Global AI in Epidemiology Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Deployment Type (On-Premise and Cloud), Application (Infection Prediction and Forecasting, Disease and Syndromic Surveillance, Monitoring Population Health and Incidence/Prevalence), End-User and Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Latin America, Middle East and Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 To 2032
Global AI in Epidemiology Market Size
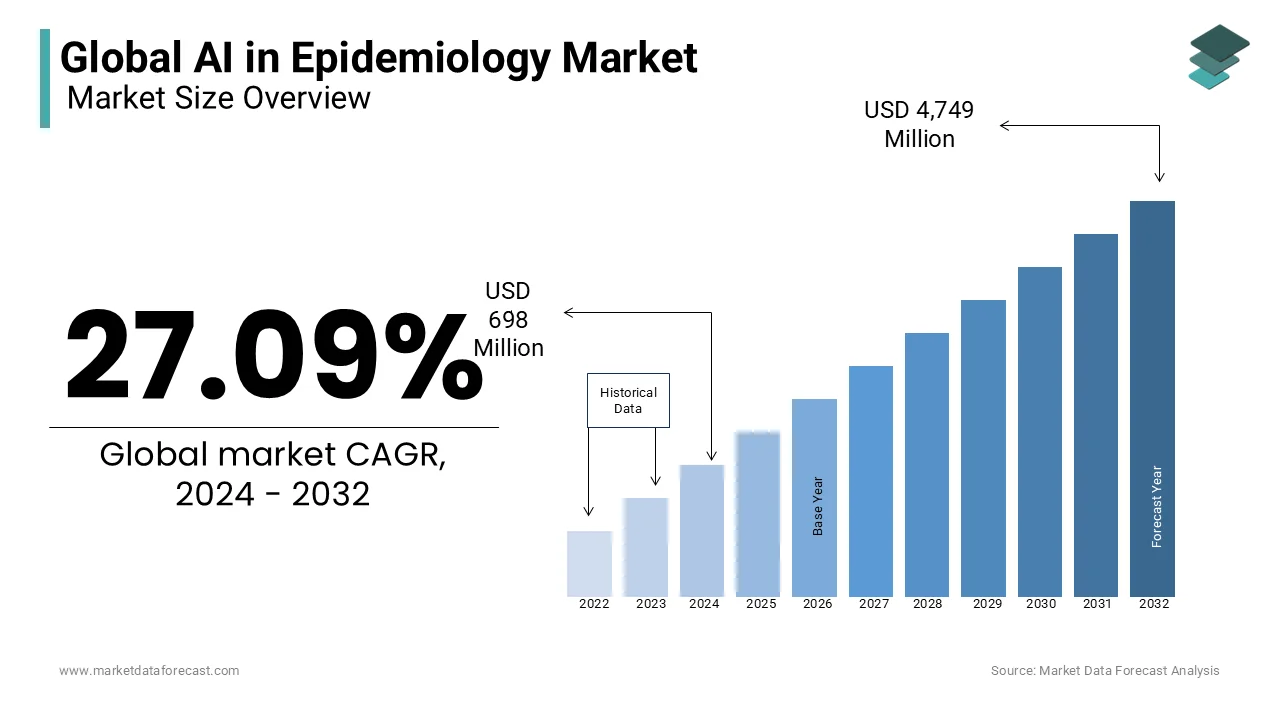
The size of the global AI in epidemiology market was worth USD 549 million in 2023. The global market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 27.09% from 2024 to 2032 and be worth USD 4,749 million by 2032 from USD 698 million in 2024.
The AI in Epidemiology is transforming how diseases are tracked, predicted, and analyzed using advanced technologies like machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and data analytics. These tools enable the integration of vast datasets—such as clinical records, genomic sequences, and environmental factors—to identify patterns and forecast disease spread with remarkable accuracy. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI platforms like BlueDot identified early signs of the outbreak nine days before the World Health Organization issued its first alert. Similarly, AI has been instrumental in improving contact tracing, with tools like MIT's SafePaths increasing accuracy by 50-70%, allowing faster containment of infectious diseases.
