Global Clean Technology Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Type (Renewable Energy Technologies, Energy Storage Solutions, Energy Storage Solutions, Water and Waste Management, Agriculture and Food Systems, and Air and Environment Management), Application (Residential, Commercial, Industrial), and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Clean Technology Market Size
The global clean technology market was worth USD 918.4 billion in 2024. The global market is projected to reach USD 2,715.27 billion by 2033 from USD 1,035.96 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 12.80% from 2025 to 2033.
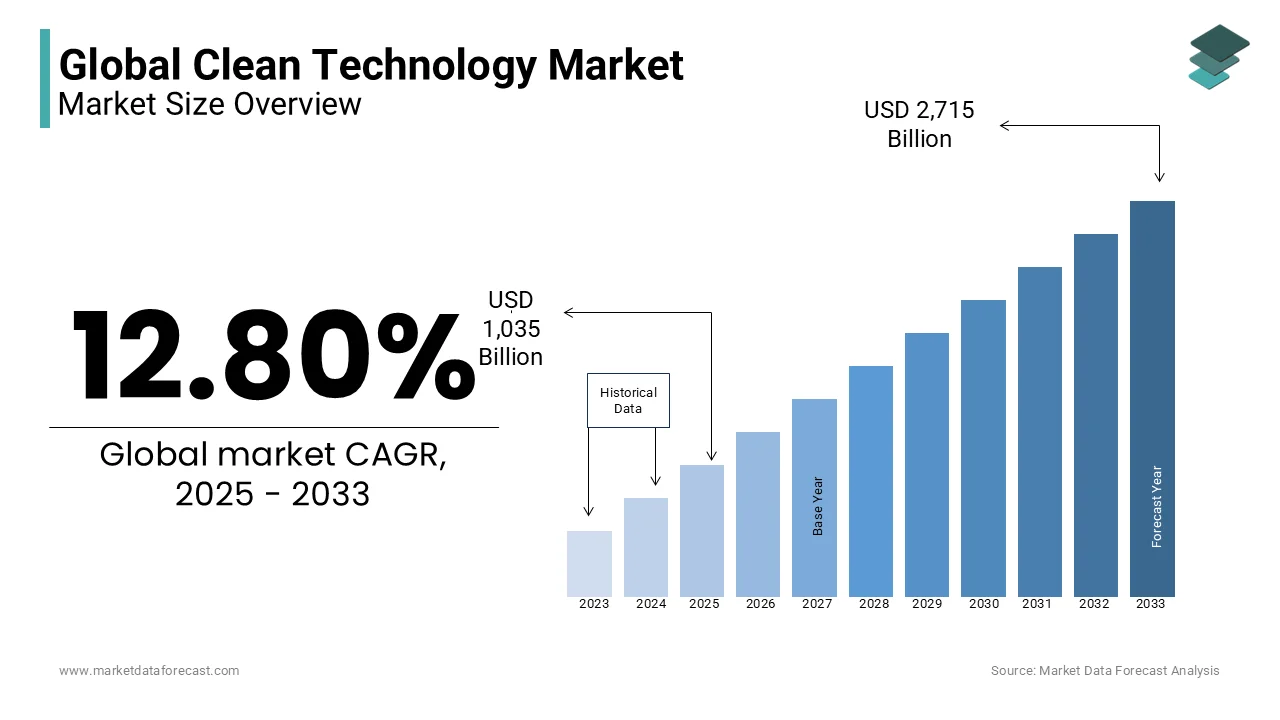
Clean Technology (Cleantech) leverage innovative solutions to reduce environmental impacts while optimizing resource efficiency. The demand for cleantech is growing significantly owing to the increasing demand for sustainability, stringent regulatory frameworks, and advancements in green technologies. Clean technology spans multiple sectors, including renewable energy, energy storage, water and waste management, sustainable agriculture, and green transportation. The key objective of this market is to minimize carbon emissions, promote circular economy principles, and enhance economic productivity without compromising environmental integrity.
The global clean technology market is experiencing unprecedented growth due to increasing government investments, corporate sustainability commitments, and consumer awareness. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global investments in clean energy technologies surpassed $1.7 trillion in 2023, accounting for nearly two-thirds of total energy investments. Meanwhile, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) reports that renewable energy capacity additions in 2023 reached an all-time high, exceeding 400 GW, primarily driven by wind and solar energy expansion.
