Asia Pacific Electrolyzer Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Segmented By Capacity, Technology, Application, And By Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Electrolyzer Market Size
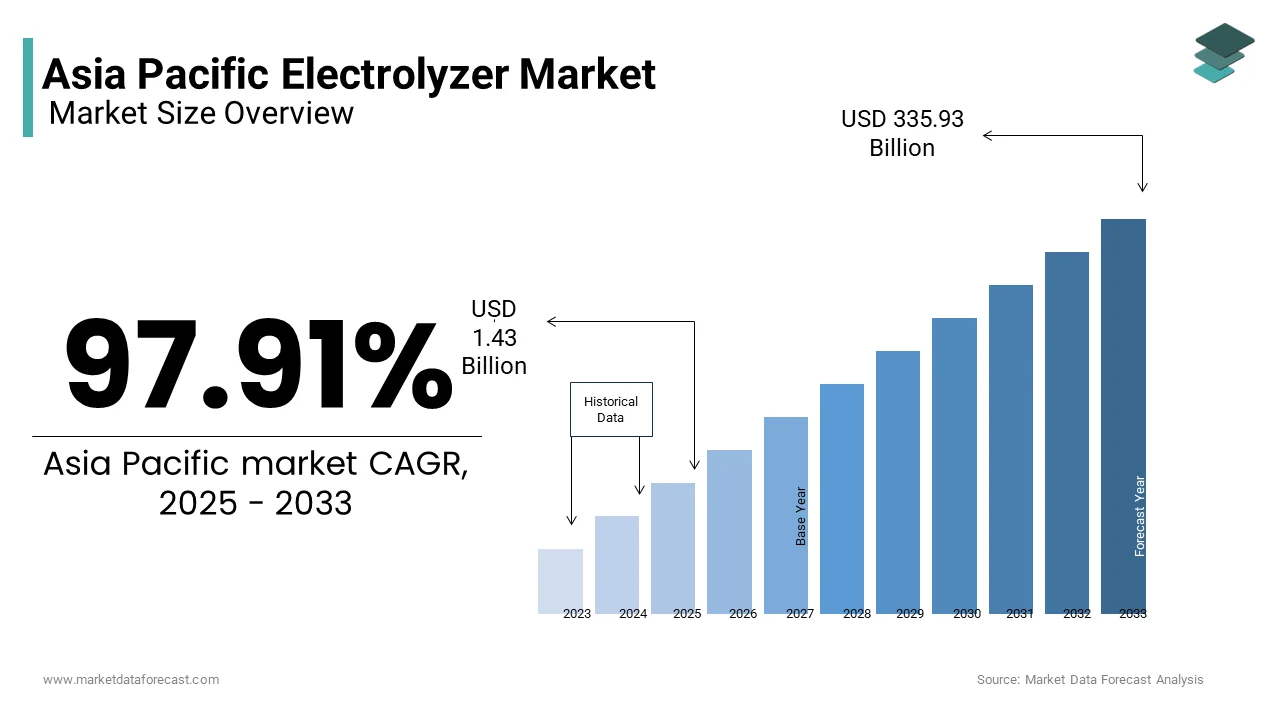
The Asia Pacific electrolyzer market size was valued at USD 0.72 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1.43 billion in 2025 from USD 335.93 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 97.91% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is emerging as a pivotal segment in the region’s transition toward sustainable energy solutions. According to BloombergNEF, the global demand for green hydrogen is projected to grow exponentially, with the Asia Pacific region accounting for nearly 40% of this demand by 2030. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are at the forefront of adopting electrolyzer technologies to produce hydrogen for industrial applications, transportation, and energy storage. The market is driven by government initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero targets. For instance, as per the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), China has committed to installing 50 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2030, positioning itself as a leader in large-scale hydrogen production.
