Global Aluminium Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Product (Sheet, Plate, Cast Products, Extrusion, Others), Alloy Type, End-use, and Region (Latin America, North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis from 2025 to 2033
Global Aluminium Market Size
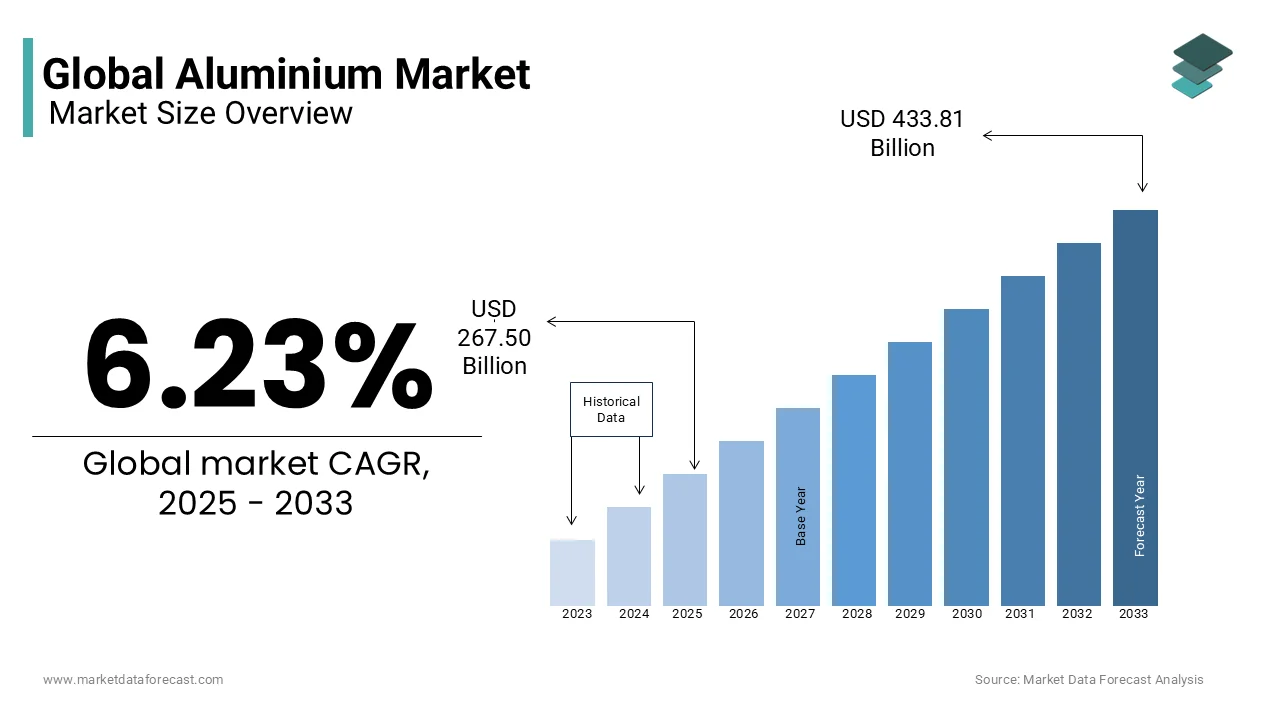
The global Aluminium market size was valued at USD 251.81 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 433.81 billion by 2033 from USD 267.50 billion in 2025. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.23%.
Aluminum is special because it is lightweight, doesn’t rust easily, conducts heat well, and can be recycled endlessly. This makes it a popular choice for projects that need to be both efficient and eco-friendly. In 2023, aluminium continues to be widely used in daily life. For example, the Aluminum Association says that about 75% of all the aluminium ever made is still being used today. This shows how good aluminium is at being reused and helping save resources.
