Global Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report – Segmented By Vehicle Type (Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)), End User (Residential, Commercial), Charging Type (On-board Chargers, Off-board Chargers) And By Region (North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Global Electric Vehicle Charging Stations Market Size
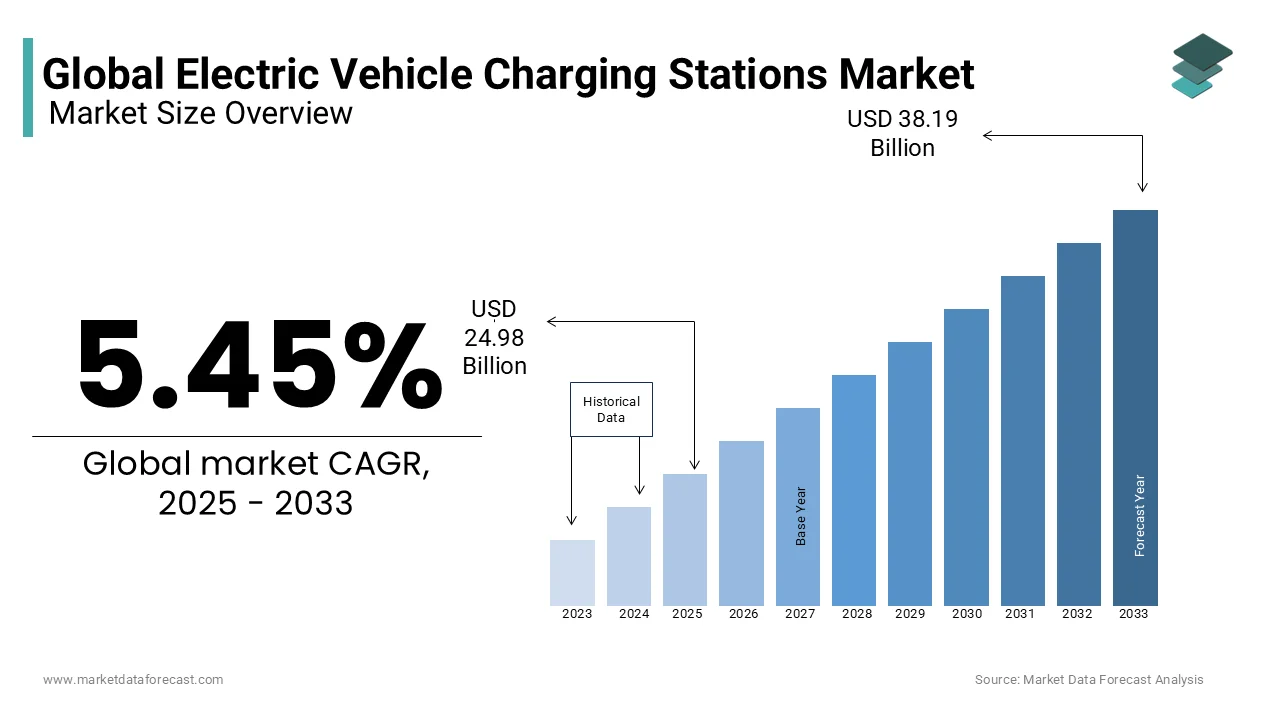
The global electric vehicle charging stations market size was valued at USD 23.60 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 27.91 billion in 2025 from USD 106.69 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 18.25% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
Market Overview
The EV charging stations, also known as electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE), provide the necessary energy to recharge plug-in electric vehicles, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). These stations are available in various forms, ranging from residential chargers installed in private garages to public fast-charging stations located along highways and urban centers. The market has gained significant traction due to increasing environmental concerns, government incentives promoting clean energy solutions, and advancements in EV technology.