AI-driven genomic epidemiology has accelerated the identification of viral variants, supported by over 100 million genomic sequences available in public databases as of 2023. Platforms like Nextstrain use this data to map genetic variations in real-time, aiding in understanding virus evolution and vaccine effectiveness. AI also enhances predictive models for diseases like Zika virus and Ebola by achieving accuracy rates exceeding 90%, which helps governments and healthcare organizations allocate resources more efficiently. Furthermore, AI has reduced the time required for genomic sequencing analysis from weeks to hours, cutting costs by up to 40% and making these tools accessible in low-resource settings. These advancements demonstrate how AI is reshaping epidemiology by enabling proactive public health responses, improved resource allocation, and more effective disease surveillance and control.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Need for Real-Time Disease Surveillance
The demand for real-time disease surveillance is a significant driver of the AI in Epidemiology market. Traditional surveillance methods often face delays in data collection and analysis, whereas AI-driven tools can process diverse datasets almost instantaneously. For example, AI systems helped track influenza outbreaks with an accuracy of over 90%, according to research by Johns Hopkins University. These tools aggregate data from electronic health records, social media, and mobility patterns to predict outbreaks and monitor disease spread, enabling faster responses. This capability is especially critical in managing pandemics, reducing healthcare burdens, and improving public health preparedness globally.
Advancements in Genomic Data Integration
Advancements in genomic sequencing technologies have fueled the adoption of AI in epidemiology, particularly in tracking pathogen evolution and identifying disease variants. As of 2023, over 100 million SARS-CoV-2 genomic sequences were uploaded to global databases like GISAID, allowing AI models to analyze mutation patterns rapidly. This integration helps predict vaccine efficacy, guide public health interventions, and monitor emerging threats. For example, AI tools have been instrumental in identifying genomic markers for drug resistance in tuberculosis and streamlining treatment strategies. The ability to harness genomic data efficiently is transforming epidemiology into a more precise and proactive science.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The integration of AI in epidemiology faces significant challenges related to data privacy and security. Sensitive health data, including patient records and genomic information, are critical for AI models but are vulnerable to breaches. A report by IBM revealed that the average cost of a healthcare data breach reached $10.93 million in 2023. Compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA further complicates data sharing and usage. These concerns discourage stakeholders from fully adopting AI technologies, which limits their potential. Addressing these issues requires robust encryption methods and transparent data governance policies to build user trust.
Limited Access to High-Quality Data
AI tools in epidemiology rely heavily on large, accurate datasets, but access to high-quality data remains a major restraint. Disparities in healthcare infrastructure leads to inconsistent or incomplete data collection, particularly in low-income regions. For instance, the World Bank estimates that 50% of healthcare facilities in low-income countries lack basic data-reporting capabilities that solely impact AI model accuracy. Additionally, data silos across institutions and incompatible formats hinder the integration of datasets needed for comprehensive analyses. Overcoming this challenge requires the development of standardized data-sharing frameworks and investments in digital infrastructure to enable equitable AI adoption worldwide.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration with Wearable Health Devices
The increasing adoption of wearable health devices presents a significant opportunity for AI in epidemiology. Wearables such as fitness trackers and smartwatches generate continuous health data, including heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns. AI can analyze this data to detect early signs of disease, monitor population health trends, and predict outbreaks. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, wearable data helped identify symptomatic individuals and track recovery patterns, showcasing its potential to revolutionize real-time epidemiological surveillance and preventative healthcare.
