Asia Pacific Machine Tools Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Segmented By Type, Technology, End-Use, And By Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Machine Tools Market Size
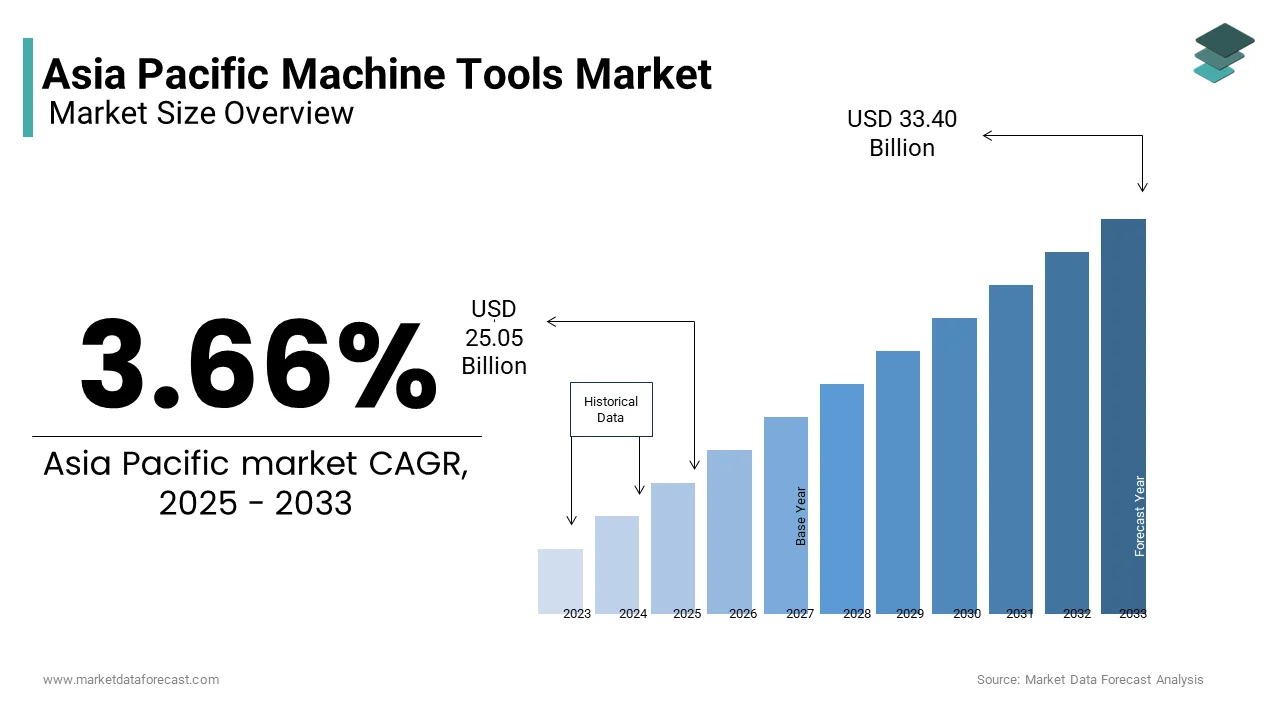
The Asia Pacific Machine tools market size was valued at USD 24.16 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 25.05 billion in 2025 from USD 33.40 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 3.66% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
MARKET DRIVERS
Industrialization and Manufacturing Growth
Rapid industrialization and manufacturing growth are key drivers of the Asia Pacific machine tools market. For example, India’s Make in India initiative aims to increase manufacturing’s share of GDP, notably in the coming years, driving investments in CNC machines and robotics. This dominance drives demand for high-precision tools in sectors like automotive and electronics. Additionally, government initiatives promoting smart factories, such as Japan’s Society 5.0 program, mandate the use of IoT-enabled machine tools, further propelling adoption.