As of 2023, there is an estimated global fleet of over 40 million electric vehicles on roads, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). This surge in EV adoption is attributed to the growing demand for robust charging infrastructure. According to the BloombergNEF, approximately 1.3 million public charging points were operational globally at the end of 2022, with China accounting for nearly two-thirds of this capacity. Furthermore, a data from the U.S. Department of Energy has shown that the average EV driver travels about 37 miles per day by emphasizing the need for widespread access to convenient charging options. Integrating EV charging stations into smart city frameworks has become imperative. Additionally, studies conducted by McKinsey & Company reveal that workplace charging facilities can increase employee satisfaction by up to 20% by showcasing their role beyond mere utility. These factors collectively illustrate how EV charging infrastructure serves not only as a functional necessity but also as a catalyst for sustainable mobility ecosystems.
Market Drivers
Government Policies and Incentives Accelerating EV Charging Infrastructure Development
Government initiatives worldwide are pivotal in driving the expansion of electric vehicle charging stations that further fuels the growth of the market. Policies such as tax credits, subsidies, and grants have significantly lowered the financial barriers for both businesses and consumers investing in EV infrastructure. According to the U.S. Department of Energy’s Alternative Fuels Data Center, federal tax incentives can cover up to 30% of the installation costs for commercial EV charging stations, capped at $100,000 per station. Additionally, the European Union’s Green Deal aims to deploy 1 million public charging points by 2025, supported by €20 billion in funding. These measures are complemented by stringent emissions regulations, such as the EU’s target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 55% by 2030, which incentivizes automakers and infrastructure providers to align with electrification goals. According to the International Energy Agency, countries with robust policy frameworks have witnessed a 40% higher growth rate in charging station installations compared to those without.
Rising Urbanization and Smart City Initiatives Boosting EV Charging Demand
Urbanization is a key driver propelling the need for electric vehicle charging stations, particularly in densely populated cities. According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, 68% of the global population is projected to live in urban areas by 2050, increasing the demand for sustainable transportation solutions. Cities like Amsterdam and Los Angeles are integrating EV charging stations into smart city plans by leveraging IoT and data analytics to optimize energy distribution and usage. According to the U.S. Federal Highway Administration, over 90% of urban trips are less than 30 miles by making EVs ideal for city commuting if adequate charging infrastructure is available. As per the World Bank, integrating renewable energy sources with EV charging networks can reduce urban carbon emissions by up to 25%.
Market Restraints
High Initial Investment Costs Hindering Widespread Adoption
The substantial upfront costs associated with establishing electric vehicle charging stations remain a significant restraint for market growth. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the installation of a single DC fast-charging station can cost between $50,000 and $100,000, depending on location and grid upgrades required. These expenses often deter small businesses and municipalities from investing in EV infrastructure, particularly in rural or underserved areas. As per the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), upgrading electrical grids to accommodate high-power chargers can increase costs by up to 30%. While governments offer subsidies, they often cover only a fraction of the total expense. For instance, the European Commission report stated that despite available funding, only 20% of EU member states have achieved their targeted charging infrastructure rollout due to financial constraints. This economic barrier limits the pace of expansion is creating gaps in accessibility and hindering equitable EV adoption.
Grid Capacity Challenges Limiting Charging Infrastructure Expansion
The strain on existing electrical grids poses another critical restraint for the EV charging stations market. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), widespread EV adoption could increase electricity demand by up to 30% by 2030 with significant grid reinforcements. In regions with aging infrastructure, such as parts of the United States, the Department of Energy warns that integrating high-power chargers may require costly upgrades to transformers and distribution networks. For example, a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) reveals that installing multiple fast chargers at a single location could overload local grids by leading to potential blackouts if not properly managed. As per the UK’s Office for National Statistics, approximately 40% of urban areas face challenges in supporting additional load capacity due to outdated systems. These limitations hinder the seamless integration of EV charging stations by delaying progress toward sustainable mobility goals.
Market Opportunities
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources Enhancing Sustainability
The incorporation of renewable energy into EV charging infrastructure presents a transformative opportunity for the market. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar and wind energy can reduce the carbon footprint of EV charging by up to 70% by making it an attractive solution for environmentally conscious stakeholders. As per the U.S. Department of Energy, pairing solar panels with EV charging stations can lower operational costs by 20-30% in regions with abundant sunlight. As per the European Environment Agency, countries like Germany and Denmark are leading efforts to integrate renewables, with over 40% of their EV charging stations now powered by clean energy. This synergy not only supports global decarbonization goals but also aligns with consumer demand for greener transportation options. The IEA projects that such integrated systems could account for 50% of all new charging installations by 2030 by creating a lucrative niche within the EV charging market.
