Global Bio-Based Naphtha Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Source (Biomass, Vegetable Oil, Used Cooking Oil, Animal Fat and Others), Application (Plastic Production ( Bio polyethylene, Bio polypropylene, Bio polyolefins and Others) and Others) and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis (2024 to 2032)
Global Bio-Based Naphtha Market Size
The size of the global bio-based naphtha market was valued at USD 1.54 billion in 2023. The global market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.8% from 2024 to 2032 and grow from USD 1.86 billion in 2024 to USD 8.44 billion by 2032.
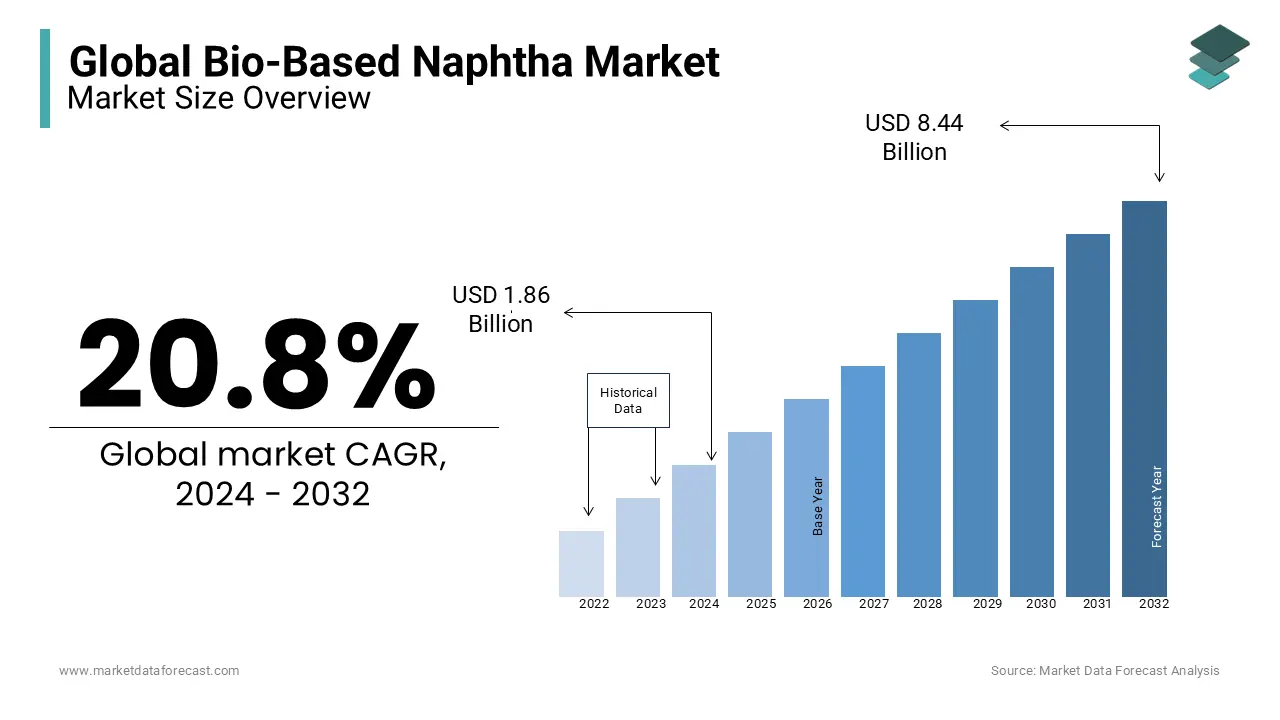
Bio-based naphtha is emerging as a sustainable alternative within the chemical and plastics industries to capitalize on the shift towards renewable materials and reduced carbon emissions. Bio-based naphtha is produced from renewable sources such as vegetable oils, agricultural waste, and other biomass, positioning it as a lower-impact substitute for traditional fossil-based naphtha in applications like polymer production, synthetic rubber, and biofuels. The environmental benefits associated with bio-based naphtha are primarily driving the expansion of the global market. Several life cycle assessments have confirmed that bio-based naphtha has a notably lower greenhouse gas impact compared to conventional counterparts. Favorable policies, especially in regions such as the European Union, are incentivizing the transition to bio-based chemicals to reduce industrial carbon footprints. Additionally, advancements in biomass processing technologies are improving yield and efficiency in bio-based naphtha production contributing to a more robust supply chain.