The clean technology sector is also witnessing significant advancements in energy storage solutions, with lithium-ion battery costs declining by 89% between 2010 and 2023, according to BloombergNEF. Additionally, the electric vehicle (EV) market is projected to reach 50% of global new car sales by 2035, as noted by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). With rising concerns over climate change and resource depletion, the cleantech industry is poised to be a cornerstone of the future global economy, fostering innovation and long-term sustainability.
MARKET DRIVERS
Government Policies and Regulatory Support
Stringent environmental regulations and government incentives are significantly driving the clean technology market. Governments worldwide are implementing policies to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable practices. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that over 130 countries have committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050, reinforcing the demand for clean technologies. In the United States, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 allocated $369 billion for clean energy investments, marking the largest federal commitment to climate change initiatives. Similarly, the European Union’s Green Deal aims to mobilize €1 trillion in sustainable investments by 2030, as stated by the European Commission. These policies foster innovation, encourage private sector participation, and accelerate the adoption of renewable energy, electric vehicles, and energy-efficient technologies.
Rising Investments in Renewable Energy and Energy Storage
The expansion of clean energy infrastructure is another key driver of the clean technology market. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), global renewable energy capacity increased by 9.6% in 2023, reaching 3,440 GW, with solar and wind power accounting for over 80% of new additions. Additionally, the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that global investments in battery storage technologies exceeded $40 billion in 2023, fueled by the demand for grid stabilization and electric vehicle adoption. China leads the sector, installing over 200 GW of new renewable capacity in a single year, as reported by IRENA. This surge in investments enhances energy security, lowers carbon footprints, and supports the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy ecosystem.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Capital and Infrastructure Costs
One of the significant restraints of the clean technology market is the high upfront costs associated with infrastructure development and technology deployment. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that achieving global net-zero emissions by 2050 would require an annual investment of $4 trillion in clean energy technologies. While long-term operational savings and sustainability benefits are substantial, the initial capital required for renewable energy projects, electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, and grid modernization remains a financial burden. The U.S. Department of Energy states that the installation cost of utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) systems averages $1,000 per kW, while offshore wind projects can exceed $4,000 per kW. These costs deter small and medium enterprises from large-scale adoption, slowing overall market expansion.
Supply Chain Constraints and Raw Material Dependence
The clean technology market is heavily reliant on critical raw materials, making it vulnerable to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) reports that over 70% of the world’s lithium, essential for battery production, is concentrated in Argentina, Chile, and Australia, while China controls 60% of global rare earth element processing. This concentration increases risks related to trade restrictions and price volatility. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), demand for key minerals such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel is expected to grow by sixfold by 2040 due to the expansion of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies. Supply chain disruptions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, further exacerbate these challenges, delaying clean energy transitions.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Energy Storage and Grid Modernization
The growing need for energy resilience presents a major opportunity for the clean technology market, particularly in energy storage and smart grid advancements. The U.S. Department of Energy states that global battery storage capacity is projected to reach 1,095 GWh by 2030, driven by increasing demand for renewable integration and electric vehicles. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), investment in electricity grids reached $330 billion in 2023, with significant funding directed toward digitalization, automation, and decentralized energy management. Smart grids and advanced storage solutions enhance energy efficiency, reduce transmission losses, and enable large-scale renewable adoption. These advancements are expected to accelerate the transition towards a decentralized energy ecosystem, improving sustainability and grid reliability worldwide.
Expansion of Green Hydrogen and Carbon Capture Technologies
The rising focus on decarbonization is driving the development of green hydrogen and carbon capture technologies. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) projects that green hydrogen production capacity could exceed 500 million metric tons annually by 2050, contributing significantly to industrial and transportation sector decarbonization. Meanwhile, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) capacity grew by 44% in 2023, with over 50 new projects announced globally. The U.S. Department of Energy has allocated $3.5 billion for direct air capture and carbon removal projects under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law. These technologies present a lucrative opportunity for industries seeking to reduce carbon footprints while aligning with global climate commitments and net-zero targets.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Intermittency and Energy Reliability Issues
One of the major challenges facing the clean technology market is the intermittency of renewable energy sources, which affects grid stability and energy reliability. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) states that solar and wind power accounted for over 14% of U.S. electricity generation in 2023, but their output fluctuates due to weather conditions. The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that battery storage and grid flexibility investments need to increase by four times to ensure a stable renewable-powered grid. Without significant improvements in energy storage and smart grid technologies, power supply disruptions and inefficiencies could hinder the large-scale adoption of renewables, particularly in industrial and urban applications requiring consistent energy availability.