Expansion into Emerging Markets Driving Global Growth
Emerging markets represent a significant growth avenue for the EV charging stations market that is driven by rapid urbanization and increasing vehicle electrification. According to the World Bank, developing nations will account for nearly 60% of global EV adoption by 2040 by necessitating robust charging infrastructure. For example, India’s Ministry of Power has announced plans to install 2,800 public charging stations by 2025 by targeting major cities and highways to support its goal of achieving 30% EV penetration. Similarly, China’s National Development and Reform Commission states that rural electrification programs have already facilitated the deployment of over 100,000 chargers in underserved areas. These initiatives are complemented by international collaborations, such as the United Nations’ Sustainable Mobility for All initiative, which aims to bridge infrastructure gaps in low-income regions.
Market Challenges
Interoperability Issues Creating Fragmentation in the Market
A lack of standardized protocols and interoperability among EV charging stations poses a significant challenge by hindering user convenience and market growth. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, over 20 different charging connectors and communication standards are currently in use globally by leading to compatibility issues for EV drivers. For instance, a study by the European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association (ACEA) reveals that 35% of EV users face difficulties accessing charging stations due to incompatible hardware or payment systems. This fragmentation is further exacerbated by proprietary software platforms, which limit cross-network usability. Additionally, the inconsistent authentication methods, such as RFID cards versus mobile apps shall create confusion and reduce the efficiency of public charging infrastructure, as per the International Transport Forum.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities Threatening Infrastructure Reliability
The increasing reliance on digital technologies in EV charging stations has exposed the market to cybersecurity risks that are posing challenge for the market key players. The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) warns that smart charging systems, which rely on internet connectivity, are susceptible to hacking, data breaches, and ransomware attacks. For example, a report by the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) identifies that nearly 40% of public charging stations lack robust encryption protocols by making them vulnerable to unauthorized access. According to the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre, cyberattacks on EV infrastructure could disrupt energy supply chains, potentially affecting up to 10,000 vehicles per station during peak usage. As charging networks expand by ensuring secure data transmission and protecting user privacy become paramount. The risk of compromised systems threatens both operational reliability and consumer confidence in EV charging solutions without addressing these vulnerabilities.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
5.45% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Vehicle Type, End-User, Charging Type and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Chargemaster, ABB, Chroma ATE Inc, Delphi Technologies PLC, Schaffner Holding AG., Siemens, AeroVironment, Inc., Pod Point, Robert Bosch GmbH and ChargePoint, Inc. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Vehicle Type
The battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) segment dominated the electric vehicle charging stations market by accounting for 63.1% of the total share in 2024 due to the BEVs' complete reliance on charging infrastructure, unlike hybrid models. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, BEVs represent over 70% of global EV sales that is driving demand for public and private charging stations. Their importance lies in their zero-emission capability by aligning with stringent environmental regulations. BEV adoption is critical to achieving net-zero targets by making robust charging networks indispensable.
The Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV) segment is anticipated to witness a fastest CAGR of 22.1% during the forecast period. This rapid growth is fueled by PHEVs' dual-fuel flexibility by appealing to consumers transitioning from conventional vehicles. According to the European Environment Agency, PHEVs accounted for 20% of new EV registrations in Europe in 2022, driven by subsidies and tax incentives. As per U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, PHEVs reduce fuel consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional hybrids, enhancing their attractiveness. PHEVs bridge the gap between fossil fuels and full electrification by fostering wider EV acceptance while supporting gradual behavioural shifts among drivers.