MARKET TRENDS
Rise in Demand for Sustainable Packaging Materials
Bio-based naphtha is increasingly in demand for producing bioplastics, especially in packaging. With growing consumer awareness, sustainable packaging has become a priority, driving companies to seek renewable alternatives. Bio-based naphtha serves as a crucial feedstock for bio-polyethylene, commonly used in eco-friendly packaging materials. For instance, studies show that bio-polyethylene can reduce carbon emissions by approximately 70% compared to fossil-based polyethylene, making it a popular choice. Legislation, particularly in the EU, aims for 55% of all plastic packaging to be recycled by 2030, further accelerating bio-based naphtha adoption in packaging applications.
Advancements in Biomass Conversion Technology
Technological innovations are making bio-based naphtha production more efficient and scalable, allowing it to compete more effectively with conventional naphtha. Innovations in biomass gasification and pyrolysis technologies are enhancing yield and reducing costs, which is essential for broader market penetration. For example, next-gen pyrolysis methods have shown a 15-20% increase in output efficiency, improving the economic feasibility of bio-based naphtha. In recent years, government funding for biofuel R&D has grown significantly, with major economies investing in these cleaner technologies to support decarbonization and sustainable energy transitions.
MARKET DRIVERS
Environmental Regulations and Carbon Reduction Goals
Stringent environmental regulations are a key driver as governments worldwide seek to curb greenhouse gas emissions. The EU, for example, has set a target to reduce emissions by at least 55% by 2030, encouraging industries to adopt low-carbon feedstocks like bio-based naphtha. Additionally, carbon taxes and incentives for renewable resources are pushing companies in petrochemicals and plastics toward sustainable alternatives. Life cycle assessments reveal that bio-based naphtha emits significantly fewer carbon emissions, aligning it with regulatory trends focused on decarbonization and circular economy principles.
Corporate Sustainability Commitments
Growing corporate commitments to sustainability are spurring demand for bio-based feedstocks. Companies across sectors—from consumer goods to automotive—are increasingly setting net-zero goals. For instance, global brands like Unilever and Coca-Cola are investing in bio-based materials to meet these targets, seeking alternatives to fossil-derived inputs. By integrating bio-based naphtha into their supply chains, businesses can demonstrate a measurable reduction in their carbon footprints, catering to consumer demand for eco-friendly products and satisfying investor pressures for responsible environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices.
Growth in Bio-Plastic Demand
The surge in bioplastics, particularly bio-polyethylene, has fuelled bio-based naphtha demand as it serves as a primary feedstock. Bioplastics are projected to make up over 2% of global plastic production by 2025, largely due to their environmental advantages and support from regulations favoring recyclable and biodegradable materials. Many packaging and automotive manufacturers now prefer bio-based materials, viewing them as sustainable alternatives to traditional plastics. This growth is positioning bio-based naphtha as a critical resource in producing materials that meet increasing eco-conscious and regulatory standards for reduced environmental impact.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Production Costs
Bio-based naphtha production remains more costly than its fossil-based counterpart due to the expenses involved in feedstock processing and conversion technologies. Biomass-derived feedstocks, such as vegetable oils and agricultural residues, can fluctuate in price and often require additional refinement to reach industry standards. Studies show that bio-based naphtha can cost up to 30% more than conventional naphtha, creating a significant barrier, especially for cost-sensitive industries. These higher costs affect pricing across the supply chain, making it challenging for bio-based naphtha to compete economically without subsidies or other financial incentives.
Limited Feedstock Availability and Infrastructure
The availability of renewable feedstocks, essential for bio-based naphtha production, can be inconsistent due to seasonal variations and competition from other biofuel industries. Additionally, the current infrastructure for biomass collection, processing, and transportation is underdeveloped, especially compared to the well-established networks for petroleum-based feedstocks, as bio-based naphtha production requires specific processing facilities, and regions with insufficient infrastructure struggle to scale production efficiently, which limits market growth. This constraint is more pronounced in developing regions, where bio-based feedstock supply chains are not yet fully operational.
