Global E-Waste Management Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Material Recovered (Metal, Plastic, Glass, and Others), Source of Waste, Treatment Technology and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global E-Waste Management Market Size
The global e-waste management market was worth USD 76.71 billion in 2024. The global market is expected to reach USD 88.68 billion in 2025 and USD 282.80 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 15.60% during the forecast period.
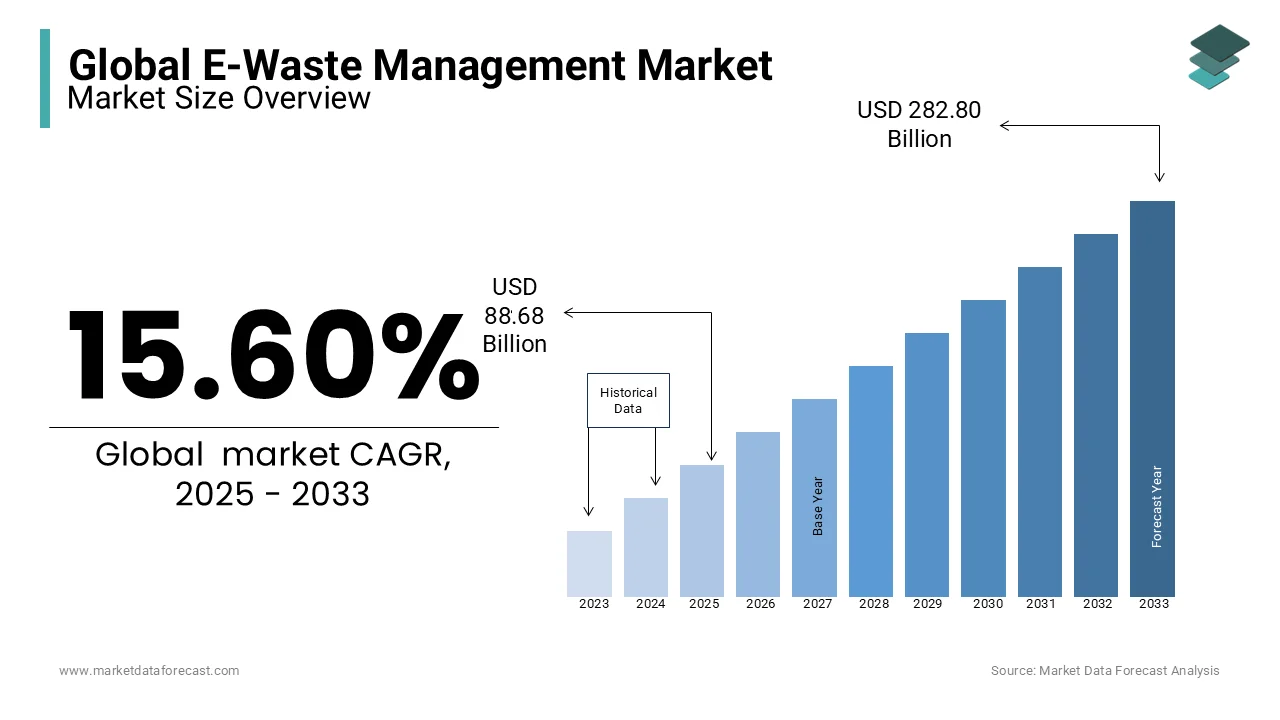
E-waste contains valuable materials like gold, silver, and palladium, with a recovery potential valued at over $57 billion annually, according to a United Nations report. Recycling processes also mitigate health risks associated with toxic substances such as lead and mercury. Innovations in e-waste processing, such as automated material recovery and eco-friendly dismantling techniques, are improving efficiency and scalability. The market's significance lies in reducing environmental degradation, conserving finite resources, and supporting a circular economy. Awareness campaigns and corporate initiatives are further promoting responsible e-waste management practices globally.
MARKET DRIVERS
Stringent Environmental Regulations
Governments worldwide are enforcing strict regulations to manage electronic waste by driving the e-waste management market. Laws such as the EU’s Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Directive mandate proper recycling and disposal of electronic products, reducing environmental pollution. Countries like India and China have introduced e-waste management rules requiring manufacturers to ensure proper collection and recycling of discarded electronics. Studies show that compliant recycling practices can prevent the release of over 2.2 million metric tons of CO2 annually. These policies not only promote sustainable practices but also encourage investment in advanced e-waste processing technologies.
