Global Bioengineered Protein Drugs Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Type (Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs), Peptide Hormones, Vaccines, Blood Factors and Peptide Antibiotics, Fusion Proteins, Cytokines and Therapeutic Enzymes), Disease and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2032
Global Bioengineered Protein Drugs Market Size
The global bioengineered protein drugs market size was estimated at USD 255.12 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 442.12 billion by 2032 from USD 271.19 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2024 to 2032.
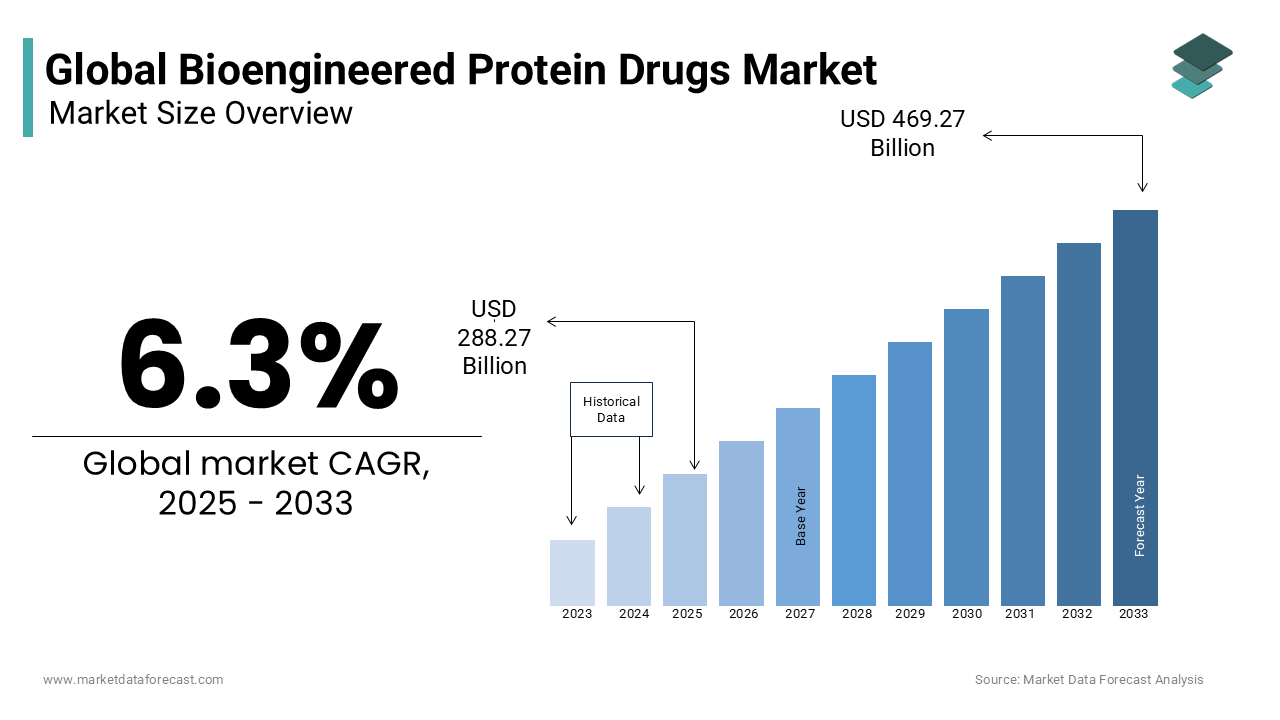
Bioengineered protein drugs focus on developing therapeutic proteins designed through advanced genetic engineering techniques to treat chronic and rare diseases. These drugs include monoclonal antibodies, insulin analogs, and growth factors with the revolutionized treatment landscape for cancer, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic conditions. For instance, monoclonal antibodies are widely used in oncology with over 100 approved therapies globally by offering precision in targeting cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues. Advancements in recombinant DNA technology have significantly enhanced the efficiency and scalability of protein drug production. Breakthroughs like PEGylation (attaching polyethylene glycol to proteins) extend drug half-life by reducing dosing frequency and improving patient compliance. The rising prevalence of conditions such as diabetes, with over 530 million people affected worldwide as of 2023, is promoting the demand for insulin analogs and other protein-based therapies. Emerging technologies, including cell-free protein synthesis and AI-driven drug discovery, are shaping the future of bioengineered protein drugs. These innovations ensure faster development and enhanced efficacy to meet the growing demand for personalized and targeted therapies.