Competition with Established Fossil-Based Naphtha
Fossil-based naphtha benefits from an established market and infrastructure, making it challenging for bio-based naphtha to gain significant market share. Fossil naphtha has a mature, cost-effective supply chain and robust customer base across the petrochemical and plastics industries. Despite the environmental benefits of bio-based options, many industries remain reluctant to switch due to the convenience, lower costs, and reliability of fossil-based naphtha. This competition can limit bio-based naphtha adoption, especially in regions or industries without strict environmental regulations incentivizing the switch to renewable alternatives.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets in Asia, Latin America, and Africa present significant growth opportunities for bio-based naphtha as they develop bioeconomy strategies and invest in sustainable industrial materials. Nations like India and Brazil have launched biofuel and bio-based initiatives to reduce fossil dependency, making bio-based naphtha a strategic addition. For example, Brazil’s large agricultural sector provides ample biomass, positioning it as a potential leader in bio-naphtha production. As industrialization continues and regulatory frameworks develop, these regions could drive substantial demand, opening new revenue streams for bio-based naphtha producers.
Advancements in Biomass Processing Technologies
Innovations in biomass conversion technologies, such as catalytic pyrolysis and advanced hydro-processing, offer opportunities to improve the cost and efficiency of bio-based naphtha production. For instance, modern pyrolysis methods have increased bio-yield by over 20%, making bio-naphtha more competitive. These advancements can lower production costs and reduce reliance on traditional feedstocks, enhancing scalability. Continuous technological improvements could address cost-related restraints, positioning bio-based naphtha as a more affordable, attractive alternative across various industries seeking sustainable feedstock options.
Growth in the Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Market
Bio-based naphtha has potential as a blending component in Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), an area with growing interest due to the aviation industry's push for decarbonization. SAF mandates, such as the EU’s “Fit for 55” plan, target a 63% reduction in aviation emissions by 2050, increasing SAF demand. As bio-based naphtha can be refined into jet fuel components, this market segment represents an expanding opportunity for producers. With aviation emissions under scrutiny, bio-naphtha producers could benefit significantly by targeting SAF applications.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fluctuating Biomass Feedstock Prices
The cost of biomass feedstocks, such as vegetable oils and agricultural residues, is highly volatile due to factors like seasonal variations, crop yields, and competing demands from other bio-based industries. This unpredictability can disrupt production planning and inflate bio-based naphtha costs, reducing its competitiveness. For instance, soybean oil prices, a common bio-feedstock, can swing by 20-30% within a year due to weather conditions and global demand. This volatility challenges producers to maintain consistent pricing, which is essential for adoption in cost-sensitive industries.
Complex Production and Conversion Processes
The conversion of biomass to bio-based naphtha involves advanced processing technologies that are complex and require significant capital investment. Processes like gasification, catalytic pyrolysis, and hydro-processing need specialized equipment and expertise, limiting new entrants and scalability. Additionally, these processes have yet to reach the efficiency levels of fossil-based naphtha production, which can deter investment. The complexity and associated high operational costs create a barrier to widespread adoption, especially among smaller firms with limited resources for such investments.
Lack of Consumer Awareness and Market Education
Unlike conventional biofuels and bioplastics, bio-based naphtha lacks broad consumer awareness, which limits demand from downstream industries. While sustainability is a growing focus, the specific applications and benefits of bio-based naphtha are less understood, even among companies seeking eco-friendly feedstocks. Without targeted education campaigns and industry collaboration to promote bio-based naphtha, potential adopters may overlook it in favor of more established renewable alternatives. This lack of market awareness represents a significant barrier to expanding bio-based naphtha's reach, particularly outside niche industrial applications.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
CAGR |
20.8% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Source, Application and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Applied Research Associates, Inc. (ARA), BASF SE, Borealis AG, Covestro AG, Diamond Green Diesel (DGD), Dow, Inc., Royal DSM N.V., Eco-Environmental, Eni Sustainable Mobility, Euglena Co., Ltd., Forge Hydrocarbons Corporation, Fuenix Ecogy, Galp Energia, SGPS, S.A., Gevo, Inc., Honeywell, Ineos Group Limited, Kaidi, LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V., Neste Oyj, Nordic ElectroFuel, Phillips 66, Preem AB, Repsol S.A., Resynergi, Inc., SABIC, Shell, St1 Oy, TotalEnergies Corbion, UPM Biofuels and Versalis SpA. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Source Insights
The vegetable oils segment held 72.2% of the global market share in 2023. The dominance of the vegetable oils segment is majorly driven by the widespread availability and well-developed agricultural infrastructure for oils such as soybean, rapeseed, and especially palm oil, which is primarily produced in Indonesia and Thailand. These two countries alone account for over 80% of global palm oil production, making it a cost-effective and reliable source of biodiesel.