Rising Consumer Electronics Usage
The rapid adoption of consumer electronics has significantly increased e-waste generation, driving demand for effective waste management solutions. Discarded devices contribute heavily to e-waste volumes with over 3.6 billion smartphone users globally and shorter product lifecycles,. For example, approximately 50 million tons of e-waste were generated globally in 2021, with projections indicating a rise to 74 million tons by 2030. This surge necessitates efficient recycling systems to recover valuable materials and reduce landfill dependency, highlighting the importance of robust e-waste management systems to address this growing issue sustainably.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Lack of Infrastructure in Developing Regions
Insufficient recycling infrastructure in many developing countries is a significant restraint in the e-waste management market. Approximately 80% of global e-waste is not formally recycled which often ending up in landfills or informal recycling sectors with unsafe practices. For instance, in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia, inadequate facilities lead to improper handling of hazardous materials by posing health and environmental risks. Establishing formal recycling facilities requires substantial investment and technical expertise is creating barriers for low-income nations. This limitation hinders the global effort to manage e-waste effectively and delays the adoption of sustainable waste management practices.
Low Consumer Awareness and Participation
A lack of awareness among consumers regarding proper e-waste disposal significantly hampers recycling efforts. Studies indicate that only 20% of e-waste is formally recycled worldwide, with many consumers discarding electronics with general waste. Inconsistent participation in recycling programs is compounded by limited knowledge about the environmental and economic benefits of recycling. Additionally, poor incentivization for returning used electronics, such as buy-back programs thereby reducing public engagement. Addressing this challenge requires widespread educational campaigns and initiatives to encourage responsible disposal, which are critical for fostering sustainable e-waste management systems globally.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Adoption of Circular Economy Models
The transition to circular economy practices presents a major opportunity in e-waste management. Companies are increasingly focusing on designing electronics for recyclability and reusability by reducing waste and conserving resources. For example, modular smartphones and repairable devices extend product lifecycles while simplifying material recovery. Circular economy initiatives could recover 7-8% of global electronic material demand annually by reducing reliance on virgin resources. Businesses that adopt these practices benefit from cost savings and enhanced brand reputation. Scaling such models aligns with global sustainability goals and creates opportunities for innovation in recycling technologies and materials design.
Advancements in Automated Recycling Technologies
Innovations in automated recycling processes, such as robotics and AI-powered material sorting, offer immense potential to improve efficiency and precision in e-waste processing. Technologies like robotic dismantling systems can extract valuable materials like gold and palladium with up to 98% purity by minimizing waste and boosting profitability. Automation reduces labor-intensive tasks and enhances the scalability of recycling facilities which shall address the rising volume of discarded electronics. Investments in such technologies create opportunities for the development of cost-effective and eco-friendly recycling solutions which fosters a competitive edge for companies in the e-waste management sector.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Illegal E-Waste Exports
Unregulated cross-border trade of e-waste poses a significant challenge for effective management. Approximately 23% of global e-waste is illegally exported to developing nations, where informal recycling methods dominate. These practices often involve hazardous processes like open burning which release toxins into the environment. For instance, Ghana’s Agbogbloshie receives large quantities of e-waste despite international bans under the Basel Convention. This not only undermines formal recycling efforts but also creates health risks for workers in these regions. Addressing this issue requires stricter enforcement of international regulations and increased transparency in e-waste tracking.
Complexity of E-Waste Components
The diverse and evolving composition of electronics complicates recycling processes. Devices often contain a mix of metals, plastics, and hazardous materials like lead and mercury, requiring specialized facilities for safe recovery. Advanced gadgets may include over 60 different elements which makes material separation costly and time-intensive. For example, the extraction of rare earth metals from e-waste is highly complex due to their small quantities and tight integration into devices. This challenge necessitates continuous innovation in recycling technologies and policies to ensure cost-effective and efficient material recovery which is a critical step toward achieving sustainable e-waste management.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
15.60% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Material Recovered, Source of Waste, Treatment Technology, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Sims Limited, Aurubis AG, Boliden Group, Electronic Recyclers International, Inc. (ERI), Umicore, Veolia Environment S.A., Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd., Global Electric Electronic Processing Inc. (GEEP), Stena Metall Group, and Tetronics International Ltd. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Material Recovered Insights
Metal recovery stands as the largest segment with approximately 60% of the Electronic Waste Management market. This dominance is due to the high value and demand for metals such as gold, silver, copper, and palladium found in electronic devices. For instance, a ton of discarded mobile phones can yield about 300 grams of gold which is significantly more than what is extracted from a ton of gold ore. The recovery of these metals not only provides substantial economic benefits but also reduces the need for mining virgin resources, thereby conserving natural reserves and minimizing environmental degradation.
