Global Edge Security Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Component (Solutions, CASB, SD-WAN, SASE, Services, Managed Services, Professional Services, Implementation & Integration, Training& Consulting, and Support & Maintenance), Organization Size, Deployment Mode, End User Industry and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Edge Security Market Size
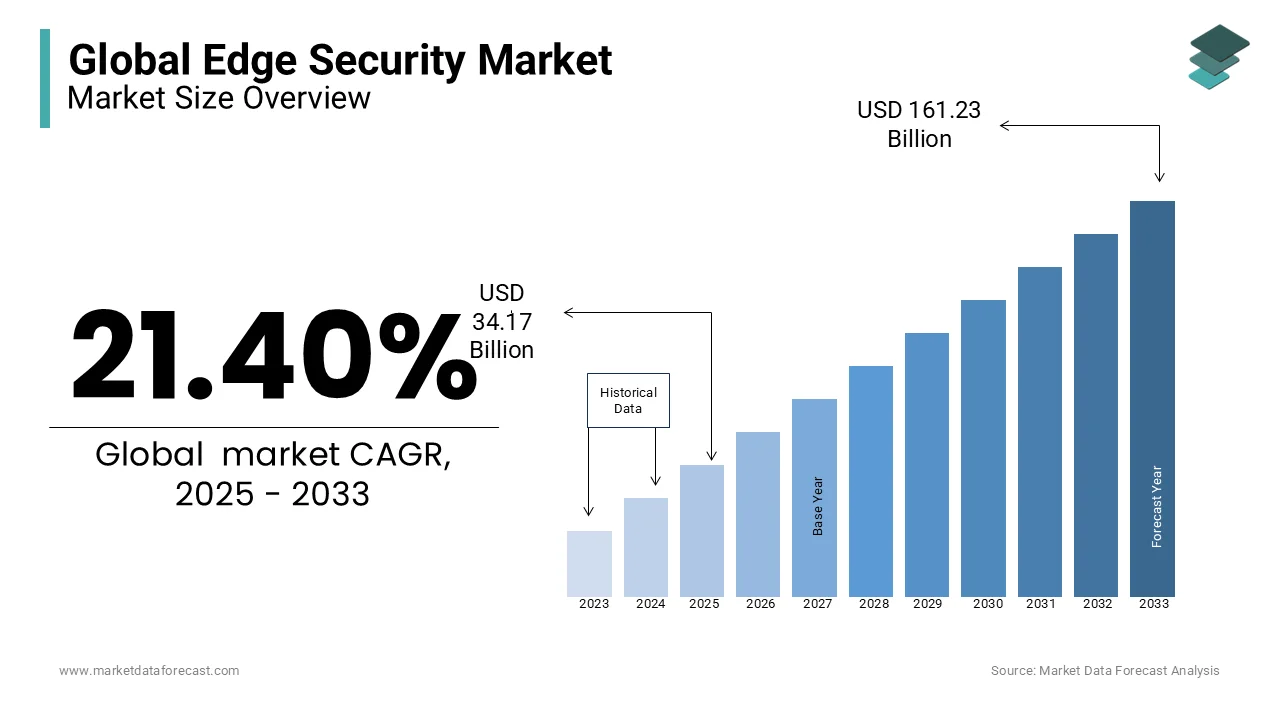
The global edge security market was valued at USD 28.15 billion in 2024. The global market is projected to reach USD 34.17 billion in 2025 and USD 161.23 billion by 2033, rising at a CAGR of 21.40% during the forecast period.
The Edge Security Market addresses the growing need to secure data and devices at the network edge, where digital interactions occur close to users and IoT devices. As organizations deploy more edge computing solutions, ensuring robust security at these remote locations becomes crucial to protect against data breaches, unauthorized access, and real-time threats. Edge security integrates techniques like zero-trust models, AI-driven threat detection, and endpoint protection, focusing on safeguarding data processed outside centralized data centers.