On the other hand, the used cooking oil (UCO) segment is expected to exhibit the fastest CAGR in the global market. This rapid growth is driven by the environmental advantages of recycling waste oil, favorable government policies encouraging low-carbon fuels, and the economic benefits of UCO, which is generally cheaper than virgin oils. The rise of UCO is particularly important to support sustainability goals as it reduces greenhouse gas emissions and aligns with global efforts to promote a circular economy.
By Application Insights
The bio-polyethylene (bio-PE) segment stood as the largest segment and accounted for 50.7% of the global market share in 2023 and the dominance of the segment is majorly attributed to its versatile applications across various industries, including packaging, automotive, and consumer goods. Bio-PE is derived from renewable resources like sugarcane, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional polyethylene. Its widespread adoption is driven by the growing demand for eco-friendly materials and the push towards reducing carbon footprints in manufacturing processes.
On the other hand, the bio-based polypropylene (bio-PP) segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 32.3% over the forecast period. This rapid growth of the bio-based polypropylene (bio-PP) segment is fueled by increasing applications in sectors such as automotive, packaging, and textiles, where bio-PP serves as a sustainable substitute for conventional polypropylene. The surge in bio-PP usage is also propelled by heightened environmental awareness and stringent regulations aimed at reducing reliance on fossil-based plastics. As industries seek greener alternatives, bio-PP's role becomes increasingly vital in advancing sustainability objectives and minimizing environmental impact.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Europe led the market and accounted for 35.6% of the total market share in 2023. Over the forecast period, Europe is also projected to witness a notable CAGR due to its strong regulatory framework favoring low-carbon alternatives and renewable energy. The European Union’s commitment to stringent carbon reduction goals has spurred demand for bio-based feedstocks. Germany, France, and the Netherlands are key countries driving this growth, with considerable investment in bio-based plastics and fuels, making Europe a frontrunner in this market segment.
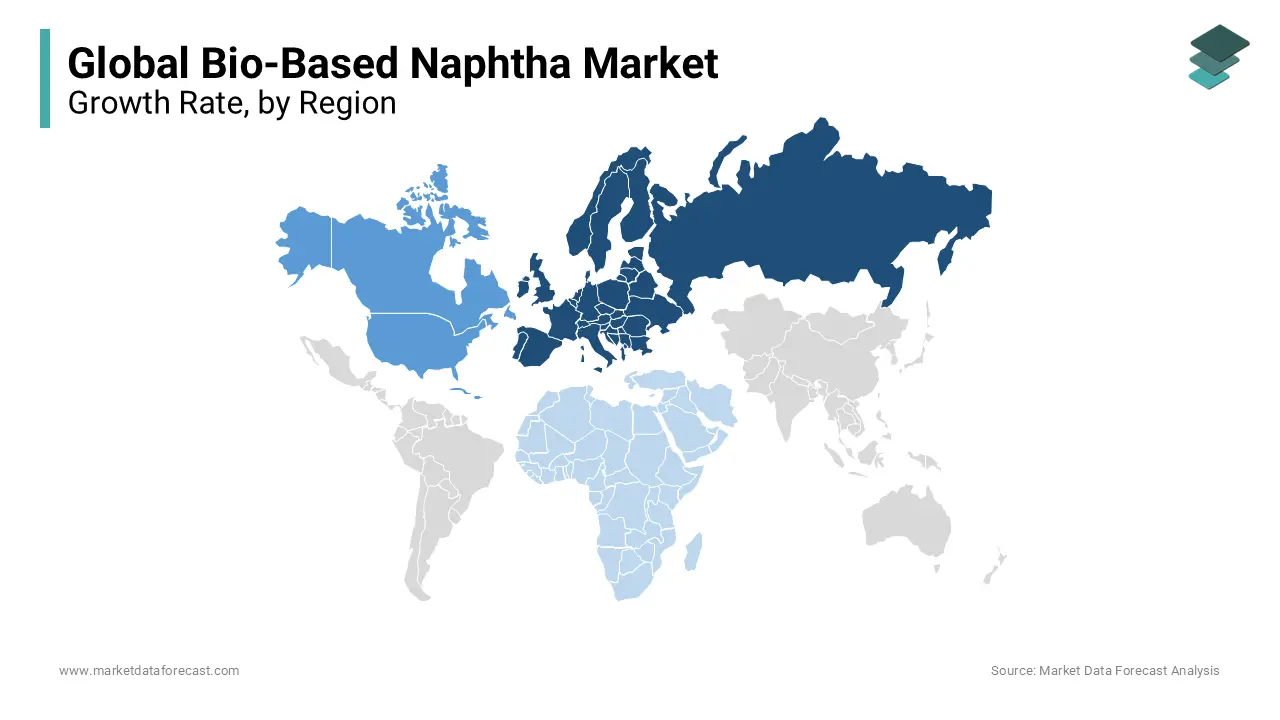
North America held 28.8% of the global market share in 2023 and is likely to showcase a healthy CAGR over the forecast period owing to the high demand for sustainable alternatives in the petrochemical and transportation sectors. The U.S. and Canada are bolstered by favorable policies, and investments in sustainable technology are expected to fuel the continued growth of North America in the global market over the forecast period.