Aluminium is not just important for industries; it also has a big impact on society. It helps make buildings more energy-efficient. The World Green Building Council found that buildings using a lot of aluminium can save up to 30% on energy use. Aluminium is also crucial for clean energy solutions, as it is used in solar panel frames and power lines. In transportation, its light weight makes vehicles more fuel-efficient. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) says replacing steel parts with aluminium in cars can reduce their weight by up to 40%, which cuts down on harmful emissions. Aluminium is also widely used in food packaging. Industry experts estimate that over 70% of canned drinks worldwide are made from aluminium. These facts show how aluminium contributes to technology, sustainability, and convenience, making it a material that will remain important for years to come.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Demand for Lightweight Materials in Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is a major driver of the aluminium market due to the increasing demand for lightweight materials that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, the global electric vehicle (EV) fleet surpassed 26 million units in 2022, with aluminium playing a critical role in EV manufacturing. Aluminium reduces vehicle weight by up to 40% compared to traditional steel, as confirmed by the Environmental Protection Agency. This shift is driven by stringent emission regulations, such as Europe’s target to cut CO2 emissions from cars by 55% by 2030. Additionally, Ducker Worldwide reports that the average aluminium content in cars is expected to rise from 179 kg in 2020 to 227 kg per vehicle by 2026. The surge in EV adoption and regulatory pressures underscores aluminium's pivotal role in modern vehicle design.
Expansion of Renewable Energy Infrastructure
The growth of renewable energy infrastructure is another significant driver of the aluminium market. Aluminium is extensively used in solar panel frames, wind turbine components, and power transmission systems due to its durability and conductivity. The International Renewable Energy Agency states that global renewable energy capacity reached 3,372 gigawatts in 2022, with solar energy accounting for over 1,000 gigawatts. Each megawatt of solar power requires approximately 20 tonnes of aluminium, as reported by the World Bank. Furthermore, the Global Wind Energy Council that the wind energy sector installed 93 gigawatts of new capacity in 2022, further boosting aluminium demand.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Disruptions
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes are increasingly becoming a significant restraint on the aluminium market. The global supply chain for aluminium is highly dependent on key producing countries like China, Russia, and Australia, which together account for over 60% of global production, as reported by the United States Geological Survey. Political conflicts, such as sanctions or export restrictions, can severely disrupt supply flows. For instance, sanctions imposed on Russian aluminium producers in 2022 led to a 15% spike in global aluminium prices, according to data from the London Metal Exchange. Additionally, trade tariffs, such as those implemented by the U.S. under Section 232, have further complicated international trade dynamics. These geopolitical uncertainties create volatility in pricing and supply, making it difficult for manufacturers to plan long-term investments. As global political landscapes remain unpredictable, these disruptions pose a significant challenge to the stability of the aluminium market.
Limited Availability of High-Quality Bauxite Reserves
Another critical restraint is the declining availability of high-quality bauxite reserves, which are essential for aluminium production. Bauxite is the primary raw material used in alumina refining, and its quality directly impacts production efficiency and costs. According to the World Bank, over 70% of global bauxite resources are concentrated in just five countries: Guinea, Australia, Brazil, Vietnam, and Jamaica. However, many of these reserves are located in regions with infrastructural challenges, making extraction costly and logistically complex. A report by the International Aluminium Institute shows that the average grade of bauxite deposits has been declining steadily over the past decade, forcing producers to invest in more advanced processing technologies. This decline in ore quality increases energy consumption and operational expenses, squeezing profit margins. Furthermore, environmental regulations often restrict mining activities in ecologically sensitive areas, further limiting access to high-quality reserves. These factors collectively constrain the growth potential of the aluminium market.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rising Adoption of Aluminium in Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector presents a significant opportunity for the aluminium market due to its increasing reliance on lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce operational costs. According to Boeing, the global fleet of commercial airplanes is projected to double by 2041, reaching over 47,000 aircraft. Aluminium alloys, which account for approximately 80% of an aircraft's structural weight, are critical in achieving these efficiency goals. The International Air Transport Association estimates that airlines saved $25 billion in fuel costs in 2022 alone by adopting lighter materials like aluminium. Furthermore, advancements in high-strength aluminium-lithium alloys have expanded their use in next-generation aircraft, as noted by the Aluminum Association. With rising air travel demand and the push for sustainable aviation, aluminium's role in aerospace manufacturing will continue to grow, offering substantial market opportunities.