Edge security solutions protect sensitive data at its source, reduce latency, and enhance compliance with regulations. Companies aim to enhance data privacy, operational efficiency, and system resilience while minimizing the risk of cybersecurity incidents by implementing real-time threat detection and response directly at the network edge,.
MARKET TRENDS
Zero Trust Architecture at the Edge
Zero Trust security frameworks are increasingly essential in edge environments, where data flows between countless remote devices. Instead of traditional network security relying on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust assumes no user or device is inherently trusted. By 2026, over 60% of enterprises are expected to implement Zero Trust security at the edge to protect against unauthorized access and insider threats. This trend supports rapid authentication, user-level access control, and continuous monitoring, which strengthens protection against data breaches in sectors like finance and healthcare where data privacy is paramount.
AI-Driven Threat Detection and Response
AI and machine learning are used to detect and respond to threats in real-time with the rise in edge computing. These tools enable automated threat detection at the edge to identify suspicious patterns and responding before cyber threats escalate. In 2023, nearly 40% of edge security solutions integrated AI-based threat detection and the number is expected to grow annually. This trend reflects the need for instantaneous response to mitigate risks in industries where downtime or data loss can be highly disruptive, such as manufacturing and transportation, enhancing both security posture and operational continuity.
MARKET DRIVERS
Proliferation of IoT and Connected Devices
The rapid growth of IoT devices, projected to reach 29 billion globally by 2030, drives the demand for edge security solutions. These devices operate outside traditional network protections, making them susceptible to cyber threats. Industries like manufacturing and healthcare, which rely heavily on IoT for real-time operations face heightened security needs. Effective edge security solutions protect these devices by ensuring secure data flow, access control, and vulnerability management by reducing the risk of breaches that could compromise sensitive data or disrupt operations.
Expansion of 5G Networks
The deployment of 5G networks facilitates low-latency, high-speed connections, enabling more edge computing applications but also increasing security vulnerabilities. Organizations must secure these faster as 5G adoption is expected to cover two-thirds of the global population by 2025. Edge security solutions play a vital role in securing data as it moves across complex 5G infrastructure by offering real-time protection to prevent cyberattacks that could compromise the vast.
Rise of Remote Work and Hybrid Environments
The shift to remote and hybrid work models has expanded the attack surface as employees access corporate data from diverse locations and devices. A survey by Daisy Corporate Services revealed that 69% of UK organizations saw a rise in security threats after implementing hybrid or remote work models. This driver emphasizes the need for edge security to protect data across distributed networks by ensuring endpoint security and threat detection beyond the corporate perimeter. As companies prioritize flexible work environments, edge security ensures data privacy and integrity are maintained while supporting modern, location-independent work practices and adapting to the evolving needs of a distributed workforce.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Complexity of Managing Distributed Environments
Securing data across distributed edge environments presents operational complexity, especially as companies deploy large numbers of IoT devices and remote locations. Each endpoint requires monitoring, which adds to the workload of security teams. Gartner survey found that 70% of organizations reported that their edge computing projects were delayed or faced significant challenges due to security concerns and integration complexities. The difficulty of integrating multiple security solutions at the edge is attribute to create challenges in maintaining consistent and effective security protocols across all devices and locations.
High Implementation and Maintenance Costs
Edge security solutions require significant investment, not only in software and hardware but also in staff training and maintenance. Small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which represent a substantial portion of potential users, often struggle with these costs. According World Economic Forum, nearly 40% of SMEs cite budget constraints as a key reason for limited security measures at the edge. The high costs associated with real-time threat detection, AI, and advanced encryption technologies make it challenging for companies with limited budgets to adopt comprehensive edge security solutions.