The Asia-Pacific region is estimated to grow at an impressive CAGR of 18.8% over the forecast period and is one of the fastest-growing regions. The rapid expansion of the Asia-Pacific market is majorly driven by increasing industrialization, rising environmental consciousness, and government initiatives to encourage sustainable energy use. China, India, and Japan hold the major share of the Asia-Pacific market as these countries have substantial investments in bio-based technologies and an emphasis on renewable energy.
In Latin America, the bio-based naphtha market is expected to witness a CAGR of 16.2% over the forecast period. The presence of vast agricultural resources to support bio-based production in the Latin American region is driving the regional market growth. Latin America also benefits from a strong base of biomass feedstock, and its focus on renewable energy initiatives is expected to support steady market growth in the future.
The market in the Middle East and Africa is expected to register a steady CAGR in the global market over the forecast period. South Africa and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) lead this region, with an increasing focus on diversifying energy sources through renewable energy investments. Though a smaller share of the market, these countries are enhancing their contributions through supportive energy policies and efforts to build sustainable energy projects, contributing to long-term market growth.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Companies playing a major role in the global bio-based naphtha market include
- Applied Research Associates, Inc. (ARA)
- BASF SE
- Borealis AG
- Covestro AG
- Diamond Green Diesel (DGD)
- Dow, Inc.
- Royal DSM N.V.
- Eco Environmental
- Eni Sustainable Mobility
- Euglena Co., Ltd.
- Forge Hydrocarbons Corporation
- Fuenix Ecogy
- Galp Energia
- SGPS, S.A.
- Gevo, Inc.
- Honeywell
- Ineos Group Limited
- Kaidi
- LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.
- Neste Oyj
- Nordic ElectroFuel
- Phillips 66
- Preem AB
- Repsol S.A.
- Resynergi, Inc.
- SABIC
- Shell
- St1 Oy
- TotalEnergies Corbion
- UPM Biofuels
- Versalis SpA
RECENT MARKET HAPPENINGS
- In July 2024, Petronas, Malaysia's state energy firm, Enilive SpA, an Italian energy company, and Euglena Co., Ltd., a Japanese biotechnology firm, reached a final investment decision to develop a biorefinery in Malaysia's Pengerang. Purpose: This collaboration aims to enhance the production of sustainable aviation fuel, hydrogenated vegetable oil, and bio-naphtha, thereby expanding their presence in the renewable energy sector.