Government Policies Promoting Automation
Government policies promoting automation and smart manufacturing are another major driver, pushing industries to adopt advanced machine tools. For instance, South Korea’s Manufacturing Innovation 3.0 strategy allocates a substantial amount for smart factory projects, including investments in CNC machines and robotics. Similarly, India’s Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation Hubs (SAMARTH) scheme incentivizes small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to upgrade outdated equipment. These regulatory frameworks not only reduce operational costs but also align with global Industry 4.0 goals, fueling market growth.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs and Maintenance Expenses
One of the primary restraints of the Asia Pacific machine tools market is the high initial investment required for installation and maintenance. This financial barrier limits adoption, particularly in developing economies like Bangladesh and Myanmar, where budget constraints are prevalent. For instance, a significant portion of SMEs in Southeast Asia face funding challenges, delaying upgrades to advanced machining solutions.
Additionally, maintenance costs account for a notable share of the total lifecycle expenses. SMEs often find these costs prohibitive, hindering widespread adoption. While leasing models and financing options exist, they remain inaccessible to many stakeholders, particularly in rural or semi-urban areas.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Raw Material Shortages
Another restraint is supply chain disruptions exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and logistical bottlenecks. Natural disasters, such as floods in Thailand and typhoons in the Philippines, further disrupt supply chains, delaying project timelines and increasing operational risks. These challenges not only hinder timely deliveries but also strain relationships with clients, impacting brand reputation and customer loyalty. Addressing these issues requires strategic planning and diversification of supply sources.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration with Smart Manufacturing Technologies
The integration of machine tools with smart manufacturing technologies presents a significant opportunity for the Asia Pacific market. Also, hybrid systems combining IoT-enabled CNC machines and robotics can improve operational efficiency. For instance, India’s Department of Heavy Industry has launched pilot projects integrating machine tools with AI-driven analytics to enhance precision engineering.
This trend is supported by government incentives promoting smart factories. Additionally, advancements in multi-axis designs have made machine tools suitable for decentralized applications, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Expansion into Emerging Applications
Emerging applications, such as renewable energy and electric vehicles (EVs), offer another promising opportunity. Similarly, the renewable energy sector’s focus on turbine manufacturing has increased demand for specialized machine tools. These factors collectively demonstrate how emerging applications are driving demand for innovative machine tool solutions, ensuring long-term market growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Competition from Alternative Technologies
One of the primary challenges facing the Asia Pacific machine tools market is competition from alternative manufacturing technologies. According to IRENA, advancements in additive manufacturing (3D printing) have reduced costs, making them attractive substitutes for traditional machining processes. This trend is reshaping manufacturing policies, with governments prioritizing alternative solutions over conventional designs. South Korea, for example, plans to integrate additive manufacturing into 50% of new industrial projects by 2025, overshadowing investments in traditional machine tools. Additionally, public pressure to adopt cutting-edge technologies is intensifying.
Environmental Concerns and Material Limitations
Another challenge is the environmental concerns associated with the materials used in machine tools. According to the Environmental Defense Fund, the production of steel and aluminum contributes significantly to carbon emissions, raising scrutiny from regulatory bodies. For example, China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment has introduced stricter emission standards for metal processing, increasing compliance costs for manufacturers. Material limitations, such as wear resistance and thermal fatigue, further complicate adoption. These challenges not only increase operational risks but also deter investments, complicating the market’s growth trajectory.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
3.66% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Tools Type, Technology, End-Use, And Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Allied Machine & Engineering, AMADA Holdings, Dalian Machine Tool Group, DMG MORI, Falcon Machine Tools, 600 Group, Yamazaki Mazak, Trumpf, Komatsu, and JTEKT. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Tools Type Insights
The metal cutting segment dominated the Asia Pacific machine tools market by capturing a 65.6% of the total share in 2024. This leading position is driven by its widespread application in precision engineering and high-precision manufacturing processes. For instance, China’s Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has mandated increased adoption of advanced machining technologies in sectors like electronics and automotive, driving demand for metal cutting tools. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing further reinforce this trend. Additionally, advancements in IoT-enabled metal cutting tools have enhanced operational efficiency, making them indispensable for industries requiring high accuracy.