Limited Recycling and Waste Management for Clean Technologies
The rapid deployment of clean technologies, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicle (EV) batteries, presents a growing challenge in waste management and recycling. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), solar panel waste is projected to reach 78 million metric tons globally by 2050, requiring urgent recycling solutions. Additionally, the U.S. Department of Energy reports that less than 5% of lithium-ion batteries are currently recycled, raising concerns about resource depletion and environmental impacts. Without effective recycling infrastructure, clean technology components could contribute to new environmental issues, contradicting the sustainability goals of the industry. Developing advanced recycling methods and circular economy strategies is essential to mitigate this emerging challenge.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
12.80% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Tesla, Inc., NextEra Energy, Inc., First Solar, Inc., Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Enphase Energy, Inc., Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, Plug Power Inc., Orsted A/S, Veolia Environnement S.A., SunPower Corporation, Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P., Schneider Electric SE, NRG Energy, Inc., Ballard Power Systems Inc., and Canadian Solar Inc. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
Renewable Energy Technologies dominate the market by holding 60.3%. In 2022, renewables accounted for over 80% of new power capacity additions globally, driven by solar and wind energy growth. This leadership stems from declining costs—solar photovoltaic prices dropped by 85% between 2010-2020 and government policies promoting clean energy adoption to combat climate change. The sector's importance lies in reducing carbon emissions IEA reports that renewables could provide nearly 90% of electricity generation by 2050 under net-zero scenarios making it pivotal for sustainable development.
Energy Storage Solutions exhibit the highest CAGR at 20% through 2025-2033. Rapid advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have reduced costs by 89% since 2010, enabling widespread deployment. Governments like the U.S. Department of Energy emphasize storage as critical for grid stability amid rising renewable integration, with investments exceeding $7 billion in 2022 alone. The segment’s explosive growth is fueled by increasing demand for electric vehicles and utility-scale projects; Wood Mackenzie forecasts global installed capacity to reach 741 GWh by 2030, up from 16 GWh in 2020, underscoring its role in decarbonizing energy systems and ensuring reliable power supply.
By Application Insights
The Industrial segment leads with 42.5% of the global market. This dominance is driven by high energy demands for manufacturing, processing, and operational activities. In 2022, industries consumed 54% of global electricity, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), underscoring its critical role in economic growth. The sector’s importance lies in enabling large-scale adoption of energy-efficient technologies and renewable integration, reducing emissions from heavy industries like steel and cement.
The Residential segment is the fastest-growing with a CAGR of 8.5%. This growth is fueled by rising urbanization, increased electrification, and government incentives for home energy solutions like rooftop solar and smart appliances. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights that residential energy consumption accounts for 20% of total U.S. energy use, with solar installations growing by 34% annually since 2020. Rising awareness of energy efficiency and net-zero homes further accelerates adoption. Globally, the IEA estimates that residential renewable capacity will triple by 2030, driven by supportive policies and declining technology costs, making it vital for reducing household carbon footprints and achieving climate goals.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia-Pacific dominated the clean technology market by accounting for 46.4% of the global market share in 2024. China is the key driver to the Asia-Pacific market and leading global renewable energy investments, with solar and wind capacity surpassing 1,200 GW in 2023, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Additionally, China produces 80% of the world’s solar panels and controls 60% of global rare earth processing, making it central to clean technology supply chains. India is also expanding rapidly, aiming for 500 GW of renewable capacity by 2030, supported by government incentives and foreign investments, according to the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE).
The Middle East and Africa (MEA) region is the speedily rising clean technology market and is expected to register a CAGR of 12.7% from 2025 to 2033. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries are accelerating clean energy projects, with Saudi Arabia investing $50 billion in renewables under its Vision 2030 plan. The UAE aims to generate 44% of its power from renewables by 2050, according to the UAE Energy Strategy. Africa, particularly South Africa and Egypt, is witnessing rapid solar and wind expansion, with South Africa’s Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Programme (REIPPP) attracting over $20 billion in investments. MEA’s abundant solar resources, government policies, and increasing foreign investments are driving its market expansion.