Lack of Standardized Protocols and Regulations
Edge security faces challenges due to inconsistent security standards and regulatory guidance across regions and industries. This lack of standardization leads to fragmented practices that further increase the risk of vulnerabilities as organizations attempt to secure diverse edge devices and networks. Approximately 60% of companies report difficulties in aligning their edge security efforts with compliance requirements due to unclear or conflicting regulations. The absence of unified standards complicates the development of cohesive security strategies in regulated sectors like healthcare and finance where stringent data protection is critical.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth of AI and Machine Learning-Driven Security Solutions
AI and machine learning present significant opportunities in enhancing edge security by enabling proactive threat detection and response. Integrating AI at the edge allows for faster anomaly detection and real-time data analysis is beneficial for high-risk sectors like healthcare and finance. Edge security solutions can become more autonomous that also reduces the need for constant human intervention and enabling a more scalable and efficient defense system. For instance, in May 2023, the U.K. launched the AI Safety Institute (AISI) with a £100 million public funding investment. The institute's goal is to assess AI-related risks and improve safety protocols, highlighting the government's dedication to the responsible integration of AI across various sectors, including cybersecurity.
Expansion in Smart Cities and Smart Infrastructure
The growth of smart cities, forecasted to reach an investment of over $1 trillion globally by 2030, creates strong demand for edge security solutions to protect interconnected infrastructure. Smart city technologies, such as connected transportation systems, utilities, and public safety networks rely on edge computing to operate efficiently. Edge security provides localized protection to these critical systems to ensure data integrity and privacy for citizens. This sector offers substantial opportunity for edge security providers as cities seek solutions to safeguard vast networks of IoT devices and sensors in real-time.
Increased Demand in the Healthcare Sector
With the rise of telemedicine and connected healthcare devices, edge security is crucial for protecting sensitive patient data outside traditional hospital networks. The demand for telemedicine will highlight the urgent need for secure edge computing in healthcare. Edge security solutions can secure patient data on wearable health devices and remote monitoring tools, addressing privacy concerns and meeting compliance requirements like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the U.S. The healthcare sector represents a strong growth area for edge security, as it looks to protect data integrity and confidentiality in increasingly digital care environments. Trusted Future research survey found that 65% of Americans use connected health technologies to answer simple medical questions, and 49% use or have used health apps to set and reach fitness, mindfulness, weight loss, and other goals.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Scalability of Security Solutions Across Diverse Edge Devices
The sheer variety of edge devices from IoT sensors to mobile devices creates a major challenge for deploying consistent security. These devices often have differing hardware capabilities, operating systems, and connectivity standards that makes unified security measures difficult. According to recent survey by Secure Network Access Report by Hughes in 2025 shows that 55% of organizations struggle to scale security across their edge environments due to device diversity. This issue complicates software updates, patch management, and real-time monitoring as each device may require tailored security approaches that impacts overall security effectiveness.
Limited Processing Power for Advanced Security Features
Many edge devices have restricted processing and storage capacities to limit their ability to run sophisticated security algorithms or AI-driven threat detection on-device. This limitation affects security, as traditional, robust protections may strain device resources, resulting in performance problems. According to TRIFECTA: Security, Energy-Efficiency, and Communication Capacity Comparison for Wireless IoT Devices research shows that nearly 50% of IoT devices lack the necessary power for advanced security software with developers to create lightweight solutions that balance security and functionality. This challenge requires innovation in creating security measures that protect without overwhelming resource-limited devices.
Data Privacy Concerns and Regulatory Compliance
As edge computing processes sensitive data locally, organizations face complex data privacy challenges and compliance requirements, especially with stricter laws like GDPR and CCPA. The challenge lies in ensuring that personal data remains secure and compliant while processed outside centralized systems. Approximately 65% of enterprises report difficulty in meeting data compliance at the edge when edge devices cross borders or operate in highly regulated industries like healthcare. Developing security solutions that maintain privacy while complying with multiple regulatory frameworks remains a significant hurdle in the Edge Security Market.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
21.40% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Organization Size, Deployment Mode, End User Industry, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Cisco Systems, Inc., Palo Alto Networks, Inc., Fortinet, Inc., Zscaler, Inc., Akamai Technologies, Inc., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., VMware, Inc., Trend Micro Incorporated, Cloudflare, Inc., and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights
The Solutions segment is the largest in accounting for 60% of the Edge Security Market share. This segment encompasses technologies like Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), and Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN). SD-WAN and SASE have seen extensive adoption as they facilitate secure, scalable, and efficient edge-to-cloud connectivity. These solutions are essential as they enable security close to data sources by reducing latency and ensuring rapid response to threats. Demand for secure and optimized remote connectivity surged due to remote work trends, with SD-WAN adoption growing by 35% in industries such as finance and healthcare.