- In April 2024, Eni, an Italian multinational energy company, announced plans to sell minority stakes in its biofuel and bioplastic units. Purpose: This strategic move is intended to raise approximately 1.3 billion euros to fund greener initiatives while maintaining resources for traditional oil and gas operations.
- In June 2024, Global Clean Energy Holdings, Inc., a renewable fuels company, entered into a definitive agreement with ExxonMobil entities to resolve ongoing disputes. Purpose: This settlement, including the termination of prior agreements and cancellation of ExxonMobil’s equity rights, allows Global Clean Energy Holdings to streamline operations and focus on its renewable fuel projects.
- In August 2024, Ineos, a global chemical company, became the sole owner of several chemical units in Lavera, France, after acquiring TotalEnergies' shares. Purpose: This acquisition is expected to strengthen Ineos's market position by consolidating its operations and enhancing its production capabilities in the region.
- In October 2024, QatarEnergy, the state-owned petroleum company of Qatar, signed a 20-year agreement to supply Shell with up to 18 million metric tons of naphtha. Purpose: This long-term deal aims to secure a stable supply of naphtha for Shell, reinforcing its feedstock availability for petrochemical production.
- In April 2023, Neste Oyj, a Finnish oil refining and marketing company, announced plans to expand its production capacity for renewable products in Singapore. Purpose: This expansion is intended to meet the growing global demand for renewable diesel and sustainable aviation fuel, thereby strengthening Neste's position in the renewable energy market.
- In May 2023, LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V., a multinational chemical company, initiated a review of its European assets and sold a Texas unit to INEOS Oxide. Purpose: These actions are aimed at optimizing LyondellBasell's asset portfolio and focusing on core business areas to enhance profitability.
- In July 2023, Mitsui Chemicals, a Japanese petrochemical producer, signed an agreement to procure bio-naphtha from Neste and Toyota Tsusho. Purpose: This procurement aligns with Mitsui Chemicals' 2050 decarbonization goal and supports the production of sustainable plastics.
- In June 2023, BP, a British multinational oil and gas company, consolidated its remaining stake in a Brazilian biofuels joint venture. Purpose: This consolidation adds $800 million of EBITDA and moves BP closer to its $2 billion bioenergy target, reinforcing its commitment to renewable energy.
- In April 2023, Global Clean Energy Holdings, Inc. entered into a Supply and Offtake Agreement with Vitol, an energy and commodities trader, for the exclusive supply and offtake of renewable products from its Bakersfield facility. Purpose: This agreement is expected to ensure a consistent supply chain for renewable diesel and naphtha, enhancing Global Clean Energy Holdings' market presence.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global bio-based naphtha market is segmented and sub-segmented into the source, application and region.
By Source
- Biomass
- Vegetable Oil
- Used Cooking Oil
- Animal Fat
- Others
By Application
- Plastic Production
- Bio Polyethylene
- Bio Polypropylene
- Bio Polyolefins
- Others
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the bio-based naphtha market?
The global bio-based naphtha market was valued at USD 1.54 bn in 2023.
What is the expected CAGR of the bio-based naphtha market?
The bio-based naphtha market is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 20.8% from 2024 to 2032.
Which region dominated the bio-based naphtha market worldwide?
Europe held the major share of the global market in 2023.
Who are the key players in the bio-based naphtha market?
Applied Research Associates, Inc. (ARA), BASF SE, Borealis AG, Covestro AG, Diamond Green Diesel (DGD), Dow, Inc., Royal DSM N.V., Eco Environmental, Eni Sustainable Mobility, Euglena Co., Ltd., Forge Hydrocarbons Corporation, Fuenix Ecogy, Galp Energia, SGPS, S.A., Gevo, Inc., Honeywell, Ineos Group Limited, Kaidi, LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V., Neste Oyj, Nordic ElectroFuel, Phillips 66, Preem AB, Repsol S.A., Resynergi, Inc., SABIC, Shell, St1 Oy, TotalEnergies Corbion, UPM Biofuels and Versalis SpA are a few of the notable players in the global market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]