is produced from rapeseed oil, while used cooking oil (UCO) and animal fats account for the remainder. However, competition with the food industry and rising prices of vegetable oils have constrained feedstock supply. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global vegetable oil prices surged by over 30% in 2022 due to geopolitical tensions and climate-related disruptions. This volatility increases production costs and complicates long-term planning for biodiesel manufacturers. Additionally, reliance on imported feedstock, such as palm oil, raises concerns about sustainability and compliance with EU regulations, further complicating supply chain stability.
Environmental Concerns and Indirect Land-Use Change (ILUC) Issues
Environmental concerns, particularly those related to indirect land-use change (ILUC), present another critical restraint for the European biodiesel market. The International Energy Agency notes that cultivating energy crops for biodiesel can lead to deforestation and biodiversity loss, undermining its environmental benefits. ILUC risks have prompted the EU to impose stricter sustainability criteria under RED II, effectively banning palm oil-based biodiesel by 2030, as reported by the European Parliament. These regulatory shifts have disrupted established supply chains and increased compliance costs for producers. Furthermore, critics argue that first-generation biodiesel, derived from food crops, may not achieve the desired carbon reduction targets. The European Environment Agency estimates that ILUC effects could negate up to 50% of the emission savings initially projected for certain biodiesel feedstocks, raising questions about their long-term viability and environmental integrity.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Second-Generation Biodiesel Technologies
A significant opportunity for the European biodiesel market lies in the development and adoption of second-generation biodiesel technologies, which utilize non-food biomass such as agricultural residues, algae, and waste materials. The International Energy Agency highlights that second-generation biodiesel can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 90% compared to fossil fuels, making it a highly sustainable alternative. Europe is investing heavily in research and innovation, with the EU allocating over €1 billion under its Horizon Europe program to support advanced biofuel projects, as stated by the European Commission. Additionally, the growing availability of waste-based feedstocks, such as used cooking oil (UCO), provides a scalable solution. According to the European Waste-to-Advanced Biofuels Association, UCO-based biodiesel production grew by 15% annually between 2020 and 2022, underscoring the potential for waste-derived fuels to meet renewable energy targets while addressing circular economy goals.
Expansion of Renewable Energy Mandates Across Member States
Another key opportunity stems from the expanding renewable energy mandates across EU member states, driven by the European Green Deal’s ambitious decarbonization agenda. The European Commission reports that by 2030, renewable energy must account for at least 42.5% of the EU’s energy mix, up from the previous target of 32%. This policy shift has spurred increased demand for biodiesel in sectors like transportation and heating, where blending mandates are being tightened. For instance, Sweden aims to achieve a 20% renewable share in its transportation sector by 2030, as per the Swedish Energy Agency. Similarly, Italy plans to phase out fossil diesel entirely by 2040, creating long-term growth prospects for biodiesel producers. These national commitments not only ensure sustained demand but also position Europe as a global leader in renewable energy innovation, attracting investments and fostering industrial growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
High Production Costs and Economic Viability Concerns
One of the major challenges facing the European biodiesel market is the high production cost, which undermines its economic viability compared to conventional fossil fuels. The International Energy Agency reports that producing biodiesel from vegetable oils costs approximately €0.80 to €1.20 per liter, significantly higher than fossil diesel prices, which averaged €0.60 per liter in 2022. This cost disparity is exacerbated by fluctuating feedstock prices and energy-intensive production processes. The European Commission highlights that subsidies and tax incentives are often required to make biodiesel competitive, placing a financial burden on governments. Additionally, rising energy costs in Europe, driven by geopolitical tensions, have further strained producers. According to Eurostat, energy costs for industrial sectors increased by 40% in 2022, making it harder for biodiesel manufacturers to maintain profitability while scaling production.
Competition with Electric Vehicles (EVs) in the Transportation Sector
Another critical challenge is the growing competition from electric vehicles (EVs), which threatens to reduce the long-term demand for biodiesel in the transportation sector. The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association states that EV sales surged by 63% in 2022, accounting for 20% of all new car registrations in the EU. This rapid adoption is supported by government policies, such as Germany’s €9,000 subsidy for EV purchases and France’s ban on internal combustion engine vehicles by 2040. While biodiesel remains essential for heavy-duty transport and aviation, the shift toward electrification in passenger vehicles limits its growth potential. The International Renewable Energy Agency warns that without diversifying applications beyond road transport, the biodiesel market risks stagnation as EV infrastructure expands and consumer preferences evolve, posing a significant threat to its future relevance.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
20.63% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Feedstock, Application, and Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Archer-Daniels-Midland Company, Ag Processing Inc., Avril Group, Biodiesel Bilbao S.L., Cargill Inc., Emami Agrotech Ltd, FutureFuel Chemical Company, G-Energetic Biofuels Private Limited, Louis Dreyfus Company, Münzer Bioindustrie GmbH, Renewable Energy Group, VERBIO Vereinigte BioEnergie AG, Wilmar International Limited and World Energy LLC |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Feedstock Insights
The vegetable oil segment dominated the European biodiesel market by occupying a share of 60.7% in the European market in 2024. Rapeseed oil is the primary contributor, particularly in Germany and France, where it accounts for over 50% of vegetable oil-based biodiesel production. Its leadership stems from its widespread cultivation, low greenhouse gas emissions, and compatibility with existing engines. The FAO reports that Europe produced 10 million metric tons of rapeseed oil in 2022, with a significant portion dedicated to biodiesel. Its importance lies in meeting EU renewable energy mandates, as it reduces lifecycle emissions by up to 70% compared to fossil fuels, making it pivotal for decarbonization efforts.