The SASE segment is the fastest-growing with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 36% over the forecast period. SASE integrates networking and security functions, such as firewall and CASB, into a unified cloud-native architecture which is essential for organizations managing hybrid and distributed workforces. Its rapid growth is driven by the shift towards cloud-based services and remote work models, which require secure, flexible, and scalable network access. The importance of SASE is highlighted by Gartner's projection that 40% of enterprises will adopt SASE by 2025 to simplify and enhance edge security, ensuring secure access regardless of location.
By Organization Size
Large enterprises segment held around 65% of edge security market share in 2024. These organizations manage vast networks of edge devices, including IoT systems and remote workforces, which require robust, scalable security solutions. The large enterprise segment drives demand for advanced edge security technologies like Zero Trust and SASE that enables them to secure distributed data environments. Security investments are prioritized in sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, where data sensitivity and regulatory requirements are stringent. As of 2023, nearly 70% of large enterprises had initiated or expanded edge security investments to mitigate evolving threats.

The SME segment is growing at the fastest rate, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 31% over the forecast period. This growth is fueled by increasing awareness of cybersecurity risks and the accessibility of cloud-based, cost-effective security solutions tailored for smaller businesses. SMEs, which traditionally had limited security budgets, now prioritize edge security to safeguard customer data and protect IoT deployments. The adoption of managed security services, which can reduce complexity and cost, is popular in this segment, with 45% of SMEs opting for managed edge security solutions as of 2023 to improve resilience against cyber threats without extensive in-house resources.
By Deployment Mode
The On-premises deployment segment is leading with 55% of edge security market sharein 2023. On-premises solutions are widely adopted by sectors with strict data control requirements, such as finance, healthcare, and government, where organizations prefer to keep sensitive data within internal infrastructure. This deployment mode offers greater control over security protocols and data storage which is crucial for industries subject to rigorous compliance standards. On-premises solutions remain popular in enterprises with existing infrastructure investments and those that prioritize latency-sensitive applications where data needs to be processed locally and securely without reliance on external networks.
Cloud deployment is the fastest-growing segment, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33% over the next five years. The flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of cloud-based edge security solutions are key drivers, especially among SMEs and companies with remote or distributed teams. Cloud deployment enables rapid implementation and real-time security updates, allowing organizations to stay ahead of evolving threats. Additionally, the rise of hybrid work environments has accelerated cloud adoption, with nearly 60% of enterprises now prioritizing cloud security models to support dynamic, multi-location operations. Cloud deployment in edge security also aligns well with the increased use of IoT, as it facilitates easier integration and centralized management of security policies across devices and locations.
By End User Industry
The BFSI sector holds the largest market share, accounting for approximately 40% of the Edge Security Market. Financial institutions handle highly sensitive customer data and perform critical real-time transactions which make edge security essential for safeguarding against cyber threats. This sector relies on edge security to ensure secure, low-latency connections, protect customer information, and comply with stringent regulatory requirements. With the increase in digital banking and mobile transactions, BFSI organizations are particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks, driving investments in advanced edge security solutions, such as Zero Trust architectures and AI-driven threat detection. This segment’s demand is sustained by ongoing digital transformation and increased cyber risks.