By End User
The residential charging stations segment dominated the Electric Vehicle Charging Stations market share of 38.1% in 2024 due to its convenience and cost-effectiveness of home charging, with over 80% of EV owners charging their vehicles overnight at home. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), residential chargers are often subsidized by governments by reducing upfront costs for consumers. They are more affordable than commercial alternatives with an average installation cost of $1,000-$2,000. Residential charging is pivotal in supporting daily urban commutes, as 90% of trips are under 30 miles, making it a cornerstone of EV infrastructure.
The commercial EV charging stations segment is attributed to hit the fastest CAGR of 32.1% during the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by increasing demand for public fast-charging networks, particularly along highways and in urban centers. According to the International Council on Clean Transportation, commercial fast chargers can deliver up to 80% battery charge in 20-30 minutes by catering to long-distance travelers and fleet operators. According to the U.S. Federal Highway Administration, over 50,000 commercial charging stations were installed in 2022 alone. Governments are also incentivizing this segment, with the European Commission allocating €1 billion to expand public charging hubs. Commercial charging plays a critical role in ensuring accessibility and reducing range anxiety by making it indispensable for sustainable mobility ecosystems.
By Charging Type
The on-board chargers segment was the largest and held a significant share in the electric vehicle charging stations market in 2024 with the growing prominence in residential and workplace charging, where most EV users charge their vehicles overnight. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, over 80% of EV charging occurs at home is driving demand for integrated on-board systems. These chargers are crucial for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, which cater to daily commuting needs by averaging 30-40 miles per charge. Their widespread adoption ensures seamless integration into existing electrical systems by making them indispensable for mass EV adoption.
The off-board chargers segment is attributed in holding the significant CAGR of 22.6% in the next coming years. This rapid expansion is fueled by the increasing demand for fast and ultra-fast charging solutions along highways and in urban centers. According to the European Alternative Fuels Observatory, DC fast chargers can deliver up to 80% battery capacity in under 30 minutes by addressing range anxiety and supporting long-distance travel. As per the U.S. Federal Highway Administration, public fast-charging stations are expected to grow by 500% by 2030 which was driven by government mandates and private investments. Off-board chargers play a pivotal role in reducing charging times and enhancing user convenience as EV adoption accelerates in the developed and developing countries.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific held the largest share of the electric vehicle charging stations market with an estimated share of 45.6% in 2024. This dominance is driven by China’s dominance in EV adoption, which boasts over 1.2 million public charging points, representing two-thirds of the global total. The region benefits from robust government policies, such as subsidies and mandates, alongside rapid urbanization. For instance, India’s Ministry of Power aims to install 2,800 new charging stations by 2025, while Japan focuses on integrating renewable energy with EV infrastructure. The region's prominence underscores its role in shaping global EV trends and supporting mass electrification.