Japan and South Korea, on the other hand, are focusing on developing advanced electrolyzer systems to support their hydrogen fuel cell vehicle industries. As per a study by the Hydrogen Council, the Asia Pacific region is expected to invest over USD 100 billion in hydrogen infrastructure by 2030, with electrolyzers playing a central role. The market conditions reflect a balance between technological innovation and policy-driven growth, supported by declining costs of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, which are essential for powering electrolyzer systems. This dynamic environment underscores the region's commitment to scaling up green hydrogen production.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Demand for Green Hydrogen
One of the primary drivers of the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is the surging demand for green hydrogen as a clean energy carrier. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global hydrogen demand is expected to increase by 50% by 2030, with the Asia Pacific region leading this growth. Green hydrogen, produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy, is gaining traction due to its potential to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors such as steel, chemicals, and refineries. In China, as per the National Development and Reform Commission, the government aims to achieve 100% renewable-powered hydrogen production by 2060, driving investments in electrolyzer technologies. Additionally, countries like Japan and South Korea are leveraging green hydrogen to meet their Paris Agreement commitments. For example, as per the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) in Japan, the country plans to establish a hydrogen supply chain capable of producing 3 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2030, requiring significant electrolyzer capacity.
Government Policies and Subsidies
Government policies and subsidies are another critical driver propelling the adoption of electrolyzers in the region. For instance, South Korea’s Hydrogen Economy Roadmap allocates USD 38 billion to develop hydrogen infrastructure, including funding for electrolyzer projects. Similarly, Australia’s National Hydrogen Strategy provides tax breaks and grants for companies investing in green hydrogen technologies. These initiatives are complemented by international collaborations, such as the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) framework, which fosters cross-border partnerships to advance hydrogen technologies.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Capital Costs
One of the significant restraints hindering the growth of the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is the high initial capital investment required for setting up electrolyzer systems. This financial barrier poses challenges, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and developing economies like Vietnam and Indonesia, where access to affordable financing remains limited. Additionally, as per the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the absence of standardized pricing models for electrolyzer components further complicates cost estimations, discouraging potential investors. While advancements in technology are gradually reducing costs, the current expense of deploying electrolyzers remains a deterrent for industries seeking immediate returns on investment, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Limited Availability of Skilled Workforce
Another restraint is the shortage of skilled professionals capable of operating and maintaining advanced electrolyzer systems. According to the World Economic Forum, the renewable energy sector faces a global talent gap, with an estimated 14 million new jobs needed by 2030 to meet sustainability goals. In the Asia Pacific region, this issue is exacerbated by the rapid pace of technological adoption outpacing workforce training programs. For instance, as per the Asian Development Bank, less than 20% of engineering graduates in Southeast Asia receive specialized training in hydrogen technologies, leaving a critical skills deficit. This lack of expertise not only delays project timelines but also increases operational risks, as improper handling of electrolyzers can lead to inefficiencies or safety hazards.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration with Renewable Energy Systems
One promising opportunity for the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market lies in its integration with renewable energy systems, particularly solar and wind power. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the region accounts for over 50% of global renewable energy capacity additions, creating a robust foundation for coupling electrolyzers with clean energy sources. In Australia, as per the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), large-scale solar farms are being paired with electrolyzer systems to produce green hydrogen for export markets, particularly in Japan and South Korea. This synergy not only enhances the economic viability of renewable projects but also addresses intermittency issues by using hydrogen as a storage medium. Such initiatives position the region as a global leader in renewable energy-based hydrogen production.
Expansion of Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure
Another significant opportunity arises from the expansion of hydrogen refueling infrastructure to support the growing fleet of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). According to the Hydrogen Council, the Asia Pacific region is projected to host over 10,000 hydrogen refueling stations by 2030, with electrolyzers playing a crucial role in supplying green hydrogen. Japan and South Korea are pioneers in this space, with Toyota and Hyundai leading the development of FCVs. As per METI in Japan, the country aims to deploy 800,000 FCVs and 900 refueling stations by 2030, requiring substantial electrolyzer capacity. Similarly, South Korea’s roadmap includes establishing 660 refueling stations by 2030, supported by localized hydrogen production.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Scalability Issues in Large-Scale Deployment
One of the foremost challenges facing the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is the difficulty in scaling up deployment to meet the demands of large-scale hydrogen production. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), while pilot projects have demonstrated the feasibility of electrolyzer technologies, transitioning to gigawatt-scale operations presents significant technical and logistical hurdles. For instance, as per a study by the Energy Transitions Commission, scaling up electrolyzers requires overcoming challenges related to material availability, system efficiency, and grid integration. In countries like India and Indonesia, where energy grids are often unstable, integrating electrolyzers with intermittent renewable energy sources poses additional complexities.