The IT & Telecom sector is the fastest-growing segment, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 34% over the next five years. This growth is driven by the expansion of 5G networks and the proliferation of IoT devices, which require robust, scalable edge security solutions to manage vast amounts of data and ensure network integrity. Telecom companies are adopting edge security to secure distributed network infrastructure and to support ultra-low latency for services such as autonomous vehicles and smart city applications. The demand for secure, high-performance edge solutions in IT & Telecom is growing as these industries expand digital services, network speeds, and device connectivity.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America currently dominates the edge security market, holding about USD 7.83 billion in 2023 of the global market share. The region is expected to grow at a CAGR of 25% over the forecast period with strong investments in IoT, edge computing, and cybersecurity across industries. The United States leads this region with significant adoption of edge security technologies, particularly in BFSI, IT, and healthcare sectors where regulatory requirements and data protection standards are stringent. High spending on advanced technologies and the presence of major edge security providers contribute to North America’s leading market position.
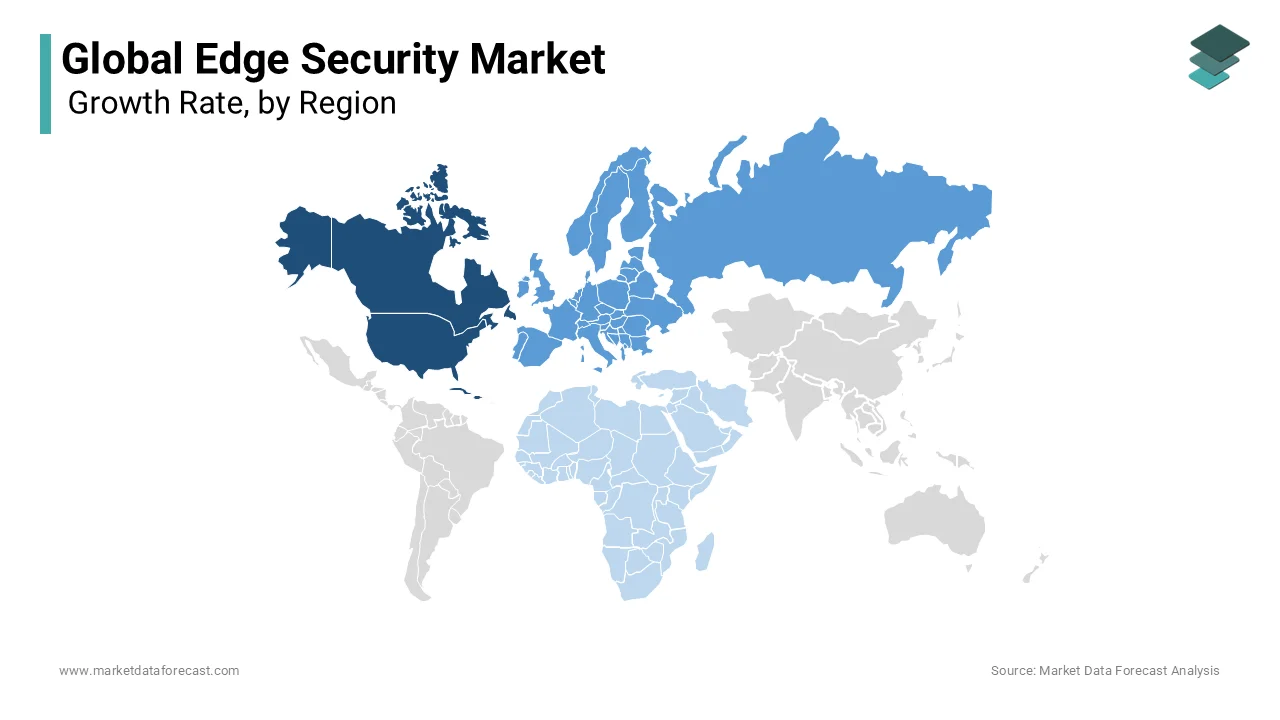
Europe holds the second-largest market share, by the end of the forecast period. Countries like the United Kingdom, Germany, and France are key players with strict data protection regulations such as GDPR, which mandate robust data security measures. Europe’s market growth is fueled by digital transformation across manufacturing and automotive industries, as well as public sector initiatives to enhance cybersecurity resilience. The region’s focus on compliance and data privacy laws continues to drive edge security adoption, as companies seek solutions that ensure data security across distributed environments.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a projected CAGR of 30% driven by rapid digitalization and the expansion of IoT and 5G networks. The region currently holds about 20% of the market share. China, Japan, and India are leading adopters spurred by substantial investments in smart city projects, telecom infrastructure, and manufacturing automation. The demand for effective security solutions is on the rise as industries across Asia-Pacific increasingly implement edge computing. The region’s growth potential is high as businesses and governments prioritize cyber resilience amid growing cyber threats targeting industrial and consumer IoT systems.