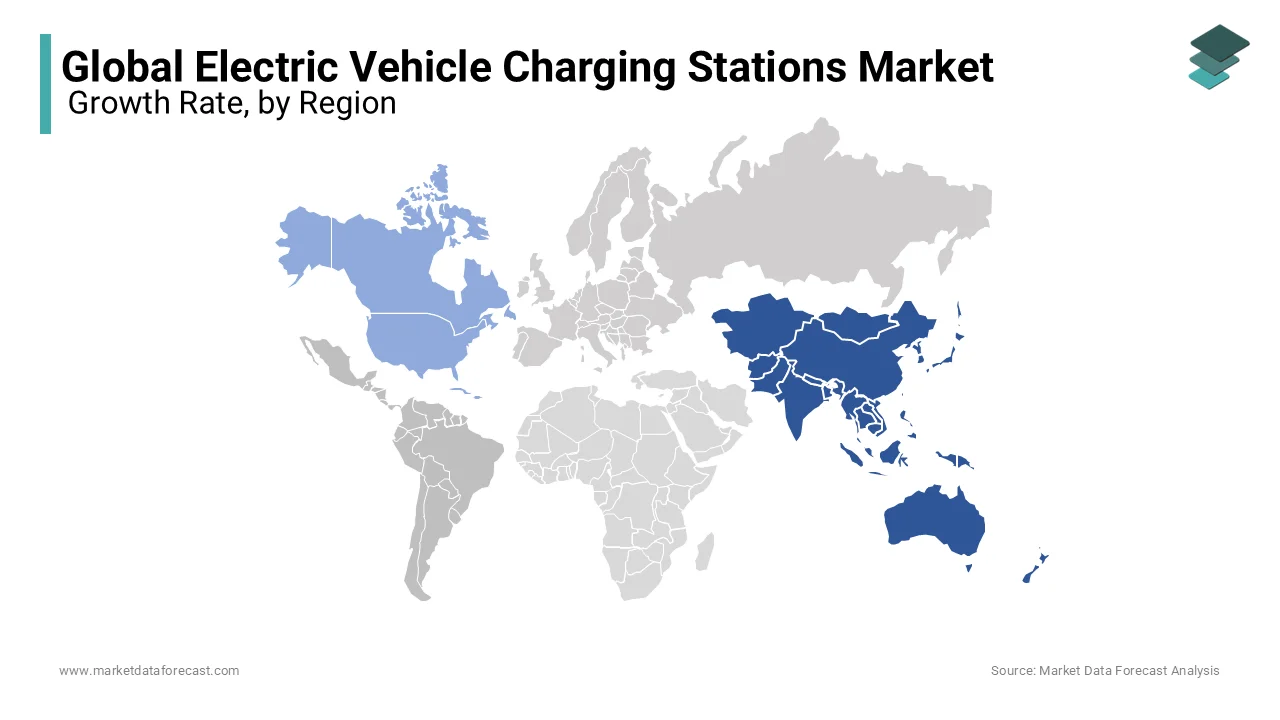
North America is the fastest-growing region with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.4% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by federal initiatives like the U.S. Department of Energy’s $7.5 billion investment in EV infrastructure under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. Additionally, California’s Air Resources Board mandates that all new vehicles sold by 2035 must be zero-emission, driving demand for charging stations. Canada’s Natural Resources Department projects a 50% increase in public chargers by 2026. The rise of private-public partnerships and technological advancements further accelerates the market expansion.
Europe, Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are poised for steady growth, supported by policy frameworks and increasing EV adoption. Europe, with 30% of global chargers, aims for 1 million stations by 2025, as per the European Commission. Latin America, led by Brazil and Mexico, expects a 25% annual growth in EV sales, driving charger demand. The Middle East and Africa, though nascent, show potential due to renewable energy integration; the UAE plans 500 new stations by 2025. These regions collectively contribute to global EV infrastructure expansion, ensuring equitable access to sustainable transportation solutions.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Chargemaster, ABB, Chroma ATE Inc, Delphi Technologies PLC, Schaffner Holding AG., Siemens, AeroVironment, Inc., Pod Point, Robert Bosch GmbH and ChargePoint, Inc. are the major companies in the global EV charging stations market.
Top 3 Players in the market
ChargePoint, Inc.
ChargePoint is a leading player in the global electric vehicle charging stations market, recognized for its comprehensive and scalable charging solutions. The company offers a wide range of products, from Level 2 chargers for residential and workplace use to fast-charging DC stations for public infrastructure. ChargePoint’s cloud-based platform enables seamless integration, remote management, and real-time monitoring of charging networks, making it a preferred choice for businesses and municipalities. Its commitment to interoperability and user-friendly interfaces has positioned it as a key enabler of EV adoption. By partnering with governments, utilities, and private enterprises, ChargePoint continues to expand its footprint globally, driving innovation and accessibility in the EV charging ecosystem.
ABB
ABB is a prominent contributor to the EV charging market, leveraging its expertise in electrification and automation technologies. The company specializes in high-power fast-charging solutions, including its Terra series, which supports ultra-fast charging for highways and urban hubs. ABB’s focus on sustainability and smart energy management aligns with global decarbonization goals, while its partnerships with automakers and energy providers enhance its reach. ABB’s cutting-edge technology, such as dynamic load balancing and grid integration, ensures efficient energy distribution and minimizes strain on electrical systems. As a pioneer in digitalization, ABB plays a vital role in advancing reliable, future-ready EV infrastructure worldwide.