Dependence on Imported Technologies
Another pressing challenge is the region’s heavy reliance on imported electrolyzer technologies, which limits local innovation and increases costs. According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), a significant portion of electrolyzer components used in the Asia Pacific are sourced from Europe and North America, where companies like Nel ASA and ITM Power dominate the market. This dependence creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain, as geopolitical tensions or trade restrictions can disrupt access to critical technologies. For example, as per the Asian Development Bank, the imposition of tariffs on imported electrolyzer systems could increase project costs by up to 25%, particularly in countries like Vietnam and Thailand. Additionally, the lack of indigenous manufacturing capabilities stifles the development of cost-effective solutions tailored to regional needs. Encouraging local R&D and fostering partnerships with global leaders are essential to reducing this dependency and ensuring sustainable growth.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
97.91% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Capacity, Technology, Application, And Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ThyssenKrupp nucera (Germany), John Cockerill (Belgium), Nel ASA (Norway), Plug Power Inc. (U.S.), Siemens Energy (Germany), Enapter S.r.l. (Italy), Cummins Inc. (U.S.), ITM Power (U.K.), McPhy Energy S.A. (France), Topsoe (Denmark) and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Capacity Insights
The "Above 2 MW" segment dominated the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market by holding a market share of a 45.6% in 2024. This is driven by the increasing demand for large-scale hydrogen production to meet industrial and energy needs. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), industries such as steel, chemicals, and refineries require massive hydrogen volumes, making high-capacity electrolyzers indispensable. For instance, China’s ambitious hydrogen strategy includes installing over 50 GW of electrolyzer capacity by 2030, with most projects focusing on systems above 2 MW to achieve economies of scale. Additional factor is the integration of these systems with renewable energy sources like solar and wind farms. As per the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), Australia is developing utility-scale electrolyzer facilities capable of producing green hydrogen for export markets, particularly in Japan and South Korea, further strengthening the dominance of this segment.
The "Less than 500 kW" segment is the fastest-growing category in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market, with a projected CAGR of 18.5% from 2025 to 2033. This rise is fueled by the rising adoption of modular and decentralized hydrogen production systems, particularly in urban areas and remote locations. South Korea, for example, as per METI, is deploying compact electrolyzers to support its growing fleet of FCVs, aiming to establish 900 refueling stations by 2030. Moreover, as per the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the declining costs of renewable energy technologies have made small-scale electrolyzers more accessible, enabling businesses and communities to produce hydrogen on-site.
By Technology Insights
The segment of Alkaline electrolyzers spearheaded the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market by accounting for a 60.4% of the share in 2024. This leading position is supported by their proven reliability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to operate at high capacities. Also, alkaline electrolyzers are widely used in industrial applications such as ammonia production and refineries due to their robust performance and compatibility with low-cost materials. For instance, China’s National Development and Reform Commission highlights that over 70% of the country’s electrolyzer installations utilize alkaline technology, driven by its scalability and efficiency in large-scale hydrogen production. Also, as per the Hydrogen Council, the availability of standardized components and established supply chains for alkaline electrolyzers makes them a preferred choice for projects requiring rapid deployment. Furthermore, advancements in system design have improved their efficiency, reducing electricity consumption, further enhancing their appeal in cost-sensitive markets.
The proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzers segment represented the swiftly advancing category in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market, with a estimated CAGR of 20.3%. This development is caused by their superior performance characteristics, including faster response times and higher purity hydrogen output, which make them ideal for dynamic applications. Also, PEM electrolyzers are increasingly being adopted in transportation and energy storage sectors, where flexibility and efficiency are critical. Japan, for example, as per METI, is investing heavily in PEM technology to support its hydrogen fuel cell vehicle industry, aiming to deploy 800,000 FCVs by 2030. The push for renewable energy integration has also accelerated their adoption, as PEM electrolyzers can seamlessly couple with intermittent solar and wind power sources, ensuring consistent hydrogen production.
By Application Insights
The industry feedstock segment became the largest application in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market, with a market share of 50.6%, as per the International Energy Agency (IEA). This dominance is attributed to the extensive use of hydrogen in industrial processes such as ammonia synthesis, methanol production, and oil refining. Additionally, as per the Hydrogen Council, the chemical industry alone consumes over 50 million tons of hydrogen annually, underscoring the critical role of electrolyzers in meeting this demand sustainably. The shift toward green hydrogen production is further amplifying the segment’s growth, as industries seek to decarbonize their operations while maintaining operational efficiency.