North America is a key player in the clean technology market, driven by strong government policies and corporate investments. The U.S. Department of Energy reports that the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 allocated $369 billion for clean energy initiatives, including solar, wind, and electric vehicles (EVs). The U.S. leads in carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects, with a 44% increase in capacity in 2023, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA). Canada is also expanding its renewable sector, aiming for 90% clean electricity by 2030, as stated by Natural Resources Canada.
Europe remains at the forefront of the clean technology market due to its aggressive climate policies and sustainability targets. The European Commission’s Fit for 55 Plan aims to cut emissions by 55% by 2030, fueling clean energy investments. The EU allocated €1 trillion for the Green Deal, focusing on renewable energy, electric mobility, and circular economy initiatives. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Europe added 60 GW of new renewable energy capacity in 2023, with Germany, Spain, and France leading in solar and wind deployment.
Latin America is emerging as a renewable energy hub, leveraging its vast natural resources for clean technology expansion. According to IRENA, Brazil’s wind and solar capacity exceeded 40 GW in 2023, making it one of the region’s largest renewable energy markets. Chile and Mexico are also advancing clean energy projects, with Chile aiming for 100% renewable electricity by 2040, as stated by the Ministry of Energy of Chile. The World Bank highlights that Latin America attracted $18 billion in renewable energy investments in 2023, driven by international funding and regional government incentives.
Top 3 Players in the Market
NextEra Energy, Inc.
NextEra Energy, Inc. is the world’s largest producer of renewable energy, specializing in wind and solar power generation. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), NextEra has installed over 65 GW of renewable energy capacity, making it a key player in the clean technology market. The company is investing $50 billion in clean energy projects from 2024 to 2030, aiming to expand its green hydrogen and energy storage solutions. NextEra’s commitment to sustainability is reflected in its zero-carbon emission goal by 2045, supported by large-scale investments in battery storage and grid modernization, as reported by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Tesla, Inc.
Tesla, Inc. is a dominant force in clean technology, driving the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and battery storage solutions. The company delivered 1.81 million EVs in 2023, capturing a 20% global market share, as per the International Energy Agency (IEA). Tesla’s Gigafactories worldwide are expanding lithium-ion battery production, with the company producing over 100 GWh of battery storage capacity annually, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. Additionally, Tesla’s solar energy division installed 4.5 GW of solar capacity in 2023, reinforcing its contribution to the clean energy transition. The company’s innovations in battery technology and grid storage are crucial for global decarbonization efforts.
Siemens AG
Siemens AG is a global leader in industrial clean technology, focusing on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and smart grid solutions. The company plays a pivotal role in wind power through Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, which has installed over 145 GW of wind energy capacity worldwide, as reported by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). Siemens is also advancing green hydrogen technology, with projects in Germany and the Middle East targeting 10 GW of electrolysis capacity by 2035, according to the European Commission. Additionally, Siemens invests heavily in smart grid solutions, with $3 billion allocated for AI-driven energy optimization technologies to improve grid efficiency and sustainability worldwide.
Top strategies used by the key market participants
Expansion of Renewable Energy Capacity
Leading companies in the clean technology market are aggressively expanding their renewable energy portfolios to meet global sustainability goals. NextEra Energy, Inc. has committed $50 billion in investments to increase wind, solar, and battery storage capacity, aiming to exceed 100 GW of renewable energy by 2030, as per the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Similarly, Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, a division of Siemens AG, has installed over 145 GW of wind energy capacity worldwide, contributing significantly to clean energy adoption, as reported by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
Advancements in Energy Storage Technologies
Energy storage is a critical enabler of the clean technology market, allowing for better integration of intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind. Tesla, Inc. has prioritized battery technology through its Gigafactories, producing over 100 GWh of lithium-ion battery storage annually, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. The company’s Megapack battery system is designed to support large-scale energy storage projects, helping utilities manage grid stability and renewable energy fluctuations.
Strategic Mergers, Acquisitions, and Partnerships
Market leaders are actively pursuing mergers and acquisitions to enhance their technological capabilities and expand market presence. Siemens AG acquired Brightly Software in a $1.58 billion deal to strengthen its digital infrastructure solutions in clean energy, as reported by the European Commission. Additionally, NextEra Energy has acquired multiple solar and wind farm assets to expand its renewable energy footprint across North America.