MARKET DRIVERS
Advancements in Genetic Engineering Technologies
The development of advanced genetic engineering tools, such as CRISPR and recombinant DNA technology, is driving the bioengineered protein drugs market. These technologies enable precise modification of genetic sequences to allow for the creation of particular and effective protein-based therapies. For example, CRISPR is being used to design proteins that target cancer cells with minimal off-target effects. Additionally, recombinant DNA technology has streamlined the mass production of therapeutic proteins like human growth hormone to reduce costs and increase accessibility. These advancements are accelerating the discovery and manufacturing of innovative treatments for chronic and rare diseases.
Increasing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The rising global burden of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, is a significant driver for bioengineered protein drugs. Over 530 million people worldwide are living with diabetes, fueling demand for insulin analogs. Similarly, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis affect approximately 1% of the global population, creating a need for monoclonal antibodies and other protein-based therapies. These drugs offer targeted action and fewer side effects than traditional treatments, making them indispensable in managing chronic conditions effectively.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Development and Production Costs
The high cost of developing and manufacturing bioengineered protein drugs is a major restraint. Producing these therapies requires advanced bioreactors, skilled personnel, and stringent quality controls, which are driving up expenses. For example, monoclonal antibody production can cost between $100-$200 per gram, which makes these drugs expensive for healthcare systems and patients. Additionally, clinical trials for protein drugs often take longer due to complex safety evaluations that further increase the costs. Limited affordability in developing regions restricts access, which poses a challenge to market expansion.
Storage and Stability Challenges
Bioengineered protein drugs require precise storage conditions to maintain stability and efficacy, and they often need refrigeration between 2°C and 8 °C. This makes distribution challenging in regions with inadequate cold chain infrastructure. For example, insulin analogs and monoclonal antibodies degrade quickly if exposed to temperatures outside the recommended range, leading to wastage. These stringent requirements increase logistics costs and limit accessibility in low-resource settings, which is expected to hinder market growth. Developing stable formulations that withstand temperature fluctuations remains a critical challenge for the industry.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Biosimilars
The growing acceptance of biosimilars offers a significant opportunity in the bioengineered protein drugs market. Biosimilars are cost-effective alternatives to branded biologics, which are specially designed to provide similar efficacy and safety. Companies can tap into a market projected to save healthcare systems billions with patents expiring for several blockbuster biologics by including monoclonal antibodies. For instance, biosimilar versions of trastuzumab, a breast cancer therapy, have reduced treatment costs by 15-30% in several regions. Regulatory support such as the U.S. FDA’s Biosimilar Action Plan will facilitate market entry by broadening access to life-saving therapies.
Adoption of AI in Drug Discovery
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the discovery and development of bioengineered protein drugs. AI tools can analyze vast datasets to identify promising protein targets and optimize drug design by reducing R&D timelines by up to 50%. For example, DeepMind’s AlphaFold has significantly advanced protein structure prediction by aiding faster and more precise drug formulation. The adoption of AI in biopharma is expected to accelerate innovation, allowing companies to create personalized therapies for complex diseases like cancer and neurological disorders, addressing unmet medical needs while improving market competitiveness.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Complexity
The stringent and evolving regulatory frameworks for bioengineered protein drugs present a significant challenge. Approvals require extensive safety and efficacy evaluations, which are both time-consuming and costly. For instance, the average timeline for FDA approval of a biologic drug is 8-10 years, further delaying market entry. Additionally, varying regulatory requirements across regions, such as stricter biosimilar guidelines in Europe versus the U.S., complicate global commercialization. These hurdles increase development costs and limit the ability of smaller companies to compete in the market.