Application in Climate-Driven Disease Predictions
The rising prevalence of climate-driven diseases, such as malaria and dengue, creates opportunities for AI-driven epidemiological models. Climate changes, such as increased temperatures and altered rainfall patterns, are expanding the habitats of disease vectors like mosquitoes. AI tools can integrate climate data with historical disease patterns to forecast outbreaks accurately. For example, AI models have predicted malaria outbreaks in sub-Saharan Africa with 90% accuracy, which enables targeted interventions. AI's ability to anticipate and mitigate climate-related health impacts becomes essential as global temperatures rise, which offers a transformative application area for AI in the epidemiology market.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Lack of Skilled Professionals
The shortage of professionals skilled in both AI and epidemiology is a significant challenge. Developing and deploying AI models for epidemiological purposes requires expertise in data science, machine learning, and public health. According to LinkedIn’s 2023 Workforce Report, the demand for AI specialists has grown by 74% annually, but the healthcare sector struggles to attract talent due to competitive industries like technology. Moreover, the gap in interdisciplinary training programs further limits the availability of professionals capable of bridging AI and epidemiology, slowing innovation and adoption rates in healthcare systems worldwide.
Bias in AI Algorithms
Bias in AI algorithms poses a critical challenge in the application of AI in epidemiology. Data used to train AI models often reflects existing disparities, such as the underrepresentation of certain demographics or regions. A 2022 study published in Nature Medicine highlighted that AI models misclassified diseases up to 30% more frequently in populations with limited data representation. This bias leads to inaccurate predictions, reinforcing inequalities in healthcare access and outcomes. Addressing algorithmic bias requires diverse and inclusive datasets alongside transparent auditing practices to ensure fairness and reliability in AI-driven epidemiological insights.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2023 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024 to 2032 |
|
CAGR |
27.09% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Deployment Type, Application, End User, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, and country-level analysis; Segment-Level Analysis, DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Google LLC (Alphabet Inc.), Amazon Web Services (AWS), NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, Oracle Corporation, SAS Institute Inc., Siemens Healthineers, Cerner Corporation (Oracle Health), and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Deployment Type Insights
The cloud deployment segment had the major share of the global AI in epidemiology market in 2023. The domination of the cloud segment is majorly attributed to the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility that cloud-based solutions offer. They enable real-time data analysis and collaboration across various geographic locations, which is crucial for monitoring and responding to disease outbreaks. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, cloud platforms facilitated the rapid sharing and analysis of epidemiological data globally, enhancing the efficiency of public health responses. The flexibility of cloud services allows healthcare organizations to adapt quickly to changing data volumes and processing needs by making them indispensable in modern epidemiological practices.
The On-Premise segment is experiencing the fastest growth and is predicted to register a CAGR of 27.3% over the forecast period. This rapid expansion is driven by organizations that prioritize data security and have the necessary infrastructure to support in-house solutions. On-premise deployments offer greater control over data management and compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, which is vital for handling sensitive health information. Additionally, advancements in hardware and software have made on-premise solutions more efficient and cost-effective, encouraging their adoption among institutions that require customized and secure data processing capabilities.
By Application Insights
The disease and syndromic surveillance segment held the dominating position in the global AI in epidemiology market in 2023 due to the critical role AI plays in monitoring and analyzing health data to detect disease patterns and potential outbreaks promptly. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, AI-driven surveillance systems were instrumental in tracking the virus's spread, enabling timely public health interventions. The ability of AI to process vast amounts of data from various sources, such as electronic health records and social media, enhances the accuracy and speed of disease detection and makes it suitable for modern epidemiological practices.
The infection prediction and forecasting segment is the fastest-growing segment and is predicted to witness a CAGR of 27.7% over the forecast period. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing reliance on AI to predict infection trends and potential outbreaks. AI models can analyze complex datasets, including climate conditions, population movements, and historical infection rates, which can accurately forecast disease spread. Such predictive capabilities are crucial for proactive public health planning and resource allocation, especially in managing emerging infectious diseases. The growing emphasis on preventive healthcare and the need for efficient epidemic preparedness are key factors propelling the expansion of this segment.
By End-User Insights
The healthcare providers segment led the AI in Epidemiology market by accounting for 40.4% of the global market share in 2023. This leadership stems from the extensive adoption of AI tools in clinical settings to improve patient care, optimize workflows, and predict disease trends. For instance, AI systems integrated with electronic health records (EHRs) enable early detection of conditions like sepsis with up to 90% accuracy by ensuring timely interventions. Telemedicine platforms and remote patient monitoring further expand AI’s role in enhancing care delivery. These advancements help healthcare providers manage resources efficiently, reduce readmissions, and support epidemic preparedness, solidifying their dominant position.