Growing Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Urbanization and infrastructure development are driving unprecedented demand for aluminium, particularly in emerging economies. The United Nations projects that 68% of the global population will live in urban areas by 2050, up from 56% in 2020. This urban shift necessitates extensive construction of buildings, transportation systems, and utilities, where aluminium plays a vital role. For instance, aluminium is widely used in window frames, roofing, and facades due to its durability and corrosion resistance. A report by the World Steel Association highlights that aluminium usage in construction grew by 6% annually between 2015 and 2020. Additionally, governments in Asia-Pacific regions, such as India and China, are investing heavily in infrastructure, with China’s Belt and Road Initiative alone expected to involve over $1 trillion in projects. These trends position aluminium as a key material for future urban growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fluctuating Raw Material Prices
A major challenge for the aluminium market is the volatility in raw material prices, particularly bauxite and alumina. The price of alumina, a critical precursor to aluminium production, can fluctuate significantly due to supply chain disruptions or geopolitical issues. For example, in 2022, alumina prices surged by nearly 30% following export bans in Guinea, a leading bauxite producer, as reported by the Financial Times. Such price swings create uncertainty for manufacturers, impacting profit margins and hindering long-term planning. The World Bank notes that bauxite mining costs have risen by 15% annually over the past five years due to declining ore quality and stricter environmental regulations. These cost pressures are exacerbated by inflationary trends, which further strain producers. Managing raw material price volatility remains a persistent challenge for the aluminium industry.
Increasing Competition from Substitute Materials
Another significant challenge is the growing competition from alternative materials like carbon fiber, magnesium, and advanced polymers, which threaten aluminium’s dominance in certain applications. Carbon fiber, for instance, is 30% lighter than aluminium and offers superior strength, making it increasingly popular in high-performance industries such as aerospace and automotive. Similarly, magnesium alloys are gaining traction in lightweight vehicle manufacturing, with the International Magnesium Association estimating a 5% annual increase in magnesium usage. These substitutes often outperform aluminium in specific applications, compelling manufacturers to explore alternatives. As innovation in material science accelerates, aluminium producers face the challenge of maintaining their competitive edge against these emerging options.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
6.23% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Alloy Type, End-use, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
RusAL (Russia),Aluminum Corporation of China Limited (CHALCO) (China), Rio Tinto (U.K.), Alcoa Corporation (U.S.), Emirates Global Aluminium (UAE), Norsk Hydro ASA (Norway), Hindalco Industries Ltd. (India), Vedanta Aluminium & Power (India), China Hongqiao Group Limited (China), and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Insights
The aluminium sheet was the biggest part of the aluminium market and makes up 40.3% of the total market in 2024. This segment is so important because aluminium sheets are used in many industries, like cars, packaging, and buildings. For example, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency says that using aluminium sheets in vehicles helps reduce their weight, which cuts fuel use by up to 15%. Also, most canned drinks around the world, over 70%, are made from aluminium sheets. These sheets are very useful because they are strong, lightweight, and can be recycled easily.
The Aluminium extrusion segment is growing faster than any other segment, with a CAGR of 6.5% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is happening because aluminium extrusions are being used more in construction and transportation. Extruded aluminium is shaped into long pieces, like frames for windows, doors, and building structures. The World Green Building Council says that using aluminium in buildings can save up to 30% of energy. In cars, extruded parts help make vehicles lighter and more fuel-efficient.
By Alloy Type Insights
The wrought alloys segment gained the top position in the aluminium market by holding a significant portion of the total share in 2024. These alloys are very popular because they are strong, don’t rust easily, and can be shaped into different forms. They are widely used in airplanes, cars, and buildings. The Federal Aviation Administration says that over 80% of airplane parts are made from wrought alloys because they are lightweight and durable. Also, wrought alloys are very recyclable, and nearly 75% of all aluminium ever made is still being used today. This makes them a key material for many industries, especially those focused on sustainability.
The Cast alloys segment are growing rapidly than any other type, with a CAGR of 5.8% which is happening because cast alloys are being used more in cars and machines. These alloys are melted and poured into molds to make engine parts and other components. The International Energy Agency says that electric vehicles (EVs) are driving this demand because cast aluminium helps make cars lighter and more energy-efficient. New technologies are also improving how well these alloys work, making them better for modern uses. With EV production expected to grow by 25% every year until 2025, cast alloys will play a big role in shaping the future of transportation.