Immunogenicity Concerns
Immunogenicity, where a patient’s immune system reacts adversely to protein drugs, is another critical challenge. Adverse reactions can range from mild allergic responses to severe complications, potentially compromising treatment outcomes. For example, monoclonal antibodies like infliximab have shown immune responses in up to 50% of patients by reducing efficacy. This necessitates extensive preclinical and clinical testing to minimize immunogenic risks by adding complexity to development. Addressing these concerns through innovative formulations and advanced screening techniques remains essential for market growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Disease, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leader Profiled |
Amgen Inc., Roche Holding AG, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Biotech, Inc.), Pfizer Inc., Sanofi S.A., Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol-Myers Squib Company, Novartis AG |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) segment dominated the market and held 60.4% of the global market share in 2023. Their dominance is attributed to their targeted therapeutic action in oncology and autoimmune diseases. For instance, mAbs like pembrolizumab have significantly improved survival rates in cancers such as melanoma. The precision of mAbs in targeting specific antigens reduces side effects compared to traditional therapies by enhancing patient outcomes. Their versatility extends to treatments for rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis and is expected to strengthen the position of the monoclonal antibodies segment further in the global market.
The therapeutic enzymes segment is predicted to be the fastest-growing segment and register a CAGR of 8.12% over the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by advancements in enzyme replacement therapies for rare genetic disorders. For example, enzyme therapies for conditions like Gaucher's disease have improved patient quality of life and reduced mortality rates. Ongoing research into enzyme engineering and delivery methods is expanding their therapeutic applications, including potential treatments for metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. The increasing prevalence of such conditions and the success of existing enzyme therapies contribute to the accelerated growth of this segment.
By Disease Insights
The autoimmune diseases and other immunodeficiency disorders segment was the largest segment in the global market and held 40.1% of the global market share in 2023. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) dominate treatments for autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn’s disease. For example, biologics like adalimumab have revolutionized care by specifically targeting inflammatory pathways and improving outcomes for millions of patients globally. The increasing prevalence of autoimmune diseases, which is over 5% of the global population, and the efficacy of bioengineered proteins in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life are escalating the segmental expansion.
The infectious diseases segment is estimated to be the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 9.4% over the forecast period. Advancements in protein-based vaccines and therapies for infections such as COVID-19, HIV, and hepatitis fuel this growth. The success of mRNA and protein-based COVID-19 vaccines highlights the potential for bioengineered proteins in combating pandemics and emerging pathogens. For instance, protein-based treatments for hepatitis B and C have shown cure rates of up to 95%, driving demand. The continuous threat of infectious diseases and focus on innovative treatments ensures this segment’s rapid growth.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America outperformed other regions and accounted for 45.1% of the global market share in 2023 due to robust biotechnology R&D and high healthcare expenditure. The U.S. alone accounts for over 60% of global biologic drug approvals with over 60 FDA-approved monoclonal antibodies. Government funding plays a crucial role, with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) allocating $45 billion annually for medical research. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases like diabetes, which affects over 37 million Americans, is attributed to driving the demand. Canada also contributes through expanding public health programs that enhance access to biologics.
Europe is a prominent regional market for bioengineered protein drugs and is predicted to account for a notable share of the worldwide market over the forecast period. The growth of the European market is majorly driven by significant investments in healthcare innovation and a favorable regulatory framework. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has approved more than 100 biosimilars by enhancing the affordability and accessibility of protein drugs. Countries like Germany invest over €12 billion annually in medical R&D, whereas the UK focuses on cancer and autoimmune disease therapies. The personalized medicine initiatives and strong adoption of monoclonal antibodies are likely to aid the European market growth.
The Asia-Pacific region is growing at the fastest pace. China leads in biotech innovation backed by the government’s National Biotech Development Strategy, which has generated a 20% annual increase in biologic drug production. India, with over 77 million diabetes cases, is investing in insulin analogs and biosimilar production to meet demand. Japan is focusing on treatments for rare diseases with the surge in protein drug R&D through its advanced healthcare infrastructure. The rising prevalence of chronic diseases and increased healthcare access are key growth drivers.
Latin America holds a substantial share of the worldwide market. Brazil leads regional growth with its robust biosimilar pipeline and increasing focus on biologics for diabetes and infectious diseases. The country’s Ministry of Health has invested heavily in public healthcare with initiatives to expand access to biologic treatments. Mexico also contributes through partnerships with global biotech firms to manufacture protein therapies locally.