The transportation category is rapidly emerging application segment in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market, with a calculated CAGR of 22.5%. This is propelled by the increasing adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and the expansion of hydrogen refueling infrastructure. Similarly, South Korea’s roadmap includes setting up 660 refueling stations by 2030, supported by localized hydrogen production. As per the Hydrogen Council, the transportation sector’s demand for hydrogen is expected to grow by 25% annually, driven by government policies promoting clean mobility solutions. Additionally, regional collaborations, such as the ASEAN Hydrogen Initiative, are fostering cross-border trade and infrastructure development, further accelerating the segment’s growth.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Top 5 Leading Countries in the Market
China was at the forefront of the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market by accounting for a 40.6% of regional capacity in 2024. The country’s dominance is driven by its aggressive hydrogen strategy. According to the National Development and Reform Commission, China is leveraging electrolyzers to decarbonize key industries such as steel, chemicals, and refineries. The government’s focus on achieving net-zero emissions by 2060 has accelerated investments in green hydrogen production, supported by subsidies and tax incentives. Additionally, China’s robust manufacturing capabilities enable it to produce electrolyzers at competitive prices, further reinforcing its leadership in the market.

Japan holds a significant position in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market which is driven by its commitment to becoming a hydrogen-based society. According to study, the country aims to produce 3 million tons of hydrogen annually by 2030, requiring substantial electrolyzer capacity. Japan’s focus on hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and refueling infrastructure has positioned it as a leader in transportation applications. As per the Hydrogen Council, Japan is investing USD 3 billion annually in hydrogen technologies, including advanced electrolyzer systems. The country’s emphasis on innovation and international collaboration ensures its continued prominence in the market.
South Korea is a key player in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market and is known for its cutting-edge hydrogen technologies. Hyundai’s leadership in FCVs has spurred demand for green hydrogen, driving investments in PEM electrolyzers.
Australia ranks among the top countries in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market by leveraging its abundant renewable energy resources. Also, the country is developing utility-scale electrolyzer facilities to produce green hydrogen for export markets, particularly Japan and South Korea. In addition, Australia’s strategic location and strong trade relationships position it as a global supplier of hydrogen, driving investments in large-scale electrolyzer systems.
India is emerging as a significant player in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market and is driven by its focus on renewable energy integration. As per the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), India’s declining renewable energy costs and supportive government policies create a conducive environment for electrolyzer adoption, ensuring steady market growth.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies playing a prominent role in the Asia Pacific electrolyzers market include ThyssenKrupp nucera (Germany), John Cockerill (Belgium), Nel ASA (Norway), Plug Power Inc. (U.S.), Siemens Energy (Germany), Enapter S.r.l. (Italy), Cummins Inc. (U.S.), ITM Power (U.K.), McPhy Energy S.A. (France), Topsoe (Denmark) and Others.
Top Players In The Market
Nel ASA
Nel ASA is a global leader in electrolyzer technology, with a significant presence in the Asia Pacific region. The company specializes in both alkaline and PEM electrolyzers, offering scalable solutions for green hydrogen production. Nel’s expertise lies in developing cutting-edge systems that integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources, making it a preferred partner for large-scale industrial projects. Its collaborations with regional governments and private players have strengthened its market position, enabling it to cater to diverse applications such as transportation and industrial feedstock. Nel’s commitment to innovation and sustainability ensures its leadership in advancing clean energy solutions across the region.
ITM Power
ITM Power is a prominent player in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market, renowned for its advanced PEM electrolyzer systems. The company focuses on delivering high-purity hydrogen for applications like fuel cell vehicles and energy storage. ITM Power’s strategic partnerships with key stakeholders in Japan and South Korea have facilitated the deployment of its technologies in cutting-edge hydrogen projects.
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy is another key player driving innovation in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market. The company leverages its expertise in engineering and renewable energy integration to deliver robust electrolyzer systems tailored to industrial needs. Siemens’ focus on large-scale hydrogen production aligns with the region’s ambitious decarbonization goals, particularly in sectors like steel and chemicals.
Top Strategies Used By Key Market Participants
Collaborations with Regional Governments
Key players in the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market are actively collaborating with regional governments to align with national hydrogen strategies and secure funding for large-scale projects. These partnerships enable companies to navigate regulatory frameworks and gain access to subsidies, fostering the development of green hydrogen ecosystems. For instance, joint ventures with government bodies facilitate the establishment of hydrogen hubs and refueling infrastructure, ensuring long-term growth opportunities for electrolyzer manufacturers.