The research labs segment is predicted to experience a promising CAGR in the global market over the forecast period. AI-driven tools in research labs accelerate disease modeling, genomic analysis, and outbreak prediction, enabling real-time insights. For example, AI models rapidly identified COVID-19 variants, aiding global vaccine development efforts. The surge in funding for AI-powered research and collaborations between academic institutions and tech companies fuels this growth. By uncovering actionable patterns in vast datasets, research labs leverage AI to advance epidemiological studies and preventive strategies, driving their rapid expansion in the market.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America dominated the global AI in epidemiology market by occupying 40.5% of the global market share in 2023. The domination of North America is expected to continue in the global market throughout the forecast period due to the region’s advanced healthcare infrastructure, significant investments in artificial intelligence technologies, and supportive government policies. The United States plays a pivotal role, with organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) leveraging AI-driven models for disease prediction and outbreak management. For instance, AI tools have significantly enhanced influenza tracking, enabling timely interventions. Canada complements these efforts with its Public Health Agency using AI for health trend analysis and policy formulation.
Europe held a substantial share of the worldwide market in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 26% during the forecast period. The region's growth is fueled by its strong focus on digital health transformation and supportive regulatory frameworks. Germany and the United Kingdom are key players in this market. Germany’s Robert Koch Institute utilizes AI to process vast datasets for disease monitoring, while the United Kingdom’s National Health Service (NHS) employs AI tools for syndromic surveillance and patient care optimization. Additionally, the European Union’s initiatives, such as the European Health Data Space, aim to standardize and enhance data sharing across member states, further accelerating AI adoption in epidemiology.
Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region in the AI in Epidemiology market. The region’s rapid expansion is driven by increasing healthcare expenditures, population growth, and the rising prevalence of infectious diseases. China leads the region with AI-powered real-time disease tracking and forecasting platforms, significantly enhancing its public health response. India’s Ministry of Health has also embraced AI tools to monitor outbreaks and optimize resource allocation. The region’s focus on healthcare modernization and technological integration positions it as a critical area for future growth in AI-driven epidemiology.
Latin America holds a smaller share of the global market. However, Latin America is expected to grow at a healthy CAGR during the forecast period. Brazil leads the region by utilizing AI tools for managing vector-borne diseases such as dengue and Zika. Mexico also invests in AI technologies to strengthen epidemiological monitoring. However, challenges like limited infrastructure persist, and the region’s focus on digital health solutions and government initiatives is driving the growth rate of the market.
The market in the Middle East and Africa is anticipated to grow at a steady CAGR over the forecast period. South Africa is at the forefront, employing AI models to predict outbreaks and guide public health strategies. In the Middle East, countries like the United Arab Emirates are integrating AI tools into their healthcare systems to improve disease surveillance and epidemic preparedness. Investments in digital transformation and innovation are expected to propel further adoption in this region.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies playing a prominent role in the global AI in epidemiology market include IBM Corporation, Microsoft Corporation, Google LLC (Alphabet Inc.), Amazon Web Services (AWS), NVIDIA Corporation, Intel Corporation, Oracle Corporation, SAS Institute Inc., Siemens Healthineers, Cerner Corporation (Oracle Health), and Others.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The AI in Epidemiology market is highly competitive, driven by rapid technological advancements, increased demand for real-time disease monitoring, and the adoption of AI-driven tools across healthcare sectors. Major technology companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Google dominate the market by providing robust AI platforms tailored for epidemiological applications, such as disease forecasting and genomic analysis. These firms leverage their expertise in machine learning, natural language processing, and cloud computing to enable advanced data integration and modeling.
Established healthcare players like Siemens Healthineers and Cerner Corporation focus on developing AI solutions specific to clinical and public health needs. These companies emphasize interoperability with electronic health records (EHRs) and compliance with regulatory standards, enhancing their value proposition to healthcare providers.