Investments in Green Hydrogen and Carbon Capture Technologies
To diversify their clean technology portfolios, companies are investing heavily in green hydrogen and carbon capture solutions. Siemens AG is working on green hydrogen projects with a target of developing 10 GW of electrolysis capacity by 2035, as per the European Commission. NextEra Energy is also investing in green hydrogen production, aligning with its zero-carbon emissions goal by 2045, as stated by the U.S. Department of Energy.
Digitalization and Smart Grid Development
Digital transformation plays a key role in optimizing energy efficiency and grid reliability. Tesla’s AI-driven energy management system, integrated with its Autobidder platform, allows automated energy trading and grid balancing, maximizing the efficiency of renewable energy assets. Similarly, Siemens AG has invested $3 billion in AI-powered smart grid solutions to enhance energy efficiency, reduce power outages, and support decentralized energy networks.
Geographic Expansion into Emerging Markets
Key players are expanding into high-growth markets such as India, the Middle East, and Africa to capitalize on rising clean energy demand. NextEra Energy is entering Latin America through solar and wind partnerships, while Tesla is expanding its presence in India, where the government aims for 30% EV penetration by 2030, as per India’s Ministry of Power. Siemens AG is actively involved in Africa’s off-grid solar and mini-grid solutions, targeting regions with limited electricity access.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global clean technology market include Tesla, Inc., NextEra Energy, Inc., First Solar, Inc., Vestas Wind Systems A/S, Enphase Energy, Inc., Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy, Plug Power Inc., Orsted A/S, Veolia Environnement S.A., SunPower Corporation, Brookfield Renewable Partners L.P., Schneider Electric SE, NRG Energy, Inc., Ballard Power Systems Inc., and Canadian Solar Inc.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The clean technology market is highly competitive, driven by rapid technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and increasing global sustainability commitments. The market features a mix of multinational corporations, specialized renewable energy firms, and emerging startups, all striving to capture a growing share of the green economy. Key players such as NextEra Energy, Tesla, and Siemens AG dominate with extensive investments in renewable energy, energy storage, and smart grid solutions.
The competition is intensifying as governments worldwide introduce aggressive net-zero targets and carbon reduction mandates, fueling demand for clean energy solutions. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), global renewable energy capacity reached 3,440 GW in 2023, with wind and solar companies competing for project contracts and grid integrations. The electric vehicle (EV) sector is also highly competitive, with Tesla, BYD, and Volkswagen leading the global transition, as EV sales surpassed 14 million units in 2023, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Additionally, competition extends into green hydrogen, carbon capture, and circular economy innovations, with companies racing to commercialize emerging clean technologies. The market remains dynamic, with increasing mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations shaping competitive positioning. Firms with advanced digitalization, efficient storage solutions, and global market reach will sustain long-term leadership in this evolving sector.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In October 2024, Rio Tinto announced its acquisition of Arcadium Lithium for $6.7 billion. This strategic move positions Rio Tinto as a leading lithium producer, a critical component for electric vehicle batteries.
- In June 2024, Clean Electric, a Pune-based developer of lithium-ion batteries, unveiled a revolutionary rapid recharging battery technology. This innovation enables electric two- and three-wheelers to fully charge in approximately 12 minutes, a significant improvement over the current 60-120 minute range.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global clean technology market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Renewable Energy Technologies
- Energy Storage Solutions
- Energy Storage Solutions
- Water and Waste Management
- Agriculture and Food Systems
- Air and Environment Management
By Application
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key drivers of growth in the clean technology market?
Major drivers include government regulations, advancements in renewable energy, rising environmental awareness, corporate sustainability commitments, and increasing investment in green technologies.
Which countries are investing the most in clean technology?
Countries such as the United States, China, Germany, and Japan are leading in clean technology investments, with strong government support, research funding, and corporate initiatives.
How is clean technology evolving with innovation?
Advances in artificial intelligence, battery storage, hydrogen fuel, carbon capture, and smart grids are driving innovation and improving efficiency in clean technology applications.
What is the future outlook for the clean technology market?
The clean technology market is expected to expand rapidly as global efforts to combat climate change intensify, supported by continued investment, policy advancements, and technological breakthroughs.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]