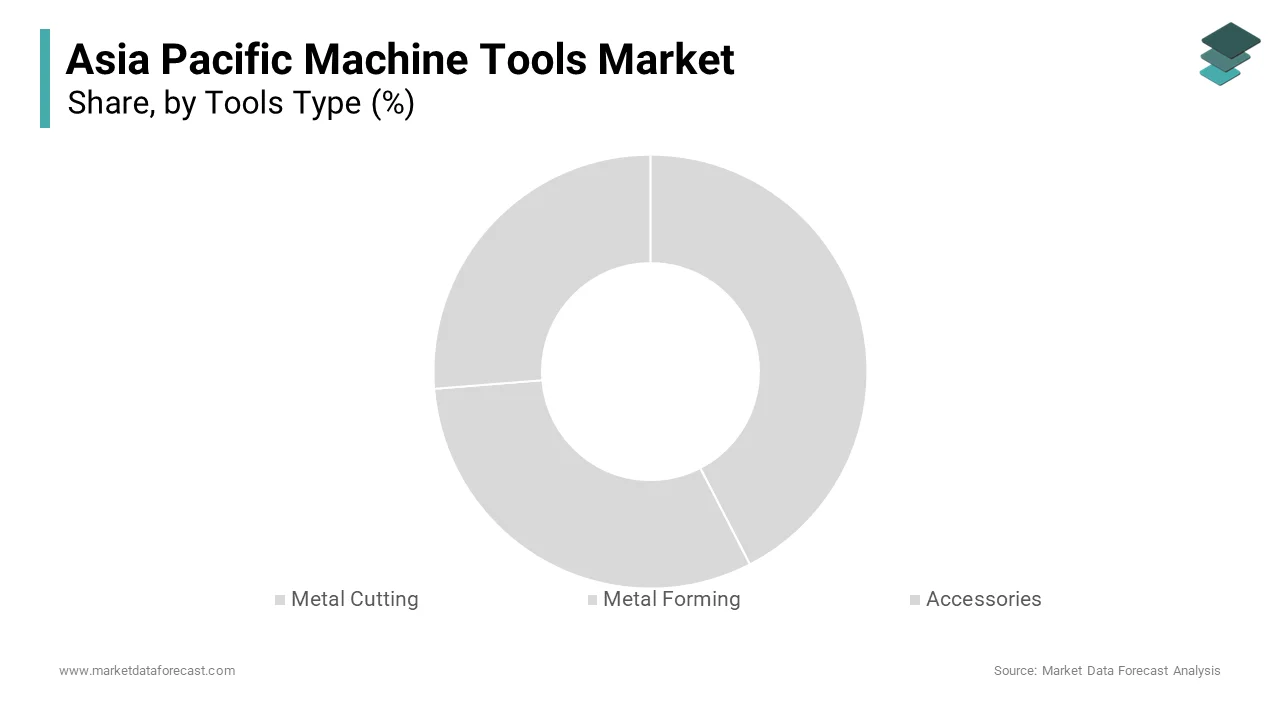
The metal forming segment is the fastest-growing, with a projected CAGR of 8.2%. This is fueled by its increasing use in emerging applications such as electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy. The rise of lightweight materials in the automotive and aerospace industries also drives adoption. Additionally, innovations in hydraulic and servo-driven presses have improved precision and speed, positioning metal forming as the fastest-growing segment in the market.
By Technology Insights
The CNC segment prevailed in the Asia Pacific machine tools market by holding a substantial share in 2024. This dominance is attributed to its superior precision, flexibility, and ability to integrate with smart manufacturing systems. According to the International Federation of Robotics, CNC machines account for a significant share of industrial automation projects in the region, exhibiting their critical role in modern manufacturing. Government policies promoting Industry 4.0 further bolster this trend. Additionally, advancements in multi-axis designs have improved productivity, making CNC machines indispensable for sectors like automotive and electronics.
The conventional segment is quickly advancing, with a CAGR of 7.5%. This upward trajectory is propelled by its affordability and suitability for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). For example, the rise of decentralized manufacturing hubs further accelerates adoption. Like, a significant share of SMEs in Southeast Asia rely on conventional tools for localized production, creating a strong pipeline for growth. Additionally, advancements in durability and ease of maintenance have extended equipment lifespan, making them cost-effective for long-term use.