By End-use Insights
The transportation segment was the largest area where aluminium is used and held 35.4% of the market in 2024. This is due to aluminium is very light, which helps cars, trucks, and planes use less fuel and produce fewer emissions. The Environmental Protection Agency says that replacing steel with aluminium in vehicles reduces their weight by up to 40%, which lowers greenhouse gas emissions. In cars, aluminium is used for many parts, and the average car now contains over 179 kg of aluminium, as Ducker Worldwide reports. With more focus on electric vehicles, aluminium will continue to be a key material in the transportation industry.
The Packaging segment is the fastest-rising area for aluminium, with a growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2% owing to aluminium is being used more for food, drinks, and cosmetic packaging. Over 70% of all drink cans worldwide are made from aluminium, as the Aluminum Association says. Aluminium packaging is also very eco-friendly because it can be recycled over and over again. In developed countries, recycling rates for aluminium packaging are over 70%, as the World Bank reports. With governments pushing to reduce plastic use, aluminium packaging is becoming more important. It’s a great solution for protecting the environment while meeting consumer needs.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Asia Pacific dominated the global aluminium market by accounting for 60.8% of production and consumption. China alone produces approximately 57% of the world’s primary aluminium, with an output exceeding 38 million metric tons in 2022, according to the United States Geological Survey. The region's growth is due to its massive industrial base, rapid urbanization, and infrastructure development. India is also emerging as a key player, with aluminium demand growing at 7% annually due to government initiatives like "Smart Cities." The region's dominance is further bolstered by cost-efficient production methods and abundant bauxite reserves, making it critical to meeting global aluminium needs.
North America holds a significant position in the aluminium market, driven by its advanced manufacturing sector and focus on sustainable practices. The U.S. is the largest producer in the region, contributing approximately 11% of global aluminium production, as per the Aluminum Association. Canada ranks third globally in aluminium production, with an output of 3.1 million metric tons in 2022. The region benefits from robust demand in automotive and aerospace industries, where lightweight materials are prioritized. Additionally, the Biden administration’s $1 trillion infrastructure plan is expected to boost aluminium consumption by 15% over the next decade, according to industry forecasts, solidifying North America's importance in the global market.
Europe is a leading region in the aluminium market due to its strong emphasis on sustainability and innovation. The European Aluminium Association reports that the region recycled over 4 million metric tons of aluminium in 2022, reflecting a recycling rate of 70%, the highest globally. Germany, France, and Norway are major contributors, supported by stringent environmental regulations and green energy adoption. Europe’s aluminium demand is fueled by its thriving automotive and packaging sectors, with electric vehicle production projected to grow by 25% annually through 2025, as stated by the European Automobile Manufacturers' Association. This focus on circular economy principles and clean technologies enhances Europe’s leadership in sustainable aluminium usage.
The Middle East is a rising star in the aluminium market, primarily due to its low-cost energy resources and strategic investments. The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries account for 10% of global aluminium production, with the United Arab Emirates being the largest producer in the region, producing 2.6 million metric tons in 2022, as per the World Bank. Africa, rich in bauxite reserves, supplies over 30% of the world’s raw material, with Guinea alone holding 25% of global reserves. The region's growth is driven by expanding smelting capacities and export-oriented strategies. These factors make the Middle East & Africa vital for both upstream and downstream aluminium value chains, ensuring their prominence in the global market.
Latin America plays a crucial role in the aluminium market due to its vast bauxite reserves and growing industrialization. Brazil is the region’s leader, ranking sixth globally in aluminium production, with an output of 1.7 million metric tons in 2022, according to the United States Geological Survey. The country’s rich natural resources and renewable energy usage in smelting operations enhance its competitiveness. Additionally, Mexico’s proximity to North America positions it as a key supplier to the U.S. automotive industry, which imports over 600,000 metric tons of aluminium annually. The region’s focus on sustainable mining practices and increasing investments in infrastructure projects further elevate its importance in the global aluminium supply chain.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
RusAL (Russia),Aluminum Corporation of China Limited (CHALCO) (China), Rio Tinto (U.K.), Alcoa Corporation (U.S.), Emirates Global Aluminium (UAE), Norsk Hydro ASA (Norway), Hindalco Industries Ltd. (India), Vedanta Aluminium & Power (India), China Hongqiao Group Limited (China) are playing dominating role in the global aluminium market.