Conversely, plastic recovery is projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8.6% over the forecast period in the electronic waste management market. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing volume of plastic components in electronic devices and the rising emphasis on sustainable practices. Innovations in recycling technologies, such as chemical and mechanical processes have enhanced the efficiency of plastic recovery that enables the conversion of e-waste plastics into reusable materials. This advancement is crucial for reducing environmental pollution and supporting the circular economy by reintroducing recycled plastics into the manufacturing cycle.
By Source of Waste Insights
Household Appliances constitute the largest segment, accounting for approximately 50% of the total e-waste generated globally. This dominance is attributed to the widespread use and frequent replacement of major and small household appliances, such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves. The rapid technological advancements and consumer demand for energy-efficient models lead to shorter product lifecycles which results in increased disposal rates. Effective management of this segment is crucial, as these appliances contain valuable materials like metals and plastics, as well as hazardous substances that require proper handling to prevent environmental contamination.
The IT and Telecommunication segment is the fastest-growing in the e-waste management market, projected to exhibit a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 9% over the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by the exponential increase in the use of information technologies and communication devices, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets. The proliferation of digitalization is coupled with the trend of frequent upgrades and the integration of advanced technologies that contributes to the escalating volume of e-waste in this category. Addressing this surge is essential, as these devices often contain precious metals and critical components that can be recovered and recycled, thereby conserving resources and reducing environmental impact.
By Treatment Technology Insights
Mechanical treatment segment is the largest segment in e-waste treatment, accounting for about 50% of global processing. This method is popular because it efficiently separates valuable materials like metals and plastics from electronic waste. Its adaptability to different types of e-waste and cost-effectiveness makes it the leading choice for recycling. Additionally, mechanical treatment supports resource recovery, reducing the need for raw material extraction and minimizing environmental harm.
Fastest-Growing Segment: Hydrometallurgical Processes
Hydrometallurgical processes, or chemical leaching, are the fastest-growing segment, with a projected CAGR of around 8.5%. This method is gaining traction because it selectively extracts precious metals like gold and silver with high efficiency. This eco-friendly process offers a sustainable solution for recovering valuable resources from electronic waste As demand for these metals rises.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
In the Electronic Waste Management market, Asia-Pacific holds a dominant position, accounting for approximately 44.6% of the global market share in 2024. This leadership is driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the widespread adoption of electronic devices in countries like China, Japan, and India. The region is projected to maintain its dominance, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.1% from 2025 to 2033 that is reflecting ongoing advancements and sustained demand for effective e-waste management solutions.
North America follows as a significant contributor to the market, with a market share of 22.42 billion in 2023. The United States, in particular, drives this dominance with its robust e-waste management infrastructure and significant R&D expenditures. The region is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2025 to 2033, indicating a swift adoption of advanced recycling technologies and a focus on enhancing e-waste processing capabilities.
Europe holds a substantial share in the e-waste management market, with countries like Germany, the United Kingdom, and France leading in the adoption of sustainable practices. The region benefits from stringent environmental regulations and a strong focus on recycling initiatives. Europe's performance is bolstered by its emphasis on environmental sustainability and comprehensive waste management policies. The market in Europe is projected to grow at a brisk pace during the forecast period, supported by technological innovations and the adoption of eco-friendly refrigeration systems.
Latin America is projected to grow at a dominant CAGR during the forecast period 2025-2033. The region's growth is attributed to the expanding retail networks and increased food consumption, driving the demand for walk-in coolers and freezers.
Middle East and Africa are experiencing growth due to increasing investments in infrastructure and a burgeoning retail sector. The market growth in this region is projected to grow significantly during the forecast period. The demand for walk-in coolers and freezers in this region is driven by the need for efficient cold storage solutions to preserve perishable goods in hot climates.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS & COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Companies playing a key role in the global e-waste management market include Sims Limited, Aurubis AG, Boliden Group, Electronic Recyclers International, Inc. (ERI), Umicore, Veolia Environment S.A., Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd., Global Electric Electronic Processing Inc. (GEEP), Stena Metall Group, and Tetronics International Ltd. The electronic waste (e-waste) management market is highly competitive shaped by the increasing global emphasis on sustainability and resource recovery. Key players in the market include established multinational corporations and regional firms that cater to localized demands. Companies such as Sims Limited, Umicore N.V., and Electronic Recyclers International dominate with extensive global networks and advanced recycling technologies, enabling efficient recovery of valuable materials like precious metals and rare earth elements.
Competition in this market is driven by several factors. Technological innovation is paramount, with companies investing heavily in automation and AI-driven sorting systems to enhance recycling efficiency and reduce costs. Regulatory compliance also plays a crucial role, as stringent environmental laws in regions like the EU and North America push companies to adopt sustainable practices. This has fostered a race to meet or exceed environmental standards, positioning compliant firms as market leaders.