The competition intensifies with the entry of specialized AI firms and startups offering niche solutions, such as contact tracing algorithms or pandemic modeling platforms. Partnerships and collaborations play a critical role, as technology firms team up with research institutions and public health agencies to scale AI adoption globally.
Regional competition varies, with North America and Europe leading innovation, while Asia-Pacific emerges as a growth hotspot due to rapid technological adoption. Companies investing in scalability, advanced analytics, and security will remain competitive in this evolving market.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In January 2022, IBM Corporation, a leader in AI and cloud computing, announced the sale of its healthcare data and analytics assets from the Watson Health business to Francisco Partners, a global investment firm specializing in technology businesses. Purpose: This strategic move aimed to streamline IBM's focus on core AI and cloud services, while allowing Francisco Partners to enhance its capabilities in healthcare data analytics.
- In March 2024, Microsoft Corporation, a global technology firm, expanded its collaboration with NVIDIA to accelerate healthcare and life sciences innovation through advanced cloud AI and accelerated computing capabilities. Purpose: This partnership seeks to leverage the power of generative AI, the cloud, and accelerated computing to enhance disease prediction and monitoring, strengthening Microsoft's position in AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- In January 2024, Google LLC (Alphabet Inc.), a multinational technology company, collaborated with the Global Health Drug Discovery Institute (GHDDI) to utilize AI technology in accelerating drug discovery for global infectious diseases. Purpose: This initiative aims to provide researchers with advanced analytics for disease modeling, enhancing Google's presence in the healthcare sector.
- In March 2024, Amazon Web Services (AWS), a subsidiary of Amazon providing cloud computing services, announced new collaborations with healthcare organizations and partners to make the promise of AI in healthcare real. Purpose: These collaborations enable healthcare organizations to derive insights from vast datasets, reinforcing AWS's position in health informatics.
- In March 2024, NVIDIA Corporation, known for its graphics processing units, expanded its collaboration with Microsoft to bring the power of generative AI, the cloud, and accelerated computing to healthcare and life sciences organizations. Purpose: This collaboration aims to accelerate research processes, positioning NVIDIA as a key player in AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- In January 2022, Intel Corporation, a leader in semiconductor manufacturing, joined the Artificial Intelligence Industry Innovation Coalition (AI3C), established to identify and solve significant societal and industry barriers through the use of AI. Purpose: This partnership aims to enhance early detection of infectious diseases, strengthening Intel's contributions to public health technology.
- In March 2024, Oracle Corporation, a multinational computer technology company, announced new collaborations with healthcare organizations to enhance AI capabilities in disease prediction and monitoring. Purpose: These collaborations are intended to expand Oracle's capabilities in epidemiological data processing, enhancing its healthcare offerings.
- In October 2024, SAS Institute Inc., a leader in analytics software, launched EpiStat, a suite of AI-driven tools for epidemiological statistics. Purpose: This suite provides public health professionals with advanced analytical capabilities, reinforcing SAS's position in health analytics.
- In March 2024, Siemens Healthineers, a medical technology company, announced new collaborations to enhance AI-powered diagnostic solutions in epidemiological studies. Purpose: These collaborations aim to aid in the accurate interpretation of medical images, enhancing Siemens' offerings in diagnostic solutions.
- In March 2024, Cerner Corporation (Oracle Health), a health information technology company, announced new collaborations with healthcare organizations to develop AI-based electronic health record systems for disease tracking. Purpose: These collaborations aim to improve data integration and disease surveillance, solidifying Cerner's role in public health informatics.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global AI in epidemiology market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on deployment type, application, end user, and region.
By Deployment Type
- On-Premise
- Cloud
By Application
- Infection Prediction and Forecasting
- Disease and Syndromic Surveillance
- Monitoring Population Health and Incidence/Prevalence
By End User
- Government and State Agencies
- Research Labs
- Healthcare Providers
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]