The competition in the aluminium market is intense, with companies striving to stand out through innovation, sustainability, and strategic expansions. One fresh perspective is the role of digital transformation in shaping competition. Leading players like Rio Tinto and Norsk Hydro are using advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize production processes. For example, predictive maintenance systems help reduce downtime in smelters, saving costs and improving efficiency. This technological edge allows them to produce aluminium faster and at lower costs than smaller competitors.
Another unique aspect is the growing importance of brand differentiation in the market. Companies are no longer just selling aluminium; they are promoting it as a "green" or "premium" product. For instance, Norsk Hydro markets its low-carbon aluminium under the brand "Hydro REDUXA," appealing to eco-conscious buyers. Similarly, Alcoa highlights its "EcoLum" brand, which guarantees reduced carbon emissions during production. This branding strategy helps companies attract specific customer segments, such as electric vehicle manufacturers or sustainable packaging firms.
Additionally, competition is driven by geopolitical alliances . Companies like Chinalco are securing long-term supply chains by partnering with governments in resource-rich countries. These partnerships give them an advantage over rivals who face raw material shortages or trade restrictions.
Finally, smaller players are adopting niche strategies, focusing on specialized products like high-strength alloys for aerospace or custom extrusions for construction. By targeting specific industries, they avoid direct competition with giants while carving out their own space. Overall, the aluminium market's competitive landscape is evolving through technology, branding, geopolitics, and niche specialization, offering new ways for companies to thrive.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Aluminum Corporation of China Limited (Chinalco)
Chinalco is the largest player in the global aluminium market, contributing significantly to production and innovation. As of 2022, Chinalco accounted for approximately 15% of global aluminium production, with an output exceeding 6 million metric tons, according to the United States Geological Survey. The company dominates due to its access to abundant bauxite reserves in China and Guinea, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials. Chinalco has also invested heavily in eco-friendly technologies, reducing its carbon footprint by 20% over the past five years, as reported by the International Aluminium Institute. Its focus on sustainability and vertical integration, from mining to refining, strengthens its leadership position. Chinalco’s growth is further fueled by China’s booming infrastructure and automotive industries, making it a cornerstone of the global aluminium market. Additionally, Chinalco contributes to the industry by advancing sustainable practices and supplying high-quality aluminium for critical sectors like construction and transportation, ensuring the market remains robust and aligned with global demand trends.
Rio Tinto Group
Rio Tinto is a leading global player, particularly in high-quality aluminium production. The company ranks second globally, producing around 3.2 million metric tons of aluminium annually, as per the Aluminum Association. Rio Tinto’s competitive edge lies in its use of renewable energy, with over 70% of its smelting operations powered by hydropower, significantly reducing emissions. The company also leads in developing advanced aluminium alloys for aerospace and automotive applications, which are lighter and stronger than traditional materials. Rio Tinto’s partnership with major automakers, like Ford and Tesla, has boosted demand for its products. Additionally, its investment in recycling technologies has positioned it as a leader in sustainable aluminium solutions. By focusing on green energy and innovative alloys, Rio Tinto not only supports the transition to electric vehicles and energy-efficient buildings but also ensures the global aluminium market remains at the forefront of technological and environmental advancements.
Norsk Hydro ASA
Norsk Hydro is another key player, known for its innovative and sustainable approach to aluminium production. Based in Norway, the company produces approximately 2.1 million metric tons of aluminium annually, as reported by the World Bank. Hydro stands out for its commitment to green energy, sourcing nearly 100% of its electricity from renewable sources. It has also pioneered the development of low-carbon aluminium, branded as "Hydro REDUXA," which reduces CO2 emissions by up to 40% compared to conventional methods. The company plays a vital role in Europe’s aluminium supply chain, supporting industries like automotive, construction, and packaging. Norsk Hydro’s focus on circular economy principles, including increased recycling efforts, ensures its growth aligns with global sustainability goals. Through its emphasis on low-carbon solutions and resource efficiency, Norsk Hydro contributes significantly to reducing the environmental impact of aluminium production while meeting the growing demand for sustainable materials worldwide.