Latin America accounts for significant global edge security market share. Brazil and Mexico are primary drivers, where industries like finance, telecommunications, and government are beginning to adopt edge security to counter rising cyber risks. Latin America’s digital infrastructure development and increased adoption of cloud services create opportunities for edge security growth. Although the region currently trails in overall market share with steady demand for cost-effective, scalable security solutions for SMEs seeking to enhance security without extensive infrastructure investments.
The Middle East and Africa region growing significantly in the global market. Countries like Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and South Africa lead in adoption, particularly within the government and defense sectors, driven by national security interests and economic diversification initiatives. Growth is supported by investments in digital transformation and smart city projects with a focus on securing critical infrastructure. While the region’s growth rate is moderate, increasing cybersecurity awareness and a drive to adopt modern technologies are fostering demand for edge security across industries.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
A few of the key participants in the global edge security market include Cisco Systems, Inc., Palo Alto Networks, Inc., Fortinet, Inc., Zscaler, Inc., Akamai Technologies, Inc., Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., VMware, Inc., Trend Micro Incorporated, Cloudflare, Inc., and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE)
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In 2023, VMware, Inc., a leader in cloud and virtualization technology, enhanced its SASE platform with secure, scalable edge solutions. These improvements are anticipated to strengthen VMware’s support for multi-cloud and hybrid work environments, reinforcing its edge security solutions for remote access.
- In 2023, Trend Micro Incorporated partnered with AWS to integrate IoT security services for cloud-based edge environments. This collaboration is anticipated to expand Trend Micro’s edge security offerings by protecting IoT deployments on AWS, which is essential for IoT-intensive edge environments.
- In 2023, Cloudflare, Inc., launched Cloudflare One, a Zero Trust network-as-a-service platform. This platform is expected to provide secure and scalable edge security, supporting organizations in transitioning to hybrid and remote work models.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global edge security market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Component
- Solutions
- CASB
- SD-WAN
- SASE
- Services
- Managed Services
- Professional Services
- Implementation & Integration
- Training& Consulting
- Support & Maintenance
By Organization Size
- Large Enterprises
- SMEs
By Deployment Mode
- On-premises
- Cloud
By End User Industry
- BFSI
- Government & Defense
- IT & Telecom
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is edge security important in the global context?
Edge security is critical globally because the rapid adoption of IoT devices, remote work environments, and 5G networks has increased the attack surface for cyber threats. With sensitive data being processed and stored at the edge, robust security ensures compliance with privacy regulations and protects against data breaches that can have international implications.
What are the primary components of edge security solutions?
Key components include secure access service edge (SASE), firewalls, zero trust network access (ZTNA), data encryption, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), and endpoint protection. These technologies collectively safeguard devices, users, and data at the edge of networks.
Which industries drive the demand for edge security solutions?
Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, energy, and telecommunications are major drivers of edge security demand. These sectors rely on edge computing for real-time decision-making, making security critical to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data.
What is the future outlook for the Edge Security Market?
The future of the Edge Security Market looks promising, with increasing investments in edge computing, AI-driven threat detection, and zero-trust architectures. The market is expected to evolve with innovative solutions addressing emerging threats, ensuring secure connectivity and data processing worldwide.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]