The animal fats segment is anticipated to progress at a CAGR of 8.2% over the forecast period. Tallow and white grease are leading this growth due to their waste-based origin and alignment with circular economy goals. The European Waste-to-Advanced Biofuels Association highlights that animal fat-based biodiesel consumption reached 2 million metric tons in 2022, driven by sustainability regulations like RED II. This segment’s rapid growth is fueled by its ability to reduce emissions by up to 85% and its lower competition with food industries. Its importance lies in diversifying feedstock options and enhancing the sustainability of Europe’s biodiesel industry.
By Application Insights
The automotive segment held the major share of 55.8% in the European market in 2024. In 2022, biodiesel consumption in this sector reached 12 million metric tons due to the EU blending mandates like Germany’s 6.7% and France’s 7% biofuel targets. The International Energy Agency highlights that biodiesel reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% compared to fossil fuels, making it critical for decarbonizing transportation, which contributes 25% of the EU’s total emissions. Its dominance stems from widespread diesel vehicle usage and stringent carbon neutrality goals under the European Green Deal, ensuring its pivotal role in achieving emission reduction targets.
The marine segment is growing promisingly and is likely to showcase a CAGR of 9.5% over the forecast period. The IMO’s sulfur cap regulation, limiting sulfur content in marine fuels to 0.5%, has accelerated biodiesel adoption, particularly in Europe. The European Maritime Safety Agency reports a 15% increase in biodiesel use for marine applications in 2022, with Scandinavia leading adoption. Biodiesel’s ability to cut sulfur oxide emissions by up to 90% makes it indispensable for compliance. This growth underscores its importance in addressing the shipping industry’s 3% global greenhouse gas contribution, aligning with Europe’s broader sustainability and climate action goals.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany held the leading position in the European biodiesel market in 2024 by capturing 31.8% of the European market share. The German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs highlights that the country’s stringent renewable energy policies, including a mandatory 6.7% biofuel blend in diesel, have driven consistent demand. Germany’s leadership is further reinforced by its abundant availability of rapeseed oil, which accounts for over 50% of its biodiesel production, as reported by the European Biodiesel Board. This reliance on domestically sourced feedstock ensures cost efficiency and reduces dependency on imports, solidifying Germany’s position as a key player in the region’s biodiesel industry.
France is another leading regional segment for biodiesel in Europe and is estimated to register a CAGR of 5.1% during the forecast period. The growth of the French market is supported by its commitment to sustainability and decarbonization. The French Ministry of Ecological Transition emphasizes that blending mandates requiring up to 7% biodiesel in transportation fuels by 2024 have significantly boosted adoption. France’s focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions aligns with EU targets, driving investments in advanced biodiesel technologies. Additionally, the country’s robust agricultural sector provides a steady supply of feedstock, such as rapeseed and used cooking oil, enabling it to meet growing demand while adhering to environmental regulations.
Italy is rapidly emerging as a leader in waste-based biodiesel production. The Italian Ministry of Environment reports that Italy has prioritized used cooking oil (UCO) and other waste feedstocks, aligning with EU circular economy principles. This approach not only reduces reliance on food crops but also enhances the sustainability of biodiesel production. Italy’s innovative strategies have positioned it as a model for other European nations, particularly in meeting RED II criteria. The growing emphasis on waste-to-energy solutions has bolstered Italy’s competitive edge, ensuring steady growth in its biodiesel sector.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the European biodiesel market include Archer-Daniels-Midland Company, Ag Processing Inc., Avril Group, Biodiesel Bilbao S.L., Cargill Inc., Emami Agrotech Ltd, FutureFuel Chemical Company, G-Energetic Biofuels Private Limited, Louis Dreyfus Company, Münzer Bioindustrie GmbH, Renewable Energy Group, VERBIO Vereinigte BioEnergie AG, Wilmar International Limited and World Energy LLC.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the European biodiesel market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Feedstock
- Vegetable Oil
- Canola Oil
- Soybean Oil
- Palm Oil
- Corn Oil
- Others
- Animal Fats
- Poultry
- Tallow
- White Grease
- Others
By Application
- Fuel
- Automotive
- Marine
- Agriculture
- Power Generation
- Others
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key drivers of the Europe biodiesel market?
The Europe biodiesel market is driven by government policies promoting renewable energy, stringent emission regulations, and the rising demand for sustainable fuel alternatives.
What role does biodiesel play in achieving Europe's carbon reduction targets?
Biodiesel helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transport sector by offering a cleaner alternative to fossil diesel, contributing to the EU’s goal of climate neutrality by 2050.
How is the demand for biodiesel changing in the European transportation sector?
Demand is increasing, especially in heavy-duty transport and maritime industries, as companies seek lower-carbon fuel options to comply with stricter emission norms.
How does biodiesel compare to other renewable fuels in Europe?
Biodiesel is widely used due to its compatibility with existing diesel engines, but it faces competition from renewable diesel (HVO) and synthetic fuels, which offer better performance and lower emissions.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]