Siemens
Siemens is a major player in the EV charging market, offering innovative and integrated solutions tailored to diverse customer needs. The company provides a broad portfolio, from compact home chargers to robust public charging stations, emphasizing scalability and efficiency. Siemens’ emphasis on smart grid integration and renewable energy compatibility underscores its commitment to sustainable mobility. By collaborating with cities, utilities, and fleet operators, Siemens addresses challenges like grid capacity and energy optimization, ensuring reliable and scalable charging networks. Its technological prominence and focus on end-to-end solutions make Siemens a critical driver of global EV infrastructure development, fostering the transition to cleaner transportation systems.
Top strategies used by the key market participants
Key players in the electric vehicle charging stations market have adopted a variety of strategic initiatives to consolidate their positions and expand their influence. One prominent strategy is partnerships and collaborations with governments, automakers, and energy providers. For instance, ChargePoint has partnered with utilities and municipalities to integrate its chargers into smart city projects, ensuring widespread adoption and accessibility. Similarly, ABB collaborates with global automakers to align its fast-charging solutions with the requirements of next-generation EVs, enhancing compatibility and user experience.
Another critical approach is product innovation and technological advancement. Companies like Siemens and Chroma ATE Inc. focus on developing cutting-edge technologies such as bidirectional charging, which allows EVs to feed energy back into the grid. This not only enhances grid stability but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, firms are investing in IoT-enabled platforms that provide real-time data analytics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance, improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Geographic expansion is another key strategy, particularly in emerging markets. Players like Robert Bosch GmbH and AeroVironment, Inc. are targeting regions with growing EV adoption rates, such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America, by establishing local manufacturing units and service networks. This ensures compliance with regional regulations while reducing costs and delivery times.
Acquisitions and mergers have been instrumental in strengthening market presence. For example, Shell’s acquisition of Ubitricity and BP’s investment in Digital Charging Solutions escalates the efforts to diversify offerings and capture larger market shares. These strategies collectively enable key players to enhance their competitive edge, drive innovation, and meet the evolving demands of the global EV charging ecosystem.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The electric vehicle charging stations market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the rapid expansion of EV adoption and the need for robust charging infrastructure. Key players such as ChargePoint, ABB, Siemens, and Robert Bosch GmbH are vying for dominance by leveraging their technological expertise, global reach, and strategic partnerships. The competitive landscape is fragmented, with a mix of established corporations and innovative startups contributing to the ecosystem. Companies are focusing on differentiation through advanced technologies like ultra-fast chargers, bidirectional energy flow systems, and IoT-enabled platforms that enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
Regional dynamics also play a significant role in shaping competition. In North America and Europe, stringent emissions regulations and government incentives have fostered a mature market, where players compete on scalability and service quality. Meanwhile, in Asia-Pacific, local manufacturers benefit from strong government support and cost advantages, intensifying rivalry. Emerging markets in Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa present untapped opportunities, attracting investments from global leaders aiming to expand their footprints.
Strategic initiatives such as mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations further intensify competition. For instance, partnerships with utilities and automakers allow companies to integrate seamlessly into broader mobility ecosystems. Additionally, pricing strategies, product innovation, and customer-centric solutions are critical battlegrounds. As demand for sustainable transportation grows, competition in this market will continue to evolve, pushing players to innovate while addressing challenges like interoperability, grid integration, and cybersecurity to maintain their edge in an increasingly dynamic industry.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THIS MARKET
- In September 2024, Siemens announced its strategic plan to carve out its electric vehicle charging business, Siemens eMobility, and integrate it with Heliox, a company specializing in DC fast-charging solutions. This move is aimed at expanding Siemens’ market reach, particularly in Europe and North America, where the demand for fast-charging infrastructure is rapidly increasing. By combining its expertise with Heliox’s advanced technology, Siemens seeks to provide a more robust portfolio of EV charging solutions and accelerate the adoption of electric mobility.