Investment in R&D for Technological Advancements
Investment in research and development is a cornerstone strategy for strengthening market presence. Companies are focusing on enhancing electrolyzer efficiency, reducing costs, and improving durability to meet the demands of diverse applications. By innovating materials and system designs, players can offer differentiated solutions that cater to specific customer needs. This emphasis on technological leadership not only enhances competitiveness but also accelerates the adoption of green hydrogen technologies across the region.
Expansion of Local Manufacturing Facilities
To meet growing demand, key players are expanding their manufacturing capabilities within the Asia Pacific region. Establishing localized production facilities reduces lead times, lowers transportation costs, and ensures proximity to critical markets. Additionally, these expansions create jobs and foster skill development, contributing to regional economic growth.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the presence of global giants like Nel ASA, ITM Power, and Siemens Energy, alongside emerging regional players. Global leaders leverage their technological expertise and extensive distribution networks to dominate large-scale projects, while regional players focus on niche markets, offering cost-effective and customized solutions. The competitive landscape is shaped by factors such as innovation, scalability, and sustainability, with companies striving to differentiate themselves through unique value propositions. Rising demand from industries like transportation, power generation, and industrial feedstock intensifies rivalry, pushing players to adopt aggressive strategies. These include forming strategic alliances, investing in R&D, and expanding production capacities. Moreover, the growing emphasis on green hydrogen production adds another layer of complexity, compelling companies to align with evolving regulatory frameworks and consumer preferences.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, Nel ASA partnered with a leading Japanese energy company to deploy large-scale alkaline electrolyzers for hydrogen production in Tokyo. This collaboration aims to support Japan’s goal of establishing a hydrogen-based society by 2050.
- In June 2023, ITM Power announced the expansion of its manufacturing facility in South Korea to meet rising demand for PEM electrolyzers. This move is expected to enhance local supply chain capabilities and reduce delivery timelines.
- In February 2023, Siemens Energy signed a memorandum of understanding with the Indian government to develop a gigawatt-scale green hydrogen project. This initiative underscores Siemens’ commitment to supporting India’s renewable energy goals.
- In September 2022, Nel ASA launched a pilot program in Australia to integrate its electrolyzers with solar farms, producing green hydrogen for export to Japan. This project highlights Nel’s focus on cross-border hydrogen trade.
- In November 2021, ITM Power collaborated with Hyundai to supply PEM electrolyzers for South Korea’s expanding network of hydrogen refueling stations, reinforcing its position in the transportation sector.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Capacity
- 500 kW to 2 MW
- Less than 500 kW
- Above 2 MW
By Technology
- Alkaline Electrolyzer
- Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer
- Solid Oxide (SOE) Electrolyzer
- Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) Electrolyzer
By Application
- Power Generation
- Industry Feedstock
- Transportation
- Building Heat & Power
- Industry Energy
- Others
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an electrolyzer, and how is it used in the Asia Pacific region?
An electrolyzer is a device that splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity. In Asia Pacific, it's used to produce clean hydrogen for energy storage, industrial processes, transportation fuel, and decarbonizing heavy industries.
What is driving the growth of the electrolyzer market in Asia Pacific?
Key growth drivers include ambitious national hydrogen strategies (especially in Japan, South Korea, Australia, and India), rising investments in renewable energy, and the urgent push to reduce carbon emissions from manufacturing and transport sectors.
What are the main application sectors for electrolyzers in the region?
Electrolyzers are being adopted in green hydrogen production, ammonia and methanol synthesis, steel manufacturing, fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), and grid energy storage systems, with increasing focus on integrating solar and wind energy sources.
What challenges are hindering widespread electrolyzer deployment in Asia Pacific?
Barriers include high capital costs, lack of large-scale hydrogen infrastructure, inconsistent policy support across countries, and the need for low-cost renewable electricity to make green hydrogen commercially viable.
What future trends are shaping the Asia Pacific electrolyzer market?
The future is moving toward modular, scalable electrolyzer systems, localized hydrogen hubs, cross-border hydrogen trade, and next-gen technologies like solid oxide and anion exchange membrane (AEM) electrolyzers for improved efficiency and durability.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]