STRATEGIES USED BY THE MARKET PLAYERS
Focus on Sustainability and Green Technologies
Sustainability is a top priority for leading aluminium companies. For example, Norsk Hydro has invested heavily in renewable energy, sourcing nearly 100% of its electricity from hydropower and developing low-carbon aluminium products like "Hydro REDUXA," which reduces CO2 emissions by up to 40%. Similarly, Rio Tinto uses over 70% renewable energy in its smelting operations and collaborates with customers to create eco-friendly aluminium solutions. These efforts help reduce the environmental impact of aluminium production while meeting the growing demand for sustainable materials. By adopting green technologies, these companies not only comply with stricter environmental regulations but also appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and industries.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Key players are expanding their operations into emerging markets to tap into growing demand. Chinalco , for instance, has secured access to bauxite reserves in Guinea, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials while strengthening its presence in Africa. Similarly, Rio Tinto has expanded its footprint in Asia-Pacific, targeting regions with rapid urbanization and infrastructure development. These expansions allow companies to meet regional demands more effectively and reduce dependency on specific markets, thereby diversifying their revenue streams and reducing risks associated with geopolitical tensions or trade restrictions.
Investment in Innovation and Advanced Alloys
Innovation is critical for staying competitive in the aluminium market. Companies like Rio Tinto and Alcoa are investing in research and development to create advanced aluminium alloys tailored for high-performance applications. For example, Rio Tinto has developed lightweight alloys specifically for electric vehicles (EVs), partnering with automakers like Tesla and Ford to meet the growing demand for fuel-efficient materials. Similarly, Norsk Hydro focuses on creating durable and recyclable alloys for construction and packaging industries. These innovations not only enhance product performance but also open new opportunities in high-growth sectors like aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In January 2025, the Australian government announced a $2 billion Green Aluminium Initiative to transition aluminium smelters to renewable energy by 2036. This funding aims to secure 20,000 jobs and maintain Australia's global competitiveness in sustainable aluminium production.
- In August 2024, Hindalco Industries unveiled a $10 billion expansion plan to grow its domestic aluminium operations and invest in its U.S.-based aluminium recycler, Novelis Inc. This move will enhance Hindalco's aluminium and copper production capabilities.
- In October 2024, Rio Tinto CEO Jakob Stausholm urged Western governments to accelerate clean energy policies for aluminium production. He emphasized the need for scalable and integrated supply chain strategies to compete with China’s dominance in green aluminium.
- In February 2025, China Hongqiao Group continued relocating aluminium smelting capacity to Yunnan Province to leverage hydropower for lower emissions. This move aligns with the company’s strategy to reduce its carbon footprint and optimize energy costs.
- In May 2024, Novelis Inc. filed for a proposed Initial Public Offering (IPO) to improve its capital structure and fund expansion in aluminium recycling and rolling. The company has not yet announced the IPO's exact timeline.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global aluminium market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on product, alloy type, end-use, and region.
By Product
- Sheet
- Plate
- Cast Products
- Extrusion
- Others
By Alloy Type
- Cast Alloy
- Wrought Alloy
By End-use
- Construction
- Transportation
- Aerospace
- Automotive
- Marine
- Packaging
- Food & Beverages
- Cosmetics
- Others
- Electrical
- Consumer Durables
- Machinery & Equipment
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the growth rate of the global aluminum market from 2025 to 2033?
The market is projected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 6.23% from 2025 to 2033.
2. What factors are likely driving the growth of the aluminum market globally?
The growth is likely driven by increasing demand for lightweight materials in industries such as automotive and aerospace, along with advancements in sustainable production and recycling technologies
3. Which regions are key players in the global aluminum market?
Asia Pacific is a dominant region due to its large manufacturing base and growing industrial demands, while Europe also plays a significant role due to its strong automotive and construction sectors
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]