- In October 2020, Chroma ATE's CCS (Combined Charging System) EV Charging Test System was adopted by a major U.S. electric vehicle manufacturer. This adoption leverages the Chroma ATE’s significant role in the development and validation of EV charging technology. The company’s advanced testing systems ensure compatibility and efficiency in EV chargers, helping manufacturers improve their charging infrastructure. By securing this deal, Chroma ATE strengthened its market position as a leader in EV charger testing and validation.
- In November 2024, ChargePoint expanded its peer-to-peer electric vehicle charging network, reinforcing its commitment to decentralized EV charging solutions. This expansion allows individual EV owners and businesses to share their private charging stations, creating a more extensive and accessible charging infrastructure. By increasing the availability of charging stations and promoting peer-to-peer sharing, ChargePoint is addressing range anxiety and making EV adoption more feasible for consumers.
- In 2024, Robert Bosch GmbH was recognized as a key player in the electric vehicle charger market due to its contributions to the industry. Bosch has been actively developing innovative charging solutions, including smart charging systems that optimize energy usage and reduce grid strain. This recognition reaffirms Bosch’s position as a global leader in EV charging technology and its commitment to supporting the transition to sustainable transportation.
- In November 2024, AeroVironment, Inc. was listed among the key competitors in the peer-to-peer electric vehicle charging market, amplifying its role in advancing innovative charging solutions. The company has been actively developing high-power charging solutions that integrate with renewable energy sources. This recognition demonstrates AeroVironment’s commitment to providing efficient and sustainable EV charging options that align with global electrification goals.
- In 2024, Pod Point was acknowledged as a major company in the electric vehicle charger market. Pod Point has been actively deploying smart home and workplace charging solutions, making EV charging more convenient for consumers. The company’s continuous expansion and innovation in the EV charging sector reinforce its position as a leading player in the marketplace.
- In 2024, Delphi Technologies was identified as a significant player in the electric vehicle charger market. As a key automotive technology supplier, Delphi Technologies has been focusing on the development of high-efficiency power electronics for EV charging systems. This recognition improves the company’s contribution to making charging solutions faster, more reliable, and widely accessible to EV users.
- In 2024, Schaffner Holding AG was listed among major companies in the electric vehicle charger market. Schaffner specializes in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) solutions, which are crucial for ensuring the reliability and safety of EV chargers. By providing high-quality components that improve charger performance, Schaffner continues to be a key supplier in the rapidly growing EV infrastructure market.
- In 2024, ABB was recognized as a key player in the electric vehicle charger market due to its prominence in fast-charging solutions. ABB has been at the forefront of developing ultra-fast chargers that significantly reduce charging times, making EVs more practical for long-distance travel. This recognition further strengthens ABB’s reputation as a leader in the global EV charging infrastructure.
- In 2024, Siemens AG was acknowledged as a major company in the electric vehicle charger market. Siemens has been making strategic investments in smart grid technology, ensuring that EV chargers can seamlessly integrate with existing power infrastructure. This acknowledgment elevates the Siemens' efforts in providing scalable, energy-efficient charging solutions for the growing EV market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global electric vehicle charging stations market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Vehicle Type
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
By End User
- Residential
- Commercial
By Charging Type
- On-board Chargers
- Off-board Chargers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current market size of the global electric vehicle charging stations market?
The global electric vehicle charging stations market size was valued at USD 27.91 billion in 2025.
What are the market drivers that are driving the global electric vehicle charging stations market?
The government policies and incentives accelerating ev charging infrastructure development and rising urbanization and smart city initiatives boosting ev charging demand are the major market drivers that are driving the global electric vehicle charging stations market.
What are the challenges faced by the global electric vehicle charging stations market?
The interoperability issues creating fragmentation in the market and cybersecurity vulnerabilities threatening infrastructure reliability are the major callenges faced by the electric vehicle charging stations market.
Who are the market players that are dominating the global electric vehicle charging stations market?
Chargemaster, ABB, Chroma ATE Inc, Delphi Technologies PLC, Schaffner Holding AG., Siemens, AeroVironment, Inc., Pod Point, Robert Bosch GmbH and ChargePoint, Inc. are the major companies in the global EV charging stations market.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]