The market in the Middle East and Africa region is estimated to progress at a steady CAGR over the forecast period. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 initiative includes significant investments in healthcare infrastructure by promoting the adoption of advanced biologics for conditions like cancer and rheumatoid arthritis. The UAE is focusing on oncology treatments, while South Africa is expanding access to biosimilars for HIV and diabetes. However, rural healthcare access remains limited by highlighting the need for infrastructure improvements.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Amgen Inc., Roche Holding AG, Johnson & Johnson (Janssen Biotech, Inc.), Pfizer Inc., Sanofi S.A., Merck & Co., Inc., AbbVie Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol-Myers Squib Company, Novartis AG are key market players.
The Bioengineered Protein Drugs Market is highly competitive, driven by innovation, strong demand for targeted therapies, and the entry of biosimilars. Established pharmaceutical giants like Amgen, Roche, and Johnson & Johnson dominate the market with extensive portfolios of monoclonal antibodies, fusion proteins, and therapeutic enzymes. Their competitive edge lies in proprietary technologies, strong R&D investments, and global distribution networks. For instance, Roche’s portfolio includes leading biologics such as trastuzumab and bevacizumab, which are widely used in oncology. The competition is intensifying with the rise of biosimilars, which offer cost-effective alternatives to branded biologics. Companies like Pfizer and Amgen are investing heavily in biosimilar development to capture this growing segment. In Europe, over 100 biosimilars have been approved, boosting affordability and increasing market penetration.
Emerging biopharma companies are focusing on niche areas such as rare diseases and personalized medicine. Advances in technologies like CRISPR and AI-driven drug discovery are enabling smaller players to develop innovative protein drugs more efficiently. Strategic partnerships and acquisitions are common as companies aim to expand their pipelines and enter new markets. For example, Sanofi’s acquisition of Kadmon Holdings strengthened its immunology portfolio. This competitive landscape is dynamic, fostering innovation to address unmet medical needs.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In October 2023, Amgen completed the acquisition of Horizon Therapeutics, a company focused on rare diseases, for $27.8 billion. This move aims to enhance Amgen’s presence in the rare disease market.
- In November 2024, Merck & Co., Inc. entered a licensing agreement with LaNova Medicines, a China-based biotech firm, for an experimental cancer drug. This $3.3 billion deal aims to bolster Merck’s oncology pipeline.
- In November 2024, BioNTech, a German biotech company, acquired Biotheus, a Chinese drugmaker, for $950 million. This acquisition is expected to strengthen BioNTech’s oncology strategy with innovative cancer therapies.
- In November 2024, Avidity Biosciences announced advancements in RNA-based therapies for cardiovascular diseases. This development aims to expand its therapeutic portfolio and market position.
- In November 2024, Novartis raised its midterm sales guidance amid U.S. expansion efforts. This strategy reflects Novartis’s aim to boost its market share and revenue growth.
- In November 2024, AbbVie received an analyst upgrade despite recent challenges, highlighting confidence in its growth potential and strategic direction.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Bioengineered Protein Drugs Market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
- Peptide Hormones
- Vaccines
- Blood Factors and Peptide Antibiotics
- Fusion Proteins
- Cytokines
- Therapeutic Enzymes
By Disease
- Autoimmune Diseases and Other Immunodeficiency Disorders
- Solid Tumors
- Diabetes
- Infectious Diseases
- Blood Disorders
- Growth Hormone Disorders, Enzyme Disorders, and Infertility
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the growth of the bioengineered protein drugs market?
Growth is driven by advancements in biotechnology, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, increased investment in R&D, and the adoption of personalized medicine.
Which regions are leading the bioengineered protein drugs market?
North America and Europe are the leading regions, owing to established healthcare systems, significant biotech investments, and high rates of chronic diseases.
What are the main challenges faced by the bioengineered protein drugs market?
Key challenges include high production costs, complex manufacturing processes, strict regulatory requirements, and issues related to immunogenicity.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