By End Use Insights
The automotive segment commanded the Asia Pacific machine tools market by capturing 45.4% of the total share in 2024. This top spot is propelled by the region’s booming automotive industry, which accounts for a considerable share of global vehicle production. For instance, China’s automotive sector alone contributes significantly to the economy, creating a robust demand for precision machining solutions in engine and transmission manufacturing. Government mandates promoting EVs further reinforce this trend. Additionally, advancements in multi-axis designs have improved productivity, making machine tools indispensable for modern automotive applications.
The mechanical engineering segment is quickly expanding, with a CAGR of 9.0%. This progress is caused by its increasing use in emerging applications such as renewable energy and industrial machinery. The rise of smart factories also drives adoption. Also, IoT-enabled machine tools improve operational efficiency, making them ideal for precision engineering in mechanical components. Besides, government incentives promoting advanced manufacturing have accelerated demand for specialized tools, positioning mechanical engineering as the fastest-growing end-use segment.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
China led the Asia Pacific machine tools market by holding a 40.5% of the regional share in 2024. The country’s dominance is driven by its massive industrial base, particularly in sectors like automotive, electronics, and aerospace. Government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing further reinforce this trend. For instance, China’s Made in China 2025 strategy mandates increased adoption of CNC machines and robotics, reducing reliance on imported tools. Additionally, advancements in IoT-enabled machine tools have improved operational efficiency, making them indispensable for large-scale industrial projects. These factors ensure China’s leadership in the market.
Japan is another key player in the market share and is driven by its focus on precision engineering and automation. Like, the country allocates a significant amount annually to develop advanced manufacturing technologies, including CNC machines and robotics. The emphasis on carbon neutrality further drives adoption. For instance, Japan’s Society 5.0 program promotes smart factories, mandating the use of IoT-enabled machine tools. Additionally, innovations in multi-axis designs have improved productivity, making them ideal for high-precision applications in automotive and electronics.
India holds a notable share of the market, with a strong emphasis on industrial modernization and government-led initiatives. Also, India’s Make in India program aims to increase manufacturing’s share of GDP by 2025, driving investments in CNC machines and robotics. The rise of EV manufacturing further accelerates adoption. Additionally, advancements in affordable designs have made machine tools accessible to SMEs, ensuring sustained market growth.
South Korea accounts for a considerable portion of the market, driven by its Manufacturing Innovation 3.0 strategy. Machine tools are integral to this initiative, particularly in sectors like automotive and electronics. The rise of EVs and renewable energy further boosts demand.
Australia & New Zealand hold a smaller share of the market, with a focus on renewable energy integration and industrial modernization. New Zealand’s commitment to sustainability has spurred demand for advanced designs, such as CNC machines, in food processing and packaging. Apart from these, Australia’s booming mining sector has increased demand for robust machine tools in mineral processing.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Allied Machine & Engineering, AMADA Holdings, Dalian Machine Tool Group, DMG MORI, Falcon Machine Tools, 600 Group, Yamazaki Mazak, Trumpf, Komatsu, and JTEKT are some of the key players in the Asia Pacific machine tools market.
Top Players in the Asia Pacific Machine Tools Market
DMG Mori Co., Ltd.
DMG Mori is a global leader in the machine tools market, renowned for its advanced CNC machining solutions tailored to high-precision industries like aerospace and automotive. The company has strengthened its presence in Asia Pacific by establishing regional manufacturing hubs in China and India. Additionally, it partnered with local SMEs in Southeast Asia to provide affordable yet reliable machining solutions, enhancing accessibility across the region.
Yamazaki Mazak Corporation
Yamazaki Mazak plays a pivotal role in the Asia Pacific market, offering cutting-edge multi-axis CNC machines designed for complex manufacturing needs. The company focuses on innovation, introducing AI-driven analytics to optimize machining processes. Its R&D investments have improved operational efficiency, making it a preferred choice for large-scale projects in sectors like automotive and electronics.
Haas Automation, Inc.
Haas Automation is a key player in the Asia Pacific market, leveraging its expertise in cost-effective and durable machine tools. The company focuses on affordability, launching budget-friendly CNC machines tailored to SMEs in emerging economies like Vietnam and Indonesia. Its emphasis on sustainability and customer-centric designs ensures long-term market presence and strengthens its reputation as an innovative player.