Additionally, geographic expansion is a key competitive strategy, particularly in rapidly industrializing regions like Asia-Pacific and Africa, where e-waste volumes are surging. Many firms are also diversifying their service offerings to include secure data destruction, IT asset management, and device refurbishment, broadening their market appeal.
Strategic partnerships and acquisitions further intensify competition, as companies aim to strengthen capabilities, extend reach, and secure long-term growth.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, Aurubis AG announced plans to expand its global recycling facilities through organic growth. This initiative focuses on building a network of recycling plants, enabling Aurubis to strengthen its capabilities in processing electronic waste efficiently and sustainably.
- In September 2023, Sims Limited launched a new e-waste processing facility in the United States. This facility is expected to enhance the company’s capacity for managing and recycling electronic waste, solidifying its position as a market leader.
- In July 2023, Boliden Group invested in advanced smelting technologies to improve precious metal recovery rates from electronic waste. This investment aims to increase processing efficiency and contribute to sustainable material recovery.
- In May 2023, Electronic Recyclers International, Inc. (ERI) expanded its partnership with Best Buy to manage the retailer’s nationwide e-waste recycling program. This collaboration enhances ERI’s processing volume and market reach.
- In March 2024, Umicore announced the development of a new battery recycling plant in Europe. This facility is anticipated to address the growing demand for sustainable recycling of end-of-life electric vehicle batteries.
- In February 2024, Veolia Environment S.A. acquired a majority stake in a leading Asian e-waste recycling firm. This acquisition is expected to expand Veolia’s footprint in the fast-growing Asian market for electronic waste management.
- In January 2024, Enviro-Hub Holdings Ltd. upgraded its e-waste processing facilities with cutting-edge technologies. This upgrade aims to enhance material recovery rates and reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste.
- In December 2023, Global Electric Electronic Processing Inc. (GEEP) merged with another e-waste recycler to form Quantum Lifecycle Partners. This merger strengthens the company’s ability to offer comprehensive IT asset disposition and recycling services across North America.
- In November 2023, Stena Metall Group invested in research and development to innovate methods for recycling complex electronic devices. This initiative enhances its capabilities in handling diverse e-waste materials.
- In October 2023, Tetronics International Ltd. partnered with a leading electronics manufacturer to develop plasma-based recycling solutions. This partnership aims to improve the efficiency and sustainability of e-waste processing.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global e-wate management market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Material Recovered
- Metal
- Precious Metals Recovery Process
- Plastic
- Chemical Process for E-waste Plastics Recycling
- Mechanical Process for E-waste Plastics Recycling
- Thermal Process for E-waste Plastics Recycling
- Glass
- Glass-to-Glass Recycling
- Glass-to-Lead Recycling
- Others
By Source of Waste
- Household Appliances
- Major Household Appliances
- Small Household Appliances
- Other Household Appliances
- Consumer Electronics
- Entertainment
- Media and Audio Production Systems
- IT and Telecommunication
- Information Technologies and Communication Devices
- Others
- Lighting Equipment
- Toys, Leisure, and Sports Equipment
- Medical Devices
- Monitoring and Control Instruments
By Treatment Technology
- Landfilling
- Mechanical Treatment
- Manual Dismantling and Sorting
- Mechanical Shredding
- Pyrometallurgical Processes
- Hydrometallurgical Processes (Chemical Leaching)
- Incineration Process for E-waste Treatment
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is e-waste management important on a global scale?
E-waste management is crucial because improper disposal of electronics can lead to environmental pollution, health hazards, and the loss of valuable resources like metals and plastics. Managing e-waste responsibly supports resource conservation and minimizes harmful emissions.
What types of electronic devices contribute most to e-waste?
The primary contributors to e-waste include consumer electronics like mobile phones, computers, televisions, home appliances, and industrial electronics like medical and automotive devices.
How does e-waste recycling benefit the environment?
E-waste recycling reduces landfill waste, prevents toxic substances like lead and mercury from leaching into the environment, and recovers valuable materials like gold, silver, and copper, reducing the need for mining.
What is the role of technology in improving e-waste management?
Technologies like AI, IoT, and robotics enhance sorting, processing, and recycling efficiency. They also enable better tracking of e-waste, ensuring proper handling and compliance with regulations.
What is the future outlook for the global e-waste management market?
The market is expected to grow due to rising electronic consumption, stricter environmental regulations, and increased public awareness. Innovations in recycling technologies and circular economy models will further drive sustainable e-waste management.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]