Top Strategies Used By Key Market Participants
Key players in the Asia Pacific machine tools market employ diverse strategies to maintain their competitive edge. Innovation is central, with companies investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced technologies like AI-driven analytics and IoT-enabled systems. Partnerships and collaborations are another critical strategy; Yamazaki Mazak partners with regional industries to enhance accessibility, while Haas Automation collaborates with governments to promote sustainable manufacturing.
Expansion into emerging markets is also a priority. Companies are establishing manufacturing units and service centers in countries like Vietnam and Thailand to cater to growing demand. Additionally, mergers and acquisitions play a pivotal role. Sustainability initiatives are gaining traction, with firms adopting eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs to align with government regulations. These strategies collectively ensure that key players remain at the forefront of technological advancements while addressing the unique demands of the Asia Pacific market.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific machine tools market is highly competitive, driven by the presence of both global giants and regional players. Global leaders like DMG Mori, Yamazaki Mazak, and Haas Automation dominate through technological superiority and extensive distribution networks, while regional players focus on affordability and localized solutions. Price wars are common, particularly in price-sensitive markets like India and Indonesia, where smaller firms struggle to compete with established brands.
Government policies promoting automation and smart manufacturing have intensified rivalry, as companies race to capture contracts for large-scale industrial projects. For instance, budget constraints in Southeast Asia have created a battleground for cost-effective solutions. Additionally, the rise of alternative manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing, poses a significant challenge, forcing machine tool manufacturers to innovate or risk obsolescence. Despite these challenges, the market remains dynamic, with innovation and strategic collaborations serving as key differentiators.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2023, DMG Mori launched its next-generation IoT-enabled CNC machines in Japan, offering real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. This move aimed to strengthen its presence in high-precision industries like aerospace and automotive.
- In May 2023, Yamazaki Mazak expanded its service network in Australia and New Zealand, ensuring better after-sales support for industrial clients. This initiative improved customer satisfaction and loyalty in the region.
- In July 2023, Haas Automation introduced its new line of eco-friendly machining solutions in South Korea, reducing operational costs by 20%. This aligned with the country’s carbon neutrality goals and positioned Haas as a leader in sustainable manufacturing.
- In September 2023, DMG Mori acquired a regional firm in India to enhance its manufacturing capabilities and offer comprehensive machining solutions. This acquisition improved accessibility for SMEs in emerging markets.
- In November 2023, Yamazaki Mazak partnered with local industries in Vietnam to provide affordable multi-axis CNC machines, catering to the growing demand for precision engineering solutions.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific machine tools market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Tool Type
- Metal Cutting
- Metal Forming
- Accessories
By Technology Type
- Conventional
- CNC (Computerized Numerical Control)
By End-Use Industry
- Automotive
- Aerospace and Defense
- Electrical and Electronics
- Consumer Goods
- Precision Engineering
- Others
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What are machine tools, and how are they used across industries in the Asia Pacific region?
Machine tools are mechanical devices used to cut, shape, and form materials into finished components, widely applied in automotive, aerospace, electronics, and heavy machinery sectors across Asia Pacific.
What’s driving the growth of the machine tools market in Asia Pacific?
Key growth factors include rapid industrialization, rising demand for high-precision parts in automotive and electronics, expansion of manufacturing hubs in countries like China, India, Vietnam, and government-led smart manufacturing initiatives.
How is technology transforming the machine tools landscape in this region?
Technological advancements such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control), automation, additive manufacturing, and IoT integration are enhancing productivity, reducing labor dependency, and enabling high-efficiency, precision-driven machining processes.
What are the major challenges facing the Asia Pacific machine tools industry?
Challenges include high initial costs for advanced machines, a growing skills gap in operating CNC and automated tools, competition from low-cost imports, and vulnerability to raw material price fluctuations.
What is the future outlook for the machine tools market in Asia Pacific?
The future is promising with strong demand from emerging economies, ongoing investment in smart factories, and increased focus on sustainability, energy efficiency, and hybrid manufacturing systems to meet global quality standards.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]